Impression And Mouth Preparation Short Answers
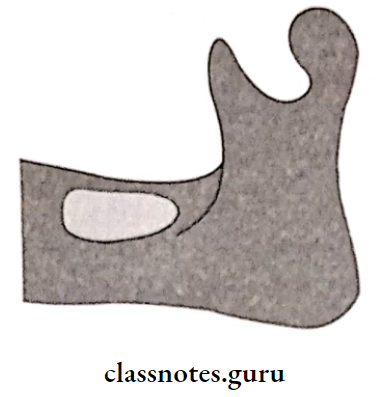
Question 1. Buccal shelf area
Answer:
Area of Buccal shelf :
Between buccal frenum & anterior border of the masseter
Boundaries of Buccal shelf :
- Medial crest of the ridge
- Distal Retromolar pad
- Lateral external oblique ridge
Significance of Buccal shelf :
- Primary stress-bearing area of the mandible
- The width of it increases as resorption continues
Question 2. Ridge Augmentation
Answer:
Definition:
Any procedure designed to enlarge or increase the size, extent, or quality of a deformed residual ridge is referred to be ridge augmentation procedures
Methods of Ridge Augmentation:
- Mandibular augmentation
- Superior border augmentation Inferior border augmentation Interpositional augmentation
- Visor osteotomy
- Onlay grafting
- Maxillary augmentation
- Onlay bone grafting Interpositional grafting Sinus lift procedure
- Combination procedures
Question 3. “Cohesion” in complete dentures.
Answer:
- It is the physical attraction of like molecules to each other
- Acts within the film of saliva
- Normal quality and adequate quantity of saliva is cohesive
- When the quantity of saliva is excessive and the quality is watery, cohesion is decreased
- When the quantity of saliva is decreased and its viscosity is increased, cohesion is decreased due to increase in the thickness of saliva
Question 4. Mylohyoid ridge importance
Answer:
- It is a rough bony crest extending from the third molar to second bicuspid region
- The mylohyoid muscle is attached to the mylohyoid ridge
- In the anterior region, the mylohyoid ridge with attached mylohyoid muscle lies close to the inferior border of the mandible
- Posteriorly, it is superior in position and the lingual flange of the denture may extend below the mylohyoid ridge if it drops vertically or slopes at 45 degrees to wards the tongue
Read And Learn More: Prosthodontics Question And Answers
Question 5. Stress-bearing areas of edentulous foundations
Answer:
These are those areas where stresses are directed are right angle
Significance:
- These are important while impression-making especially in the selective pressure technique
- Stresses are applied only over the stress-bearing areas
- These areas are different in the maxilla as well as the mandible
Primary Stress-Bearing Areas In Maxilla:
- Hard palate
- The postero-lateral slopes of the residual alveolar ridge
Primary Stress Bearing Areas In Mandible:
- The postero-lateral slopes of the residual alveolar ridge
Secondary stress-bearing area:
- Maxilla
- Mandible
- Rugae
- Maxillary tuberosity
- Anterior lingual border
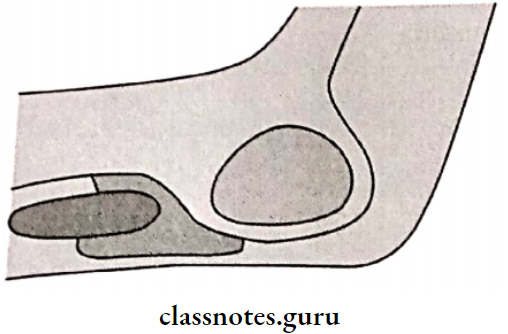
Question 6. Retromolar papilla
Answer:
- It is described as a pear-shaped papilla It is a small elevation
- It is a residual scar formed after the extraction of the third molar
- It lies along the line of the ridge
- The denture should terminate at the distal end of the pear-shaped papilla
- Beading this area improves retention
Question 7. Objectives of complete denture impressions
Answer:
- Retention: It is the resistance to displacement away from the tissue surface. It is a mucosa-borne phenomenon.
- Support: It is the resistance to the occlusal forces in the vertical direction. It is a bone-borne phenomenon.
- Stability: It is resistant to lateral shifting.
- Preservation of remaining structures.
Question 8. Diagnostic casts.
Answer:
Requirements:
- Should be:
- Free of voids
- Smooth surface
- Provide good denture support
- Walls should be tapering outward
- Smooth tongue space
- Free of moisture
- Occlusal table parallel to the floor.
Uses:
- Measure the undercuts Determine the path of insertion
- Treatment planning
- Perform mock surgery Evaluate the arch
- Assess retention & stability
- Determine secondary retentive forms
Question 9. Saliva’s influence on denture retention & stability.
