Healing Of Oral Wounds Important Notes
- Types Of Healing
- Healing by the first Intention
- Hero edges of the wound are approximated
- The healing process is fast
- Healing by secondary intention
- There is tissue loss, wound edges cannot be opposed
- The wound contracts to reduce in size, granulation tissue fills the wound and epithelisation occurs
- This is healing by secondary intention
- Healing by the first Intention
- Factors Affecting Healing
- Physical factors
- Location of wound – A wound in an area with a good vascular bed heals more rapidly
- Immobilization – constant movement causes disruption of new connective tissue formation
- Severe trauma – arrest rapid healing
- Local temperature
- Hyperthermia – accelerates healing
- Hypothermia – delays healing
- X-ray radiations
- Low doses – stimulates healing
- Large doses – suppresses healing
- Anaemia – delays healing
- Age of patient
- Young patient – heals rapidly
- Elder patient – healing is retarded
- Nutritional factors – protein, vitamin deficiency delays healing
- Hormonal factors – ACTH and cortisone inhibit the growth of granulation tissue formation
- Diabetes mellitus – retards repair of wound
- Physical factors
- Types Of Biopsy
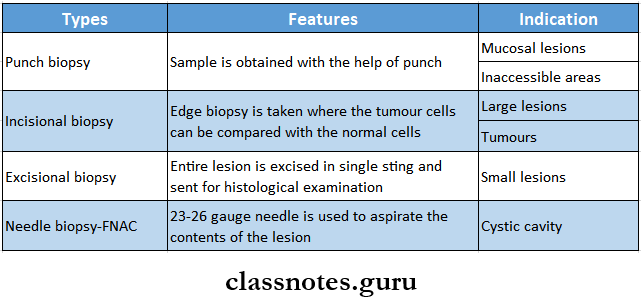
- Incisional – removal of small piece for examination
- Excisional – total excision of small lesion
- Methods Of Biopsy
- Surgical excision by scalpel
- Surgical removal by cautery
- Laser
- Removal by biopsy forceps
- Aspiration
- Exfoliative cytology technique
- Result Of The Cytology Smear
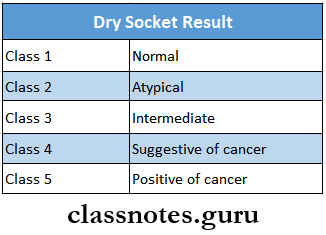
- Class 1 – Normal – only normal cells are observed
- Class 2 – Atypical – Presence of minor atypia
- Class 3 – Indeterminate – Wider atypia, represents precancerous lesion
- Class 4 – Suggestive of cancer – few malignant cells, many cells with borderline characteristics
- Class 5 – positive for cancer – malignant cells present
- Complications Of Fracture Wounds
- Delayed union
- Fibrous union
- Nonunion
- Lack of calcification
- Storage Media For The Preservation Of Teeth
- Milk
- Saliva
- Saline
- HBSS
- Propolis
- Viaspan
- Coconut water
- Types Of Oral Implants
- Endodontic
- Endosseous
- Subperiosteal
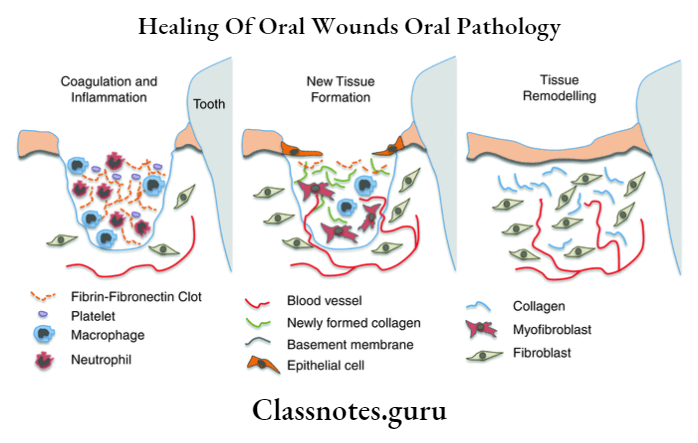
Healing Of Oral Wounds Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Write about the healing of extraction wound and mention its complications
Answer:
Healing Of Extraction Wound
- Immediate reaction
- Coagulation of blood
- Entrapment of RBC into fibrin mesh
- Vasodilation and engorgement of blood vessels
- Mobilization of leukocytes
- Presence of areas of contraction of clot
- First week
- Growth of fibroblast into wound
- Formation of granulation tissue
- The proliferation of epithelium at the periphery
- The osteoblastic activity of alveolar bone
- Organization of blood clot
- Second week
- Penetration of new capillaries into centre of clot
- Degeneration of remnants of PDL
- Fraying of bony socket
- Epithelium proliferation at periphery
- Fragments of necrotic bone
- Third week
- Complete formation of granulation tissue
- Presence of young trabeculae
- Early bone formation
- Remodeling of cortical bone
- Fourth week
- Bonefilling
- Healing of crest of the bone
