Oral Medicine Tumours Short Essays
Question 1. Hemangioma
Answer:
Hemangioma
- They are relatively common benign proliferative lesions of vascular tissue origin
Hemangioma Clinical Features:
- Age And sex: Early-age females are commonly affected
- Site: Intraorally over
- Tongue
- Lip
- Buccal mucosa
- Palate
- Within jawbones
- Within salivary gland
- Hemangioma Presentation
- They are usually raised, multinodular, red or purple lesions
- When a hemangioma is compressed with the help of a slide it blanches
- Once the pressure is released, its reddish appearance returns due to the refilling of the tumor cells with blood
- It is soft and compressible
- The size of the lesion varies from time to time
- Port wine stain is often seen over the face
- Jawbones involvement
- Mandible is more commonly affected
- It produces slow enlarging, painful, expansile jaw swelling
- It may cause erosion of the bone
- Loosening of the teeth
- Anesthesia or paraesthesia of the skin and oral mucosa
Hemangioma Differential Diagnosis:
- Pyogenic granuloma
- Mucoceles
- Kaposi’s sarcoma
- Salivary gland neoplasm
Read And Learn More: Oral Medicine Question and Answers
Hemangioma Management:
- Local excision for smaller lesions
- Larger lesions are treated by excision after pretreat¬ment of the lesion with sclerosing agents to reduce the size of the lesion
Question 2. AOT
Answer:
AOT Origin: reduced enamel epithelium
AOT Clinical Features:
- Age: Young age
- Sex: Female
- Site: Maxillary anterior region
AOT Presentation:
- Slow enlarging, small, bony hard swelling
- Elevation of the upper lip
- Displacement of teeth
- Expansion of cortical plates
- Asymptomatic
- Nodular swelling over gingiva
AOT Radiographic Features:
- Well-defined, unilocular, radiolucent area
- Interior small radiopaque foci
AOT Treatment:
Surgical enucleation
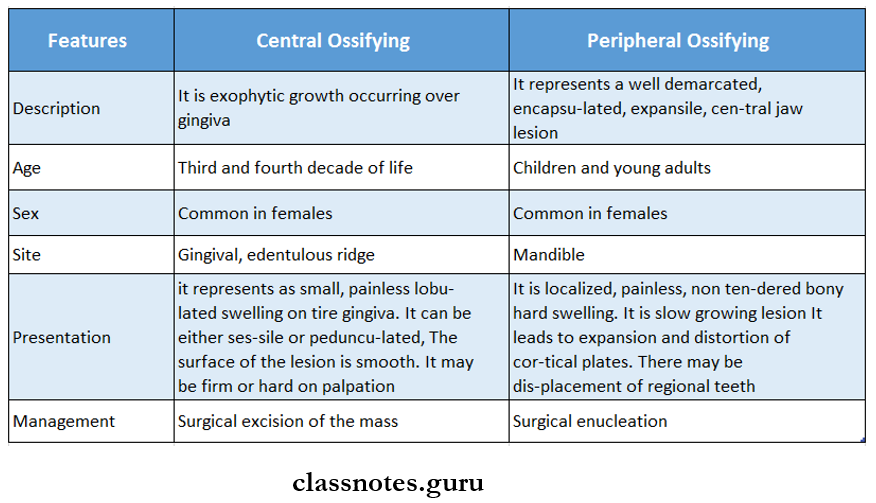
Question 3. Ossifying fibroma
Answer:
Ossifying Fibroma
Question 4. Malignant melanoma.
Answer:
Malignant Melanoma
- Malignant Melanoma is a malignant neoplasm arising from melanocytes of the skin and mucous membrane
Malignant Melanoma Clinical Features:
- Age And sex: It affects older aged people
- Sites:
- Hardpalte
- Maxillary alveolar ridge
- Less frequently,
- Lower jaw
- The floor of the mouth
- Tongue
- Buccal mucosa
- Parotid gland
Malignant Melanoma Presentation
- It initiates as a macular pigmented lesion
- Some of them appear as inflamed area
- The pigmented lesions are dark brown or bluish-black
- Initially, they are rapidly growing, large painful dif¬fuse mass
- Surface ulceration may occur It may be secondarily infected
- It spreads rapidly and destroys the involved bone
- It leads to the loosening and exfoliation of teeth
- There may be a metastasis of the tumor cells to distant sites.
Malignant Melanoma Management:
Radical surgery with prophylactic neck dissection is done
Question 5. Kaposi sarcoma.
Answer:
Kaposi Sarcoma
- Kaposi Sarcoma is a malignant neoplasm arising from the endothelial cells of the blood capillaries
Kaposi Sarcoma Etiology:
- Genetic predisposition
- HIV
- Immunosuppression
- Environmental factors
Kaposi Sarcoma Clinical Features:
- Sites: Maxillary gingival, tongue
- Clinical stages:
1. Patch Stage:
- Patch Stage is the initial stage of the disease and during this, a pink, red, or purple macule appears over the oral mucosa
2. Plaque Stage:
- Plaque Stage continues into the plaque stage with time and during this stage, the lesion appears as a large, raised plaque
3. Nodular Stage:
- The nodular Stage is the last stage of the disease
- The nodular Stage is characterized by the occurrence of multiple nodular lesions on the skin or the mucosa
Kaposi Sarcoma Differential Diagnosis:
- Pyogenic granuloma
- Hemangioma
- Angiosarcoma
Kaposi Sarcoma Management:
- Radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy.
