CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 8 Application Of Integrals Important Questions
Question 1. Using integration, find the area bounded by the curve y ²= 4x, y-axis, and y = 3.
Or,
Using integration, find the region’s area bounded by the line 2y = – x + 8, x-axis. x = 2 and x = 4.
Solution:
Given curve is y² = 4x ….(1)
and given line is y = 3 …..(2)
From equations (1) and (2):
Point of intersection is B(9/4, 3)
Read and Learn More CBSE Class 12 Maths Important Question and Answers
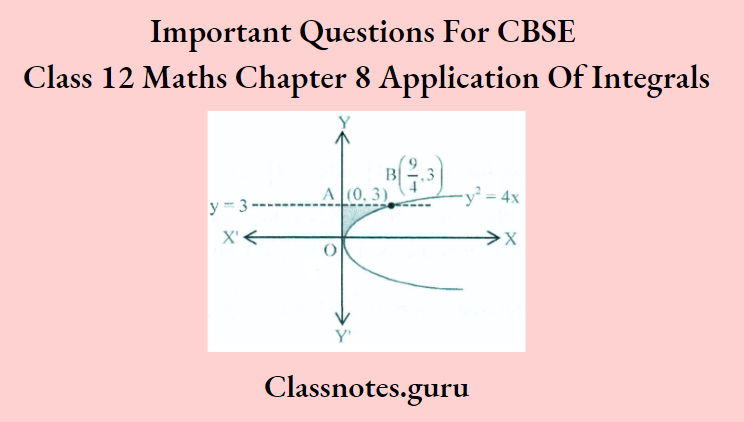
⇒ Required Area = \(\int_0^3\) x dy
= \(\frac{1}{4} \int_0^3 y^2, d y=\frac{1}{4}\left[\frac{y^3}{3}\right]_0^3=\frac{1}{4}\left[\frac{3^3}{3}-\frac{0}{3}\right]=\left(\frac{1}{4}, \frac{27}{3}\right)=\frac{9}{4} \text { sq. units }\)
Or,
Given lines are 2y + x = 8, x = 2 and x = 4
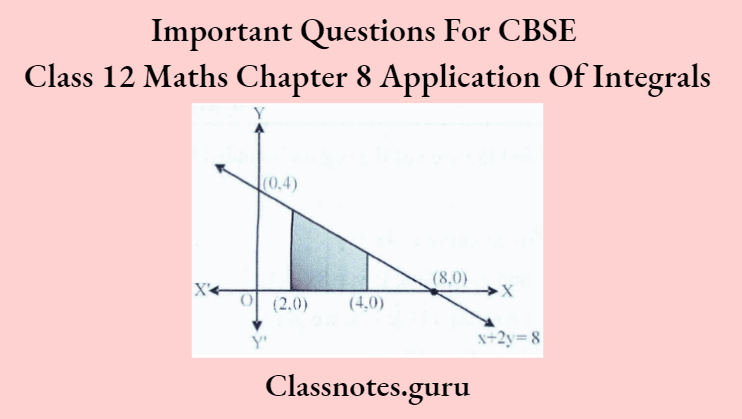
⇒ Required area = \(\int_2^4 y \mathrm{dx}=\int_2^4\left(\frac{8-\mathrm{x}}{2}\right) \mathrm{dx}\)
= \(\int_2^4\left(4-\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{x}\right) \mathrm{dx}=\left[4 \mathrm{x}-\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}^2}{2}\right)\right]_2^4\)
= \(\left[4 \times 4-\frac{1}{4}(4)^2\right]-\left[4 \times 2-\frac{1}{4}(2)^2\right]\)
=12-7=5
∴Required Area = 5 sq. units
Application Of Integrals Class 12 Important Questions
Question 2. Using integration, find the area bounded by the circle x² + y² = 9.