Read And Learn More: Oral Pathology Question And Answers
Healing of Extraction Wound Complications:
- Dry socket
- It is focal osteomyelitis of the tooth socket in which the blood clot has disintegrated or been lost
- Dry socket Clinical Features:
- Loss of blood clot
- Radiating pain
- Foul odour
- Metallic taste
- Fibrous healing of extraction wound
- Occurs when extraction is accompanied by loss of lingual and labial or buccal cortical plates and periosteum
- It is asymptomatic
- Fibrous Healing Of Extraction Wound Treatment
- Excision of lesion
- Bony repair
Question 2. Dry socket
Answer:
Dry Socket
Dry Socket is focal osteomyelitis of the tooth socket in which the blood clot has disintegrated or been lost
Dry Socket Etiology:
1. Bim’s hypothesis
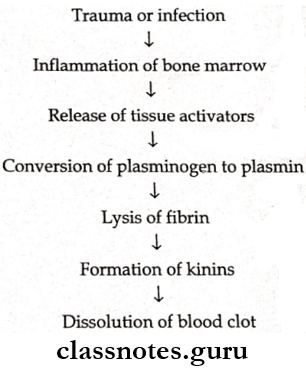
2. Nitzan’s theory
- Suggests a relationship between the fibrinolytic activity of anaerobic bacteria and dry socket
Dry Socket Predisposing Factors:
- Infection
- Decreased blood supply
- Debilitating conditions
Dry Socket Clinical Features:
- Loss of blood clot
- Radiating pain
- Foul odour
- Metallic taste
Dry Socket Management:
- Irrigation of socket
- Smoothening of bony margins
- Packing with pompom
- Analgesics
- Hot saline mouth bath
- Chemical cauterization
- Regular follow up
Dry Socket Prevention:
- Doing extraction gently
- Instruct the patient not to rinse for 24 hours
- Prescribe vitamin B complex and vitamin C
Question 3. Exfoliative cytology
Answer:
Exfoliative Cytology
Exfoliative cytology is introduced by Papanicolaou and Traunt
Exfoliative Cytology Indications:
- Herpes simplex
- Herpes zoster
- Pemphigus Vulgaris
- Pemphigoid
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Aphthous ulcer
- Candidiasis
Exfoliative Cytology Technique:

Exfoliative Cytology Results:
Question 4. Factors affecting the healing of oral wound
Answer:
Factors Affecting The Healing Of Oral Wound
- Age
- Faster healing occurs in younger individuals compared to older individuals
- Type of tissue
- Fast healing occurs in epithelial tissues
- Delayed healing in neural tissues
- Location of wound
- Good vascular area- fast healing
- Mobility of wound
- Movement of the site of wound delays healing
- Trauma
- Mild trauma- fast healing
- Severe trauma- retards healing
- Local temperature
- High temperature- Fast healing
- Low temperature- delay healing
- Radiation
- Low dose- stimulates healing
- High dose- Retards healing
- Nutritional factors
- Nutritional deficiency- delays healing
- Vitamins and proteins- speed up healing
- Infections
- Low-grade infection- stimulates healing
- Severe infections- interfere with healing
- Hormonal factors
- Trephones- accelerate healing
- ACTH, cortisone- delays healing
Question 5. Healing of fractured wound
Answer:
Healing Of Fractured Wound
- Bleeding occurs immediately at the site of the fracture, hematoma is formed which is converted into blood clot
- Stages of healing
- Stage 1 – formation of fibrous callus
- The proliferation of fibroblasts and endothelial cells in the bone marrow as periosteum
- These cells enter the fracture site and organise the clot
- Development of edema
- Inflammatory cell infiltration
