Growth And Development Of Cranial And Facial Region Important Notes
- Pre natal life is divided into
- Period of ovum – 2 weeks from time of fertiliztion
- Period of embryo – 2nd week to 8th week
- Period of fetus – 9thweek
- Branchial arch derivatives
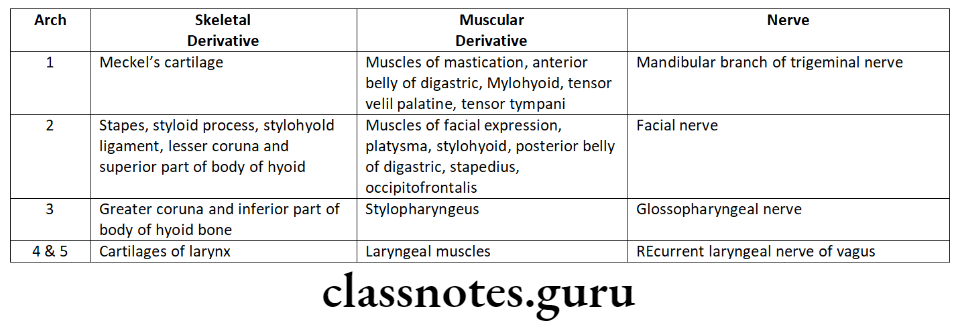
- Remnants of Meckel’s cartilage
- Mental ossicles
- Incus and malleus
- Anterior ligament of malleus
- Sphenomandibular ligament
- Spine of sphenoid
- Synchondroses – fusion of two adjacent bones by cartilages
- Synostosis – early fusion of two adjacent bones by bone
- Syndesmosis – fusion of two adjacent bones by fibrous ligament
- Ossification of synchondroses
- Spheno occipital – at age of 18 years
- Sphenoethamodial – by 5-25 years
- Inter sphenoidal – at birth
- Intra occipital – by 3-5 years
Growth And Development Of Cranial And Facial Region Long Essays
Question 1. Describe in detail about pre-natal growth of the maxilla.
Answer.
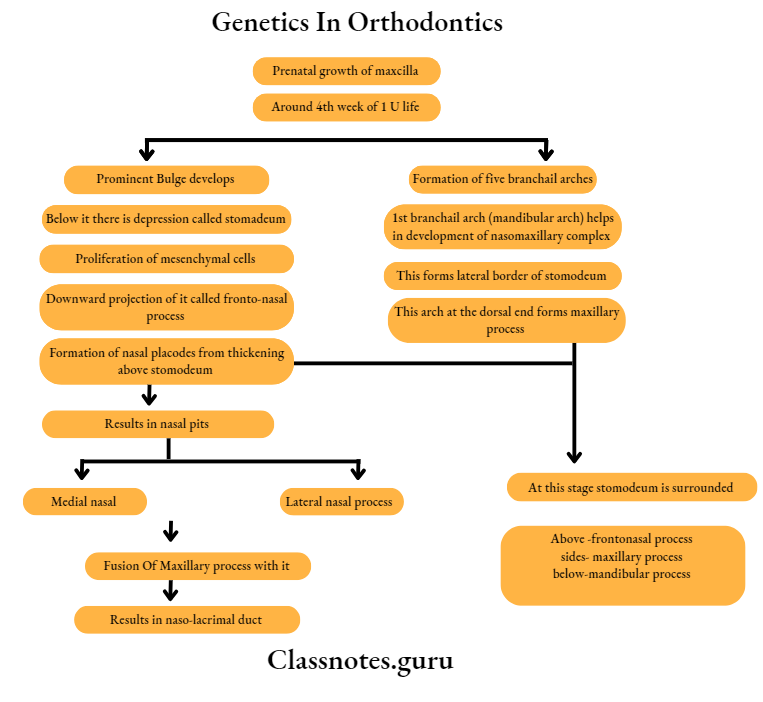
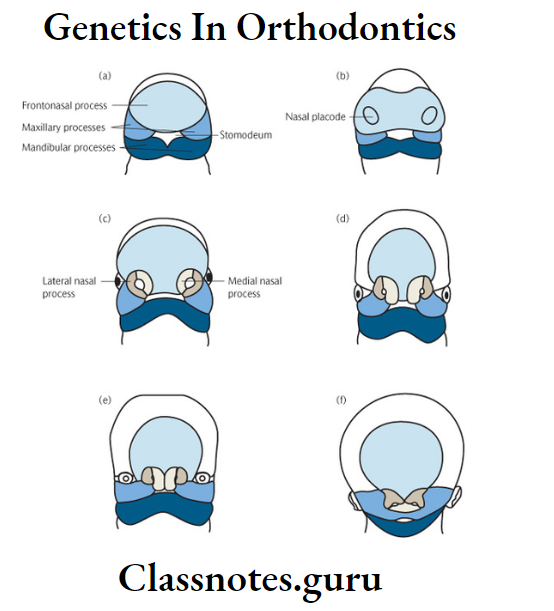
Formation Of Different Parts:
Oral Cavity: From stomodeum, which is a depression below the prominent bulge of fore brain
Lower lip: Through fusion of 2 mandibular processes
Cheek: From maxillary process
Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Short And Long Essay Question And Answers
Nose: Frontonasal process, divides into medial and lateral nasal process
- Maxillary process fuses first with lateral nasal process and later medial nasal process and forms nasal placodes
