Instruments Important Notes
1. Classification Of instruments
- According To Marzouck:
- Exploring Instruments
- Tweezer
- Retractor
- Probe/Explorer
- An instrument For Tooth Structure Removal
- Excavators
- Chisels
- Restoring Instruments
- Spatulas
- Burnishers
- Condensers
- Carvers
- Finishing And Polishing Instruments
- Stones
- Brushes
2. Types Of Grasps:
- Modified pen
- Inverted pen
- Palm and thumb
- Modified palm and thumb
3. Materials Used For Sharpening Stones:

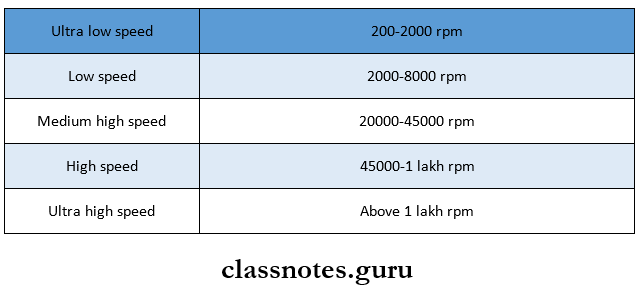
4. Speed Ranges:
5. Common Shank Design
- Straight
- Latch type
- Friction grip
6. Different Instruments
Chisels:
- Has a straight shank and bevel on one side only
- Used with both pull and push motion
- Used to cleave or split undermined enamel
- Used to flatten pulpal floors
Enamel Hatchet:
- The cutting edge is parallel with the long axis of the handle and beveled on one side
Enamel Hatchet Uses:
- To split undermined enamel
- For placing grooves
Gingival Marginal Trimmer:
- It is an enamel hatchet with a curved blade
- It is 4 figure formula instrument
- Has cutting edge at an angle more than 90° to the axis of the blade
Gingival Marginal Trimmer Uses:
- For bevelling gingival margin
- For bevelling axiopulpal line angle
Hatchet:
- It has the cutting edge of the blade directed in the same plane as that of the long axis of the handle
- It is beveled
Hatchet Uses:
- For preparing retentive areas in anterior teeth
- For sharpening internal line angles for DFG
Hoe:
- The cutting edge is perpendicular to the long axis
Hoe Uses:
- To give form to the internal parts of the cavity used on the enamel of posterior teeth
Angle Former:
- Angle Former is a combination of GMT and chisels
Angle Former Use:
- For sharpening line angles or obtaining retention in dentin
Spoon Excavator:
- The cutting edge is either claw-like or circular
- The circular is known as discoid
- Claw-like is known as cloud
Spoon Excavator Uses:
- For removing caries
- For carving amalgam
Knives:
- Used for trimming excess filling material
Files:
- Used to excess filling material, especially on gingival margins
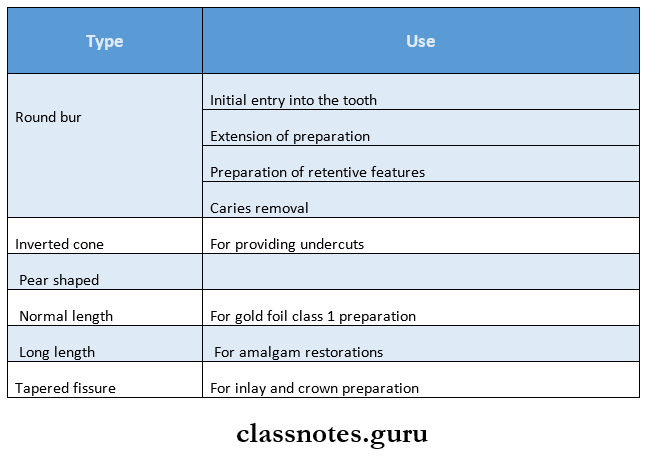
7. Types Of Burs:
Instruments Viva Voce
- When the second number in the instrument formula is 90100, the pair is used on the distal gingival margin
- When the second number is 7585 it is used in the mesial margin
- 100 and 75 pairs are used for inlayonlay preparation
- 90 and 85 pairs are used for amalgam preparations
- The modified pen grasp and inverted pen grasp are used universally
- The modified palm and thumb grasp is usually employed in the area of the maxillary arch
- Low speed is used for caries excavation, finishing, and polishing procedures
- High speed is used for efficient cutting and removing old restorations
- The neck of the instrument tapers from the shank diameter to a smaller size immediately adjacent to the head
- The neck transmits rotational and translational forces to the head
- Carbide burs normally have blades with slight negative rake angles