Irrigation And Intracanal Medicaments Important Notes
- Sodium hypochlorite
- It acts as
- Lubricant during instrumentation in root canal
- Solvent for dissolution of pulp
- Antiseptic and disinfectant by combining both protoplasm of bacterial cell and destroying it
- Bleaching agent by releasing nascent oxygen
- It is used in concentration varying from 0.5-75%
- Very Potent antimicrobial agent
- Effectively dissolves pulpal remnants
- Disadvantages
- Inability to remove smear layer
- Unpleasant taste
- Toxicity
- It acts as
- Advantages of alternate use of sodium hypochlorite and hydrogen peroxide in root canal preparation
- Effervescent reaction which pushes debris out of the canal
- Solvent action of sodium hypochlorite on the organic debris of pulp tissue
- Disinfecting and bleaching action of both solutions
Irrigation And Intracanal Medicaments Long Essays
Intracanal Medicaments In Endodontics
Question 1. What are various root canal irrigants? Write in detail requirements and techniques of irrigation.
Answer.
Irrigant:
Irrigant is a liquid used to lubricate the canal walls and flush out the debris and micro-organisms from the root canals
Irrigant Types:
Chemically Non-Active
- Water:
- Saline
- LA
- Chemically Active [ACDE]:
- Alkali – Sodium Hypochlorite
- Acids – HCl
- Antibacterial agents – Chlorhexidine
- Chelating agents – EDTA
- Detergents – Sodium lauryl sulfate
- Enzymes – Streptokinase
- Oxidizing agents – Hydrogen peroxide
Requirements:- Should have antimicrobial activity
- Should be non-toxic and biocompatible
- Should dissolve necrotic and vital pulp tissues
- Should be tissue or debris solvent
- Should serve as lubricant
- Should have low surface tension
- Should be non-reactive to periapical tissues
- Should not be easily neutralized in the canal and should retain its effectiveness
- It should be of moderate cost and ease to store
Read And Learn More: Endodontics Question and Answers
Irrigant Techniques:
Irrigant Techniques Manual
- Syringe Irrigation With Needles:
- It involves dispensing an irrigant into the root canal using irrigation needles of varying gauges
- Gauge 27-30
- Depth of insertion 2-3mm from the working length
- Design – blunt-ended size vented needle
- Brushes:
- Bristles help in cleaning the uninstrumented recesses of the radicular pulp spaces
- Manual Dynamic Agitation:
- In this, a well-fitted greater taper gutta-percha master cone is moved up and down the instrumented canal containing irrigant in short 2-3mm strokes
Irrigant Techniques Machnine Assisted
- Rotary brushes
- Consist of micro brushes attached to rotary handpieces
- Continuous irrigation during instrumentation
- It contains an irrigant delivery unit attached to the Quantec-E-irrigation system
- Sonic irrigation
- involves sonic waves
- Ultrasonic irrigation
- Operates at frequencies of 25-30kHz
- Pressure alternation devices
- EndoVac
- RinsEndo
Endodontic Irrigation Techniques
Question 2. Enumerate the various root canal irrigants. What are the functions of irrigants? Write in detail on chlorhexidine and sodium hypochlorite as intracanal irrigants.
Answer.
Intracanal Medicaments In Endodontics
Irrigant: Irrigant is a liquid used to lubricate the canal walls and flush out the debris and micro-organisms from the root canals
Irrigant Types:
Irrigant Chemically Non-Active
- Water:
- Saline
- LA
- Chemically Active [ACDE]:
- Alkali – Sodium Hypochlorite
- Acids – HCl
- Antibacterial agents – Chlorhexidine
- Chelating agents – EDTA
- Detergents – Sodium lauryl sulfate
- Enzymes – Streptokinase
- Oxidizing agents – Hydrogen peroxide
Functions Of Irrigant In Endodontics
- Remove dentinal shaving
- Germicidal
- Increase efficiency of instruments
- Dissolve necrotic tissue and remove it
- Bleaching action
Chlorhexidine:
