Introduction To Complete Dentures
Definitions Of Complete Dentures
- Complete denture: A removable dental prosthesis that replaces the entire dentition and associated structures of the Maxilla or mandible.
- Residual ridge resorption:
- It is alveolar remodeling that occurs due to changes in the functional stimulus of bone.
- It is diminishing the quality and quantity of the residual ridge after teeth are removed.
Classification Of Complete Dentures
1. Progression of residual ridge resorption by Atwood.
- Order 1: Pre extraction
- Order 2: Post extraction
- Order 3: High, well-rounded
- Order 4: Knife edged
- Order 5: Low, well-rounded
- Order 6: Depressed.
Complete Dentures Important Notes
- Surfaces of complete denture:
- Occlusal surface
- Impression surface
- Polished surface
- Parts of complete denture:
- Denture base
- Denture flange
- Denture borders
- Denture teeth
- Objectives of complete denture:
- Should be compatible with the surrounding oral environment
- Should restore oral function
- Should be in harmony with the function of speech respiration and deglutition
- Should be aesthetically acceptable
- Should preserve the remaining oral tissues.
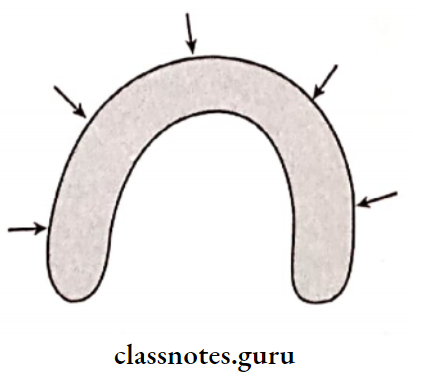
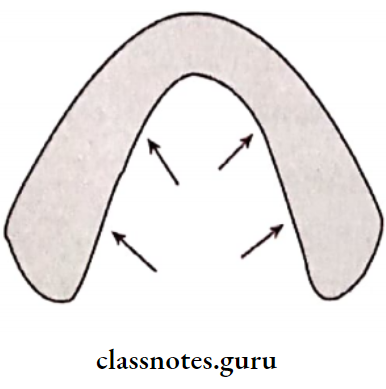
- Direction of residual ridge resorption:
- Maxillary ridge – Upward and lingual direction
- Mandibular anterior ridge – Downward and lingual direction
- Mandibular posterior ridge – Downward and buccal direction.
- Angular stomatitis (also known as perleche or angular cheilosis) occurs commonly due to:
- Decreased VDO or
- Deficiency of ‘Riboflavin or Thiamine’ or
- Due to Candida infection.
- Denture stomatitis:
- It refers to pathological reactions of the denture-bearing palatal mucosa
- Types:
- Type 1 – Localized inflammation
- Type 2 – Generalized inflammation
- Type 3 – Granular type
- Predisposing factors for Candida-associated denture stomatitis:
- Aging
- Malnutrition
- Immunosuppression
- Radiation therapy
- Diabetes
- Antibiotics
8. Epulis fissuratum:
- It is soft tissue reaction that appears in the sulcular area due to over-extension of the denture flanges
- It is treated by shortening and smoothening the denture border
9. Papillary hyperplasia:
- It results from Candida infection and improper relief of the palatal area in the denture
- Small lesions are treated by curettage
- Large lesions are treated by split-thickness suprapenosteal excision
Complete Dentures Short Essays
Question 1. Denture induced hyperplasia
Answer:
The hyperplastic reaction of mucosa over the borders of the denture
Cause of hyperplasia:
- Trauma due to unstable dentures:
Features of hyperplasia:
- Deep ulceration
- Fissuring
- Inflammation
Management of hyperplasia:
- Surgical excision
- Correction of dentures
Question 2. Epulis fissuratum
Answer:
It is a soft tissue reaction that appears in the sulcular region due to overextension of the denture flange.
Read And Learn More: Prosthodontics Question And Answers
Symptoms of Epulis fissuratum:
Single or numerous lesions showing flaps of hyperplastic connective tissue
- Deep ulceration
- Fissuring
- Inflammation at the depth of the sulcus
Treatment of Epulis fissuratum:
- Excision of tissues
- Shortening and smoothening of denture border
Question 3. Indications and contra indications of complete denture Answer:
complete denture Indications:
- Presence of adequate edentulous ridges with sufficient vertical space
- Serious loss of masticatory functions
- Impairment of aesthetics, speech, and psychological well being
- In patients where remaining teeth cannot be retained
Contraindications:
- An edentulous patient who has not worn dentures in many years
- Unmanageable mechanical problems
- Patient with no salivary function due to radiation
- Altered systemic health
- Allergic to acrylic resinPatient with severe or total paralysis of motor nerves of tongue, cheeks, lips, or floor of the mouth
- Excessive loss of maxilla or mandible
- Large maxillary or mandibular tori.
