NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Motion And Measurement Of Distances Long Question And Answers
Question 1. Arrange the following lengths in their increasing magnitude 1 metre, 1 centimetre, 1 kilometre, 1 millimetre
Answer:
We know that,
1 kilometre (km) = 1000 metre (m)
1 metre (m) = 100 centimetre (cm)
1 centimetre (cm) = 10 millimetre (mm)
Hence, the increasing order of given units is as follows 1 millimetre <1 centimetre <1 metre <1 kilometre
Question 2. The height of a person is 1.65 m. Express it Into cm and mm.
Answer:
Given, the height of a person = 1.65 m
We know that,
1 metre (m)= 100 centimetre (cm)
1 metre (m)- 1000 millimetre (mm)
The height of a person in cm
= 1.65 × 100 cm = 165 cm
Read and Learn More Class 6 Science Question And Answers
The height of a person in mm
= 1.65 × 1000 mm = 1650 mm

Question 3. The distance between Radha’s home and her school is 3250 m. Express this distance into km.
Answer:
Given, the distance between Radha’s home and her school = 3250 m
We know that,
1 km = 1000 machine
1 m = \(\frac{1}{1000}\) km
Now, the distance between Radha’s home and her school in km
3250 × \(\frac{1}{1000}\)
= \(\frac{3250}{1000}\)
= 3.25 km
Question 4. While measuring the length of a knitting needle, the reading of the scale at one end is 3 cm and at the other end is 33.1 cm. What is the length of the needle?
Answer:
Accurate scale reading begins from zero as shown below

But here the reading on the scale begins with 3 cm
Thus, the error in the scale
= 3 cm- 0 cm = 3 cm
Now, the other end on the scale reads = 33.1 cm
Thus, the actual length of the needle = (Reading on the other end Error reading of the first end)
= 33.1 cm – 3 cm = 30.1 cm
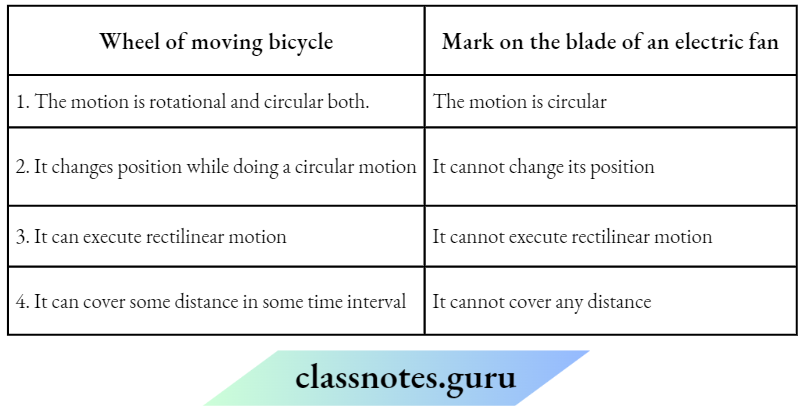
Question 5. Write the similarities and differences between the motion of a bicycle and a ceiling fan that has been switched ON.
Ans.
Similarities are given below
- The wheels of a bicycle and a ceding fan execute a rotational motion on a fixed axis.
- The particles of both exhibit circular motion except the particles at the centre.
- Differences are given below
- A bicycle changes its position while exhibiting circular motion but a ceiling fan does not change its position.
- Bicycles can execute rectilinear motion with translational motion but ceiling fan do not execute rectilinear motion.
Question 6. It is not accurate to measure a length with elastic tapes. Explain why?
Answer:
Elastic tapes are stretchable and their length can be increased during the measurement if it is not handled with care. Therefore, the measurement done by elastic tapes may be greater than the actual length of the object. So, we can say that elastic tapes are not accurate for measuring a length.
Question 7. Three students measured the length of a corridor and reported their measurements. The values of their measurements were different. What could be the reason for the difference in their measurements? (Mention any three)
Answer:
The reasons may be as follows:
- Their scales of measurement may not be standard or they may be using different scales of measurement.