- Chlorhexidine is biguanide
- Available as oral rinses
- Used in concentration 0.2-2%
Chlorhexidine Advantages:
- Longer antibacterial action
- Used with sodium hypochlorite
- When chlorhexidine comes in contact with sodium hypochlorite there is the formation of parachloroaniline which is cytotoxic
- It interferes with the seal of the root filling
- Flushing with normal saline is a must
- Biocompatible
Chlorhexidine Disadvantages:
- Does not dissolve pulp tissue
Sodium Hypochlorite Solution
- It is a clear, pale, green-yellow liquid
- A strong odour of chlorine
- Easily miscible with water
- Decomposes by light
Sodium Hypochlorite Mechanism:
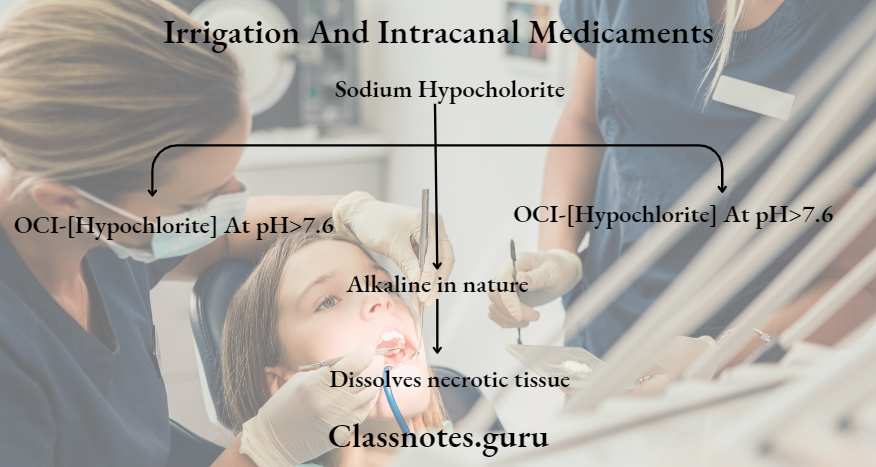
Intracanal Medicaments In Endodontics
Factors Affecting Sodium Hypochlorite Mechanism Activity:
- Increases:
- Volume of solution
- Heating of solution
- Time of contact
- Decreases:
- Strong time
- EDTA
Hypochlorite Mechanism Activity Advantages:
- Dissolve tissue
- Antibacterial and bleaching action
- Lubricate canal
- Economical
Hypochlorite Mechanism Activity Disadvantages:
- High surface tension
- Irritate tissue
- Irritate eyes
- Causes inflammation of the gingiva
- Bleaches clothes
- Bad odour and taste
- Corrosive to instruments
Intracanal Medicaments In Endodontics
Hypochlorite Mechanism Activity Combined With:
- Calcium hydroxide
- EDTA
- Chlorhexidine
Irrigation And Intracanal Medicaments Short Essays
Question 1. Irrigating Solution.
Answer.
Irrigating Solution Properties:
- Broad spectrum
- Inactive endotoxin
- Dissolve debris
- Debride the canal
- Good lubricant
- Less toxic
- Prevent/dissolve smear layer
Irrigating Solution Functions:
- Remove dentinal shaving
- Germicidal
- Increase efficiency of instruments
- Dissolve necrotic tissue and remove it
- Bleaching action
Irrigating Solution Commonly used:
- Chemically Non-Active:
- Water:
- Saline
- LA
- Chemically active [ACDE]:
- Alkali – Sodium Hypochlorite
- Acids – HCl
- Antibacterial agents – Chlorhexidine
- Chelating agents – EDTA
- Detergents – Sodium lauryl sulfate
- Enzymes – Streptokinase
- Oxidizing agents – Hydrogen peroxide
Root Canal Irrigation Solutions
Question 2. Ideal requirements of intracanal medicaments. Describe in detail about medicaments.
Answer.
Intracanal Medicaments Functions:
- Destroy remaining bacteria
- Useful in treatment of apical periodontitis
Intracanal Medicaments Properties:
- Germicidal
- Non-irritant
- Stable
- Low surface tension
- Should not induce immune response
- Should not interfere with repair
- Should not stain tooth
Intracanal Medicaments Chemicals Used:
- Essential oils – Eugenol
- Phenolic compounds – Phenol, Aldehydes
- Calcium hydroxide
- Chlorhexidine gluconate
- Corrticosteroid antibiotic
- Antibiotic
- Halogens – Sodium hypochlorite, Iodine
Question 3. Calcium Hydroxide.
Answer.
Calcium Hydroxide
Intracanal medicament
Calcium Hydroxide Forms:
- Paste form
- Powder form
Calcium Hydroxide Indication:
- Weeping canal
- Treatment of Phoenix abscess
- Resorption
- Apexification
- Pulp capping
- Decrease post-operative pain
- As sealer
- For periapical lesion
Calcium Hydroxide Disadvantages:
- Difficult to remove
- Decreases setting time
Calcium Hydroxide Functions:
- Inhibits root resorption
- Stimulates periapical healing
- Encourage mineralization
Question 4. Composition and uses of mineral trioxide aggregate.
Answer.
Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Composition:
- Tricalcium silicate
- Tricalcium aluminium oxide
- Silicate oxide
- Bismuth oxide
- Calcium
- Phosphate
- Water
Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Uses:
- As root end filling material
- Used in Pulpotomy
Sodium Hypochlorite In Endodontics
Irrigation And Intracanal Medicaments Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. Hydrogen Peroxide.