Answer:
- Thick & ropy saliva loss of retention
- Thin & watery saliva compromised retention
- Watery serous saliva is more retentive
- In xerostomia there is no adhesion
- Ptyalism leads to gagging
- Xerostomia Soreness & irritation
Question 10. Retention in maxilla
Answer:
Retention factors present in maxilla are
- Large denture-bearing area
- Thick and ropy saliva
- Interfacial surface tension
Question 11. Maxillary anatomical structures
Answer:
Limiting structures:
- Labial frenum
- Labial vestibule
- Buccal frenum
- Buccal vestibule
- Hamular notch
- Posterior palatal seal area
Supporting structures:
- Primary stress-bearing areas
- Hard palate
- Postero-lateral slopes of the residual alveolar ridge
- Secondary stress-bearing areas
- Rugae
- Maxillary tuberosity
- Alveolar tubercle
- Relief areas:
- Incisive papilla
- Cuspid eminence
- Mid-palatine raphe
- Fovea palatine
Question 13. Final impression methods in complete denture
Answer:
- Dry gauze is placed in floor of the mouth to remove the saliva
- It is removed just before making an impression
- Impression material is manipulated and loaded onto the tray
- The tray is rotated in the horizontal plane and inserted into mouth using the anterior handle
- Tray is seated completely by applying alternating pressure over the posterior handles
- Patient is asked to touch his upper lip with his tongue
- Passive movements are performed
- After material gets set and examine for any defects
Question 14. Realeff effect
Answer:
Complete dentures rest on the basal seat area which is primarily oral mucosa and residual alveolar ridge
- The oral mucosa is displaceable and compressible Hanau described this factor as “resiliency and like effect”- Realeff effect
- It helps an important role in all steps of complete denture fabrication as in
- Primary impression
- Border moulding
- Final impression
- Jaw relation
- Try in
- Remount
- Follow up
- Mechanical or pathological reasons cause fibrous changes in the residual ridge, making it resilient
- It is more commonly seen in Mandibular residual ridges
- Maxillary anterior ridges
Factors Affecting Realeff Effect
- Consistency of mucosa
- Excess bone loss during extraction
- Person’s general health
- Elderly tissues
- Smaller forces produce distinct compression
- Parafunctional habits
- Single complete denture
Question 15. Materials used for master impression.
Answer:
Requirements:
- Low viscosity
- Form a thin layer of impression.
- Should be uniform
Materials Used:
- Zinc oxide eugenol paste impression
- Medium-bodied elastomeric impression materials
Question 16. Anterior & posterior vibrating lines.
Answer:
1. Anterior Vibrating Lines:
- It is an imaginary line lying at the junction between the immovable tissues over the hard palate & the slightly movable tissues of the soft palate.
- Shape: Cupid bow shape
Method to Measure:
- By Valsalva maneuver: The patient is asked to close his nostrils firmly & gently blow through his nose
- By asking the patient to say “ah”
2. Posterior Vibrating Line:
- It is an imaginary line located at the junction of the soft palate that shows limited movement & the soft palate that shows marked movement
Method to Measure:
- Conventional method
- Fluid wax technique
- Arbitrary scraping of the master cast Extended palatal technique
Question 17. Modiolus.
Answer:
It is a point where 8 muscles meet at the angle of mouth
They are:
- Depressor anguli oris
- Levator anguli oris
- Risorius
- Orbicularis oris
- Buccinator
- Zygomatic major
- Quadralus labii superioris
- Quadralus labii inferioris
Question 18. Hamular notch.
Answer:
- It is the depression situated between the maxillary tuberosity and the hamulus of the medial pterygoid plate It is soft area of loose connective tissue
- The tissues in this area can be safely displaced to achieve the posterior palatal seal
- The distolateral border of the denture base rests in the hamular notch
Significance:
- The denture border should extend till the hamular notch
- If the border is located anteriorly near the maxillary tuberosity, the denture will not have retentive properties as the denture will lie on non-resilient tissues in such cases
Question 19. Retromylohyoid fossa.
Answer:
- It belongs to the posterior part of the alveolilingual sulcus
- It lies posterior to the mylohyoid muscle
Boundaries:
- Anteriorly retro mylohyoid curtain
- Posterolaterally superior constrictor of the pharynx
- Posteromedially palatoglossus and lateral surface of the tongue
- Inferiorly sub mandibular gland
Question 20. Syneresis & imbibition.
Answer:
- Process of water sorption by hydrocolloids is known as imbibition
- Syneresis is a process where the gel may loose water by exudation of fluid
- Syneresis & imbibition can result in dimensional changes & therefore inaccurate casts
- To avoid this hydrocolloids should be poured immediately
Question 21. Advantages of the perforated stock tray.
Answer:
- It is used for impression materials like alginate
- Holes present in it are advantageous
- It helps in retaining the material while impression making
- It retains the material by mechanical interlocking
