Instruments Short Essays
Question 1. Classify hand-cutting instruments.
Answer:
According To Gv Black:
1. Cutting Instruments.
- Hand
- Hatchet
- Chisel
- Hoe
2. Condensing Instruments Pluggers.
3. Plastic Instruments.
- Plastic filling instrument
- Cement carriers
- Carvers
4. Finishing And Polishing Instruments.
- Orangewood sticks
- Polishing points
5. Isolation Instruments
- Saliva ejector, evacuating tips.
6. Miscellaneous
- Mouth mirror, probe.
Question 2. Hand-cutting instruments.
Answer:
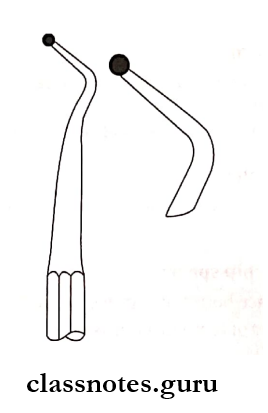
1. Excavators:
Excavators Types:
- Hatches:
- The cutting edge of the blade is directed in the same plane as that of the long axis of the handle
- It is beveled
- Uses:
- Used in anterior teeth for preparing retentive areas
- Sharpening of line angles
- In preparation for a direct gold restoration
- Uses:
- Hoes:
- The cutting edge of the blade is perpendicular to the axis of the handle
- Uses:
- Planing tooth preparation walls
- For forming line angles
- Uses:
- The cutting edge of the blade is perpendicular to the axis of the handle
- Angleformers:
- Monoangled instrument
- The cutting edge is at 90 degrees to the bladder
- Uses:
- Sharpening line angles
- Creates retentive features in dentin in gold restoration preparation
- Uses:
- Spoon Excavator:
- Blades are slightly curved and cutting edges are either circular or clawlike
- Uses:
- To remove caries
- Carves amalgam or direct wax pattern
- Uses:
- Blades are slightly curved and cutting edges are either circular or clawlike
2. Chisels:
- Used for cutting enamel
- Grouped into
1. Straight, Slightly Curved Or Bangle chisels:
- It has a straight shank and blade with a bevel on only one side
- The edge is perpendicular to the axis of the handle
2. Enamel Hatchet:
- Paired instrument
- Blade angle 4590°
- Bevel Unibevel/Bibeveled
Enamel Hatchet Use:
- Unibevelled Instrument:
- Cleaving of enamel
- Planning of dentinal walls
- Beveled:
- Use in a chopping motion
- Refine line and point angle
3. Gingival Margin Trimmer:
- It is a modified hatchet with opposite curva¬ture and bevels
- Paired instrument Distal and mesial
- Instrument formula 7585 Mesial GMT, 95100 Distal GMT
Gingival Margin Trimmer Use:
- Planning of gingival cavosurface margin
- Removal of unsupported enamel
- Bevel axiopupal line angle in Class 2
Question 3. Bur design.
Answer:
- The design of the bur includes the following
1. Blade Or Cutting Edge:
- It is in contact with the horizontal line or face
2. Tooth Face:
- The sides of the tooth head of the cutting edge in the direc¬tion of the rotation is the tooth face
3. Back Of The Tooth:
- The opposite of the bur tooth is the back of the tooth
4. Rake Angle:
- Rake Angle is the angle between the rake face and the radial line
- Positive Rake Angle Radial line is ahead of the rake face
- Negative Rake Angle The Rake face is ahead of the radial line
- Zero Rake Angle Rake face and radial line coincide
5. Clearance Angle:
- Clearance Angle is the angle between the back of the tooth and the work
- Mostly it is straight and clearly defined
6. Tooth Angle:
- Tooth Angle is the measurement between the face and the back
7. Flute Or Chip Space:
- Flute or chip space is the space between successive teeth
- The number of teeth in a bur is 6 or 8
Question 4. Instrument Nomenclature.