Answer.
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen Peroxide is clear, odourless liquid
Hydrogen Peroxide Mechanism:
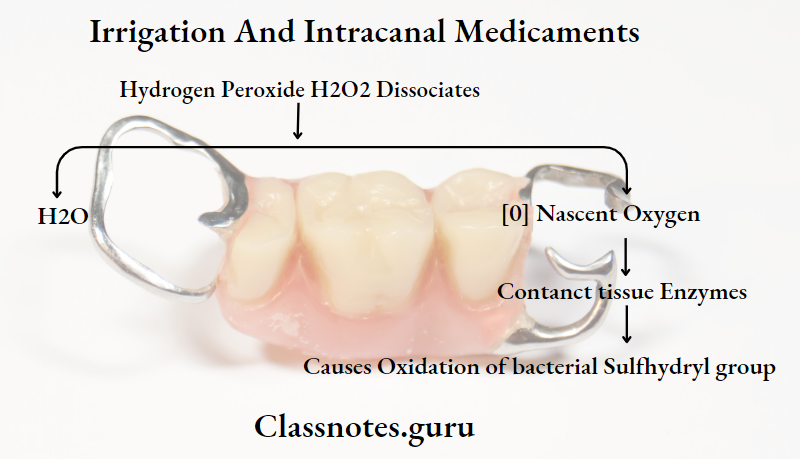
Use: As an irrigating solution
Combine with: 5.2% NaOCl
Question 2. Eugenol.
Answer.
Eugenol
Eugenol is an intracanal medicament
Eugenol Effects:
Eugenol Low Dose [Beneficial]:
- Inhibits PG synthesis
- Inhibits nerve activity
- Inhibits chemotaxis
Eugenol High Dose [Harmful]:
- Induces cell death
- Inhibits cell respiration
Eugenol Uses:
- Intracanal medicament
- Root canal sealer
- Temporary sealant
Calcium Hydroxide Intracanal Medicament
Question 3. RC Prep.
Answer.
RC Prep Composition:
- EDTA
- Urea peroxide
- Carbowax
RC Prep Properties:
- Lubricant
- Cleaning agent
- Antibacterial
RC Prep Uses:
- Allows deeper penetration of medicament into the dentin
Question 4. Ledermix.
Answer.
Ledermix Composition:
- Gluco corticosteroid
- Triamcinolone
- Dimethyl chlortetracycline
Ledermix Uses:
- Initial dressing agent
- Reduces incidence of pain
- Provide rapid relief
- Useful in cases of infection and inflammation
Question 5. PBSC.
Answer.
PBS
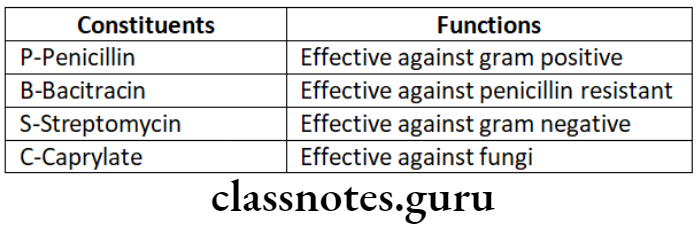
PBSC Route Of Administration:
PBSC Form-Paste Form:
- Injected into root canals
- Impregnated on paper points
Advance – Nystatin Replaces Caprylate
PBSC Disadvantage:
- The patient may have an allergy to penicillin
Calcium Hydroxide Intracanal Medicament
Question 6. Schilder’s Objectives for cleaning and shaping of Canal.
Answer.
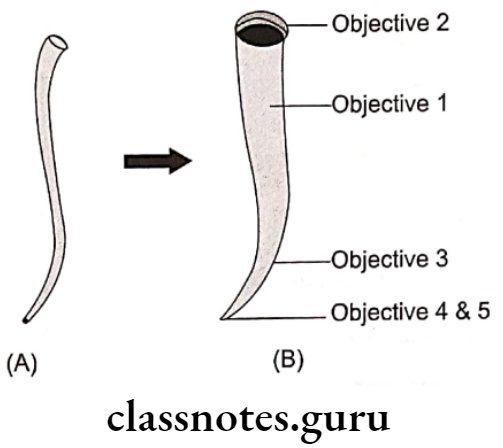
Schilder’s Objectives For Cleaning And Shaping Of Cana
- Root canal preparation should develop continuously tapering cone
- Making preparations in multiple planes to introduce the concept of flow
- Making the canal narrower apically and wider coronally
- Avoid transportation of foramen
- Keep the apical opening as small as possible
Irrigation And Intracanal Medicaments Viva Voce
- EDTA is used at a concentration of 15%
- MTAD is a Mixture of Tetracycline, Acid [citric acid], and Detergent
