Orthognathic Surgery And Osteotomy Procedures Important Notes
1. Indications Of Sagittal Split Osteotomy:
- Mandibular prognathism
- Mandibular retrognathia
- Bimaxillary protrusion
- Skeletal open bite
- Mandibular excess
2. Classification Of Osteotomy Procedures:
- Mandibular Body Osteotomies
- Mandibular body osteotomies
- Anterior body
- posterior body
- Midsymphysis
- Segmental Subapical
- Anterior
- Posterior Total
- Genioplasties
- Augmentation
- Reduction
- Straightening
- Lengthening
- Mandibular body osteotomies
- Mandibular ramus osteotomies
- Sub condylar
- Bisagittal split
- Maxillary osteotomy procedures
- Segmental
- Single Tooth
- Interdental
- Anterior
- Posterior
- Total
- Superior repositioning
- Inferior repositioning
- Advancement of maxilla
- Leveling of maxilla
- Segmental
Read And Learn More: Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Question and Answers
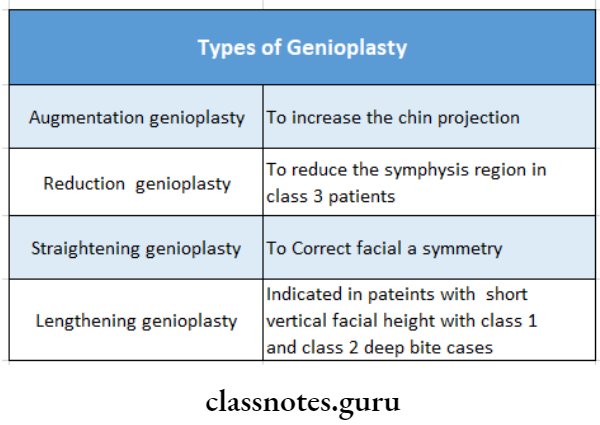
3. Types Of Genitoplasty:
- Augmentation genioplasty
- Reduction genioplasty
- Straightening genioplasty
- Lengthening genioplasty
4. Treatment For Mandibular Prognathism:
- Sagittal split osteotomy with mandibular setback Oblique sub condylar osteotomy
5. Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomy:
- First described by Trauner and Obwegesser
- Modified by Dalpont, Hunsuck, and Epker It is the most popular and versatile procedure
- Performed on mandibular ramus and body
- The osteotomy splits the ramus and the posterior body of the mandible sagitally
- This allows either setbacks or advancement
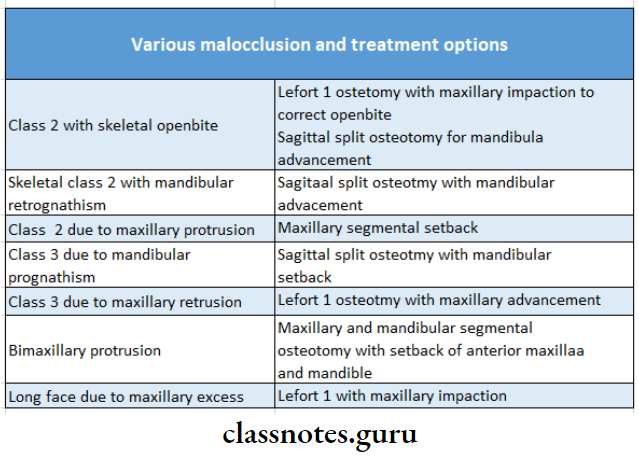
6. Various Malocclusion And Their Treatment Options;
Orthognathic Surgery And Osteotomy Procedures Long Essays
Question 1. Pre-operative planning in orthognathic surgery.