- The length of the scale may not be proper, i.e. the length of the scale may be shorter than the length they want to measure.
- There may be some errors in the scale which they are using or they may not be using the correct method of observing the scale.
Question 8. While travelling in a train, it appears that the trees near the track are moving whereas co-passengers appear to be stationary. Explain the reason.
Answer:
While travelling, trees near the track seem to be moving back (i.e. opposite to the direction of motion of a train) because there is a relative motion between outside trees and the moving train. In the case of co-passengers, the relative motion between us and co-passengers is zero, so they appear to be stationary.
Question 9. The blades of a moving electric fan are different in the following ways:
Answer:
Question 10. Boojho was riding his bicycle along a straight road. He classified the motion of various parts of the bicycle as
- Rectilinear motion
- Circular motion and
- Both rectilinear as well as circular motion.
Can you list one part of the bicycle for each type of motion? Support your answer with a reason:
- Rectilinear motion: Rectilinear motion The handle of a bicycle will always move in a rectilinear path because it cannot do circular or rotatory motion.
- Circular motion: Circular motion The paddles of the bicycle will always move circularly around its chain fixing system because it cannot move in a forward direction without the whole chain system
- Both rectilinear and circular: Both rectilinear and circular The wheels of the bicycle will move in rectilinear as well as in circular motion because the wheel as a whole will move forward and its point or particles around the rim will execute circular motion
Question 11. A student measures the length of his classroom four times using a stick
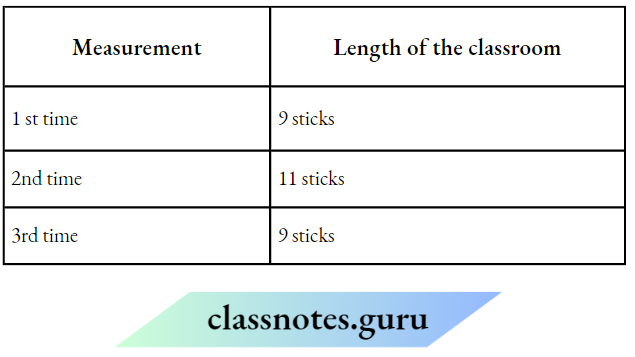
Based on the above observation, answer the following questions.
1. Which measurement is likely to be wrong?
- 1 st time
- 2nd time
- 3rd time
- 4th time
Answer: 3. 3rd time
2. Anil and his friend measured the length of the same classroom using their feet. Will their measurements be the same? Explain your answer.
Answer:
Their measurement will be different because the length of their feet may be different.
3. Which of these is a standard unit of length?
- Leg
- Stick
- Hand
- Metre
Answer: 4. Metre
Question 12. Identify the different types of motion in the following word diagram.
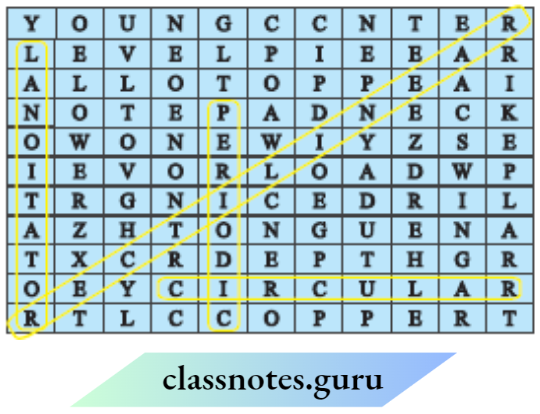
Answer:
Different types of motion are represented in word diagrams are
- Rectilinear motion
- Circular motion
- Periodic motion
- Lanotator
Question 13. Which type of motion does the rotation of the minute arm involve? Choose Yes or No for the correct response.