Question 4. Residual ridge resorption.
Answer:
- It is alveolar remodeling that occurs due to change in the functional stimulus of bone tissue
- It is a chronic progressive change in the bone structure, which results in severe impairment in the fit & function of the prosthesis
Cause of Residual ridge:
- Excessive forces over non stress-bearing areas cause activation of osteoclasts
Clinical Features of Residual ridge:
- Decreased depth & width of sulcular
- Decreased vertical dimension at occlusion
- Reduced lower facial height
- Anterior rotation of mandible
- Increase in relative prognathism
- Increased mandibular arch
- Decreased maxillary arch
- Effects support, stability & retention of dentures
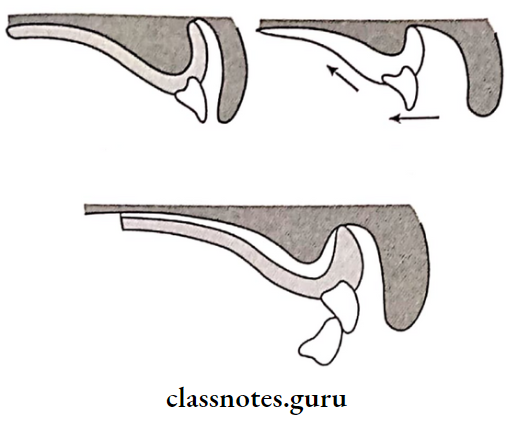
Treatment of Residual ridge:
- Ridge augmentation to increase the height of the ridge
- Vestibuloplasty to increase the depth of the sulcus
Question 5. Burning mouth syndrome
Answer:
Burning sensation in the structures in contact with the dentures without any visible change in the mucosa
Features of mouth syndrome:
- Pain in the morning
- Dry mouth
- Persistent altered taste
- Generalized symptoms
Etiology of mouth syndrome:
- Irritation by ill-fitting dentures
- Constant masticatory activity
- Excessive friction on the mucosa Candidal infection
- Nutritional deficiency
- Xerostomia
- Medication
Management of mouth syndrome:
- Counseling
- Repair of ill-fitted denture
- If there is no denture deficiencies then it requires psychological counseling
- An implant-supported denture fabrication may be carried out
Question 6. Denture stomatitis
Or
Denture sore mouth
Answer:
It is the pathological reaction of the palatal portion of the denture-bearing mucosa
Types of Denture stomatitis:
- Type I: Localized simple infection
- TypeII: Erythematous type
- Type III: Granular type
Etiology of Denture stomatitis:
- Candida albicans
Predisposing Factors of Denture stomatitis:
- Local factors:
- Dentures
- Xerostomia
- High carbohydrate diet
- Use of broad-spectrum antibiotics
- Smoking
- Systemic factors:
- Old age
- Diabetes mellitus
- Nutritional deficiency
- Immune defect
- Malignancy
Treatment of Denture stomatitis:
- Good oral hygiene
- Keep the denture as clean as possible
- Avoid wearing dentures at night
- Clean the dentures by brushing, soaking, and then brushing again
- If the denture contains metal work do not use anything that contains bleach.
Management of Denture stomatitis:
- 0.2-2% chlorhexidine
- Removal & cleaning of dentures after every meal
- Avoid night wearing of dentures
- Polishing of denture
- Administration of anti-fungal drugs
- Surgically: Elimination of crypts, by cryosurgery
Complete Denture Viva Voce
- Surfaces of complete dentures are described by Fish.
- The Fit of the denture depends on the accuracy of the impression surface.
- Occlusal surface aids in mastication
- The polished surface is the external surface of the complete denture
- Result of residual ridge resorption
- Prognathic appearance
- Wide mandible, narrow maxilla
- Concave profile
- The ratio of anterior maxillary residual ridge resorption to anterior mandibular residual ridge resorption is 1:4.
- Factors affecting residual ridge resorption (RRR)
- RRR – directly proportional to bone resorption fac- tor/bone formation factor
- RRR directly proportional to the pressure/ damping factor
- RRR directly proportional to the anatomic factor
- The cause of Epulls fissuratum is over-extension of the denture flange
- Treatment of Epulis fissuratum is shortening and smoothening the denture
- The cause of papillary hyperplasia is a candidal infection
- Treatment of papillary hyperplasia
- Small lesions curettage
- Large lesions split thickness subperiosteal excl sion
- A diffuse erythematous zone under denture covered area is a sign of denture stomatitis
- Cause of flabby ridge excessive load on the residual ridge
- Cause of traumatic ulcer
- Overextended flanges
- Occlusal imbalance
- Burning mouth syndrome is common in females older than 50 years.
