Ulcers Importance Notes
1. Different Ulcers
2. Painless And Painful Ulcer
3. Edge of ulcer in different ulcers
Types of ulcers Q&A
Ulcers Short Essays
Question 1. Nonhealing ulcers
Answer:
Nonhealing Ulcers Are
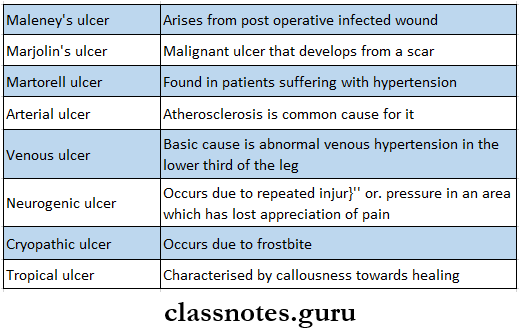
- Venous Ulcer: Venous Ulcer is commenest ulcer of the leg
- Venous Ulcer Etiology:
- Abnormal venous hypertension in the lower third of the leg, ankle, and dorsum of foot
- Venous Ulcer Treatment:
- Elevation of affected limb
- Passive movement of limb
- Active movement of calf muscles
- Application of blue line bandage
- Systemic antibiotics
- Venous Ulcer Etiology:
- Diabetic Ulcer:
- Diabetic Ulcer Etiology:
- Slight injury in glucose-laden tissues
- Ischaemia
- Infection
- Peripheral neuritis
- Diabetic Ulcer Sites:
- Toes and feet
- Sole
- Leg
- Diabetic Ulcer Feature:
- Ulcer is deep and spreading
- Diabetic Ulcer Treatment:
- Diabetic control
- Antibiotics- to control infection
- Excision of ulcer
- Diabetic Ulcer Etiology:
- Tuberculous Ulcer:
- Tuberculous Ulcer Etiology:
- Bursting of cold abscess
- Tuberculous Ulcer Features:
- Oval in shape
- Multiple in number
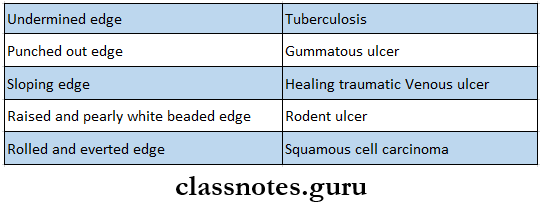
- Has thin reddish blue and undermined edge
- It is usually shallow
- Mild pain occurs
- Presence of slight induration
- Tuberculous Ulcer Treatment
- Antitubercular treatment
- Excision and grafting
- Tuberculous Ulcer Etiology:
Read And Learn More: General Surgery Question and Answers
Question 2. Define and classify ulcers.
Answer
Ulcers Definition: Ulcer is a break in the continuity of the covering epithelium
Ulcers Classification
1. Clinical Classification
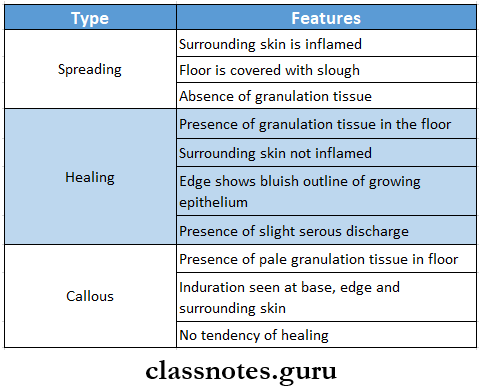
2. Pathological Classification
- Nonspecific
- Traumatic
- Mechanical – dental ulcer of tongue
- Physical – x-ray of bum
- Chemical – application of caustics
- Arterial
- Atherosclerosis, Raynaud’s disease, Buerger’s disease
- Venous – in post phlebitis limb
- Neurogenic
- Infective – pyogenic
- Tropical – in people living in tropical countries
- Crvopathic – due to cold injur)
- Martorell’s ulcer – hypertensive
- Bazin’s ulcer
- Diabetic ulcer
- Miscellaneous
- Traumatic
- Specific ulcers
- Tubercular ulcer
- Syphilitic ulcer
- Actinomycosis
- Meleney’s ulcer
- Malignant
- Epithelioma
- Rodent ulcer
- Malignant melanoma
Oral ulcers questions and answers
Question 3. Tubercular ulcer
Answer:
Tubercular Ulcer
- Such ulcer develops due to bursting of cold abscess
- Clinical features
- Shape – oval in shape
- Border – irregular crescentic
- Number – multiple in number
- Edge – thin reddish blue and undermined
- Pain – slight pain is present
- Floor – pale granulation tissue seen on the floor
- Base – slight induration is present
Tubercular Ulcer Treatment
- Antitubercular drugs
- Excision and skin grafting in nonhealing ulcer
Question 4. Rodent Ulcer
Answer:
Rodent Ulcer
- Basal cell carcinoma is called rodent ulcer
- Common sites are inner and outer canthus of the eye, the eyelids bridge of the nose, and around the nasolabial fold.