- These sinks and forms nasal pits
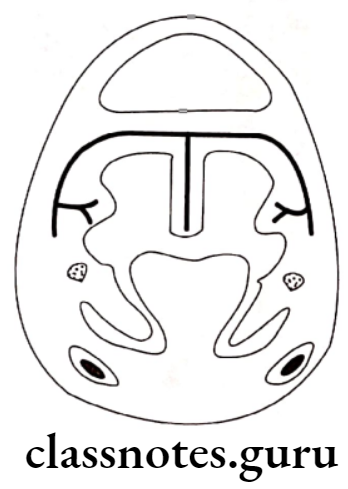
Development Of Palate:
- Palatal shelves are given out from maxillary process
- These shelves grow medially
- Initially, these grows down to the tongue vertically
- Later, during 7th week of IU life, shelves turns upwards due to
- Changes in bio-chemical and physical connective tissue
- Changes in blodd supply
- Appearance of intrinsic shelf force
- Rapid differential miototic activity
- Muscular movements
- Withdrawal of the embryonic face from against the heart prominence
Fusion Of Palatal Shelves:
- At 8 1/2 weeks of IU life
- These are covered by epithelial lining
- Epithelial cells degenerate
- Connective tissue intermingle with each other resulting in their fusion
- Initially fusion occurs over central region forming secondary palate
- Fusion progresses both anteriorly and posteriorly
- Mesial edges fuse with lower end off nasal septum
- Thus palate is formed along with the separation of two nasal cavities with that of oral cavity
Question 2. Describe in detail the prenatal growth of mandible.
Answer.
- About 4th week of IU life, pharyngeal arches are laid down on the lateral and ventral aspects of foregut.
- Separated by 4 branchial grooves
- First arch is called mandibular arch
- The mandibular processes of both sides grow towards each other and fuse in the mid line
- Results in formation of lower lip and lower jaw.
