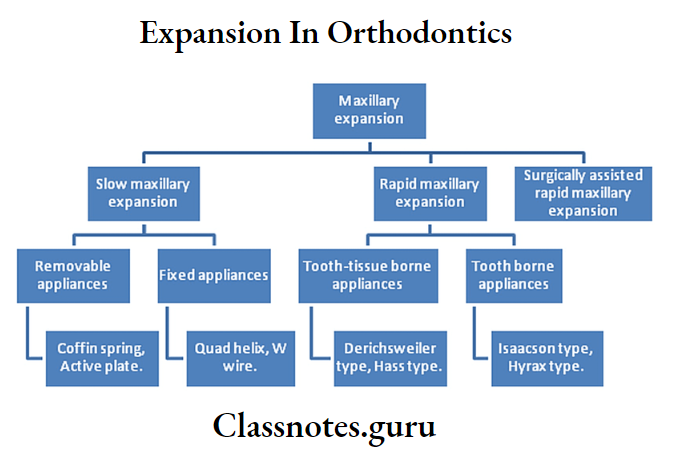
Expansion
- Types of expansion appliances
- Rapid maxillary expansion [RME]
- Should be initiated prior to ossification of the mid-palatal suture
- Time of ossification of mid-palatal suture
- 16 years – in girls
- 18 years – in boys
- Contraindication of RME
- Single tooth crossbites
- In adults with severe anteroposterior skeletal discrepancies
- Vertical growers
- Periodontally weak condition
- Schedule of activation of expansion screw
- For patients upto 15 years – 90° rotation in morning and evening
- For patients over 15 years – 45° rotation 4 times a day
- Quad helix
- Uses:
- Expand a narrow arch
- Rotation of molars
- Brings
- Orthopaedic movement in children
- Orthodontic movement in adults
- Uses:
Expansion Long Essays
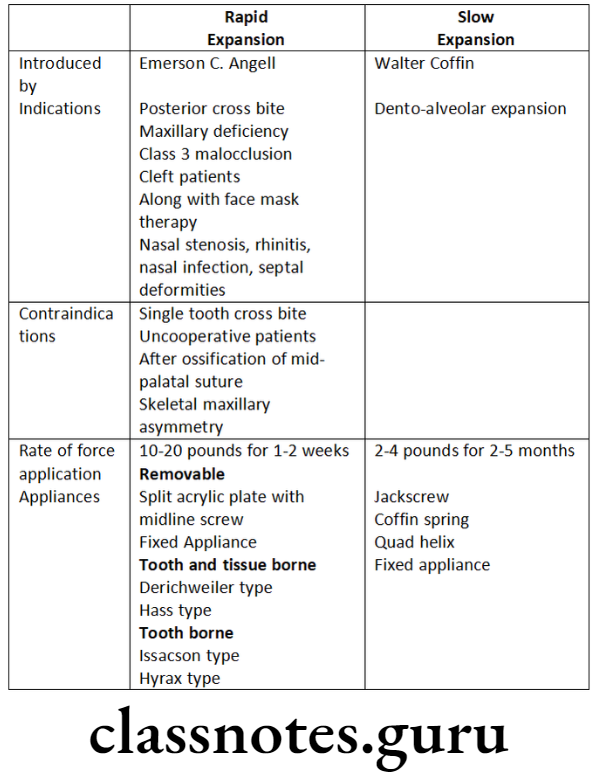
Question 1. Explain slow and rapid expansion, their indications, contraindications, and appliances used.
Answer.
Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Short And Long Essay Question And Answers
Effects Of Rapid Maxillary Expansion:
- Open mid-palatal suture:
- By compresses PDL
- Bends buccal alveolar process and slowly opens the suture
- Triangular opening:
- Maximum opening at incisor region
- Reduces over posterior part of palate
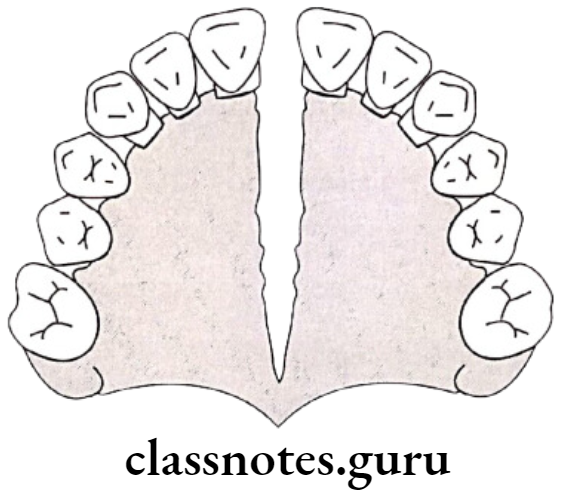
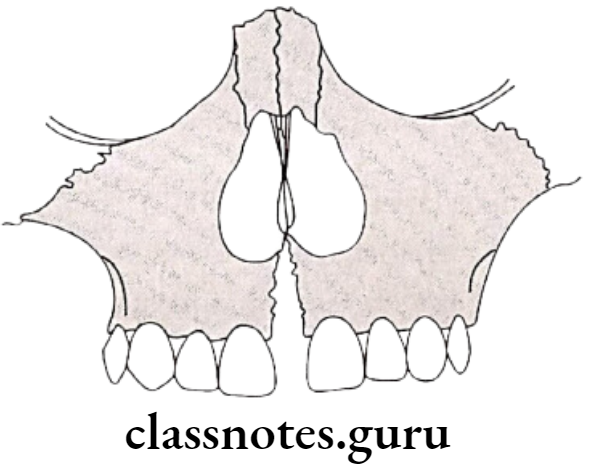
- Maximum opening towards oral cavity
- Less opening towards nasal aspect
- Midline diastema
- Buccal tipping of maxillary posteriors
- Downward and backward mandibular rotation
- Increase in mandibular plane angle
- Displacement adjacent cranial bones
- Increase in intra-nasal space
- Reduction in airway resistance
Expansion Short Essays
Question 1. Expansion screws.
Answer.
- A typical expansion screw consists of an oblong body with two halves, each half consisting of threaded inner side that receives one end of a double-ended screw
- The screw has a central basing with four holes, which receive a key used to turn the screw
- The turning of screw to 90 degrees brings about linear movement of 0.18mm
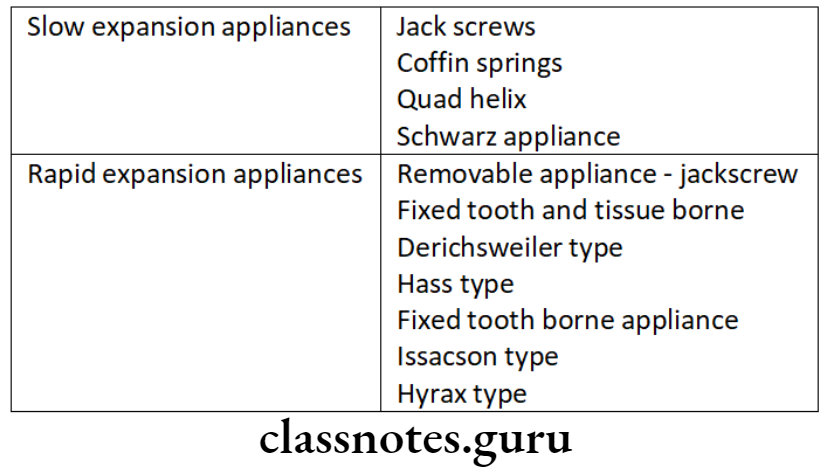
- Various types of expansion used in removable and fixed appliances are
- Jackscrew
- Coffin springs
- Qual helix
- Isacson
- Hyrax
- Derischweiler
- Activation schedules
According to Timms:
- In patient upto 15 years of age – 90 degrees rotation in the morning and evening
- In patient over 15 years old – 45 degrees activation 4 times a day
According to Zimring and Isacson:
- In growing individuals
- Two turns each day for 4-5 days and later one turn per day till the desired expansion is achieved
- In non-growing adults
- Two turns each day for first 2 days and later one turn per day for next 5-7 days and one turn every alternate day till the desired expansion is achieved
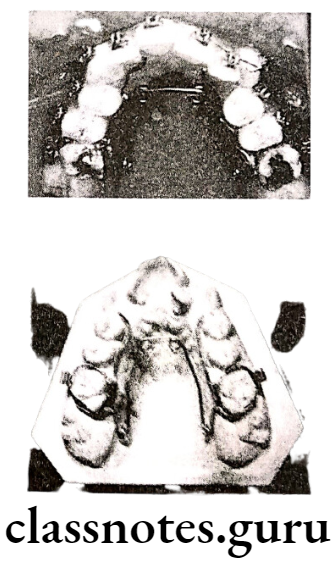
Question 2. Quad Helix Appliance.
