NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Getting To Know Plants Long Question And Answers
Question 1. Correct the following statements and rewrite them in your notebook.
- Stem absorbs water and minerals from the soil
- Leaves hold the plant upright
- Roots conduct water to the leaves
- The number of petals and sepals In a flower is always equal
- If the sepals of a flower are joined together, Its petals are also joined together
- If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil is joined to the petal
Answer:
- Correct statements are as follows
- Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
- Roots hold the plant upright.
- The stem conducts water to the leaves.
- The number of petals and sepals in a flower can be equal or different.
- If the sepals of a flower are joined together, its petals are not necessarily joined together.
- If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil may or may not be necessarily joined together.
Read and Learn More Class 6 Science Question And Answers
Question 2. Can you find a plant in your house or In your neighbourhood, which has a long, but weak stem? Write its name. In which category will you place it?
Answer: Yes, we can find money plants in our house as well as in our neighbourhood, which have a long, but weak stem. It is classified as a climber. It readily climbs up by taking support from neighbouring structures such as a tree or a rod, etc.

Question 3. What is the function of a stem?
Answer: The functions of a stem in a plant are as follows
- It conducts water from the roots to the leaves and other parts of the plants.
- It conducts food from leaves to other parts of the plants.
- It bears leaves, flowers and fruits.
- It provides support to the plant.
Question 4. Which of the following leaves have reticulate venation? Wheat, Tulsi, Maize, Grass, Coriander (dhania), China rose.
Answer: Leaves of tulsi, coriander and China rose have reticulate venation.
Question 5. If a plant has fibrous roots, what type of venation do its leaves have?
Answer: If a plant has a fibrous root, its leaves have parallel venation.
Question 6. If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation, what kind of roots will it have? If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation, then the plant is likely to have tap roots. Is it possible for you to find out whether a plant has tap roots or fibrous roots by looking at the impression of its leaf on a sheet of paper?
Answer: Yes, it is possible to find whether a plant has a taproot or fibrous root by looking at the impression of its leaf on paper. If the leaf has parallel venation, the roots ofthe plant will be fibrous root the leaf has reticulate venation, the root will be tap root.
Question 7. What are the parts of a flower?
Answer: The parts of a flower are as follows
- Petals
- sepals
- Stamens
- Pistil
Question 8. From the following plants, which of them have flowers?
Grass, maize, wheat, chilli, tomato, tulsi, peepal, sheesham, banyan, mango, jamun, guava, pomegranate, papaya, banana, lemon, sugarcane, potato, groundnut.
Answer: All ofthe given plants produce flowers. But in some plants such as peepal, sugarcane, grass, etc. the flowers are very small The plants which produce prominent flowers are

Question 9. Name the part of the plant which produces food. Name this process.
Answer: The part plant which produces food is the leaf. This process is known as photosynthesis.
Question 10. In which part of a flower, you will find the ovary?
Answer: Ovary is found in the lowermost part of the pistiL
Question 11. Name two plants in which one has joined sepals and the other has separate sepals.
Answer: Flowers with joined sepals are found in Hibiscus, Datura, cotton, tomato (anyone). Flowers with separate sepals are found in mustard, lotus, lily, jasmine, and rose (anyone).
Question 12. The table lists four different groups of plants and their features
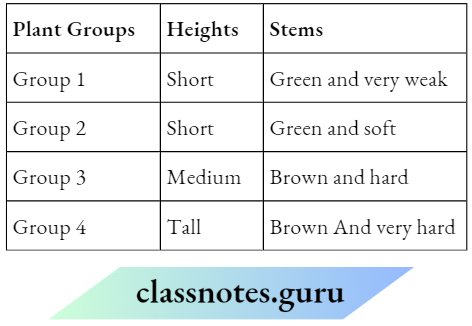
The Picture Shows A Garden Plant.