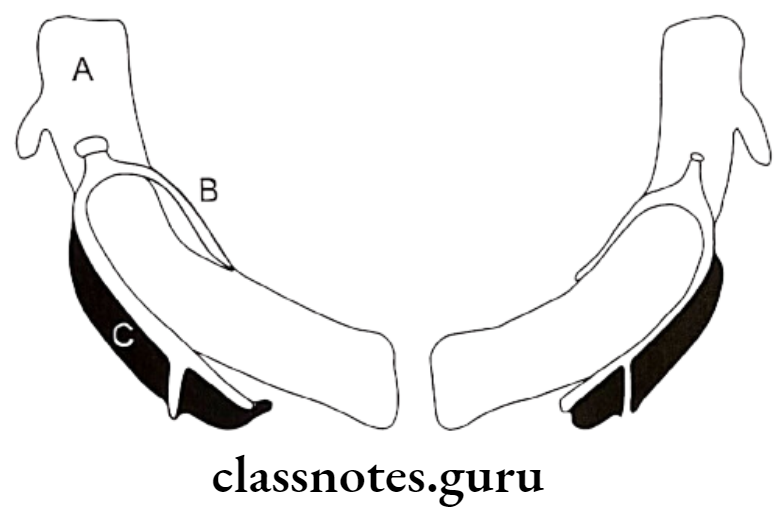
Meckel’s Cartilage:
- Around 41st – 45th day of IU life

- Mental ossicles
- Incus and Malleus
- Spine of Sphenoid
- Anterior ligament of malleus
- Spheno mandibular ligament
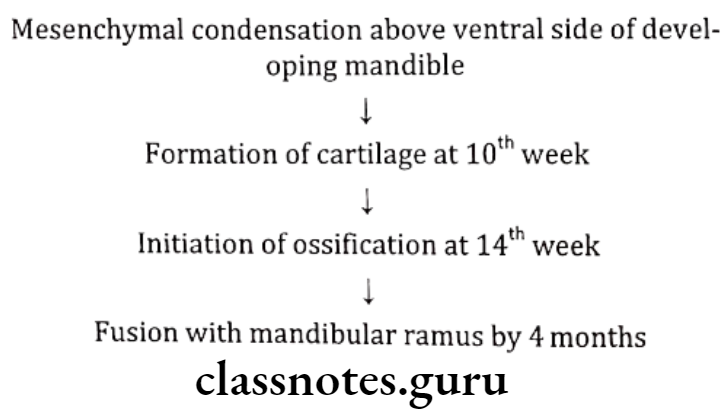
Condylar Process:
At 5th week of IU life
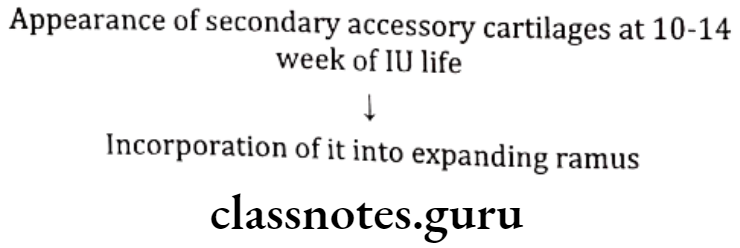
Coronoid Process:
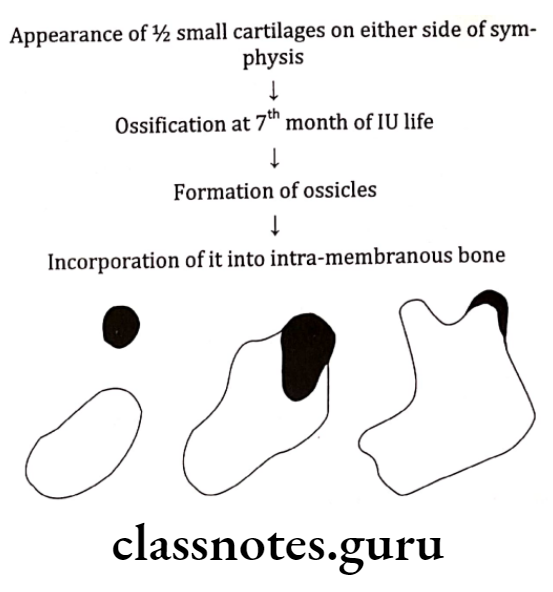
Mental Region:
Question 3. Describe in detail, post natal growth of maxilla.
Answer.