Answer:
Assessment Of Patient:
- Includes:
- Patient’s chief complaint
- Patient’s expectations
- Medical status of the patient
- Patient’s Examination:
- Hard & soft tissues examination
- TMJ evaluation
- Measurement Of Facial Proportions:
- Dividing facial contour in 3 horizontal planes & comparing them
- Dividing facial contour in 3 vertical planes & comparinging them
- Facial profile examination
- Radiographic Examination:
- Conventional radiography: For assessing any pathology
- Cepholometric analysis
- Hard & soft tissue landmarks are marked & jaw & face
- contour is analysed
- Special radiography done
- Facial photography: For maintaining records
- For computer-aided analysis
- For treatment planning
- For comparing pre- & post-operative appearance
- Model Surgery:
- Involves the construction of occlusal models
- Predict any occlusal problems
- Modify orthognathic movements
- Treatment Planning:
- All data is collected
- Analysis is done
- Review all orthodontic & surgical options
- Decision made on whether surgical or orthodontic treatment is required
Phases Of Treatment:
- Pre orthodontic preparatory phase
- Treatment of periodontics & restorative problems
- Pre-surgical orthodontics
- Orthodontically aligning of teeth
- Surgical phase
- Model surgery done
- Fabrication of splint
- Osteosynthesis done
- Post-surgical phase
- 4–8 weeks after surgery
- Closing of spaces present
- Removal of orthodontic brackets
- Applying retainers
- Prosthodontics phase
- Placement of implants
- Periodontal management
- Esthetic restoration
Orthognathic Surgery And Osteotomy Procedures Short Essays
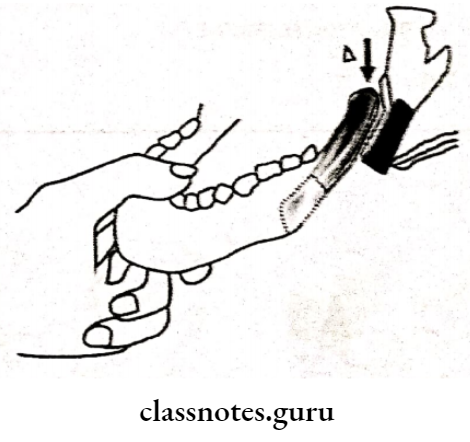
Question 1. Bilateral sagittal split osteotomy.
Answer:
Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomy
Described by Obwegeser & Trauner
Procedure Of Bilateral Sagittal Split:
- Bite block inserted on opposite side
- Incision made on lateral ascept of anterior border of the ramus
- Extend the incision into the vestibular depth
- Soft tissue dissection done
- Soft tissues are reflected
- Medial bone cut is done through lingual cortex
- Cut extended upto second molar region bite block is removed
- Separate the segments with the help of osteotome
- Accordingly, advancement or setback is done
- Fix the fragment
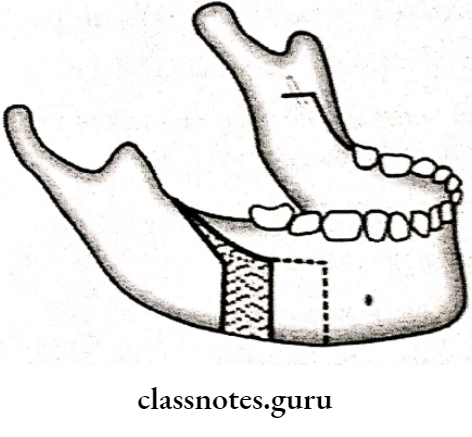
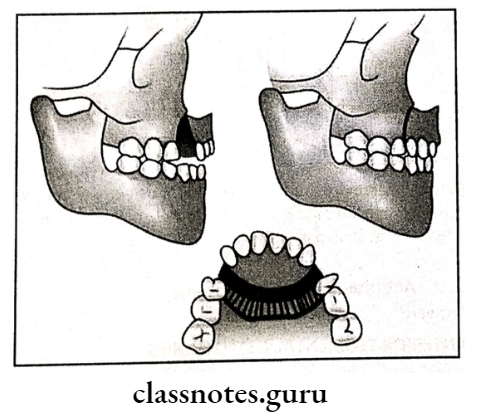
Question 2. Anterior maxillary osteotomy.
