Ceramics Important Notes
1. Composition Of Porcelain
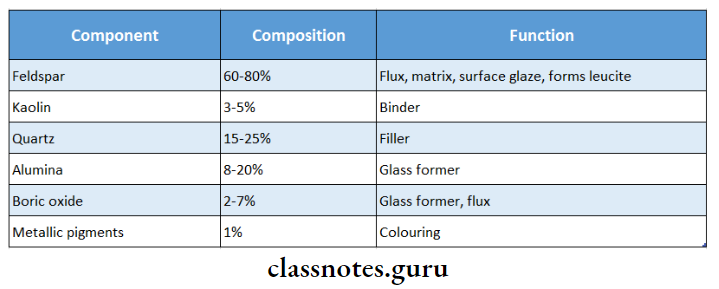
2. Feldspar
- Feldspar is the primary constituent of porcelain
- When melted it forms a crystalline phase called leucite and a glass phase
- Leucite is the basic glass former
3. Bonding Of Porcelain To Metal Occurs By:
- Chemical bonding
- Mechanical bonding
4. Indications Of Ceramics
- Aesthetics
- Large defects or previous restorations
- Wide Faciolingual defect
5. Contraindication Of Ceramics
- Heavy occlusal forces
- Inability to maintain a dry field
- Deep subgingival preparations
Read And Learn More: Operative Dentistry Short And Long Essay Question And Answers
Ceramics Short Answers
Question 1. Aluminous Porcelain.
Answer:
Aluminous Porcelain:
- Aluminous Porcelain is a ceramic consisting of a glass matrix phase and at least 35 alumina
- Introduced by Mclean and Hughes
Aluminous Porcelain Preparation:
The concentration of alumina crystals and glass powder are mixed, pre fritted at 1200°C
↓
Mixture is grounded
↓
Incorporated into the glass matrix
Aluminous Porcelain Advantages
- Increase strength, toughness, and elasticity
Aluminous Porcelain Example:
- Hi-Cream
Question 2. Castable Ceramic/Dicor.
Answer:
Castable Ceramic:
Castable Ceramic/Dicor Composition:
- 55% – Tetrasilicic fluoride crystals
- 45% – Glass Ceramic
Castable Ceramic/Dicor Advantages:
- Marginal fit
- High strength
- High surface hardness
- Wear resistance
Ceramics Viva Voce
- Components of CAD/CAM – scanning device, CAD- computer-aided design, CAM – computer-assisted manufacture
- Occlusal reduction – 1.5-2 mm
- Occlusal divergence – 6-8° per wall
- Isthmus width – 1.5 mm
- Axial depth of proximal box – 1.5 mm
- Cavosurface angle – 90°
- The gingival margin of the proximal box should be placed supragingival