1. Which group does the garden plant belong to?
- Group 1
- Group 2
- Group 3
- Group 4
Answer: 2. Group 2
2. Which Group Of Plants Most likely needs support to grow?
- Group 1
- Group 2
- Group 3
- Group 4
Answer: 1. Group 1
Question 13. Three similar potted plants were taken to conduct an activity to determine the conditions essential for plant growth. Plant A was kept in sunlight, but not watered. Plant B was kept in sunlight and watered. Plant C was watered and kept in a dark room.
- Which plant will grow best and which plant(s) will not show proper growth?
- The above experiment lists two main factors necessary for plant growth
- Leaves were taken from each of the plants and boiled to remove the green colour. They then had an iodine solution placed on the leaves. Describe and explain what would be observed for leaves A and B.
Answer: Plant TV will grow best and plants ‘A‘ and ‘C’ will not show proper growth.
The two main factors necessary for plant growth are sunlight and water.
The result will not be the same as the leaf from plant ‘A’ will show no change In colour due to the absence of starch, but the leaf from plant ‘B’ will turn bluish-black because of the presence of starch.
Question 14. Ajit wants to test If plants need sunlight to make food. He keeps a potted plant in sunlight, After five days, he tests for the presence of starch In the leaves.

How can Ajit improve his test?
- He should choose a plant with larger green leaves.
- He should test another plant without leaves under the Sun.
- He should test a similar plant kept in the dark for five days,
- He should cover the plant with a transparent glass box to keep it warm.
- Which of the following statements Is true? Write ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ to mark your responses.

Answer:
- He should test a similar plant kept in the dark for five days.
- No, Yes, Yes
Question 15. Identify the Incorrect statements and correct them.
- Anther Is a part of the pistil.
- The visible part of a bud is the petals.
- Lateral roots are present In a tap root.
- Leaves perform the function of transpiration only
Answer:
- It is an incorrect statement as another is a part of the stamen.
- It is an incorrect statement as the visible parts ofthe bud are sepals.
- It is a correct statement.
- It is an incorrect statement as leaves also perform photosynthesis along with transpiration.
Question 16. Read the functions of parts of a plant given below
- Fixes plant to the soil
- Prepares starch
- Takes part in reproduction
- Supports branches and bears flowers.
- In the diagram given in the below figure, write the names of the parts whose function you have just read in the appropriate space.
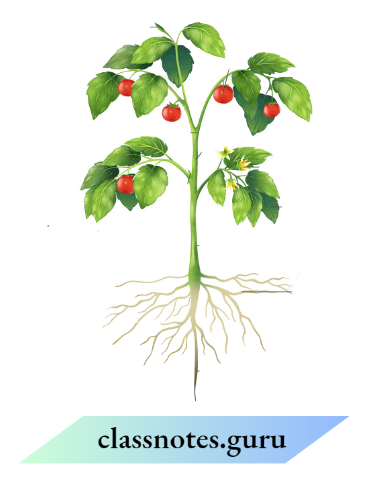
Answer: The functions of parts of a plant are
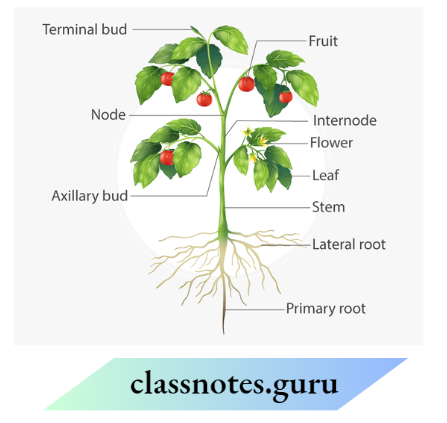
Question 17. Observe the figure and attempt the questions that follow it.