Answer:
Anterior Segmental Osteotomies:
- Indications:
- Pre-maxillary protusion
- Deep bite
- Anterior open bite
1. Wassmund Procedure:
- Blood supply is from palatal mucoperiosteum Vertical incision given in the premolar region
- A small vertical incision given in the midline to expose the anterior nasal spine
- Premolars are extracted
- Buccal bone cuts are made
- The palatal cortical plate is cut vertically
- · Detach the nasal septum
- Mobilize the segment
- Reposition it to the desired position
- Fix it
- Closure of wound
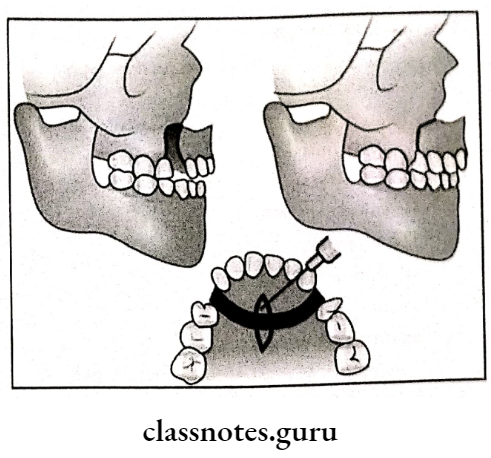
2. Wunderer’s Procedure:
- Blood supply is from buccal mucoperiosteum
- Horizontal incision is given across the palate
- Vertical incisions made in buccolabial sulcus
- A small vertical incision given in the midline to expose the anterior nasal spine
- Extract the premolars
- Buccal bone cuts given
- Detach nasal septum
- Mobilize palatal bone cut
- Mobilize anterior segment
- Fix & sutured it
Question 3. Mandibular hypertrophy.
Answer:
Features Of Mandibular Hypertrophy:
- Extraoral features:
- Concave profile
- Anterior facial divergent
- Prominent chin
- Intraoral features:
- Class 2 malocclusion
- Lingually tilted lower incisors
- Anterior cross bite
- Narrow upper arch
- Wide lower arch
- Posterior crossbite
- Crowded upper teeth
- Spacing present in lower teeth
Treatment Of Mandibular Hypertrophy:
- Chin cup therapy to restrict maxillary growth
- In nongrowers
- Surgical mandibular setback which is followed after split osteotomy
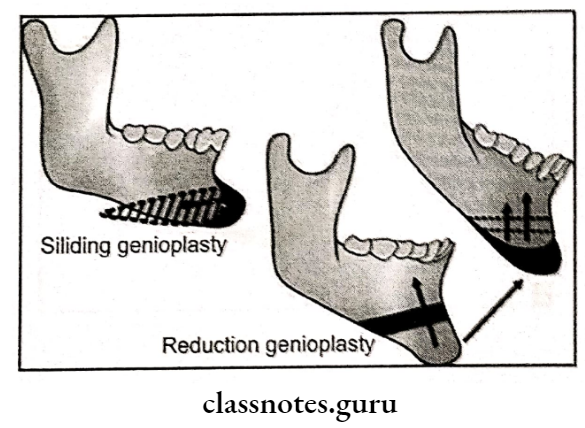
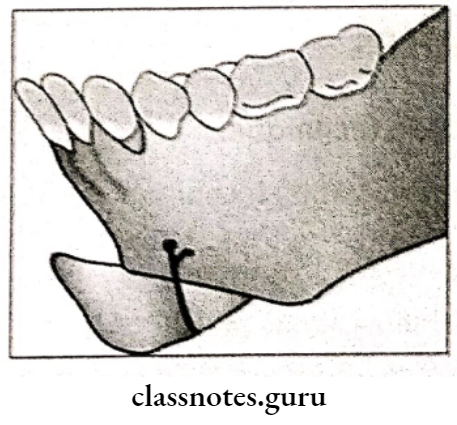
Question 4. Genioplasty.
Answer:
Genioplasty
Used as an adjunctive
Types Of Genioplasty:
- Augmentation Genioplasty:
- Deglove inferior border of the symphysis
- Periosteal releasing incision given
- Horizontal osteotomy cut given at the apices of canine
- Segment is mobilized
- Removal of bony interferences
- Check for the facial contour
- Fix the superior body
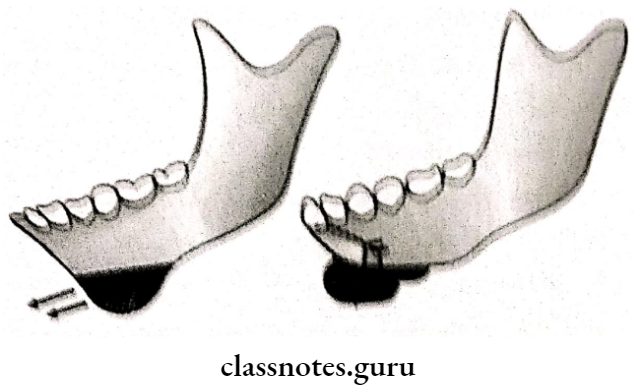
- Reduction Genioplasty:
- Horizontal osteotomy cuts are given
- Setback the fragment
- Excise the bony interference
- Fix the fragment
- Straightening Genioplasty:
- Horizontal osteotomy cut are given
- Shift segment laterally
- Lengthening Genioplasty:
- Horizontal osteotomy cut are given
- Segment is shifted inferiorly
- Bone graft is sandwiched between the fragments.
