Orthodontics Lab Procedures Definitions
- Soldering
- It is a process of joining metals by the use of a filler metal that has a lower fusion temperature than that of the metals being joined.
- Welding
- Involves the joining of two metals without introducing a third metal.
Orthodontics Lab Procedures Important Notes
- Types of solders
- Investment soldering
- Freehand soldering
- Composition of flux
- Borax glass – 55%
- Boric acid – 35%
- Silica – 10%
- Gases used for soldering.
- Gas air/oxygen torch flame
- Hydrogen
- Natural gas
- Acetylene
- Propane
Orthodontics Lab Procedures Short Essays
Question 1. Soldering and Welding.
Answer.
Soldering: It is a process of joining metals by the use of a filler metal that has a lower fusion temperature than that of the metals being joined.
Types of soldering:
Investment soldering:
Indication: Presence of large contact area between metals
- In need of precision
Procedure: By embedding metals in investment
Freehand soldering:
- Indication: Common orthodontic procedures
- Procedures: Soldering by holding metals precisely
Steps of freehand soldering:
- Clean the surfaces
- Assemble the parts
- Select proper solder and flux
- Select proper joint
- Flux application
- Application of solder
- Quenching
Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Short And Long Essay Question And Answers
Indications of freehand soldering:
- Join parts of appliances
- Fastens attachments to bands
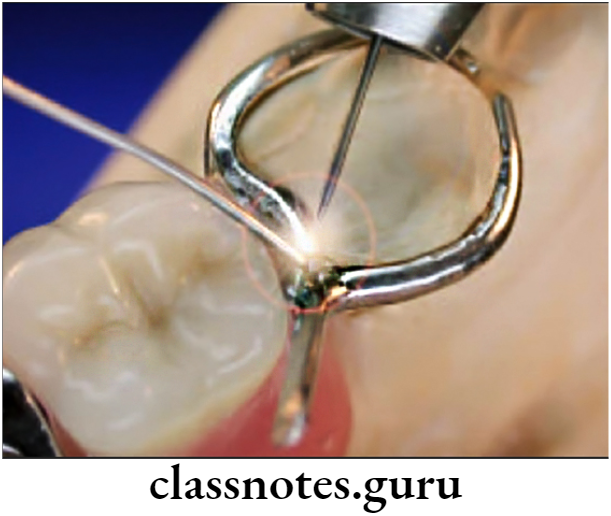
Welding: Involves joining of two metals without introducing a third metal
Welding Procedure:
- Selection of electrode
- Placement of metals between 2 electrodes
- Maintain pressure on it
- Switch on electrode
- Keep it for sometime
Indications of welding:
- For banding
- For brackets and molars tubes
Question 2. Shape Memory Alloy – Nickel titanium alloy is a shape memory alloy.
Answer.
Synonym: Nitinol (Nickel Titanium Naval Ordinance Laboratory)
Inventor: William R. Buchler
Introduced by: Andersen in 1971
Properties of shape memory alloy:
- Super elasticity
- Shape memory
- High working range
- Low stiffness
Advantages of shape memory alloy: Procedure low and more constant force on teeth
Disadvantages of shape memory alloy:
- Cannot be bent
- Cannot be soldered/welded
Orthodontics Lab Procedures Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. Solder and Flux.
Answer.
Solder: Alloys used as filler metal between two metals
Properties of solder:
- Resist tarnish and corrosion
- Low fusion temperature
- Free-flowing
- Similar strength as the metals to be joined
- Colour similar to metals to be joined
- Ex – Gold, silver, copper, zinc, tin and nickel
Flux: means flowing
- Important for good solder joint
Uses of flux:
- Removal of oxide coating of solder
- Dissolves impurities
- Prevents oxidation
- Reduces melting point
Flux Composition:
- Borax glass – 55%
- Boric acid – 35%
- Silica – 10%
Question 2. Antiflux.
Answer.
Flux:
- Means flowing
- Important for good solder joint
Uses of Flux:
- Removal of oxide coating of solder
- Dissolves impurities
- Prevents oxidation
- Reduces melting point
Composition of Flux:
- Borax glass – 55%
- Boric acid – 35%
- Silica – 10%
Antiflux:
- Confines flow of molten solder
- Ex. Lead pencil markings
- Graphite lines
- Iron rouge
Question 3. Gases used for soldering.
Answer.
- Gas air/oxygen torch flame
- Hydrogen
- Natural gas
- Acetylene
- Propane
Question 4. Sensitization and stabilization of stainless steel.
Answer.
Sensitization: At 400-900 c, stainless steel resists corrosion and tarnish
- At lower temperatures, carbon reacts with the surface granules and forms chromium iron carbide causing tarnish and corrosion
- This can be prevented by decreasing carbon content or by cold working of stainless steel
Stabilization:
- The process to prevent sensitization
- For it, two/more metals are added, for example, titanium, niobium
Question 5. Irreversible Hydrocolloids (Alginate).
Answer.
Advantages of Irreversible Hydrocolloids:
- Easy to manipulate
- Comfortable
- Inexpensive
- Pleasant taste
- Hydrophilic
- Biocompatible
Disadvantages of Irreversible Hydrocolloids:
- Tears easily, and require immediate pouring
- Incompatible with epoxy resin
Composition of Irreversible Hydrocollids:
- Potassium Alginate
- Calcium sulfate dehydrate
- Potassium sulfate
- Diatomaceous earth
- Sodium phosphate
- Glycol
- Pigments
- Sodium silicofluoride
Orthodontics Lab Procedures Viva Voce
- Gold foil filling is the best example of cold welding
- Welding is a process of joining two metals directly under pressure
- The space provided between the metals to be joined is 0.5 mm
- Borax glass is the main component of dental flux
- The oxidized layer in the metallic surfaces to be joined is removed by antireflux
- Nickel in dental solder gives a white color to the solder
- The copper component in solder gives the yellow color
- Fusion temperature exceeding 150 degrees is used for brazing
