Health Care Delivery System Definitions
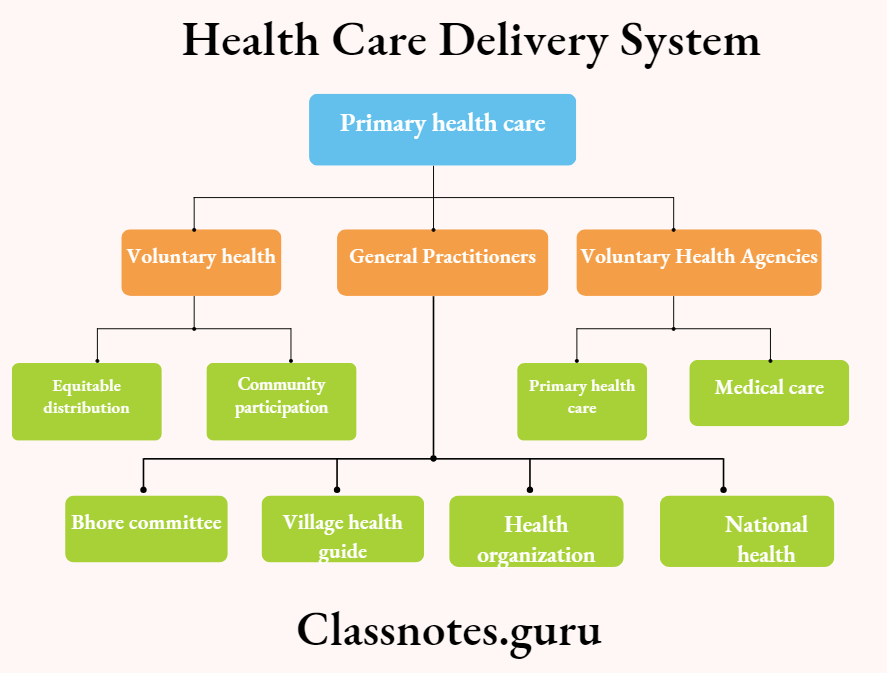
Primary health care
- Essential health care based on practical, scientifically sound, and socially acceptable methods and technology made universally accessible to individuals and families in the community through their full participation and at the cost that the community and the country can afford to maintain at every stage of their development in the spirit of self-determination
Voluntary health agencies
- Voluntary health agencies may be defined as an organization that is administered by an autonomous board, which holds meetings, collects funds for its support chiefly from private sources, and expends money, whether with or without paid workers, in conducting a program directed primarily to furthering the public health by providing health services or health education, or by advancing research or legislation for health, or by a combination of these activities
Health Care Delivery System Important Notes
1. Components of alma ata declaration are:
- Education about health problems and their preventive and controlling methods
- Adequate supply of safe water and basic sanitation
- Provision of essential drugs
- Promotion of food supply and proper nutrition
- Maternal and child health care including family planning
- Immunization against infectious diseases
- Prevention and control of endemic diseases
- Appropriate treatment of common diseases and injuries
Read And Learn More: Percentive Communitive Dentistry Question And Answers
2. Principles of primary healthcare
- Equitable distribution
- Community participation
- Intersectoral coordination Appropriate technology
- Focus on prevention
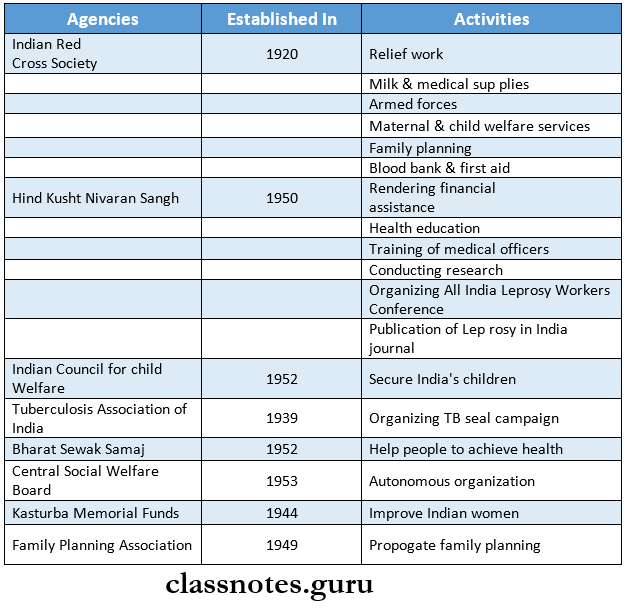
3. Voluntary health agencies in India
- Agencies
- Indian Red Cross Society
- Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh
- Indian Council for Child Welfare
- Tuberculosis Association of India
Read And Learn More: Percentive Communitive Dentistry Question And Answers
- Bharat Sewak Samaj
- Central Social Welfare Board
- Kasturba Memorial Funds
- Family Planning Association
Health Care Delivery System Questions
Health Care Delivery System Long Essays
Question 1. Describe existing dental health services in India
Answer:
Public Health Sector:
1. Primary Health Care:
Primary health centers:
- Each center covers a population of 1,00,000 and is spread over about 100 villages
- Primary health centers act as a referral unit for 6 sub-centers
- Functions
- Medical care
- Maternal and child health including family planning
- Safe water supply and basic sanitation
- Prevention and control of locally endemic disease
- Collecting and reporting vital statistics
- Education about health
- National health programs
- Referral services
- Training of health workers, health guides, local dais, and health assistants
- Basic laboratory health services
- Sub-centers
- Sub-centers are the peripheral outpost of the existing health delivery system in rural areas
- Sub-centers cover a population of 5000 in general and 3000 in hilly, tribal, and backward areas
- One male and one female multipurpose health worker attends each sub-center
- Each supervises the work of 6 health workers
- Sub-centers function is limited to mother and child health care, family planning and immunization
2. Hospitals/Health Care:
- Community health care
- Hospitals upgrade public healthcare
- Hospitals cover an 80,000 to 1.2 lakh population with 30 beds and specialists who refer a patient directly to a state-level hospital
- Rural hospital
- Rural hospital upgrades the rural dispensaries to public health center
- District hospital
3. Health Insurance Scheme:
- The Health Insurance Scheme is limited to industrial workers and their families
- They provide reasonable medical care plus some essential preventive and promotive health services
- Employees state insurance
- Health Insurance Scheme provides medical care in cash and kind