- Removal of necrotic cells, connective tissue, and bone fragments from fracture site by phagocytosis, proteolysis and osteolysis
- Replacement of clot by granulation tissue
- Formation of fibrous callus at fracture site
- Stage 2 – Formation of primary bone callus
- Replacement of fibrous callus by immature bone
- Formation of primary bone callus
- Fibrous and primary bone callus binds the fracture fragments of bone together
- Stage 3 – Formation of secondary bone callus
- Replacement of primary bone callus by mature bone
- Remodelling of secondary callus by resorption
- Restoration of normal jaw outline
Question 6. Biopsy
(or)
Types of biopsy
Answer:
Biopsy
Biopsy is the removal of part of tissue for the purpose of histological examination and analysis
Types Of Biopsy
Question 7. Complications of wound healing
Answer:
Complications Of Wound Healing
- Infection
- Wounds provide a portal of entry to microorganisms and result in infection
- Keloid and hypertrophic scar formation
- Keloids are overgrown scar tissues
- Hypertrophic scars are more cellular and vascular
- Hypopigmented or hyperpigmented areas
- Cicatrization
- It refers to late reduction in the size of scar
- Implantation cyst
- Epithelial cells may get entrapped in the wound and proliferate to form cyst
Question 8. Reimplantation
Answer:
Reimplantation
Reimplantation refers to the insertion of a vital or nonvital tooth into the same alveolar socket from which it was removed
Reimplantation Indications:
- Broken instruments in canals
- Presence of foreign body In periapical tissue
- Tooth apex present in close proximity to nerve and vessels
- Inaccessible areas
- Persistent chronic pain
- Accidental avulsion of tooth
Reimplantation Contraindications:
- Medically compromised
- Periodontal involvement
- Missing buccal/lingual plate
- Nonrestorable tooth
Reimplantation Technique:

Question 9. Complications of healing of extraction socket
Answer:
Complications Of Healing Of Extraction Socket
- Dry socket
- It is focal osteomyelitis of the tooth socket In which the blood clot has disintegrated or been lost
- Clinical features
- Posh of blood dot
- Radiating pain
- Foul odour
- Metallic taste
- Fibrous healing of extraction socket
- Occurs when extraction Is accompanied by loss of lingual or buccal cortical plates and periosteum
- It is asymptomatic
Healing Of Oral Wounds Viva Voce
- Healing refers to the replacement of damaged tissue by living tissue to restore function
- Replacement of lost tissue by granulation tissue is called repair
- Cicatrization refers to late reduction in the size of scar
- Biopsy refers to removal of tissue from a living organism for the purpose of microscopic examination and diagnosis
- Granulation tissue formation occurs in healing by secondary intention
- Exfoliative cytology is the study of cells that exfoliate or abraded from body surfaces
- Replantation refers to the insertion of a vital or nonvital tooth into same alveolar socket from which it was removed or lost
- Dry socket is most common and painful complication in the healing of extraction wound
- Implants are any foreign material fixed or inserted into body tissue
- Osseointegration is a direct structural and functional connection between ordered living bone and the surface of a load-carrying implant