Solution:
The whole area enclosed by the given circle will be 4 times the area of the region AOBA bounded by the curve, x-axis, and the ordinates x = 0 and x = 3 [as the circle is symmetrical about both the x-axis and y-axis]
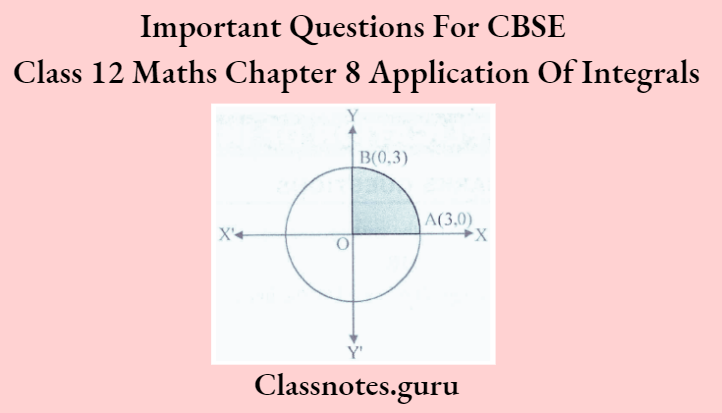
⇒ Required area = \(4 \int_0^3 y d x=4 \int_0^3 \sqrt{3^2-x^2} d x \quad\left[x^2+y^2=3^2 \text { gives } y= \pm \sqrt{3^2-x^2}\right]\)
As the region AOBA lies in the first quadrant, v is taken as positive. Integrating, we get the whole area enclosed by the given circle
⇒ Required area = \(4\left[\frac{x}{2} \sqrt{3^2-x^2}+\frac{3^2}{2} \sin ^{-1}\left(\frac{x}{3}\right)\right]_0^3\)
= \(4\left[\left(\frac{3}{2} \times 0+\frac{3^2}{2} \sin ^{-1}(1)\right)-0\right]=4\left(\frac{3^2}{2}\right)\left(\frac{\pi}{2}\right)=9 \pi \text { sq. units }\)
Question 3. Find the area of the region bounded by curve 4x²=y and the line y = 8x + 12. using integration.
Solution:
Given curve is 4x²= y….(1)
and given line is y = 8x + 12…..(2)
From equation (1) and (2), we get:
4x² – 8x – 12 = 0
⇒ x² – 2x – 3 = 0
⇒ (x-3) (x + 1) = 0 =3 x = 3, -1
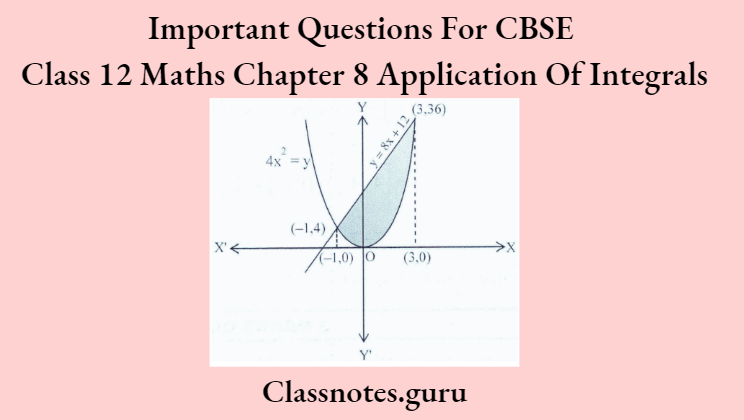
From equation (1); when x = 3, y = 36 and when x = – 1 ⇒ y = 4.
So, point of intersection of the curve and line tire (3, 36) and (-1,4).
⇒ Required Area = \(\int_{-1}^3\left\{(8 x+12)-4 x^2\right\} d x=\left[\frac{8 x^2}{2}+12 x-\frac{4 x^3}{3}\right]_{-1}^3\)
= \((36+36-36)-\left(4-12+\frac{4}{3}\right)=36+\frac{20}{3}=\frac{128}{3} \text { sq. units }\)

Class 12 Maths Chapter 8 Important Questions With Solutions
Question 4. Using integration, find the area of the region bounded by the curves x² + y² = 4, x =√3y, and the x-axis lying in the first quadrant.
Solution:
Given curve x² + y² = 4 is a circle with center (0, 0) and radius 2.