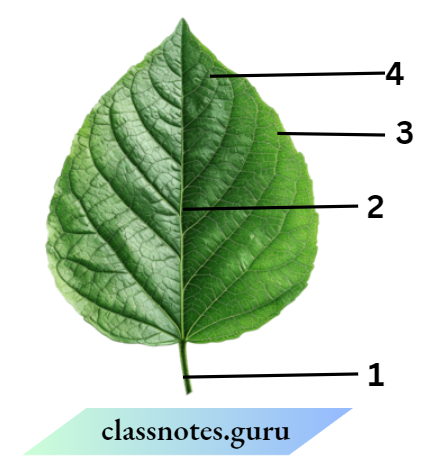
- Label the parts 1, 2, 3 and 4 in the figure.
- What type of venation does the leaf have?
- What type of venation is seen in grass leaves
Answer: 2. In the given figure
- Petiole
- Midrib
- Lamina
- Vein
The leaf has reticulate venation, and the veins in the leaf occur in an irregular way forming a net-like pattern. Grass leaves have parallel types of venation. In which the veins run parallel to each other on both sides of the midrib.
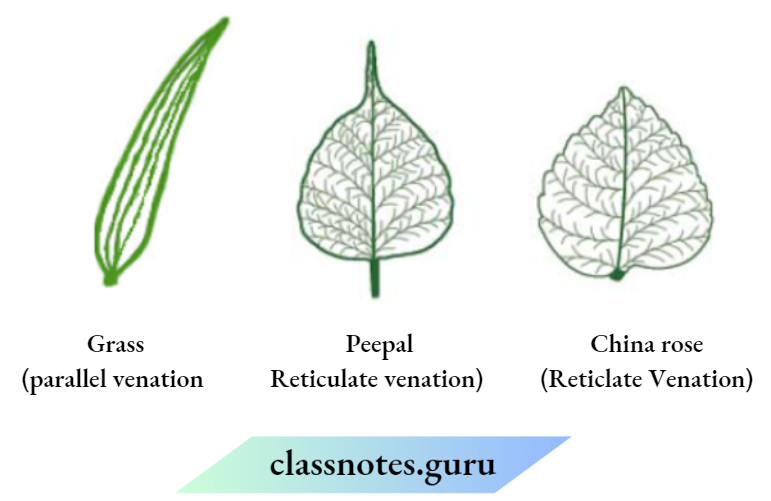
Question 18. Draw the veins of leaves given in the figure below and write the type of venation.
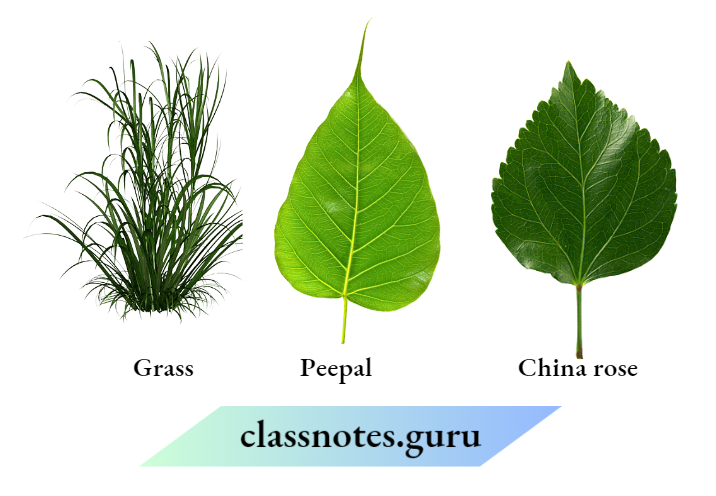
Answer:
The veins of leaves and their type of venation is
Question 19. Sudha fills two beakers with equal amounts of water she places a plant in beaker 1 with the roots of the plant dipped in water. She tightly covers the mouth of both beakers with plastic sheets. She leaves the beakers in sunlight and notes the amount of water in each beaker after 3 days

What Is Sudha trying to find out?
- Do plants need water to live?
- Do plant roots absorb water?
- Does water help plants to stand straight?
- Does water evaporate faster in sunlight?
Suppose the beakers are not covered with plastic sheets. Will the amount of water in the beakers remain the same as shown in the table? Explain your answer.
Answer:
- Do plant roots absorb water?