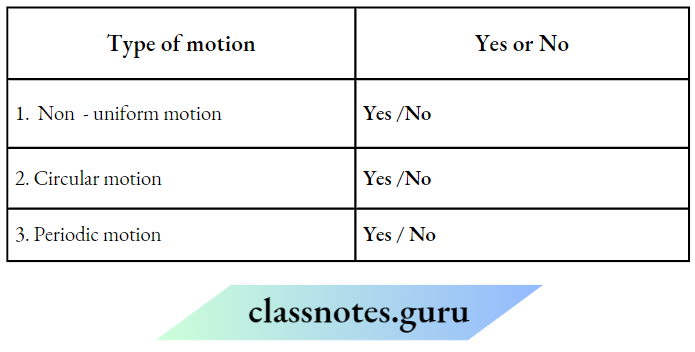
Answer:
1. No
2. No
3. Yes
4. Yes
Question 14. Which of these could Jenny use to measure her son’s __________________ height? Choose Yes or No for the correct Competency response.

Answer:
1. Yes
2. No
3. Yes
Question 15. Four children measured the length of a table which was about 2 m. Each of them used different ways to measure it.
Which one of them would get the most accurate length? Give reasons for your answer.
- Shyam measured it with a half-metre-long thread.
- Gurmeet measured it with a 15 cm scale from her geometry box.
- Reena measured it using her handspan.
- Salim measured it using a 5 m-long measuring tape.
Answer: 4. Salim measured it using a 5 m-long measuring tape.
- Salim will measure it most accurately for the following reasons
- The length 2 m which he wants to measure can be measured using this scale only in a single attempt.
- This scale is the standard scale and will measure the correct measurements.
- Other scales given are either non-standard or have a length less than the length we want to measure.
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Motion And Measurement Of Distances Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Are all the measurements for the room and table using everybody’s foot and handspan respectively, equal?
Answer:
The measurement of a room and table using the foot and handspan of different persons will not be equal. This is because the footsteps and handspan of every person are not the same so, their distance can vary.
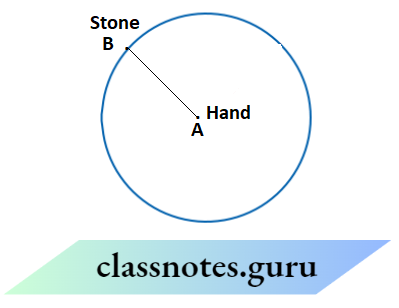
Question 2. Boojho is not sure why we say that the distance of the stone from your hand is the same when we whirl it around. Can you help him understand this? Remember that the stone is held with string.
Answer:
Distance is actually defined as the length between two places. It is clear from the diagram that when we whirl the stone, the length between points A and B , i.e. between hand and stone does not change.
Hence, the distance is the same.
Question 3. Give two examples of each of the modes of transport used on land, water and air.
Ans.
There are mainly three main modes of transport which are given below
- Land transports: Those transports that run on land are called land transports,
- Example: Bus and truck.
- Water transports: Those transports that run on water are called water transports,
- Example: Boat and ship.
- Air transports: Those transports that run in the air are called air transports
- Example: Aeroplanes and helicopters.
Question 4. Why can a pace or a footstep not be used as a standard unit of length?
Answer:
A pace or a footstep cannot be used as a standard unit of length because the length of a footstep, forearm length and handspan of different persons is different. Since standard units must be similar at all places of the world and in all kinds of conditions. It should not depend upon body parts and natural phenomena. So, footsteps and other such measuring systems cannot be used as a standard unit
Question 5. Why could you not use an elastic measuring tape to measure distance? What would be some of the problems you would meet in telling someone about a distance you measured with an elastic tape?
Answer:
Elastic substances have the property of elasticity, i.e. these can be stretched by applying some force. Therefore, an elastic measuring will not give an accurate measurement. In elastic tape measurement, the measurement of the same object may be different due to its stretching.
Question 6. Give two examples of periodic motion.
Answer:
Two examples of periodic motions are
- The motion of the earth around the sun
- To and fro movement of the bob of a pendulum
Question 7. We need standard units of measurement for a quantity. Explain why?