- Most common pattern is a nodule-ulcerative lesion a slow-growing small nodule that undergoes central with pearly, rolled margins.
- Tumour enlarges in size by burrowing and by destroying the tissues locally like a rodent and hence the name “rodent ulcer”.
Question 5. Marjolin’s ulcer
Answer:
Marjolin’s Ulcer
- Marjolin’s Ulcer is a squamous carcinoma arising in a chronic benign ulcer or scar
- Marjolin’s Ulcer is a long-standing venous ulcer
Marjolin’s Ulcer Features:
- Slow-growing malignant lesion
- Edges may be everted and raised
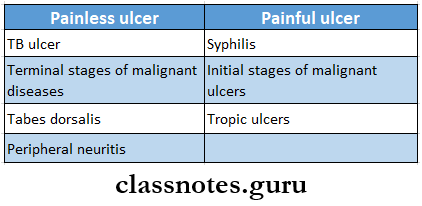
- It is a painless ulcer
- There is no lymphatic metastasis
Marjolin’s Ulcer Treatment:
Wide excision of the lesion along with a margin of at least 1 cm
Question 6. Diabetic ulcer
Answer:
Diabetic Ulcer Etiology:
- Slight injury in glucose-laden tissues
- Ischaemia
- Infection
- Peripheral neuritis
Diabetic Ulcer Sites:
- foes and feet
- Sole Leg Feature:
- An ulcer is deep and spreading
Diabetic Ulcer Treatment:
- Diabetic control
- Antibiotics- to control infection
- Excision of ulcer
Question 7. Tropical ulcer
Answer:
Tropical Ulcer
- These ulcers occur in the legs and feet of persons living in tropical countries
- Caused by Vincent’s organisms
Tropical Ulcer Etiology:
- Malnutrition
- Anaemia
- Avitaminosis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Tropical Ulcer Features:
- Edges are slightly raised
- Presence of discharge
- Remains of the same size for many months and years
- It destroys the surrounding tissues
- Pustule develops
- This burst forms painful ulcers
- The ulcer heals leaving a scar
Peptic ulcer disease Q&A
Question 8. Snail track ulcer
Answer:
Snail Track Ulcer
- Snail track ulcers are oral ulcers in syphilitic patients
- They appear in 3-6 weeks after the development of chancre
- These are small, round, and superficial erosions
- These coalesce to form ulcers
- Ulcers are narrow, curved, and shallow
Short notes on ulcers with answers
Question 9. Arterial ulcer
Answer:
Arterial Ulcer
- Arterial ulcers are caused due to
- Peripheral arterial disease
- Inadequate circulation
- Atherosclerosis
- Trauma
- Infection
- It is a painful ulcer
- Ulcers tend to be punched out
- It destroys the whole skin and deep fascia
- Expose the tendons on the floor of the ulcer
- Sites Involved Are
- Anterior and lateral aspects of leg
- On the toe
- Dorsum of the foot
- Heel
Ulcers Viva Voce
- Marked induration of the edge is a characteristic feature of carcinoma.
- A leather slough on the floor of the ulcer is seen in the Gummatous ulcer.
- The black mass on the floor suggests malignant melanoma.
- Callous ulcer shows no tendency toward healing.