- Employees state insurance
- Central government health scheme
- Central government health scheme provides comprehensive medical care to central government employees
4. Others:
- Health care of railway employees
- Provide health services to railway hospitals, health units, and clinics
- Defense medical services
- Under the banner “Armed Forces Medical Services”
Private Sector:
1. Privater Hospitals, Polyclinic, Nursing Homes and Dispensaries:
- Provide a large share of the health services
2. General Practitioners:
- Constitute 70% of the medical profession
- They provide mainly curative services
Indigenous Systems of Medicine:
- Provide bulk of medical care to the rural people
Voluntary Health Agencies:
- It may be defined as an organization that is administered by an autonomous board that holds meetings, collects funds for its support chiefly from private sources, and expends money, whether with or without paid workers, in conducting a program directed primarily to furthering the public health by providing health services or health education, or by advancing research or legislation for health, or by a combination of these activities
National Health Programmes:
- National Malaria Eradication Programme
- National Filaria Control Programme
- National Tuberculosis Programme
- National Leprosy Eradication Programme
- Diarrhoeal Diseases Control Programme
- STD Control Programme
- National Programme for Control of Blindness
- Iodine Deficiency Disorder Programme
- Universal Immunization Programme
- National Family Welfare Programme
Types Of Health Care Delivery Systems
Question 3. Define Primary healthcare
Answer:
Primary Healthcare Definition:
- Essential health care based on practical, scientifically sound, and socially acceptable methods and technology made universally accessible to individuals & families in the community through their full participation and at the cost that the community and the country can afford to maintain at every stage of their development in the spirit of self-determination
Primary healthcare Principles:
- Equitable distribution
- Health services must be shared equally by all people ( rich, poor, urban or rural residents)
- Public health center aims to redress social injustice by shifting the center of gravity of the health care system from cities to rural areas
- Community participation
- The community must be involved in the planning, implementation, and maintenance of health services
- The involvement of individuals, families, and communities in the promotion of their health and welfare is an essential component of public health center
- In China, community participation is in the form of bare-foot doctors
- In India, village health guides and local dais provide public health care by overcoming cultural and communication barriers
- Intersectoral coordination
- Planning with other sectors should be carried out to avoid unnecessary duplication of activities
- For it, the administrative system of the country has to be reviewed, their resources reallocated & suitable legislation introduced
- To improve oral health care more attention must be given to policies & strategies that require multi-sectoral cooperation & action
- Appropriate technology
- It is defined as technology that is scientifically sound, adaptable to local needs, and acceptable to those who apply it & to those for whom it is used, and that can be maintained by the people themselves in keeping with the principles of self-reliance with the resources the community & country can afford
- This applies to using costly equipment procedures and technology when cheaper, scientifically valid, and acceptable ones are available
- Focus on prevention
- Health services should however not only be curative but should also promote health and healthy lifestyles with an emphasis on prevention
Health Care Delivery System Short Essays
Question 1. Primary health care.