Answer:
We need standard units of measurement because the units like handspan, foot, and cubit differ from person to person. So, for a uniform measurement, the standard unit of measurement is required.
Question 8. Can the length of the pipe be measured correctly with a ruler? Explain your answer
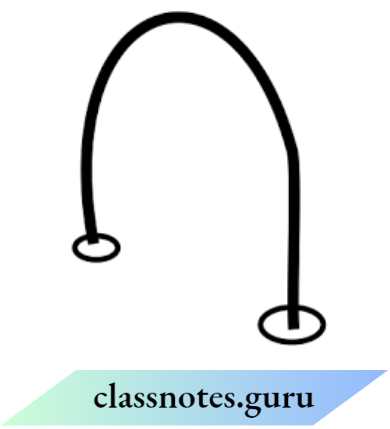
Answer:
The length of the pipe cannot be measured correctly because a ruler can measure the length of straight objects.
Question 9. Correct the following.
- The motion of a swing is an example of rectilinear motion.
- 1 m = 1000 cm
Answer:
- The motion of a swing is an example of periodic motion.
- 1 m = 100 cm
Question 10. Mamta Is measuring a piece of wood with a broken meter scale. Her friend Kanchan corrects her by measuring It from any full mark of meter scale.
- State the values that Kanchan reflects here.
- Give one correct way to measure
Answer:
- Kanchan is intelligent, helpful and has good knowledge of the subjects,
- One correct way to measure from a broken scale is to start with full marks.
Question 11. There was a quarrel between Ram and Shyam as the measured length of his school table was different from each other. Prlya came and said that calculation of length by Shyam Was more accurate and gave a simple explanation for It.
- State the values that Priya reflects here.
- Mention the cause for different measurements of Ram and Shyam.
Answer:
- Priya is intelligent and has good knowledge upto class 6th
- As length measured by Shyam is from measuring tape which is not elastic as of Ram, so they have different measurements.
Question 12. Describe in detail how the thickness of a thin wire can be determined.
Answer:
First of all, take a round pencil and try to wrap the given wire around the pencil making 25 turns forming a coil. Now, measure the length of the wire that turns the formed coil. Divide the total length of the coil by number of turns. This is the thickness of the wire
Question 13. The photograph given In the figure shows a section of a grille made up of straight and curved Iron bars. How would you measure the length of the bars of this section, so that the payment could be made to the contractor?
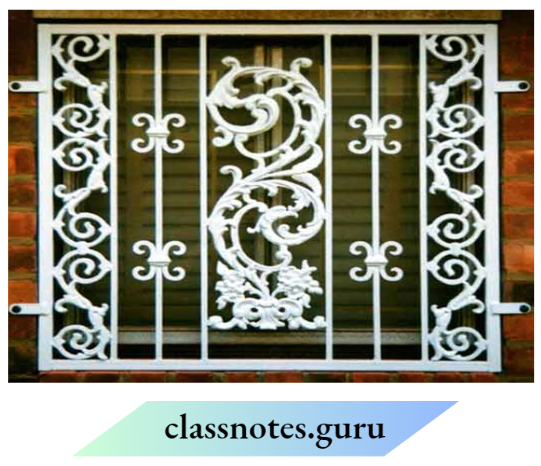

Answer:
To measure the length of the bars of the grille, the straight part of the iron bar is measured directly with measuring tape and the curved part is firstly measured with thread, then after measuring tape is used to measure the length of the thread.
Question 14. The picture shows the minute arm of a clock rotating

Question 15. A car is moving on a road. Suddenly, the driver applies the brakes and stops the car. What can you say about the two states of the car, i.e. when it is moving and when it stops?
Answer:
An object is said to be at rest when it does not change its position with time. If an object changes its position concerning time, it is said to be in motion.
Question 16. Can an object be in motion and rest simultaneously for different observers? Give an example and consequence.