Answer.
Example of slow maxillary expansion appliance
Introduced by Walter coffin
- Wired used: 0.038 inch
- Parts
- Bands: Over first molar
- Helices: 2 anteriors helices
- 2 posterior helices
- Bridge: Anterior bridge – Connencts anterior helices
- Palatal bridge: Connects anterior and posterior helices
- Outer arms: Free ends adjacent to posterior helices
- Soldered on lingual aspect of molar bands
- Uses: Expansion of narrow arch
- Rotation of molars
- Skeletal expansion: During mixed dentition periods
- Activation: Pre-stretching of molar bands before cemenstation.
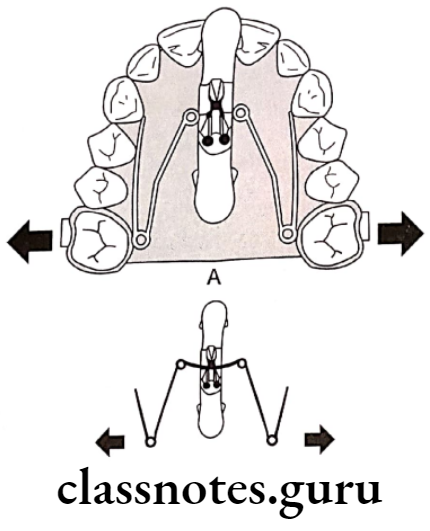
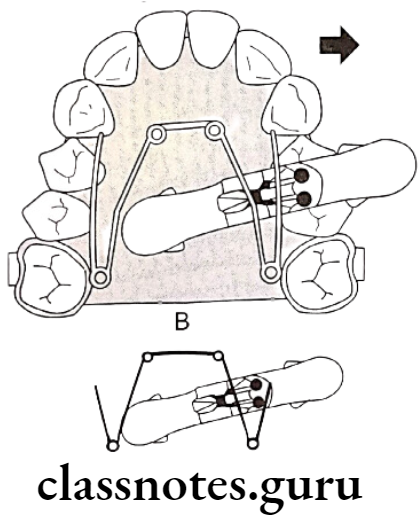
Question 3. Rapid v/s slow expansion.
Answer.

Expansion Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. Hyrax Appliance.
Answer.
Tooth bone fixed appliances used for rapid maxillary expansion
Hyrax – Hygienic rapid expander
Designs Of Hyrax Appliance:
- Wire used – Heavy guage wire
- Extensions of screw wire are adapted over palatal contour and soldered to molar bonds
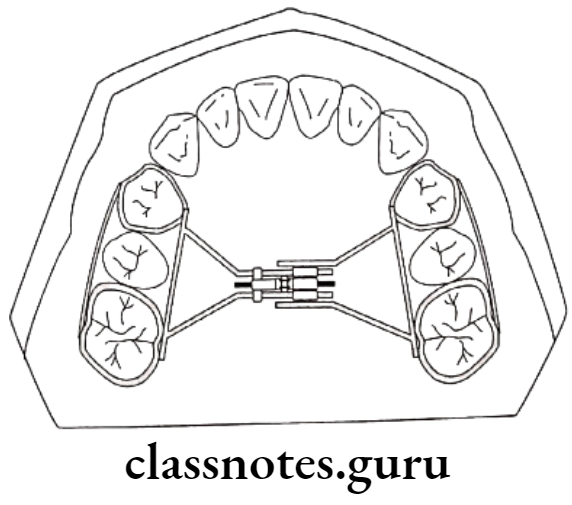
Question 2. Coffin Spring.