Post Natal Growth Of Maxilla:
- Mechanism involved in it
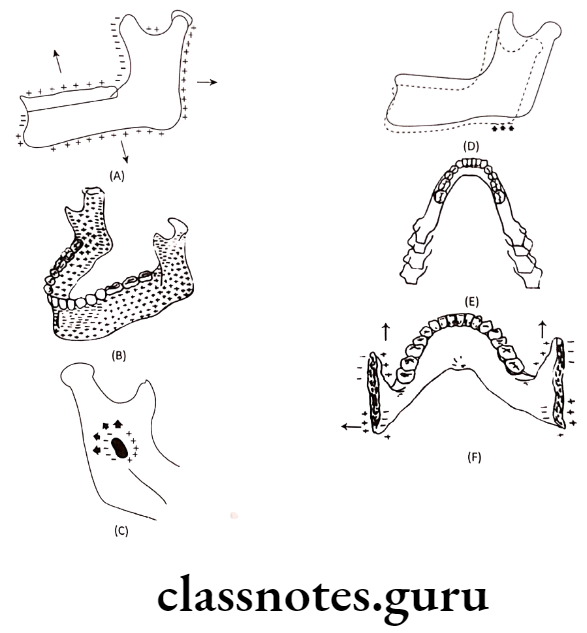
Displacement:
- Secondary displacement: Growth of maxilla occurs in downward and forward diretion due to growth of middle cranial fossa
- Primary displacement: Growth of maxilla occurs in forward direction due to growth of maxillary tuberosity in posterior direction.
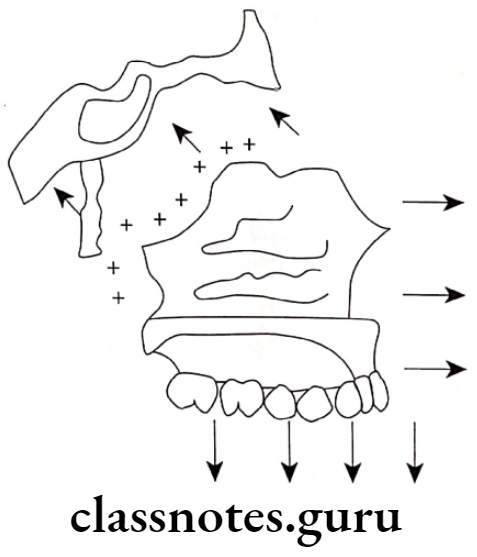
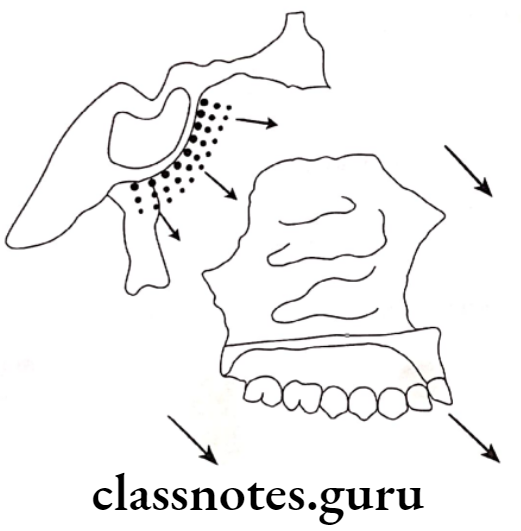
Growth At Sutures:
Sutures involved are
- Fronto-nasal
- Fronto-maxillary
- Zygomatico-temporal
- Zygomatico-maxillary
- Pterygo-palatine

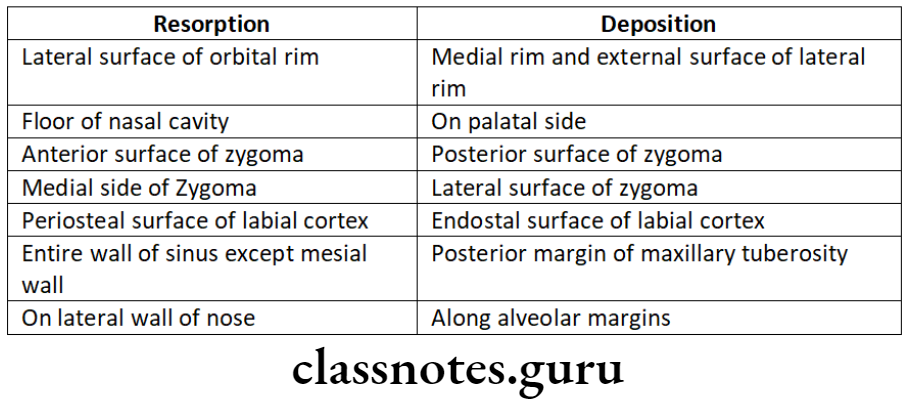
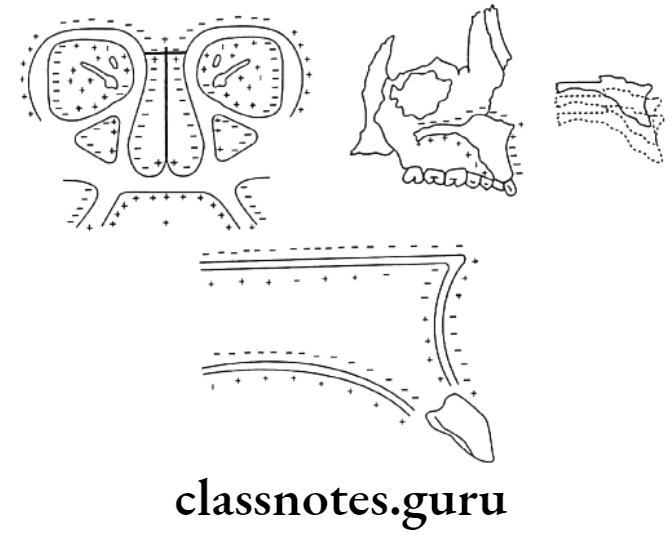
Surface Remodeling
- Growth of bone occurs due to the relative deposition and resorption of different parts
- This occurs in a balanced fashion
Question 4. Define growth and development explain post natal growth of mandible. Describe in detail post natal growth of mandible.