And line is x = √3y
Now, for the point of intersection of the line and circle, we have:
⇒ 4y² = 4 ⇒ y = ± 1
For y = 1; x = √3
So. point C is (3, 1)
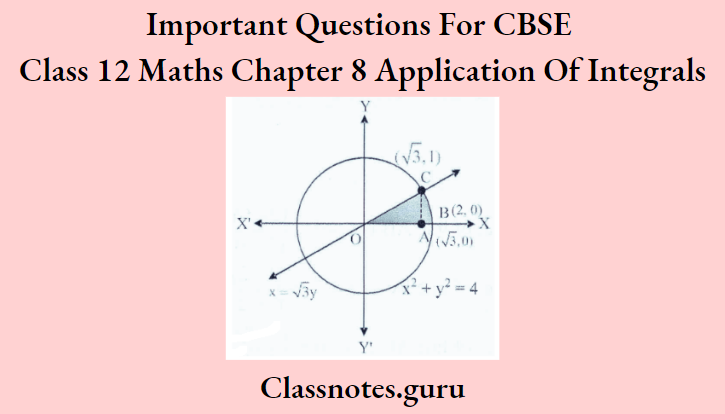
Required area = area of OACO + Area of ABCA
= \(\int_0^{\sqrt{3}} y_{\text ({line })} d x+\int_{\sqrt{3}}^2 y_{\mid \text {circle } \mid} d x=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \int_0^{\sqrt{3}} x d x+\int_{\sqrt{3}}^2 \sqrt{4-x^2} d x\)
= \(\frac{1}{2 \sqrt{3}}\left[x^2\right]_0^{\sqrt{3}}+\left[\frac{x}{2} \sqrt{4-x^2}+\frac{4}{2} \sin ^{-1}\left(\frac{x}{2}\right)\right]_3^{-2}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2 \sqrt{3}}(3)+\left\{2 \sin ^{-1}(1)-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}-2 \sin ^{-1}\left(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)\right\}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}+\left(2 \times \frac{\pi}{2}\right)-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}-2 \times \frac{\pi}{3}=\frac{\pi}{3} \text { sq.units }\)
Application Of Integrals Important Questions CBSE
Question 5. Using the method of integration, find the area of the triangle ABC. coordinates of whose vertices are A(2. 0), B(4, 5) and C(6, 3).
Solution:
Vertices of ΔABC are A(2,0), B(4,5) and C (6,3)
Equation of line AB: y = 5/2(x – 2)
Equation of line BC: y = 9-x
Equation of line AC: y= 3/4(x-2)
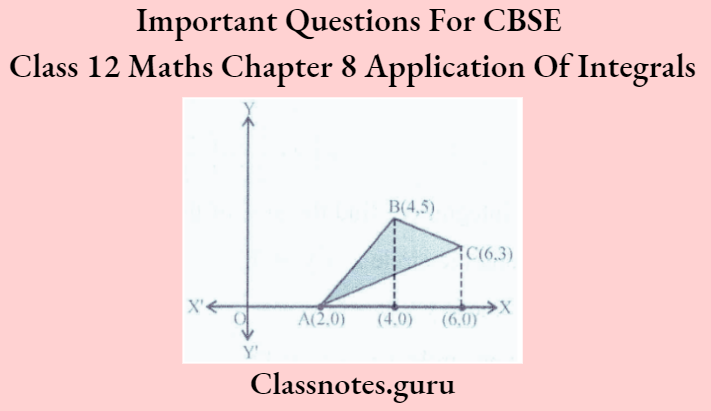
⇒ Required Area of ΔABC = \(\int_2^4(\text { line } \mathrm{AB}) \mathrm{dx}+\int_4^6(\text { line } \mathrm{BC}) \mathrm{dx}-\int_2^6(\text { line } \mathrm{AC}) \mathrm{dx}\)
= \(\frac{5}{2} \int_2^4(x-2) d x+\int_4^6(9-x) d x-\frac{3}{4} \int_2^6(x-2) d x\)
= \(\frac{5}{2}\left[\frac{x^2}{2}-2 x\right]_2^4+\left[9 x-\frac{x^2}{2}\right]_4^6-\frac{3}{4}\left[\frac{x^2}{2}-2 x\right]_2^6\)
= \(\frac{5}{2}[(8-8)-(2-4)]+[(54-18)-(36-8)]-\frac{3}{4}[(18-12)-(2-4)]\)
= \(\left(\frac{5}{2} \times 2\right)+8-\left(\frac{3}{4} \times 8\right)=5+8-6=7 \text { sq. units }\)
Question 6. Using the method of integration, find the area of a triangle whose vertices arc (1, 0), (2, 2), and (3, 1).
Solution:
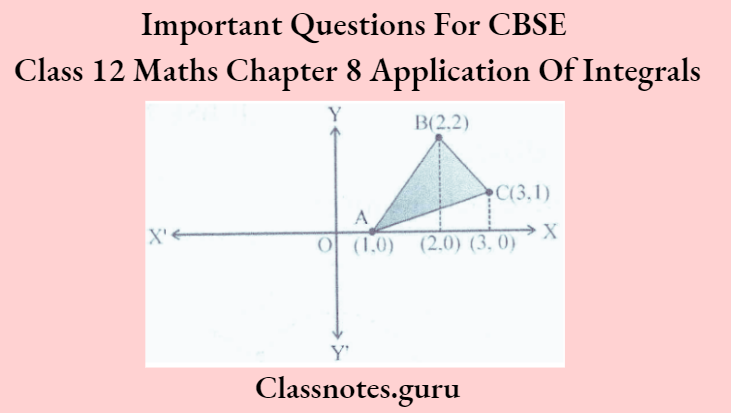
Equation of line AB is y – 0 = \(\frac{(2-0)}{(2-1)}(x-1) \Rightarrow y=2(x-1)\)
Equation of line BC is y – 2 = \(\frac{(1-2)}{(3-2)}(x-2) \Rightarrow y=(-x+1)\)
Equation of line AC is y – 0 = \(\frac{(1-0)}{(3-1)}(x-1) \Rightarrow y=1/2(x-1)\)
⇒ Required Area = \(\int_1^2(\text { line } A B) d x+\int_2^3(\text { line } B C) d x-\int_1^3(\text { line } A C) d x\)
= \(\int_1^2 2(\mathrm{x}-1) \mathrm{dx}+\int_2^3(-\mathrm{x}+4) \mathrm{dx}-\int_1^3 \frac{1}{2}(\mathrm{x}-1) \mathrm{dx}\)
= \(2\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}^2}{2}-\mathrm{x}\right)_1^2+\left(\frac{-\mathrm{x}^2}{2}+4 \mathrm{x}\right)_2^3-\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}^2}{2}-\mathrm{x}\right)_1^3\)
= \(2\left[(2-2)-\left(\frac{1}{2}-1\right)\right]+\left[\left(\frac{-9}{2}+12\right)-(-2+8)\right]-\frac{1}{2}\left[\left(\frac{9}{2}-3\right)-\left(\frac{1}{2}-1\right)\right] \)
= \(\left(2 \times \frac{1}{2}\right)+\left(\frac{-9}{2}+6\right)-\frac{1}{2}(4-2)=1+\frac{3}{2}-1=\frac{3}{2} \text { sq. units }\)
CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 8 Extra Questions
Question 7. Using integration, find the region’s area in the first quadrant enclosed by the x-axis, the line y = x, and the circle x² + y² = 32.
Solution:
Given line is y = x ….(1)
and given circle is x² + y² = 32….(2)
From equations (1) and (2); we have
2x² = 32 ⇒ x = ± 4
∴ y = ± 4
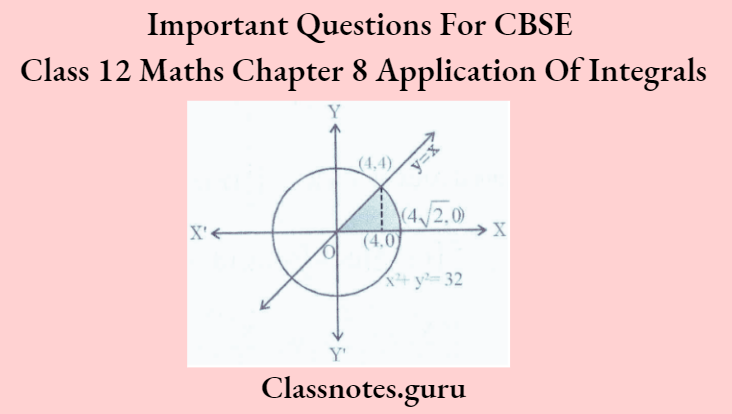
Now; (4, 4) lies in 1st quadrant
⇒ Required Area = \(\int_0^4 x d x+\int_1^{4 \sqrt{2}} \sqrt{32-x^2} d x\)
= \(\left(\frac{x^2}{2}\right)_0^4+\left[\frac{x}{2} \sqrt{32-x^2}+\frac{32}{2} \sin ^{-1}\left(\frac{x}{4 \sqrt{2}}\right)\right]_{-4}^{4 \sqrt{2}}\)
= \((8-0)+\left[\left(0+16 \times \frac{\pi}{2}\right)-\left(8+16 \times \frac{\pi}{4}\right)\right]=4 \pi \text { sq. units }\)