- The amount of water in both beakers will not remain the same and will reduce because of the evaporation.
Question 20. The pictures show four different plants.
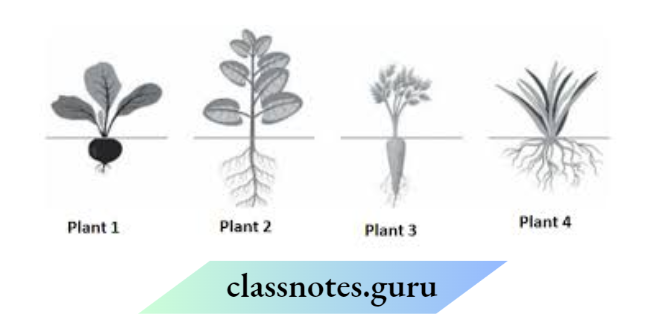
Which plants have the same type of roots?
- Only plant 1 and plant 2
- Only plant 2 and plant 3
- Plant 1, plant 2 and plant 3.
- Plant 2, plant 3 and plant 4
- Why is the root of plant1 thick and round?
Answer:
- Plant 1, plant 2 and plant 3
- The root of plant 1 is thick and round because these roots store food for the plant.
Question 21. The picture shows different parts of a flower.
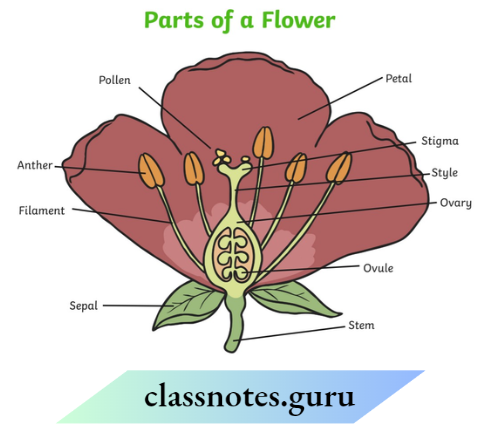
- How many petals can be seen in the picture?
- What Is Label X?
Answer:
- 3 petals can be seen in the picture.
- Label X is the filament.
Question 22. Observe the picture of an activity given as a figure, carried out with leaves of plants and a polythene bag.

- Now answer the following
- Which process is demonstrated in the activity?
- When will this activity show better results on a bright sunny day or a cloudy day?
- What will you observe in the polythene bag after a few hours of setting up the activity?
- Mention any one precaution you must take, while performing this activity.
Answer: The process demonstrated in the activity is transpiration.
- The activity will show the best results on a bright sunny day because transpiration is maximum in sunlight.
- After a few hours of setting up the activity, one observes small droplets of water inside the polythene bag.
- A major precaution one must take while performing the activity is that the polythene bag should be cleaned and its mouth should be sealed properly. Also, the twig should be fresh with 10-12 leaves.
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Getting To Know Plants Short Question And Answers
Question 1. What kind of stem do the money plant, beanstalk, gourd plants and grapevines have?
Answer: All these above-mentioned plants, i.e. money plants, beanstalk, gourd plants and grapevines have soft, green and weak stems and are climbers.
Question 2. Do all the leaves have petioles?
Answer: No, all the leaves do not have petioles. In some plants, leaves are attached directly to the plant stem.
Question 3. Can you name the process that makes water drops appear on the polythene cover?
Answer: The process that makes water droplets appear inside the polythene cover is known as transpiration. This occurs due to the loss of water from the leaves.
