Pathogenesis Of Periodontal Diseases Important Notes
1. Cytokines
- The three proinflammatory cytokines that have a central role in periodontal tissue destruction are interleukin-1, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor, TNF
- The properties of these cytokines that relate to tissue destruction involve stimulation of bone resorption and in-duction of tissue degrading proteinases
- IL-1 exists in alpha and beta forms
- Both forms are the main constituents of the osteoclast activating factor
- It is a potent stimulant of osteoclast proliferation, differentiation, and activation
- TNF is also found in alpha and beta forms
- IL-1 and TNF-a induce the production of proteinases in mesenchymal cells including matrix metalloproteinases which may contribute to tissue destruction
Read And Learn More: Periodontics Question and Answers
Pathogenesis Of Periodontal Diseases Short Essays
Question 1. Cytokines.
Answer:
Cytokines Definition: ‘Cell protein’ is used for molecules that transmit information/signals from one cell to another.
Cytokines Actions:
- Acts as fibroblast, macrophages, keratinocytes, and PMNs
- Release MMP’s
- Degrade connective tissue matrix
Pathogenesis Of Periodontal Diseases Short Answers
Question 1. Define cytokine.
Answer: Cytokine
Question 2. Interleukin 1.
Answer: Interleukin is cytokines
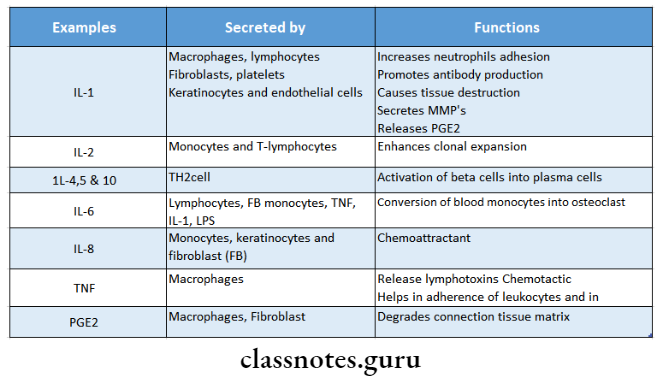
Interleukin 1 Secreted By:
- Macrophages, lymphocytes
- Fibroblasts, platelets
- Keratinocytes and endothelial cells
Interleukin 1 Functions:
- Increases neutrophils adhesion
- Promotes antibody production
- Causes tissue destruction
- Secretes MMP’s
- Releases PGE2
Question 3. Prostaglandin.
Answer:
- Short range hormone
- Present in inflammatory exudates, leukotrienes
- Released from – Mast cells and basophils
Prostaglandin Example: PGE2
Prostaglandin Functions:
- Osteoclastic resorption
- Degrades connection tissue matrix
Question 4. Bacterial Endotoxin.
Answer:
Location: Outer membrane of Gram-ve bacteria
Bacterial Endotoxin Pathogenesis:
- Penetrate gingival epithelium
- Produce fatty and organic acids, amines, VSCs, indole, ammonia, and glycans
Bacterial Endotoxin Effects:
- Direct activation of host responses
- Produce leukopenia
- Activate Factor XII, Complement system
- Cytotoxic effects on fibroblast
- Tissue Necrosis
- Bone resorption
Question 5. Virulence Factors.
Answer:
The properties that enable the bacterium to cause disease are termed virulence factor
- Fimbriae Helps in adherence of A. viscous (for example) on the saliva-coated tooth surface
- Exotoxin’s Toxic Effect on PMNs
- Lipopolysaccharides – Activates host response
- Peptidoglycan – Activates complement system
- Immunosuppressive activity
- Enzymes
- Collagenase-Degrades collagen
- Hyaluronidase – Alters gingival permeability
- Others Damage host cells
- Degrade antibody
- Damage keratinocytes