Answer.
Growth And Development Of Cranial And Facial Region Short Essays
Question 1. Synchondrosis.
Answer.
- Usually cartilage is replaced by bone
- But at the margins of junction of various bones, there is presence of bands of cartilages
- These are called “Synchondrosis”
Types Of Synchondrosis:
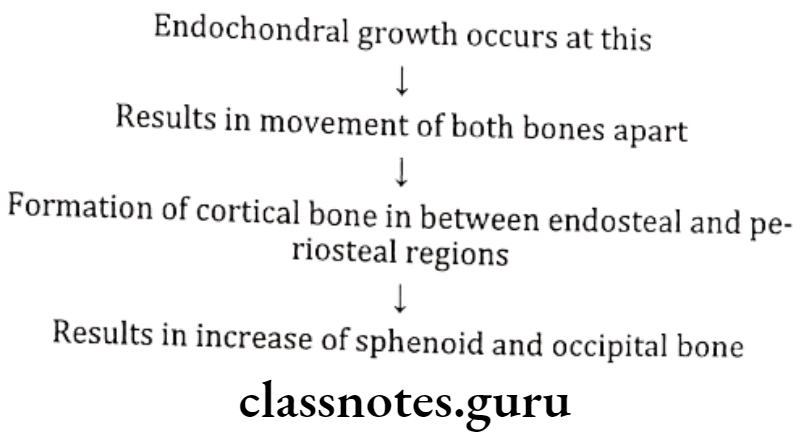
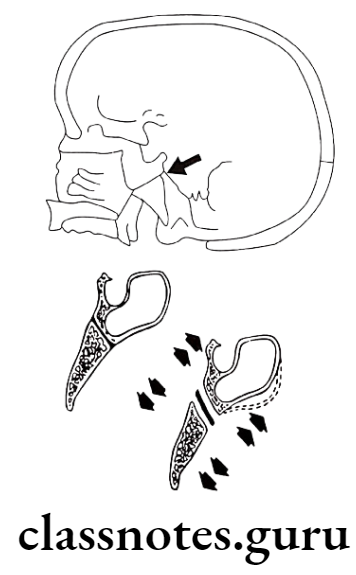
Spheno-occipital Synchondrosis:
- Bones involved: Sphenoid and Occipital
- Active: At 12-15 years of age
- Fusion: AT 20 years of age
Significance:
- Provides pressure adapted bone growth
- Carriers anterior part of cranium forwards
Spheno-ethmoid Synchondrosis:
- Bone involved: Sphenoid and ethamoid
- Ossification: 5-25 years of age
Inter-sphenoidal Synchondrosis:
- Between 2 sphenoid bones
- Ossify at birth
Intra-occipital Synchondrosis: Ossify at 3-5 years of age
Question 2. Spheno-occipital synchondrosis.