Question 5. Cephalometry
Answer:
- Introduced by Broadbent in USA & Hofrath in Germany in 1931
- Describes analysis & measurements made on the cephalometric analysis
Types Of Cephalometry:
- Lateral cephalogram
- Frontal cephalogram
Uses Of Cephalometry:
- For diagnosis
- To study dental & soft tissue structures
- For the classification of skeletal & dental abnormalities
- Assess facial type
- For treatment planning
- For presuming results
- For predicting growth-related changes
- For research work
Question 6. Treatment for mandibular prognathism.
Answer:
Treatment For Mandibular Prognathism
- Sagittal split osteotomy with mandibular setback
- Oblique sub condylar osteotomy
- Described by Obwegeser & Trauner
Procedure Of Treatment For Mandibular Prognathism:
- Bite block inserted on the opposite side
- Incision made on the lateral aspect of the anterior border of the ramus
- Extend the incision into the vestibular depth
- Soft tissue dissection done
- Soft tissue reflected
- Medial bone cut done in second molar region
- The bite block is removed
- Separate the segments with the help of osteotome
- Setback is done
- Fix the fragment
Orthognathic Surgery And Osteotomy Procedures Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Shift cone technique.
Answer:
Shift Cone Technique
Shift Cone Technique is an object localization technique
Technique Of Shift Cone:
- A standard radiograph is taken
- The tube is shifted either mesially or distally
- Second radiography is taken
- If an object appears on the same side, then it is located lingually
- If the object appears on the opposite side in the radiograph, then it is located buccally
- Also called same lingual opposite buccal [Slob Technique]
Question 2. Indications of sagittal split osteotomy.
Answer:
Indications Of Sagittal Split Osteotomy
- Mandibular prognathism
- Mandibular retrognathia
- Bimaxillary protrusion
- Skeletal open bite
- Mandibular excess
Question 3. Classification of Osteotomy procedures.
Or
Mandibular orthognathic producers.
Answer:
- Mandibular Body Osteotomies:
- Mandibular body osteotomies:
- Anterior body
- posterior body
- Midsymphysis
- Segmental Subapical:
- Anterior
- Posterior
- Total
- Genioplasties:
- Augmentation
- Reduction
- Straightening
- Lengthening
- Mandibular body osteotomies:
- Mandibular Ramus Osteotomies:
- Sub condylar
- Bisagittal split
- Maxillary Osteotomy Procedures:
- Segmental:
- Single Tooth
- Interdental
- Anterior
- Posterior
- Segmental:
- Total:
- Anterior
- Posterior
- Superior repositioning
- Inferior repositioning
- Advancement of maxilla
- Levelling of maxilla
- Total:
Question 4. Define orthographic surgery.
Answer:
Orthographic Surgery
- Orthognathic surgery is the art and science of diagnosis treatment planning & execution of treatment by combining orthodontics & oral & maxillofacial surgery to correct musculoskeletal endosseous & soft tissue deformities of the jaws & associated structures.
- In severe skeletal deformities, orthodontic along may compromise stability & esthetics & surgery alone may compromise function & stability.
Ortho gnathic Surgery And Osteotomy Procedures Viva Voce
- Genitoplasty is done to correct the deformities of the chin without altering the denture-bearing part
- Anterior maxillary osteotomy is combined with an anterior subapical mandibular osteotomy to correct bimaxillary protrusion
- In reduction genioplasty, the symphysis part of the mandible is reduced so that chin will attain a straight profile
- Lefort I osteotomy are commonly performed procedure for the treatment of maxillary retrognathia
- Apertognathia is a condition in which there is open bite deformity
- During genitoplasty there are chances of injuring mental nerve