Answer:
Yes, a person driving a car is at rest concerning another person who is sitting in the same car but he is in motion concerning a person standing roadside. The state of motion and rest depends upon the observer or reference point.
Question 17. Briefly explain the type of motion performed by the earth.
Answer:
The earth performs two types of motion. One of the motions is when it moves around the sun, then it is said to possess circular motion and on the other hand, it also rotates about its axis, called rotational motion.
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Motion And Measurement Of Distances Very Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Are there any early modes of transport that are not in use today? „
Answer: Yes, for example, bullock cart, horse cart, camel cart, etc.
Question 2. Explain how people know how far they have travelled.
Answer: By measuring distance by a particular standard unit of measurement, we can measure how far they have travelled.
Question 3. What would you suggest Paheli and Boojho do, to measure the length of the whole desk? Page 76
Answer: They should use a small length of string instead of a cricket wicket and bails to measure the length of the desk.
Question 4. How can we use a string to measure distance less than the length of the string
Answer: By marking 1/2,1/4 and 1/8 of string length.
Question 5. How would you decide whether an object is in motion or at rest?
Answer: An object is said to be at rest when it does not change its position with time, while an object is said to be in motion when it changes its position with time
Question 6. Mention the two contributions in the 20th century towards transportation.
Answer: The two contributions in the 20th century towards transportation are electric trains and supersonic aeroplanes.
Question 7. Mention some modes of transportation of ancient times.
Answer: In ancient times, there were some modes of transportation like bullock carts, horse carts, camel carts, etc.
Question 8. Name one method of ancient times which is used to measure the length.
Answer: Handspan is one of the methods, which was used to measure the length in ancient times.
Question 9. Mention the name of the universally accepted system of measurement.
Answer: The system of international units is a universally accepted system of measurement.
Question 10. State how many kilometres are there in 1 metre.
Answer: There are \(\) kilometre in 1 metre
Question 11. Give the name of the device used to measure the girth of a tree.
Answer: The device which is used to measure the girth of a tree is a measuring tape.
Question 12. Name the motion exhibited by a freely falling stone.
Answer: The motion exhibited by a freely falling stone is rectilinear.
Question 13. Give the name of the motion possessed by the vehicles on a straight road.
Answer: Rectilinear motion is the motion possessed by vehicles on a straight road.
Question 14. State whether the hour hand of a wall clock is at rest or in motion.
Answer: Due to the changing position of the hand of a wall clock, it always is in motion.
Question 15. State an example of a rotational motion.
Answer: One example of rotational motion is the motion of the earth about its axis.
Question 16. Explain the term non-periodic motion.
Answer: Non-periodic motion is a motion which does not repeat in equal intervals of time.
Question 17. Name the type of motion possessed by the planet around the sun.
Answer: The motion possessed by the planets around the sun is circular motion.
Question 18. Give the name of the motion that a simple pendulum exhibits.
Answer: Periodic motion is exhibited by the simple pendulum.
Question 19. How are the motions of the wheel of a moving bicycle and a mark on the blade of a moving electric fan different? Explain.
Answer: The motions of the wheel of a moving bicycle and a mark on
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Motion And Measurement Of Distances Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. One metre is ___________cm.
Answer: 100
Question 2. Five kilometres is ______ m.
Answer: 5000 [v 1 km = 1000 m]
Question 3. The motion of a child on a swing is ________
Answer: Periodic motion
Question 4. Motion of the needle of a sewing machine is ___________
Answer: Periodic motion
Question 5. The motion of a wheel of a bicycle is ______
Answer: Circular motion
Question 6. Different modes of ___________ are used to go from one place to another _____
Answer: Transport
Question 7. The length of a curved line can be measured by using ___________
Answer: Thread or measuring tape
Question 8. The metric system for measurement was created by the ___________
Answer: French
Question 9. The SI unit of length is ___________
Answer: Metre
Question 10. 2000 cm is equal to ___________ metre
Answer: 20
Question 11. Motion is the change In ___________of in object.