Answer.
Synchondrosis
- Synchondrosis are defined as the bands of cartilage present at the junction of various bones during the bone formation
- These synchondrosis form important growth sites in the base of skull
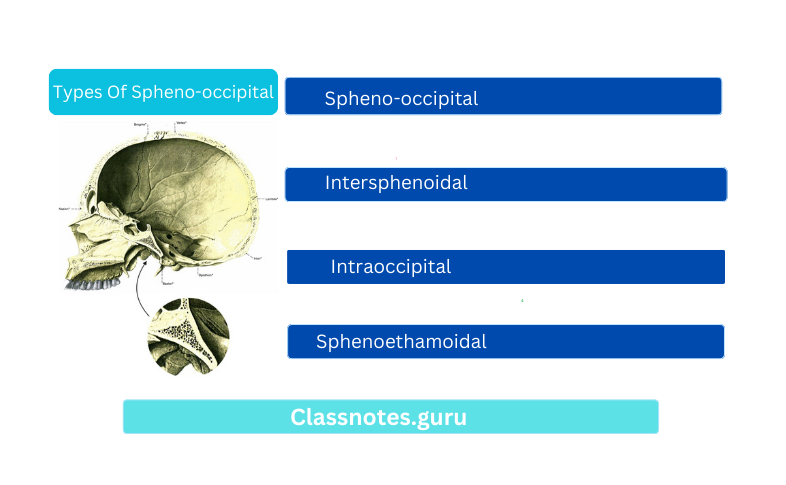
Types Of Spheno-occipital
- Spheno-occipital
- Intersphenoidal
- Intraoccipital
- Sphenoethamoidal
Spheno-Occipital Synchondrosis:
- Bones involved: Sphenoid and Occipital
- Active: At 12-15 years of age
- Fusion: At 20 years of age

Significance Of Spheno-occipital synchondroses:
- Spheno-occipital Synchondroses are responsible for most of the lengthening of cranial base between foramen magnum and sella turcica
- It is major contribution of endochondral growth till 20 years
- Elongation of synchondroses in combinatin with drift and remodeling contribute to cranial base lenghthening
Question 3. Growth of cranial base
Answer.
- Growth of cranial base occurs during 4th– 8th week of IU life
- During this there is condensation of mesenchymal tissue derived from the primitive streakm neural cresr and occipital sclerotomes around the developing brain
- A capsule is formed around brain calledectomenix that gives rise to future cranial base
- From around 40th day the capsule is slowly converted to cartilage
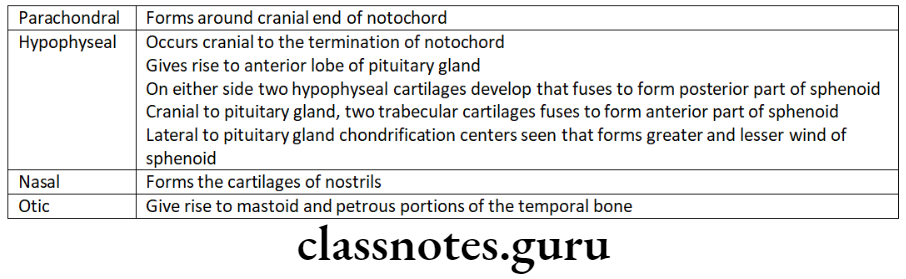
Conversion Of Mesenchymal Cells Into Cartilage:
- It occurs in 4 regions
Chondro Cranial Ossification:
