Matricing Important Notes
1. Matrices
Matricing Short Essays
Question 1. Define matrix. Discuss different types of matrices
(or)
Define Matrix. Describe matrices used for class 2 restoration.
(or)
Matrices used in operative dentistry
Answer:
Matrix Definition:
Read And Learn More: Operative Dentistry Short And Long Essay Question And Answers
- Matrix is a device that is applied to a prepared tooth before the insertion of the restorative material to assist in the development of the appropriate axial tooth contours and to confine the restorative material excess
Types Of Matrices:
1. Based On The Mode Of Retention
- With retainer- Tofflemire matrix
- Without retainer- Automattrix
2. Based On The Type Of Band
- Metallic nontransparent matrices
- Non-metallic transparent matrices
3. Based On The Type Of Cavity
- Matrix For Class 1 Cavity
- Double band tofflemeir
- Matrices For Class 2 Cavity Preparation
- Single banded tofflemeir matrix
- Rigid material supported sectional matrix
- Ivory no. 8
- Ivory no 6
- Copper band matrix
- Matrices For Class 3 Cavities
- Mylar strip matrix
- S-shaped matrix
- Matrices For Class 4 Cavities
- Custom lingual matrix
- Mylar strip matrix
- Matrices For Class 5 Cavities
- Window matrix
- Cervical matrix
Matrices For Class 2 Restoration:
1. Ivory Matrix No. 1:
- For unilateral class 2
Ivory Matrix Parts:
- Claw
- Arms – 2 semicircle arms with pointed projections
- Tightening screw
- Band has a slightly projected part in the middle that is placed gingivally
Ivory Matrix Placement:
- Select and place the band
- Place the retainer
- Tighten the screw
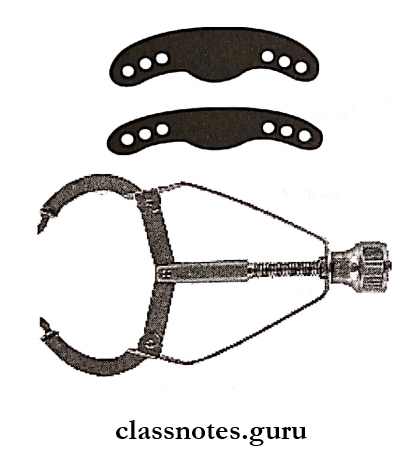

2. Ivory Matrix No. 8:
- Band thin sheet of metal
- Circumference of it adjusted by screw
- Used in unilateral/bilateral cases
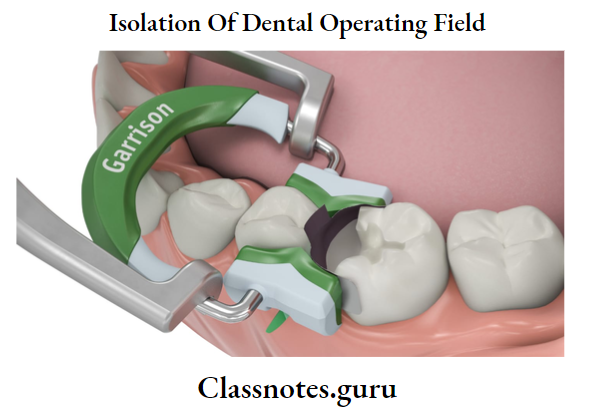
3. Tofflemire Universal Matrix Band Retainer:
- Used in all types of tooth preparations
Tofflemire Universal Matrix Band Retainer Parts:
- Head
- Slot
- Knurled nuts – Large and small
Tofflemire Universal Matrix Band Retainer Placement:
- Open large Knurled nut
- Open a small knurled nut in the opposite direction
- Secure both ends of the band
- Place the band into a diagonal slot
- Tighten small knurled nut
- Place the retainer around the tooth
- Tighten large knurled nut
4. Compound Supported Matrix:
- Place the band around the tooth
- Secure it by sealing with an impression compound
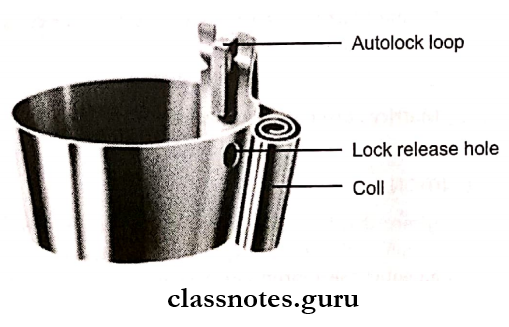
5. Auto-Matrix:
- Preformed bands are available
- Adapt the matrix around the tooth
- Tighten the band with a locking device
6. T-Shaped Matrix:
- Made of brass, copper, or stainless steel
- The long arm of T surrounds the tooth and overlaps the short arm
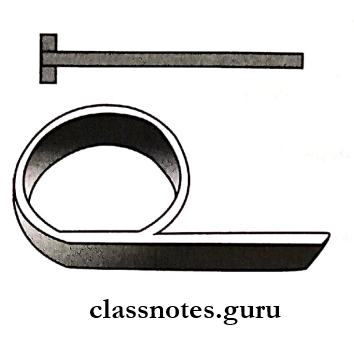
Question 2. Matrix Band and Retainer.