Question 4. Look at the figure below. Who do you think is watering their plant correctly? Paheli or Boojho? Why
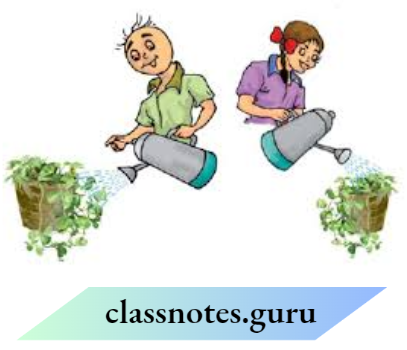
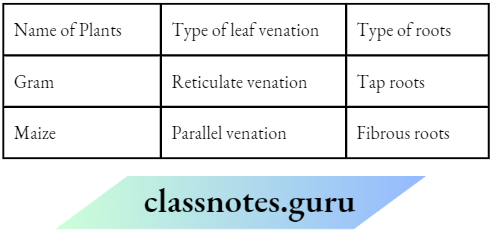
Answer: I think that Paheli is watering the plants correctly. This is because she is sprinkling water on the roots, which helps in the upward conduction of water. How are the types of roots and leaf venation in a plant related to each other? Fill in the table below to justify your answer.
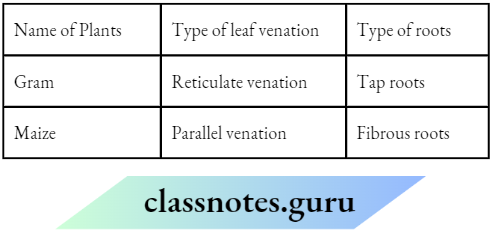
Answer: The table below shows the relation between the roots and leaf venation types in a plant.
Question 5. Write the name of the material that goes up in the stem and that which comes down.
Answer: The stem is like a street with two-way traffic. Through it, water and minerals go up while it conducts food from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
Question 6. Write down two examples of trees, shrubs, herbs and creepers growing near your area.
Answer: Two examples of trees – Oak and banyan (barged). Two examples of shrubs- the China rose and jasmine. Two examples of herbs are tomato and wheat. Two examples of creepers are pumpkin and watermelon.
Question 7. Can the stem of a plant be compared with a street with two-way traffic? Give reason.
Answer: Yes, the stem of a plant can be compared with a street with two ways traffic because
It carries water and minerals from the roots to the leaves and other parts ofplantin an upward direction.
It takes the food prepared by the leaves to other parts of the plant.
Question 8. Is it right to call the leaf as food factory of the plant? Justify your answer.
Answer: Yes, the leafs called as food factory of the plant. It is because the main function of a leaf is to synthesise food by the process of photosynthesis.
Question 9. Roots are necessary to keep the plants healthy and alive. Explain.
Answer: Roots absorb minerals and water from the soil. Both of these are needed for the manufacture of food from plant leaves. So, roots are necessary to keep the plant healthy and alive.
Question 10. Taproot is different from the fibrous root. Explain how.
Answer: The differences between tap and fibrous roots are
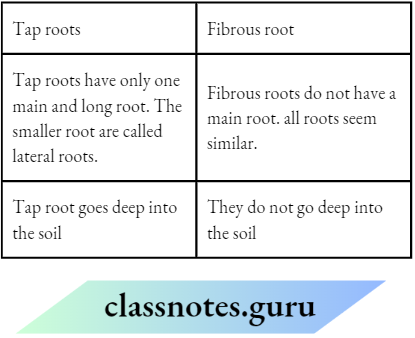
Question 11. The type of leaf venation and root in plants are related interestingly. Explain the statement.
Answer: The relation between the type of leaf venation and the type of roots is as follows
- The plant having leaves with reticulate venation has tap roots, for Example sunflower plant.
- The plant having leaves with parallel venation has fibrous roots, Example wheat.
Question 12. Will a leaf taken from a potted plant kept in a dark room for a few days turn blue-black when tested for starch? Give a reason for your answer.
Answer: No, a leaf from a potted plant kept in the dark will not turn blue-black when tested for the presence of starch. This is because all the stored starch would have been used up by the plant. No fresh starch would be synthesised due to the non-availability of sunlight.
Question 13. Boojho wanted to test the presence of starch in leaves. He performed the following steps
- He took a leaf and boiled it in water.
- He placed the leaf in a Petri dish and poured some iodine over it
- He did not get the expected result. Which step did he miss? Explain.
Answer: Boojho did not get the expected results in his experiment because he missed an important step in the procedure. He did not boil the leaf in spirit to remove chlorophyll. It is necessary to remove chlorophyll because it interferes with the test for starch. It is also essential to remove chlorophyll from leaves so that the leaves get decolourised.
Question 14. Suggest the type of root system In grass. Also, explain that root system.
Answer: In grass, a fibrous root system is present. In such types of roots, there is no main root, instead many roots arise from one region. These grow horizontally in the soil and make a bushy/clustered appearance.
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Getting To Know Plants Assertion-Reason Questions
Question 1. The following questions consist of two statements. Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- A is false, but R is true
1. Assertion (A) The Lamina of the leaf is green and helps in photosynthesis.
Reason (R) It is green due to the presence of green-coloured pigment.
2. Assertion (A) Roots are aerial parts of the plants.
Reason (R) Their main function is to absorb water and minerals from the soil.
3. Assertion (A) In tap root, the main root is present.
Reason (R) The smaller roots arising from the main root are called lateral roots.
4. Assertion (A) Transpiration helps in the movement of water from roots to leaves.
Reason (R) Transpiration is the loss of water from the stomata on leaves. As water evaporates from leaves, it creates a suction force that pulls water from the roots through the plant.
Answer:
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
A is false, but R is true. A can be corrected as Shoot is the aerial part ofthe plant whereas roots are present deep in the soil (underground)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A. It can be corrected as In tap root one main root is present which grows vertically downward into the soil.
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 2. Assertion (A) Plants with weak stems that cannot stand upright but spread on the ground are called creepers.
Reason (R) Plants that take support and climb up are called climbers.
Answer: Plants that take support and climb up are called climbers.
Question 3. Assertion (A) The Female part of the flower is called a pistil.
Reason (R) Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is called pollination.
Answer: 2. Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is called pollination.
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Getting To Know Plants Very Short Questions and Answers
Question 1. Plants are classified into three main categories. Explain briefly.
Answer: Based on the size and nature of the stem, die plants are classified into three main categories, i.e. herbs, shrubs and trees.
Question 2. What is the usual name of medium-sized plants with hard and woody stems whose many branches arise just above the ground?
Answer: Shrubs
Question 3. All plants are of the same size. Do you agree?
Answer: No, all plants are of different sizes. According to their size, they are classified as herbs, shrubs and trees.
Question 4. Herb is different from a shrub. Explain.
Answer: The herb is a small plant with a tender and green stem. Whereas, the shrub is bigger than an herb and has a strong and thicker stem.
Question 5. Give the term for each of the following.
- These are small plants with green, soft, tender stems.
- These are bigger than herbs with thick and hard stems and branching at the base.
Answer: Herbs Shrubs
Question 6. It Is given that a plant Is very tall and has a hard, thick stem with branching on the upper part of the plant. Based on the given characteristics, categorise the plant.
Answer: Based on the given characteristics, it can be concluded that the given plant is a tree.
Question 7. Money plant Is an example of a creeper. Do you agree? Explain.
Answer: No, a money plant is not an example of a creeper. It is an example of a climber as it grows or climbs up by taking the support of neighbouring structures.
Question 8. Differentiate between vein and midrib.
Answer: A large number of linear structures that spread to all parts of the leaf are called veins. Whereas, the main vein (thick vein) in the middle of the leaf is called midrib.
Question 9. The leaves of grass are different from those of mango. Explain.
Answer: The leaves of grass show parallel venation whereas mango leaves have reticulate venation.
Question 10. leaves when treated with iodine give a blue-black colour. Give the reason.
Answer: The leaf gives a blue-black colour due to the presence of starch in it.
Question 11. In some plants, roots do not have any main root but all the roots are similar. Give some examples of such fibrous roots.
Answer: Examples of plants with fibrous roots are maize, wheat, rice, etc.
Question 12. Name the part of a plant which helps in holding the plant to the soil.
Answer: The roots anchor the plant to the soil.