Answer:
Primary health care Definition:
- Essential health care based on practical, scientifically sound, and socially acceptable methods and technology made universally accessible to individuals and families in the community through their full participation and at the cost that the community and the country can afford to maintain at every stage of their development in the spirit of self-determination
Primary health care Functions:
Medical care:
- Maternal and child health including family planning
- Safe water supply and basic sanitation
- Prevention and control of locally endemic disease
- Collecting and reporting vital statistics
- Education about health
- National health programs
- Referral services
- Training of health workers, health guides, local dais and health assistants
- Basic laboratory health services
Primary health care Principles:
Equitable distribution:
- Community participation
- Intersectoral coordination
- Appropriate technology
- Focus on prevention
Question 2. Bhore committee.
Answer:
Bhore committee
- Appointed in 1943 with Sir Joseph Bhore as its chairman
- Bhore committee suggested one public health center for 40,000 population
- Bhore committee aimed to provide integrated, curative & preventive health care to the rural population with an emphasis on preventive & promotive aspects
- Bhore committee aimed to serve a population with 6 medical officers,
- Demonstration of public health nurses & other supporting staff
Bhore committee Synonyms:
- Health Survey and Development Committee
- Comprehensive Health Care
- Meaning the provision of integrated preventive, curative & promotional health services from “Womb to Tomb”.
Healthcare Delivery Models
Question 3. Village health guide.
Answer:
Village health guide
- The village health guide was introduced on 2nd October 1977
- A village health guide is a person mostly a woman with an aptitude for social service
- Characteristics: they should be
- Permanent resident of the local community
- Have a minimum formal education of at least up to VI standard
- Acceptable to all sections of the community
- Able to spare at least 2-3 hours every day for community health work
- After selection, they undergo training in the nearest primary health center for 200 hours spread over 3 months and receive Rs 200/- per month as a stipend
- On completion of training, they receive a working manual and a kit of simple medicines belonging to the modern & traditional systems of medicine
- Duties:
- Treatment of simple ailments and activities in first aid
- Mother and child health including family planning
- Health education and sanitation
- The target is to have one village health guide for each village or 1000 rural population
Question 4. Voluntary health agencies in India.
Answer:
Voluntary health agencies in India
- It may be defined as an organization that is administered by an autonomous board that holds meetings, collects funds for its support chiefly from private sources and pends money, whether with or without paid workers, in conducting a program directed primarily to furthering the public health by providing health services or health education, or by advancing research or legislation for health, or by a combination of these activities
Functions:
- Supplementing the work of government agencies
- Education
- Demonstration
- Guarding the work of government Agencies
- Advancing Health Legislation
Question 5. World Health Organization.
Answer:
World health organization
- World Health Organization is a specialized, largest, non-political most prominent, self-governing, influential, multilateral health agency of Strengthens training of various categories of oral health
- United Nations with headquarters in Geneva
- World Health Organization came into force on 7th April 1948
Health organization Membership:
- Health organization Membership is open to all countries
Health organization Work:
- Prevention and control of specific diseases
- Development of comprehensive health services
- Family Health
- Environmental Health
- Health statistics
- Bio-medical research
- Health literature and information
- Co-operation with other organizations
Health organization Structure:
- The World Health Assembly
- The Executive Board
- The Secretariat
Health organization Who Agenda:
- Promoting development
- Fostering health security
- Strengthening health systems
- Harnessing research, information and evidence
- Enhancing partnership
- Improving performance
Health organization Who Journals:
- Bulletin of the World Health Organization
- Weekly Epidemiological Record
- WHO Drug Information
Health Care System Exam Questions
Question 6. Importance of national oral health policy.