Answer:
Matrix Band And Retainer:
Matrix Band And Retainer Retainer:
- Holds the band in position and shape
Matrix Band And Retainer Band:
- A piece of metal/polymeric material used to give support and form to the restoration while insertion and setting
Matrix Band And Retainer Materials:
- Stainless steel
- Polyacetate
- Cellulose acetate
- Cellulose nitrate
Matrix Band And Retainer Dimensions:
- Width –¼ %” to 3/8″ for permanent
- 1/8” to 5/16″ for deciduous
- Thickness – 0.0015″ to 0.002″
Matrix Band And Retainer Functions:
- Confines the restoration
- Provide good contour
- Provide surface texture
- Prevent overhanging
Matrix Band And Retainer Requirement:
- Rigid
- Adaptability
- Easy to use
- Easy to removal
- Non-irritant
- Sterilizable
- Inexpensive
Question 3. Non-metallic matrix.
(or)
Matrices for tooth-colored materials
Answer:
Non-Metallic Matrix:
- Used for tooth-colored restoration
Non-Metallic Matrix Types:
- Celluloid strips – For silicate cement
- Cellphone strips – For resins
- Mylar strips – For composite and silicate
Non-Metallic Matrix Technique:
- Obtain the desired length of the matrix
- Burnish it over the tooth
- Placement of wedge
- Restoring the tooth
- Hold the matrix till the initial setting
Non-Metallic Matrix Indications:
- Class 3 and Class 4 restoration
Non-Metallic Matrix Advantage:
- Simple to Use
- Economic
Non-Metallic Matrix Disadvantage:
- Lack of stability
Matricing Short Answers
Question 1. Functions of the matrix.
Answer:
Functions Of The Matrix:
- Functions Of Matrix Are
- Rigidity
- Establishment of proper anatomic contour
- Restoration of correct proximal contact relation
- Prevention of gingival excess
- Convenient application
- Ease of removal
Question 2. Automatic.
Answer:
Automatic:
- Bands are performed and disposable
- Height of band-3/16″-5/16″
- The thickness of band – 0.038-0.05 mm
Automatic Steps:
Adapt matrix around the tooth
↓
Tighten the band with a locking device
↓
Restore the tooth
↓
Cut the band with a plier
Automatic Indications:
- Tilted and partially erupted teeth
- Complex amalgam restoration
Automatic Advantages:
- Simple
- Convenient
- Good visibility
Automatic Disadvantage:
- Expensive
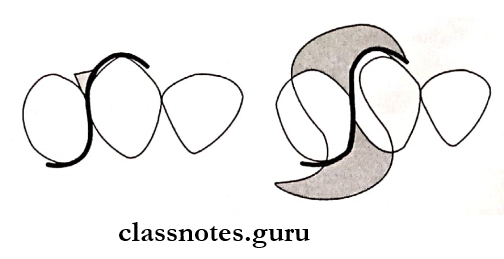
Question 3. S-shaped matrix.
Answer:
S-Shaped Matrix:
S-Shaped Matrix Indications:
- Restoring the distal part of the canine and premolar
- Class 2 slot restoration
S-Shaped Matrix Advantages:
- Good contour
S-Shaped Matrix Disadvantage:
- Cumbersome
S-Shaped Matrix Technique:
- Twist the band in S shape
- Place interproximal over facial
- The surface of the tooth and the lingual surface of the bicuspid
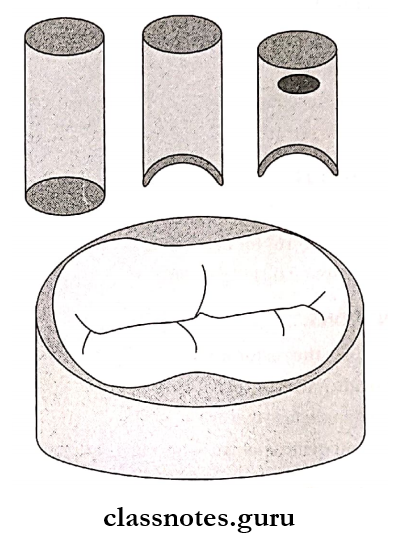
Question 4. Copper Band.
Answer:
Copper Band:
Copper Band Application:
Select an appropriate copper band that surrounds the tooth
circumferentially 1-2 mm beyond the preparation margins
↓
Mount it over the softened stick of compound
↓
Fill it with restoration
↓
Place it over the tooth
Copper Band Indication – Class 5 preparation
Copper Band Advantage – Simple, Good contour
Question 5. Sectional matrix system.
Answer:
Sectional Matrix System
- It consists of dead soft metal matrices available in various shapes, thicknesses, and sizes
- They are selected according to the tooth to be restored
Sectional Matrix System Indications:
- For small to moderate class 2 cavities involving one or both proximal surfaces in posterior teeth
- For both amalgam and composite restorations
Sectional Matrix System Advantages:
- Easy to use
- Good visibility
- Contact dimensions are adequate
- Gingival adaptation of restoration is good
Sectional Matrix System Disadvantages:
- Expensive
- Matrix bands may become dented easily
Matricing Viva Voce
- Matrix system consists of a matrix band, retainer, and wedges
- The thickness of a matrix band is 0.002 inches
- Matrix retainers are gadgets used to retain the matrix bands in position
- Tofflemire matrix band retainer is ideal to use when MOD preparation is done
- Automatrix is a retainer less matrix system with 4 types of bands used to fit all teeth
- Ideally the matrix band should be positioned 1mm apical to the gingival margin and 1-2 mm above the adjacent marginal ridge
- Tofflemire matrix is the universal matrix
- Compound-supported matrix is also called custom- made matrix or anatomical matrix
- T band matrix is performed T-shaped matrix without a retainer
