Obturation Of Root Canal Important Notes
- Techniques of heat compaction of gutta percha
- Vertical compaction
- Injectable gutta percha
- Thermo-mechanical compaction
- Core carrier technique
- Composition of gurra percha cones
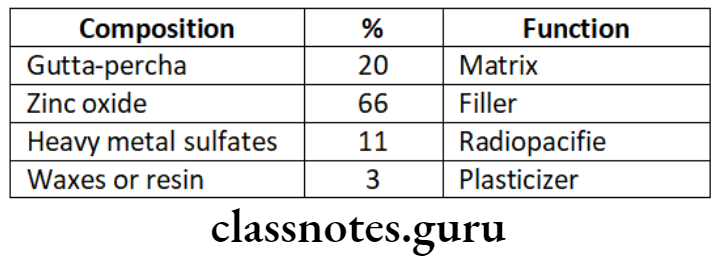
- Ideal requirements of filling material
- Easy to introduce and easy to remove
- Seal canal laterally as well as apically
- Impervious to moisture
- Should not shrink after insertion
- Should be bactericidal
- Should not stain the tooth
- Should not irritate periapex
- Should be sterile
Root Canal Obturation Techniques
Obturation Of Root Canal Long Essays
Question 1. Describe briefly different obturation techniques. Add a note on materials used for obturation.
Answer.
Obturation Methods:
Use Of Cold Guttapercha:
- Lateral compaction
Use Of Chemically Softened Guttapercha:
- Chloroform
- Halothane
- Eucalyptol
Read And Learn More: Endodontics Question and Answers
Use Of Heat-Softened Guttapercha:
- Vertical compaction
- System B
- Sectional compaction
- Thermoplasticized
- Solid core
- Mcspadden
Obturation Of Root Canal Lateral Compaction:

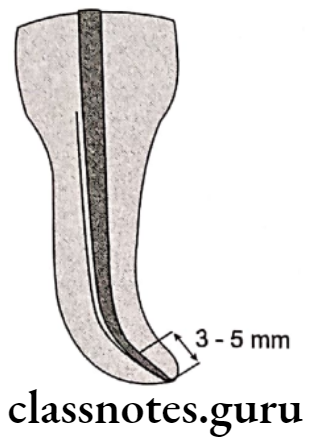
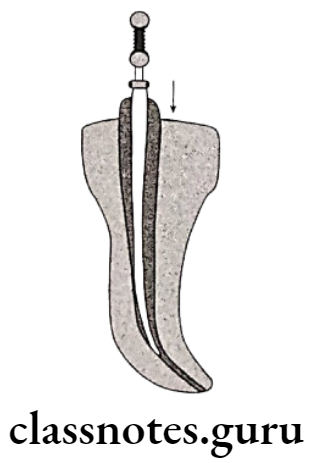
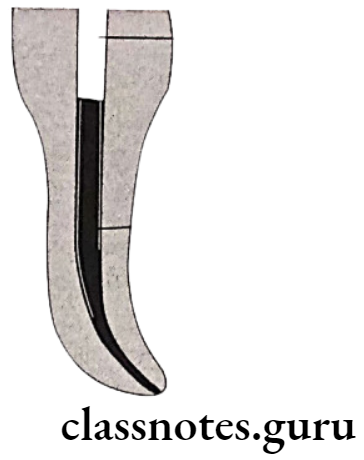
Obturation Of Root Canal Advantages:
- Reduces over filling
Obturation Of Root Canal Disadvantages:
- Do not produce homogenous mass
- May not fill canal irregularities
Obturation Of Root Canal Obturating Materials:
- Plastics – GP, resilon
- Solid/metal core – Silver points, gold
- Cements and pastes – Hydron, MTA, Calcium phosphate
Obturation Of Root Canal Properties:
- Easily introduced
- Seal canal
- Stable
- Baceriostatic
- Non-staining
- Radiopaque
- Non-irritating
- Sterile
- Easily removed
- Imprevious to moisture
Obturation In Endodontics
Question 2. What are the various obturation techniques? Write in detail about thermoplasticized technique.