Answer:
Importance of National Oral Health Policy
- It creates awareness about health problems and means to solve them
- It supplies safe drinking water and basic sanitation
- Concentrates on rural healthcare
- Supports health planning and health program implementation
- Provide support to health protection and promotion
- Act on widespread malnutrition
- Research healthcare delivery
- Creates greater coordination of different systems of medicine
- Resolves preventive and promotive oral health services
- Strengthens training of various categories of oral health care personnel care personnel
- Ensure statutory warning on the wrappers and advertisement of sweets, chocolates and other sugar retentive items
- Guide oral health research appropriate to the needs of the country.
Health Care Delivery System Short Question And Answers
Question 1. International Red Cross.
Answer:
International red cross
- The International Red Cross is a non-political, non-official international humanitarian organization devoted to the service of mankind. In China, community participation is in the form of peace and war
- International red cross was founded by Henry Dunant in 1859
- Dunant organized local people to bind the soldiers’ wounds and to feed and comfort them during the bloody battle in Solferino, Italy between the armies of imperial Austria and the Franco-Sardinian alliance
- Its emblem was a red cross on a white background
Principles:
- Humanity
- Impartiality
- Neutrality
- Independence
- Voluntary service
- Unity
- Universality
Question 2. Functions of primary health center.
Answer:
Functions of Primary Health Center
- Medical care
- Maternal and child health including family planning
- Safe water supply and basic sanitation
- Prevention and control of locally endemic disease
- Collecting and reporting vital statistics
- Education about health.
Question 3. Community participation.
Answer:
Community participation
- The community must be involved in the planning, implementation, and maintenance of health services
- The involvement of individuals, families, and communities in the promotion of their health and welfare is an essential component of public health center
- In China, community participation is in the form of bare-foot doctors
- In India, village health guides and local dais provide public health care by overcoming cultural and communication barriers
Question 4. Work of WHO.
Answer:
Work of WHO
- Prevention and control of specific diseases
- Development of comprehensive health services
- Family Health
- Environmental Health
- Health statistics
- Bio-medical research
- Health literature & information
- Co-operation with other organizations
Question 5. National health program.
Answer:
National health program
- National Malaria Eradication Programme
- National Filaria Control Programme
- National Tuberculosis Programme
- National Leprosy Eradication Programme
- Diarrhoeal Diseases Control Programme
- STD Control Programme
- National Programme for Control of Blindness
- Iodine Deficiency Disorder Programme
- Universal Immunization Programme
- National Family Welfare Programme
Primary Health Care Delivery System
Question 6. Elements of primary health centers.
Answer:
Elements of Primary Health Centers
- The Alma Ata declaration has outlined 8 essential components of primary healthcare
- Education about prevailing health problems and meth- Co-operation with other organizations ods of preventing and controlling them
- Promotion of food supply and proper nutrition
- An adequate supply of safe water and basic sanitation
- Maternal and child health care including family planning
- Immunization against infectious diseases
- Prevention and control of endemic diseases
- Appropriate treatment of common diseases and injuries
- Provision of essential drugs
Question 7. Recommendations of the Bhore committee.
Answer:
Recommendations of the Bhore Committee
- Integration of preventive and curative services to all administrative levels
- Development of primary health centers in 2 stages
- As short-term measure
- As a long-term program
- Major changes in medical education which includes 3 months of training in preventive and social medicine to prepare social physicians
Question 8. World health organization
Answer:
World health organization
- World Health Organization is a specialized, largest, non-political most prominent, self-governing, influential, multilateral health agency of the United Nations with headquarters in Geneva
- World Health Organization came into force on 7th April 1948
health organization Membership
- Health organization Membership is open to all countries
health organization Work
- Prevention and control of specific disease
- Development of comprehensive health services
- Family Health
- Environmental Health
- Bio-medical research
- Health literature and information
- Co-operation with other organizations
health organization Structure
- The World Health Assembly
- The executive board
- The Secretariat
Health Care Delivery System Pdf
Health Care Delivery System Viva Voce
- Health care services to be shared equally by all people ensures the principle of equitable distribution.
- The village health guide Scheme was introduced on 2nd October 1977
- Kasturba Memorial Fund is raised with the main objective of improving women
- Indian Red Cross Society was established in 1920.
- The functioning of voluntary health agencies involves pioneering new procedures
- Gram Sevikas are an integral component of the Kasturba Memorial fund
- India falls into the WHO regional organization of Southeast Asia region
- The International Red Cross was founded by Henry Dunant
- The headquarters of the Family Planning Association of India is located in Bombay
