Miscellaneous Short Essays
Question 1. Mandibular retroguathism.
Answer.
- Refers to more backward placement of jaw.
Features of retrognathism:
- Facial profile – convex
- Facial divergence – Posterior divergent
- Anteroposterior relation – Class 2
- Mento labial sulcus – Deep
- Hyperactive mentalis activity
- Reduced nasolabial angle
Treatment of retrognathism:
- In growing patients – Myofunctional therapy Ex. Activator, FR2
- In non-growing patients
- Orthodontic camouflage – Extraction of 1st premolars
- Mandibular advancement
Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Short And Long Essay Question And Answers
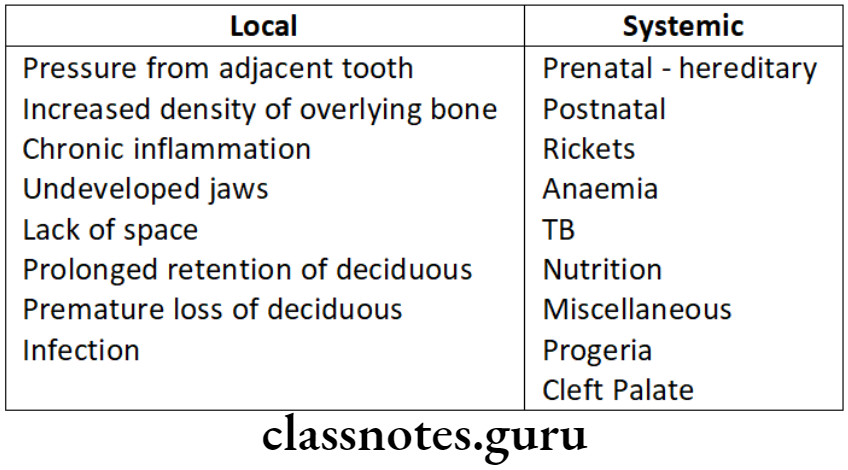
Question 2. Causes of Canine impaction.
Answer.
Question 3. Mechanism of Bone Growth.
Answer.
Bone Deposition and resorption
- Together with bone deposition and resorption is called bone remodeling
Effects of bone deposition and resorption:
- Change in size
- Change in shape
- Change in proportion
- Change in bone relationship with adjacent structures
Cortical Drift
- Movement of bone occurs towards bone deposition called cortical drift
- If bone deposition and resorption are equal
- Thickness of bone remains, constant
- If bone deposition is more than resorption
- The thickness of bone is more toward the deposition
Displacement
- Movement of whole bone as a unit
Primary displacement:
- Displacement of bone as a result of its own growth
Secondary displacement:
- Displacement of bone as a result of growth of adjacent bone
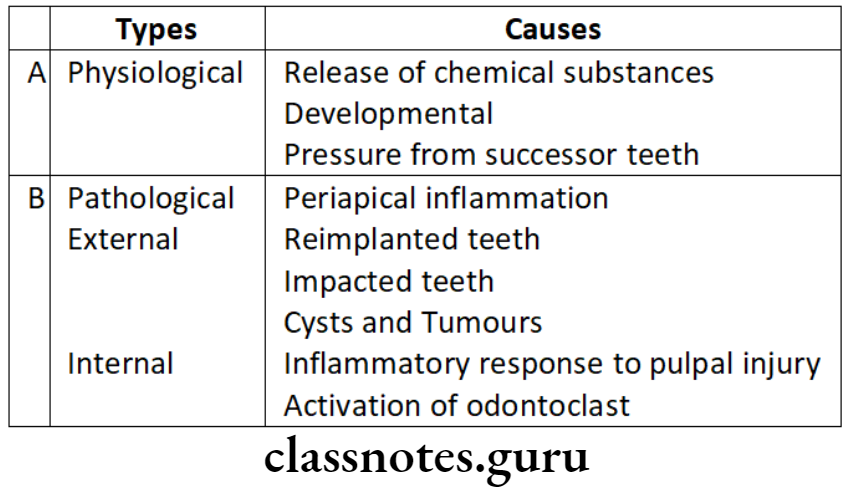
Question 4. Causes of Root resorption.
Answer.
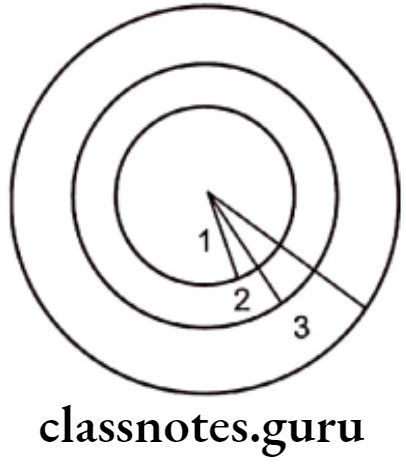
Question 5. Envelope of Discrepancy.
Answer.
- It helps in treatment planning
- The choice of treatment depends on the movement of the teeth required
- By orthodontic (fixed mechanotherapy) the tooth can be moved only at a specific distance
- If the movement of teeth beyond this limit is required, orthopedic/functional appliances can be used
- Beyond this limit, the treatment of choice is orthognathic surgery
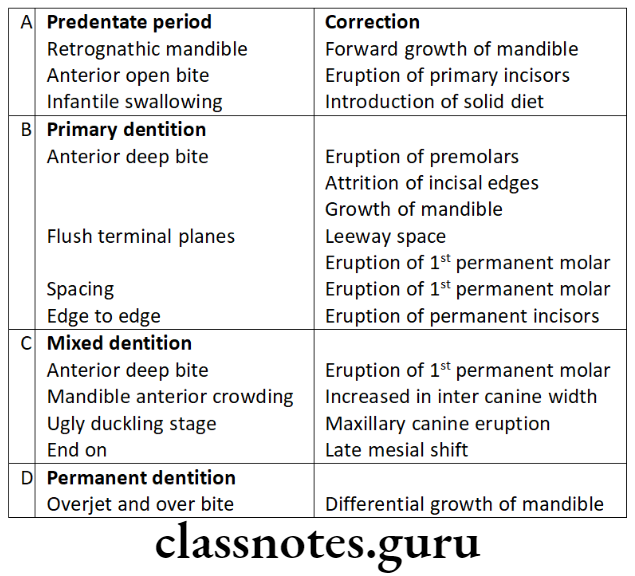
Question 6. Self-correcting Anomalies/Transient Malocclusions.
Answer.
Miscellaneous Short Questions And Answers
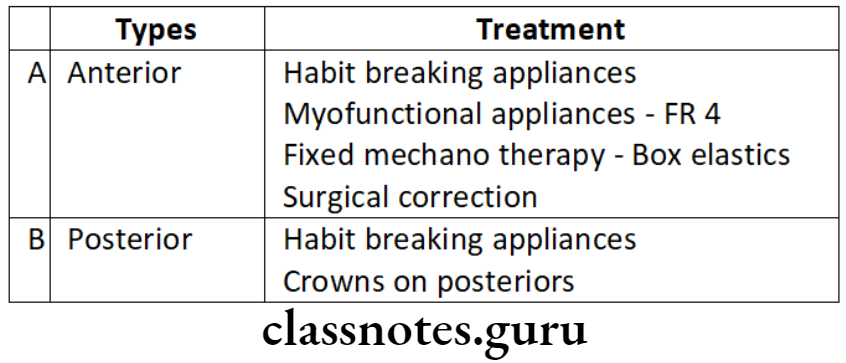
Question 1. Apertognathia.
Answer.
It is a condition in which there is space between upper and lower teeth when some teeth are in contact at one/more points
Question 2. Growth site and Growth center.
Answer.
Growth site:
- These are growth fields that have a special significance in the growth of a particular bone
- Posses intrinsic growing potential
Example. Condyle, maxillary tuberosity
Growth Centres:
- These are growth sites that control the overall growth of bone
- Have growth potential
Example. Epiphyseal plates of long bones
Question 3. Cranial Base Flexure.
Answer.
- During the embryonic phase, the cranial base is flexed between the pituitary fossa and sphenoccipital junction
- It is accompanied by developing brain stem
Cranial Base Flexure Results
- Downward placement of foramen magnum
- Aids in increased neurocranial capacity
- Downward displacement of the face
Age: 10th week of IU life, Angle – 65th
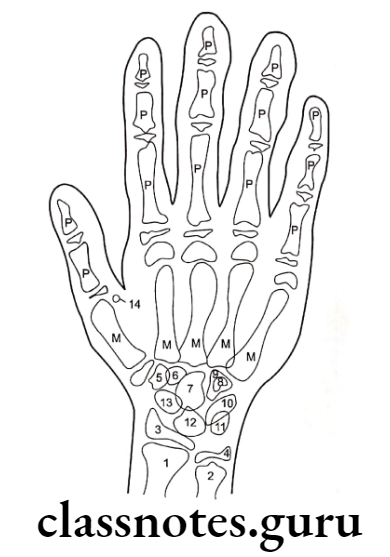
Question 4. Carpal Index.
Answer.
- One of the skeletal maturity indicator
- Used as a part of hand wrist
- Carpals – consist of eight small bones arranged in
Proximal Row
- Scaphoid
- Triquetral
- Lunate
- Pisiform
Distal row
- Trapezium
- Trapezoid
- capitate
- Humate
- These bones show specific patterns of appearance, ossification, and union
- These are compared with standards
Question 5. Torquing Auxillaries.
Answer.
Torquing Auxillarie Springs:
- Made of stainless steel /Ni – titanium
- Force exerted is directly proportional to the diameter and modulus of elasticity of the material of the wire
- Stainless steel exerts greater force
Question 6. Sterilization in Orthodontics.
Answer.