- Cartilages of cranial base now undergoes ossification
- It undergoes both intramembranous and endochondral ossification
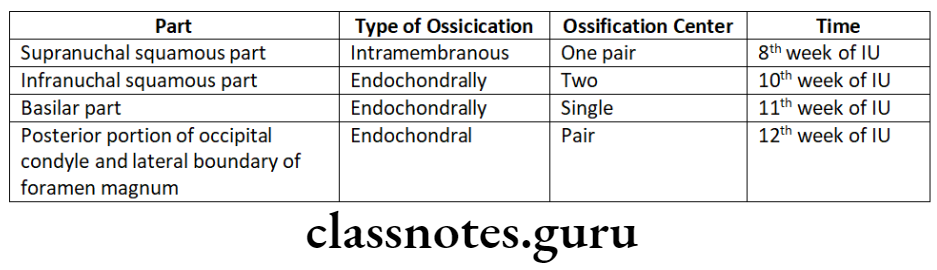
Occipital bone:
- Shows both type of ossification
- Seven ossification centres are seen – 2 intramembranous and 5 endochondral
Temporal bone:
- Ossifies from 11 centres
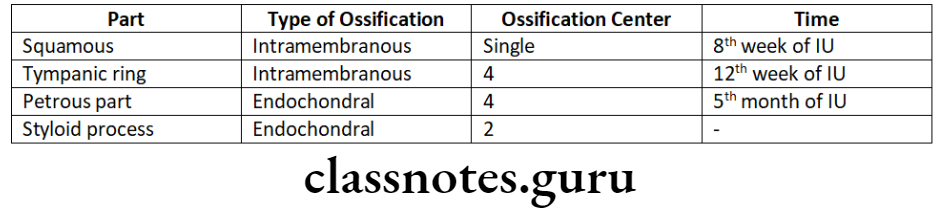
Ethmoid bone:
- Shows only endochondral ossification
- Has three ossification centres
- One-located centrally, forms medial floor of the anterior cranial fossa
- Two-located bilaterally in nasal capsule
Sphenoid bone:
- Ossifies both intramembranously and endochondrally
- Have atleast 15 ossification centres
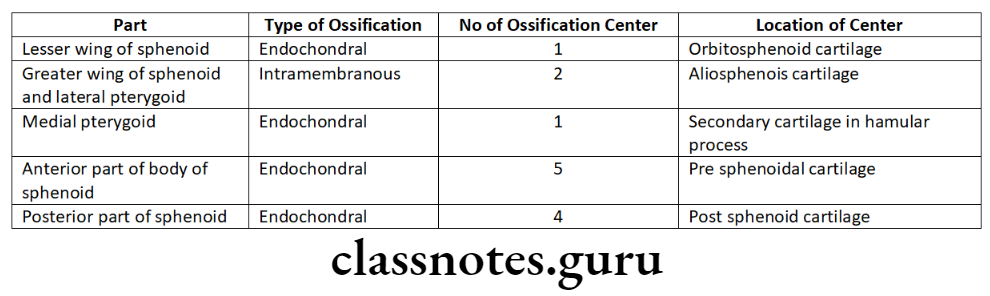
Nature Of Growth
- Growth of cranial base is highly uneven
- Anterior and posterior part grow at different rates
- Between 10th – 40th week of IU life, growth
- Anterior part – increases 7 times
- Posterior part – Increases 5 times
Growth And Development Of Cranial And Facial Region Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. Remnants of Meckel’s cartilage.
Answer.
- Mental ossicles
- Incus and Malleus
- Spine of sphenoid
- Anterior ligament of malleus
- Spheno-mandibular ligament
Question 2. Sutures involved in post-natal growth of maxilla.
Answer.
- Fronto-nasal suture
- Fronto-maxillary suture
- Zygomatico temporal suture
- Zygomatico maxillary suture
- Pterygo palatine suture
Question 3. Butler’s field theory.
Answer.