Answer.
Obturating Methods:
Obturating Methods Use Of Cold Guttapercha:
- Lateral compaction
Obturating Methods Use Of Chemically Softened Guttapercha:
- Chloroform
- Halothane
- Eucalyptol
Obturating Methods Use Of Heat-Softened Guttapercha:
- Vertical compaction
- System B
- Sectional compaction
- Thermoplasticized
- Solid core
- Mcspadden
Thermoplasticized Gutta Percha Technique
Thermoplasticized Gutta Percha Principle:
- It comprises a pressure apparatus consisting of an insulated electrically heated syringe barrel and a seledction of needles ranging from 18-25 gauge size
- The plunger is designed to prevent backward flow of the gutta percha
Thermoplasticized Gutta Percha Technique:
- Canal preparation
- Drying of canal
- Sealer is coated on the canal walls
- Gutta percha is electrically heated in a handheld gun that contains a chamber surrounded by a heating element
- Selected needle is positioned at 3-5mm short of the working lenght
- Gutta percha is gradually injected by sqeezing the trigger of the gun and the needle is gradually withdrawn as the canal gets filled apically
- Gutta percha is then compacted using pluggers of appropriate size
- Similarly the rest of the canal is filled
Question 3. Root canal sealers.
Answer.
Root Canal Sealers
- Root canal sealers are necessary to fill irregularities and minor discrepancies between the canal walls and filling
Root Canal Sealers Requirements:
- Should be tacky
- Should create a hermetic seal
- Should be radiopaque
- Should be miscible
- Should be bacteriostatic
- Should set slowly
- should insoluble in oral fluids
- Should not shrink
- Should not stain
Root Canal Sealers Functions:
- Antimicrobial agent
- Lubricant
- Binding agent
- Fills the space between material and canal walls
- As obturationg material
- Give radiopacity
Root Canal Sealers Classification:
Eugenol:
- Eugenol Silver Containing:
- Kerr sealer
- Powder
- Zinc oxide
- Silver
- Thymol iodide
- Liquid
- Oil of cloves
- Canada balsam
- Powder
- Kerr sealer
- Eugenol Silver Free:
- Grossman’s sealer
- It consists of
- Powder
- Zinc oxide
- Staybellite resin
- Bismuth subcarbonate
- Barium sulphate
- Sodium borate
- Liquid
- Eugenol
- Powder
Eugenol Medicated:
- Iodoform
Eugenol Non-Eugenol:
- Hydron
- Glass ionomer
- Diaklet
- It is chemically polyketone
- It consists of
- Powder
- Zinc oxide
- Bismuth phosphate
- Liquid
- Polyvinyl resin
- Powder
Eugenol Advantages:
- Good adhesion to tooth
- Rapid set
- High tensile strength
Eugenol Disadvantages:
- Tacky in texture
- Difficult to manipulate
Gutta Percha Obturation Method
Obturation Of Root Canal Short Essays
Question 1. Ideal requirements of root canal sealers. Add a note on AH26.
Answer.
Root Canal Sealers Requirements:
- Should be tacky
- Should create hermetic seal
- Should be radiopaque
- Should be miscible
- Should be bacteriostatic
- Should set slowly
- Should be insoluble in oral fluids
- Should not shrink
- Should not stain
AH26:
- This is an epoxy resin containing sealer
- It is adhesive, well tolerated by tissues and provides good seal
AH26 Disadvantages:
- Staining of tooth structure as it contains silver
- It is insoluble in solvents
AH26 Plus:
- This eliminates all the disadvantages associated with AH26
Question 2. Obturating materials.
Answer.
Obturating materials Materials:
- Plastics – GP, resilon
- Solid/metal core – Silver points, gold
- Cements and pastes – Hydron, MTA, Calcium phosphate
Obturating Materials Properties:
- Easily introduced
- Seal canal
- Stable
- Bacteriostatic
- Non-staining
- Radiopaque
- Non-irritating
- Sterile
- Easy removed
- Imprevious to moisture
Question 3. Gutta Percha.
Answer.
Gutta Percha
Endodontic filling material
Gutta Percha Forms:
- Alpha
- Beta
- Amorphous
Gutta Percha Available Forms:
- GP points
- Auxillary points
- Greater taper
- Syringe
- Medicated
Gutta Percha Advantages:
- Compactibility
- Inertness
- Dimensional stable
- Tissue tolerance
- Radiopacity
- Plasticity
- Dissolve in some solvents
Gutta Percha Disadvantages:
- Lack of rigidity
- Lack of adhesiveness
- Easily displaced
Warm Vertical Compaction Technique
Question 4. Grossman’s Sealer.
Answer.
Grossman’s Sealer Composition:
Grossman’s Sealer Powder:
- Zinc oxide
- Staybelite resin
- Barium sulfate
- Bismuth subcarbonate
- Sodium borate
Grossman’s Sealer Liquid:
- Eugenol
Grossman’s Sealer Properties:
- Plasticity
- Slow setting time
- Good sealing
Grossman’s Sealer Disadvantage:
- Require vigorous mixing
- Setting time – 2 hours at 37°C
Grossman’s Sealer Influenced By:
- Quality of ZnO and pH
- Mixing
- Humidity
- Temperature and dryness of slab and spatula
Obturation Of Root Canal Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. Composition of Grossman’s sealer.
Answer.
Grossman’s Sealer Powder:
- Zinc oxide
- Staybelite resin
- Barium sulfate
- Bismuth subcarbonate
- Sodium borate
Grossman’s Sealer Liquid:
- Eugenol
Question 2. Diaket
Answer.
Diaket
- By Schmidt in 1951
Diaket Composition:
Diaket Powder:
- Zinc Oxide
- Bismuth phosphate
Diaket Liquid:
- 2,2 dihydroxy – 5,5 dichlorodiphenyl methane
- Triethanolamine
- B-diketone
- Caproci acid
- Copolymers
Diaket Advantages:
- Good adhesion
- Fast setting
- Stable
- Superior tensile
Diaket Disadvantages:
- Toxic
- Tacky
- Setting is effected by phenol
Root Canal Filling Materials
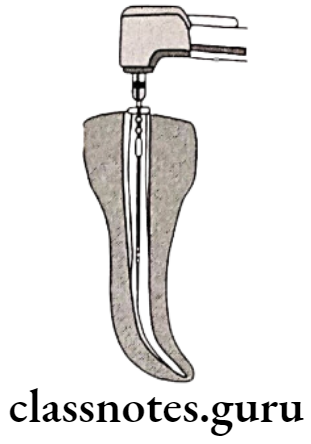
Question 3. McSpadden compaction.
Answer.
Mcspadden Compaction Technique:

McSpadden Compaction Advantages:
- Less time
- Easy to insert
- 3D obturation
McSpadden Compaction Disadvantages:
- Unable in narrow and curved canals
- Frequent breakage
- Overfilling
- Shrinkage of guttapercha
Question 4. AH Sealer
Answer.
AH26:
- This is an epoxy resin containing sealer
- It is adhesive, well tolerated by tissues, and provides a good seal
AH26 Disadvantages:
- Staining of tooth structure as it contains silver
- It is insoluble in solvents
AH26 Plus:
- This eliminates all the disadvantages associated with AH26
Root Canal Filling Materials
Obturation Of Root Canal Viva Voce
- Gutta-percha cones may be kept sterile in screw-crapped vials containing alcohol.
- Lateral compaction is easy and quick to perform.
- Tug back refers to the apical seal fit of the master cone.
- Inadequate obturation is the most common cause of RCT failure.
- Silver cones are contraindicated in filling a root canal if the tooth is to be restored with a post and care.
- Ideally, the length of the post and core should be 2/3rd of the root canal.
- Injectable gutta-percha is especially useful while managing canal irregularities.
- Thermafill contains a center carrier which is grooved along 600 of their circumference. and has a coating of gutta-percha.
- The silver cone is stiffer than gutta-percha.
- Endorez is a visible light-curable urethane dimethacrylate resin-based sealer.