Answer:
- Order Purpose of instrument Example: Excavator
- Suborder Manner of use Example: Push or pull
- Class Form of working end Example: Hatchet, chisel
- Subclass shape of the shank Example: Monoangle
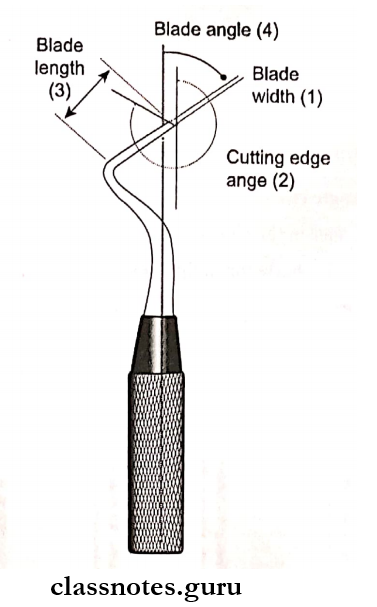
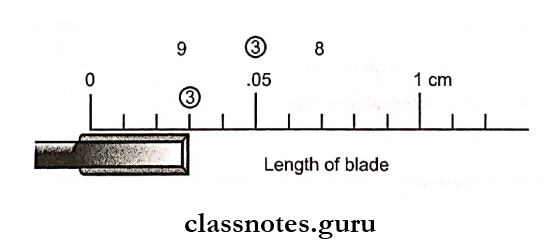
Question 5. Instrument Formula.
Answer:
Unit-1:
- Blade width
- Represents the width of the blade in tenths of a millimeter
Unit-2:
- Blade length
- Expressed in millimeter
Unit-3:
- Blade angle
- The angle formed between the blade and the long axis of the instrument
- Expressed in 100th of a circle
Unit-4:
- Cutting edge angle
- The angle formed between the cutting edge and the long axis of the handle
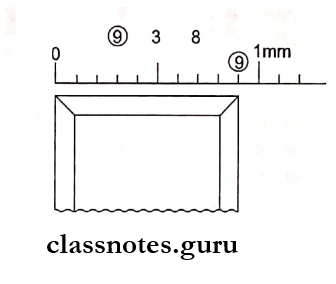
Question 6. Chisels.
Answer:
Chisels Types:
1. Straight Chisels:
- Straight blade in line with handle and shank
- Cutting edge on one side
2. Monoangle Chisels:
- Blade angle to the shaft
- Maybe medially or distally
3. Biangle Chisel:
- Two angles between the shaft and blade
- Unibevelledmedially or distally
4. Triangle Chisel:
- 3 angles in the shank
- Used for flattening the pulpal floor
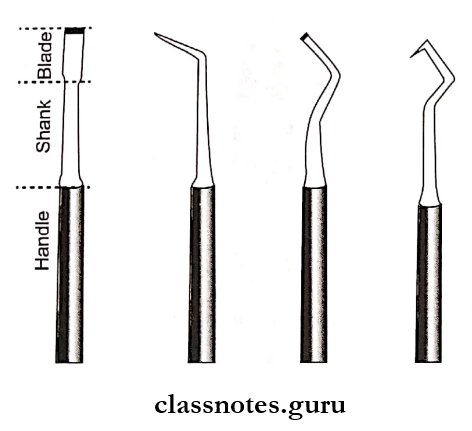
Question 7. Excavators.
Answer:
- Used for removal of caries
- Refining internal line angles
Excavators Types:
1. Hatchet:
- The blade of the hatchet is perpendicular to the shaft
- The cutting edge is parallel to the shaft
- Paired i.e. right and left
- Used for delicate cutting
2. Hoe Excavators:
- Single planed instrument
- Unibevelled
- Used with a push motion
- Used for cutting axial walls
3. Spoon Excavators:
- Paired instruments
- Double planed instruments
- Used for removal of the decayed dentin
4. Cleoid Excavator:
- Blade resembles a claw
- Used for amalgam carving, excavating decay in difficult areas