- The human dentition is divided into four fields: incisor, canine, premolar and molar
- The most distal tooth in each field is the most susceptible to changes or variations which include absence of tooth, variation in size, shape and structure
- This is called Butler’s field theory
- Ex – lateral incisors, second premolars and third molars are most variable in this group
- Canine is the least variable in their group
- Butler’s field theory does not apply in lower anterior region, where mandibular central incisor is more commonly missing than lateral incisor
Growth And Development Of Cranial And Facial Region Viva Voce
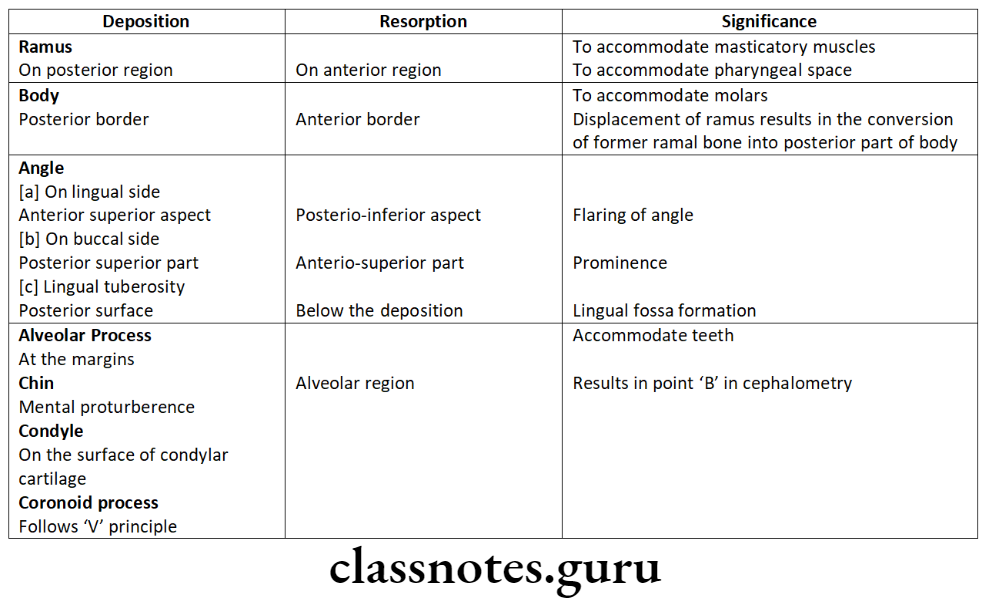
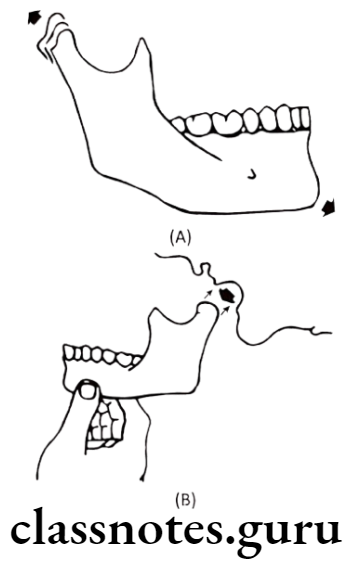
- Mandible grows in length by resorption at the anterior border and bone deposition at posterior border of ramus
- A single ossification center occurs for each half of mandible
- Maxilla has three ossification centres: one for maxilla proper and remaining two for pre maxilla.
- Mandible ossification centre is present in area of future mental foramen.
- Maxilla ossification centre is present in infraorbital foramen.
- Mandibular condyle is the only bone that shows both apposition and interstitial growth
- Sphenomandibular ligament extends from lingula to spine of sphenoid
- Congenital defects can occurs during period of embryo of prenatal life.
- Embryo proper is mainly formed by inner cell mass or embryoblast
- Branchial arches are formed by 4th week of IU life
- Development of face starts by 4-8 week.
- Development of palate occurs by 6-9 weeks.
- Development of tongue occurs by 4th week
- Development of maxillary sinus occur by 3rd month
- primary palate is derived from frontonasal process
- Secondary palate is derived from two palatal shelves and nasal septum
- Tongue is derived from tuberculumimpar, two lingual swellings and hypobranchial eminence.
- Meckel’s cartilage is primary cartilage of first arch.
- Reichert’s cartilage is primary cartilage of second arch
- Mandible develops develops as intramembranous bone
- At birth skull consists of 45 bones which later ossifies to 22 bones.