Question 13. Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil. Why are these needed?
Answer: Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil. These are needed for the manufacture of food from plant leaves.
Question 14. Roots are helpful in the conservation of soil. Explain.
Answer: Roots help in holding the soil together. In this way, roots prevent the soil from being blown away by wind or washed away by water and thus, help in the conservation of soil.
Question 15. Differentiate between sepals and petals.
Answer: The small, green-coloured leaf-like structures seen in flowers are called sepals. Whereas, petals are the big, brightly coloured leaf-like structures seen in flowers.
Question 16. Plants also have reproductive organs like animals. Name the reproductive part of plants.
Answer: Stamens and pistil are the male and female reproductive parts of plants, respectively
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Getting To Know Plants Fill In The Blanks
1. The type of venation found in pea is Reticulate
2. Water comes out of the leaf by a process called transpiration
3. The small green leaves at the base of flowers are known as Sepals
4. The swollen basal part of the pistil is the Ovary, which bears the
5. Stamen has two parts called Anther, filaments.
6. The young unopened flower is termed a bud
7. Sepals, Petals stamens and pistils are the parts of a flower. Stamen Is made up of anther and filament and It represents the male part of the flower. The female part of the flower is called the pistil The basal, swollen part of the pistil is called the ovary which contains the ovules.
8. Loss of water through leaves is called Transpiration
9. The unwanted plants that grow in a field are called weeds
10. Mango leaves have venation reticulate
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Getting To Know Plants True Or False
1. Stem bears branches, flowers and fruits. True
2. The arrangement of veins in the leaf lamina is called venation. True
3. Leaves are generally multicoloured. False, leaves are generally green in colour
4. Lateral roots are present in a tap root. True
5. Anther is a part of the pistil. False, another is a part of the stamen
6. Pollen grains are present in the anther of the pistil. False
7. Wheat has parallel venation and fibrous roots. True
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Getting To Know Plants Match The Columns
Question 1. Match the Column 1 with Column 2.
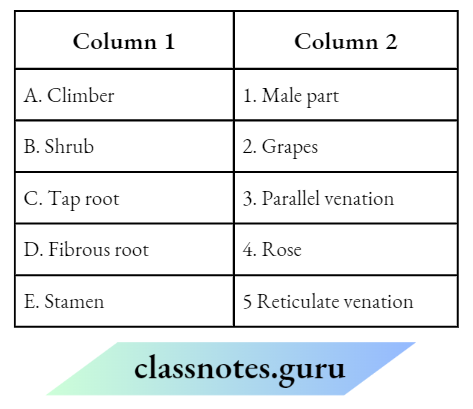
Answer: A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
Question 2. Match the Column 1 with Column 2.
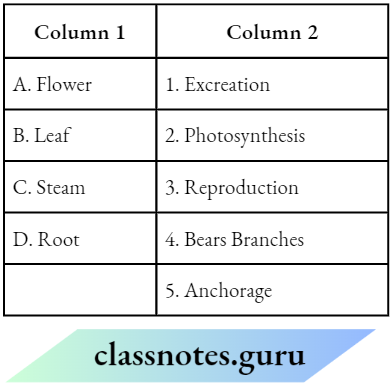
Answer: A-3, B-2, C-4,D-5
Question 3. Match the Column 1 with Column 2.
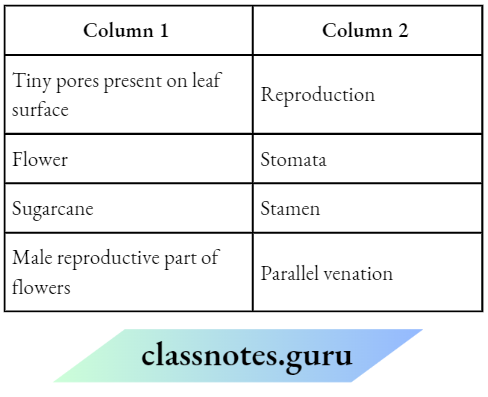
Answer: A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