Answer.
- Removable slow expansion appliance by Walter Coffin
- Wire used: 1.25 mm thick
- Design: Omega shaped wire – Over mid-palatal region
- Free ends of wire: Embedded in acrylic
- Activation: Pulling two sides apart
- Use: Dento-alveolar expansion in adults
- Skeletal expansion in younger patients
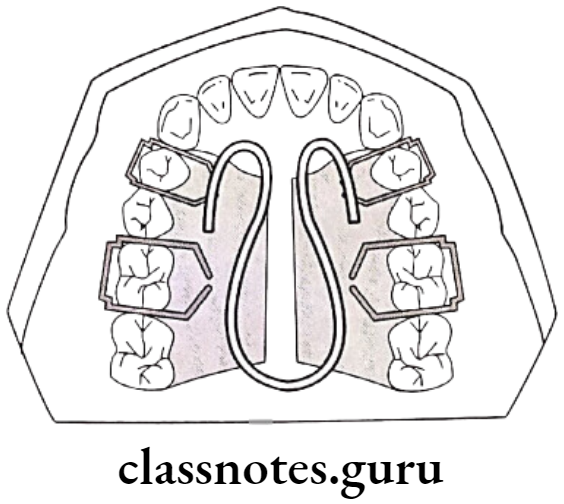
Question 3. Expansion Appliance.
Answer.
- Appliance for RME
- Removable – Split acrylic plate
- Fixed
- Tooth and tissue borne
- Derichsweiler type
- Hass type
- Tooth borne
- Issacson type
- Hyrax type
- Appliances for Slow Expansion
- Jack screw
- Coffin spring
- Quad helix
- Fixed appliance
Question 4. Slow Expansion Appliance.
Answer.
- Jack screw:
- It is incorporated in the appliances
- Have more spread out activation schedule
- Have smaller pitch
- Coffin spring:
- Removable slow expansion appliance by Walter Coffin
- Wire used – 1.25 mm thick
- Design – Omega shaped wire – Ove mid-palatal region
- Free ends of wire – Embedded in acrylic
- Activation – Pulling two sides apart
- Use – Dento-alveolar expansion in adults
- Skeletal expansion in younger patients
- Quad helix:
- Introduced by Walter coffin
- Wire used – 0.038 inch
- Parts
- Bands – Anterior bridge – Connects anterior helices
- Palatal bridge – Connects anterior and posterior helices
- Outer arms – Free ends adjacent to posterior helices
- Soldered on lingual aspect of molar bands
- Uses: Expansion of narrow arch
- Rotation of molars
Question 5. Types of Expansion Screws.
Answer.
- 3D screws
- Split midline screw
- Jack screw
Expansion Viva Voce
- Coffin spring and quad helix are used for palatal expansion
- Rapid palatal expansion should be carried out prior to ossification of midpalatal suture
- In rapid expansion two turns daily of 0.5mm is done
- In slow expansion the rate is 0.5 mm per week
- In rapid expansion, the ratio of skeletal to dental expansions is 4:1
- In slow expansion, the ratio of skeletal to dental expansions is 1:1
- In rapid expansion, force generated – 2-4 pounds
- In slow expansion, force generated – 10-20 pounds
- Treatment completed in rapid expansion – 1-2 weeks
- Treatment completed in slow expansion – 2-5 months