Histamines And Antihistamines Important Notes
1. Antihistamines
- Antihistamines Uses
- Common cold
- Anti-allergic
- Insect bite
- Idiopathic pruritis
- Motion sickness
- Vertigo
Pharmacology of antihistamines questions
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question and Answers
Histamines And Antihistamines Short Essays
Question 1. Mention four newer antihistamines with their advantages.
Answer:
- Newer Antihistamines are:
- Fexofenadine
- Loratadine
- Cetrizine
- Azelastine
- Mizolastine
- Terfenadine
Newer Antihistamines Advantages:
- Donot impair psychomotor performance
- Produce no subjective effects
- No sedation as they poorly cross the blood-brain barrier
- No anticholinergic side effects
Question 2. Mention four therapeutic uses of HI blockers.
Answer:
Uses of H1 Blockers:
1. Allergic reactions
- Block the effects of released histamine
- Control Immediate types of allergies like Itching, urticaria, angioedema
- Cetrizine has an adjuvant role In seasonal asthma
2. Prurltldes
- Older H1 blockers are used In Idiopathic pruritus
3. Common cold
- Provide symptomatic relief by anticholinergic and sedative actions
4. Motion sickness
- Promethazine and diphenhydramine are used prophylactically in motion sickness
- It should be taken one hour before the journey
5. Vertigo
- Inhibits vestibular sensory nuclei in the inner ear
6. Preanasethetic medication
- Promethazine is used for it
- It includes the following groups
Pharmacology of antihistamines questions
7. Cough
- Provide symptomatic relief
8. Parklsonism
- Provide symptomatic relief
9. Acute muscle dystonia
- Due to Its central anticholinergic action
10. As sedative, hypnotic, and anxiolytic
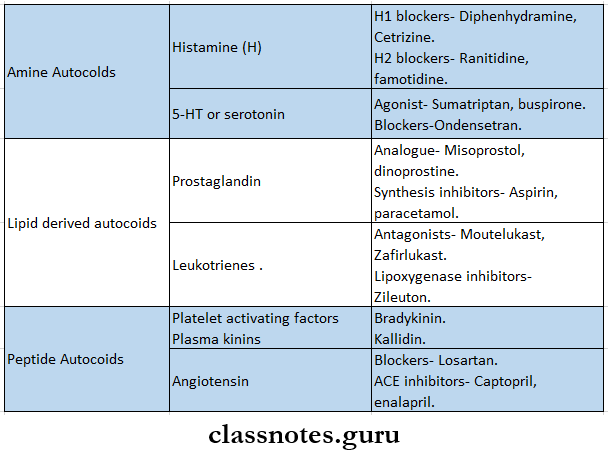
Question 3. Autocoids
Answer:
- Autocoids are substances formed in various tissues, have complex physiological and pathological actions, and act locally at the site of synthesis
- They are called local hormones
- They serve as transmitters or moderators in the nervous system
- They have brief action and are destroyed locally
Question 4. Antihistamines
Answer:
- Antihistamines are the drugs that competitively antagonize the action of histamine at H1 receptors
Antihistamines Classification
Antihistamines Uses:
- Allergic disorders
- Priorities
- Common cold
- Cough
- Motion sickness
- Preanasethetic medication
- Vertigo
- Parkinsonism
- Acute muscle dystonia
- As sedative, hypnotic, anxiolytic
- To control mild blood transfusion and saline infusion reactions
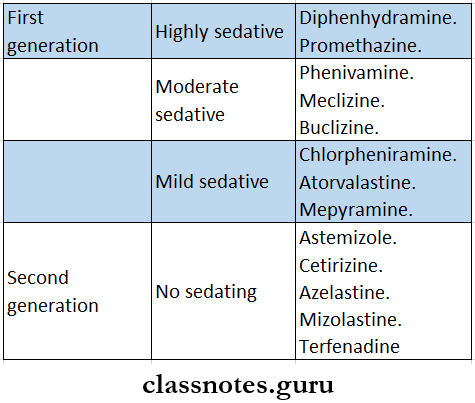
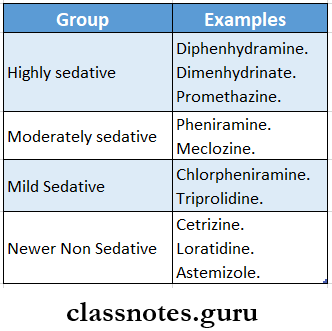
Question 5. Enumerate two nonsedative Antihistamines and mention four uses of them.