Definition: Defined as the destruction of all life forms
Types of Instruments:
- Critical – Penetrate the mucosa
- Semi-critical – Touches mucosa but does not penetrate
- Least critical – Surfaces touched during treatment
Instruments Requiring Sterilization:
- Mirrors
- Explorers
- Banding and bonding instruments
- Bands
- Pillers
- Ligature directors
Question 7. Growth Trends.
Answer.
By overlapping consequent cephalograms Tweed, designed a pattern of growth called “Growth trends”
Groups
Type A
- Simultaneous growth of maxilla and mandible
- 25% of case
- ANB angle unchanged
Type A subdivision
- Protruding maxilla
- ANB angle increased
Type B
- Increase in maxillary growth
Type B subdivision
- ANB angle large
- Unfavorable
Type C
- Increased growth of the mandible
- Decreased ANB angle
Type C Subdivision
- Mandibular incisors touches lingual surfaces of maxillary incisors
Question 8. Growth Curve.
Answer.
- Indicates the degree of difference between two growing individuals in all four planes including the time factor
- As everyone does not have the same growth pattern, deviation from normal growth pattern cannot be diagnosed
- Thus the growth of such individuals is compared with a standard growth chart
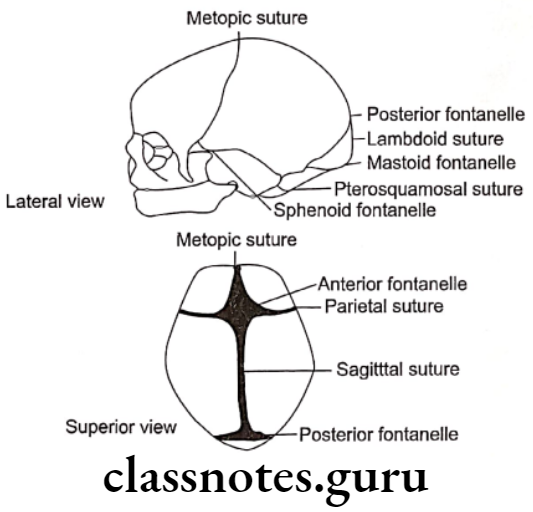
Question 9. Fontanelles.
Answer.
- They bridge the gap between bones that limit them.
- Made up of durameter, primitive periosteum and aponeurosis
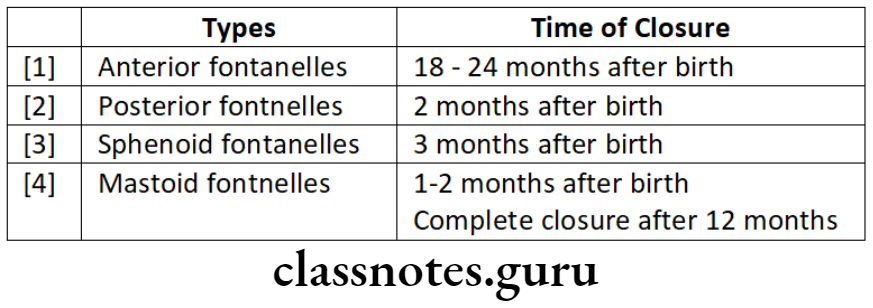
Frontanelles Importance:
- Indicates brain development
- A depressed level indicates dehydration
- Increased level indicates increased intracranial pressure
Question 10. Safety valve mechanism.
Answer.
- Increase in inter-canine width is one of the important factor in overcoming incisal liability
- At the age of 12, maxillary anterior prolines such that inter-canine width increase
Significance of safety value mechanism:
- This increase in maxillary inter canine width hinders the forward growth of the mandible
- This increase in width behaves like it holds the forwardly growing mandible
Question 11. Curve of Spee.
Answer.
- It is antero-posterior curve of occlusion
- It begins from the tip of lower canine to the cusp tips of bicuspids and molars upto the condyle
Significance of curve of Spee:
- Normal value – 1.5 – 2mm
- If the curve is extended, it forms a circle of about 4 diameter
- It represent the axial alignment of lower teeth
- It requires a gradual progressive increased mesial tilting of teeth towards the molar
Question 12. Anterior bite plane and its mode of action.
Answer.
Uses of anterior bite plane: For treatment of deep bite
Mode of action:
- Consist of the flat ledge of acrylic behind the upper anterior
- When the patient bites the mandibular incisors contact the bite plane, thus dis occlude the posterior due to which they are free to erupt
Components of anterior bite plane:
- Adam’s clasp on molar – As a retainer
- Labial bow – Counter any forward component of force on upper anterior
Question 13. Orbital law of canine.
Answer.
- It is used in Simon’s classification
- Orbital plane perpendicular to Frankfort horizontal plane is used
- This plane is dropped down from the bony orbital margin directly under the pupil of the eye
- According to Simon, this plane should pass through the distal third of the upper canine
- This is known as “Simon’s law of canine “or” Orbital law of canine”
Orbital law of canine significance:
- It is used to describe malocclusion in a sagittal plane
- When the dental arch is farther from the orbital plane it is called protraction
- When the dental arch is closer then it is called retraction