Answer: Position
Question 12. The motion of an object or a part of it around a fixed point is Known as ___________ motion.
Answer: Circular
Question 13. A body repeating its motion after a certain Interval of time is in ___________ motion
Answer: Periodic
Question 14. In rectilinear motion, the object moves ___________ a ___________ line
Answer: In, Straight
Question 15. A plucked string of a star executes ___________ motion.
Answer: Oscillatory
Question 16. The motion that repeats itself after a regular interval of time is _____________________
Answer: Periodic motion
Question 17. A stone falling from a height exhibits _______________________motion.
Answer: Rectilinear
Question 18. The length between the tip of the middle finger and the chin of an outstretched arm is ______________
Answer: Yard
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Motion And Measurement Of Distances True Or False
Question 1. An elastic tape cannot give a true measurement
Answer: True
Question 2. A cloth merchant uses a meter rod to measure the length of the cloth.
Answer: True
Question 3. From a broken meter scale, measurement can be done from a zero mark.
Answer: False
Question 4. One metre is equal to 1000 cm.
Answer: False
Question 5. The SI unit of distance is cm.
Answer: False
Question 6. The motion of the earth about its axis is rotatory.
Answer: True
Question 7. A flying bird in the sky is at rest.
Answer: False
Question 8. The motion of the wheel of a car is rectilinear as well as circular motion.
Answer: True
Question 9. The object which does not change its position time is said to be at rest.
Answer: True
Question 10. A centimetre is a smaller unit than a millimetre.
Answer: False
Question 11. The measuring tape is used to measure the girth of a tree.
Answer: True
Question 12. A spinning top shows circular motion.
Answer: True
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Motion And Measurement Of Distances Assertion-Reason Question And Answers
The following questions consist of two statements Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below.
- Both A and R are true and it is the correct explanation of A.
- Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true but R is false
- A is false but R is true
Question 1.
Assertion (A): The SI unit of length is metres.
Reason(R): A yard gives the accurate measurement of length.
Answer: 3. A is true but R is false
A yard does not give the correct length because a yard is the length from the chin to the thumb of an outstretched arm. It may vary from person to person.
Question 2.
Assertion (A): While travelling? bus and co-travellers appear to be stationary.
Reason (R): The position of co-passengers is not changing concerning each other.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and it is the correct explanation of A.
Co-travellers appear to be stationary because all are moving at the same speed, so the positions of co-passengers are not changing concerning each other.
Question 3.
Assertion (A): The motion of the earth around the sun is periodic.
Reason (R): The earth repeats its motion after a fixed interval of time.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and ft is the correct explanation of A.
The earth repeats its motion every 1 year, hence its motion is periodic.
Question 4.
Assertion (A): A rolling ball on the ground shows only rectilinear motion.
Reason (R): A rolling ball moves from one place to another
Answer: 4. A is false but R is true
An assertion is false because the rolling ball shows both rectilinear and rotational motion.
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Motion And Measurement Of Distances Match The Columns
Question 1. Match Column A with Column B
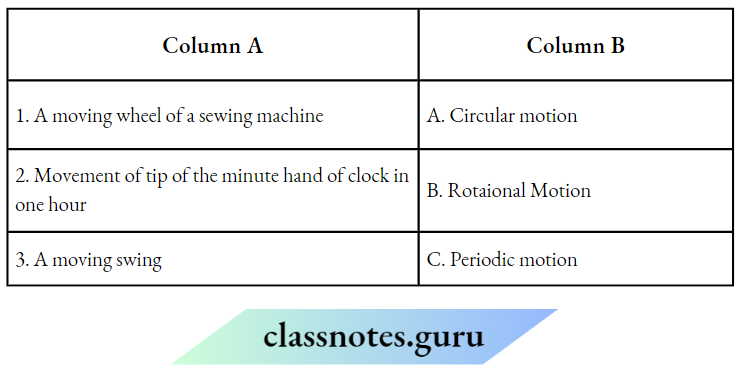
Answer: 1- B, 2- A, 3- C