Answer:
Non Sedative Antihistamines:
- Fexofenadine
- Loratadine
- Cetrizine
- Azelastine
- Mizolastine
- Terfenadine
Non Sedative Antihistamines Uses:
- Allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, hay fever
- Control sneezing and runny nose, red watering eyes
- Urticaria, dermographism, atopic eczema
- Acute allergic reactions to drugs and food
Classification of antihistamines questions
Histamines And Antihistamines Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Cyproheptadine
Answer:
Cyproheptadine is a serotonin antagonist
Cyproheptadine Actions:
- Blocks 5-HT2
- Blocks H1 receptors
- Blocks cholinergic receptors
- Increases appetite
Cyproheptadine Uses:
- Promote weight gain in children and poor eaters
- To control intestinal manifestations of carcinoid tumors
Question 2. Non sedative Antihistamines
Answer:
Non Sedative Antihistamines:
- Fexofenadine
- Loratadine
- Cetrizine
- Azelastine
- Mizolastine
- Terfenadine
Non Sedative Antihistamines Uses:
- Allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, hay fever
- Control sneezing and runny nose, red watering eyes
- Urticaria, dermographism, atopic eczema
- Acute allergic reactions to drugs and food
Non-Sedative Antihistamines Advantages:
- Donot impair psychomotor performance
- Produce no subjective effects
- No sedation as they poorly cross the blood-brain barrier
- No anticholinergic side effects
Question 3. Cetrizine
Answer:
- Cetrizine is non sedative Antihistamines
- It can metabolite of hydroxyzine with a marked affinity for peripheral H1 receptors
- It is well absorbed orally
- It attains high and long-lasting concentration in the skin
Cetrizine Actions:
- Inhibits the release of histamine and cytotoxic mediators from platelets
- Inhibits Eosinophil chemotaxis during the secondary phase of the allergic response
Cetrizine Uses:
- Upper respiratory allergies, pollinosis, Urticaria, atopic dermatitis
- Adjuvant to seasonal asthma
Uses and side effects of antihistamines questions
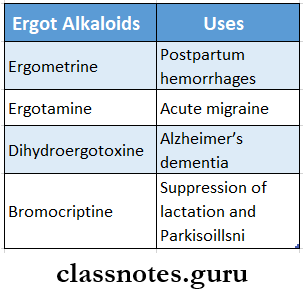
Question 4. Ergometrine
Answer:
- Ergometrine is an amine ergot alkaloid
- It is a very weak Agonist
- It has no antagonist action on alpha-adrenergic receptors
- The emetic potential is low
- They are rapidly and completely absorbed
- The plasma half-life is 1-2 hours
- Onset of action

Ergometrine Uses:
- To control and prevent postpartum hemorrhage
- To prevent uterine atony
- To ensure normal involution
Question 5. Promethazine
Answer:
- Promethazine is a highly sedative H1 antagonist
Promethazine Uses:
- Allergic disorders
- Pruritis
- Common cold
- Preanasethetic medication
- Parkinsonism
Question 6. Prostaglandins
Answer:
- Prostaglandins are biologically active derivatives of 200-carbon atom polyunsaturated fatty acids
- They are major lipid-derived autocoids
Prostaglandins Actions:
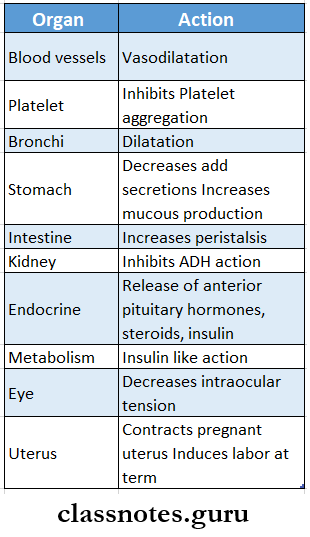
First and second-generation antihistamines MCQs
Question 7. Uses of ergot alkaloids
Answer: