Epidemiology Of Gingival And Periodontal Diseases Definitions
1. Epidemiology
- Epidemiology is defined as the study of the distribution and determinants of health-related states or events in specified populations and the application of this study to the control of health problems
2. Index
- Numerical values describing the relative status of the population on a graduated scale with definite upper and lower limits designated to permit and facilitate comparisons with other populations that are classified by the same criteria and methods are referred to as index
3. Incidence
- Incidence is defined as the number of new cases of a specific disease occurring in a defined population during a specified time
Read And Learn More: Periodontics Question and Answers
4. Prevalence
- The total number of all individuals who have an attribute or disease at a particular time divided by the population at risk of having the attribute or disease at this point in time or midway through the period
Epidemiology Of Gingival And Periodontal Diseases Long Essays
Question 1. Define epidemiology. Write in detail about indices used in assessing gingival inflammation.
Answer:
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is defined as the study of the distribution and determinants of health-related states or events in specified populations and the application of this study to the control of health problems
Indices Used To Assess Gingival Inflammation:

1. Papillary marginal attachment index by Schour and Massler:
- The gingival unit is divided into three parts
- Papillary gingiva
- Marginal gingiva
- Attached gingiva
- The presence or absence of inflammation in each unit is recorded and scored
- -0- Absence of inflammation
- -1- Presence of inflammaion
- The severity of gingivitis is assessed by the following scoring
- Papillary gingiva-0-5
- Marginal gingiva-0-3
- Attached gingiva- 0-3
2. Gingivitis component of the periodontal disease:
- Teeth selected- 3, 9, 12,19, 25, 28
- Sulcus depth is examined in these teeth and scored
3. Gingival index by Loe and Silliness:
- All teeth are examined
- The surfaces examined are:
- Distal facial papillaae
- Facial margin
- Mesial facial papillae
- Lingual margin
- Scoring is done
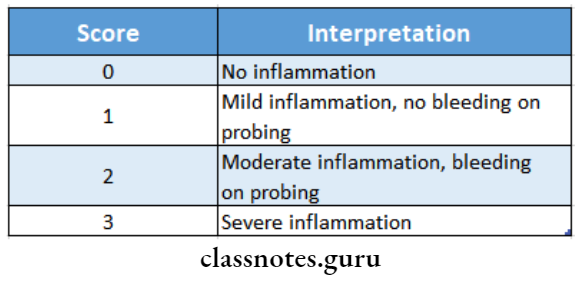
Interpretation:

4. Indices of gingival bleeding:
- Sulcular bleeding index by Muhlemann and Son
- All teeth are examined
- Four gingival units are scored
- Labial and lingual marginal gingiva
- Mesial and distal papillary gingiva
- The probe is helped parallel with the long axis of the tooth and scoring is done after 30 seconds
Scoring:
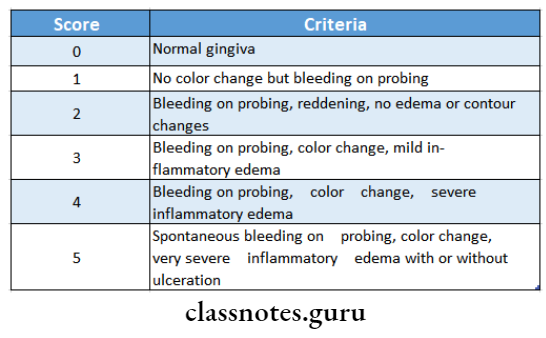
- Papillary bleeding index by Muhlemann
- A blunt periodontal probe is inserted into the gingival sulcus, bleeding is examined and scored
Scoring:
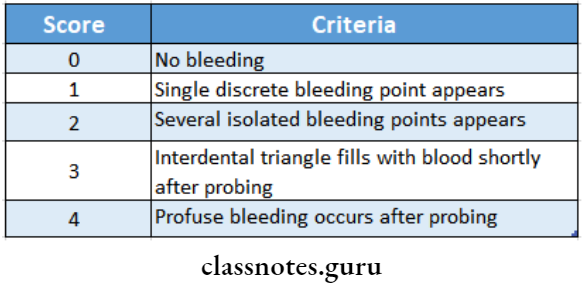
- Bleeding point index by Lennox and Kopczy
- It determines the presence or absence of gingival bleeding interproximal and on facial and lingual surfaces of each tooth
- Interdental bleeding index by Caton and person
- A triangular-shaped interproximal cleaner is inserted to depress the interproximal papillae up to 2 mm
- The presence or absence of bleeding within 15 seconds is noted
- Gingival bleeding index by Ainamo and Bay
- The presence or absence of gingival bleeding is determined by gentle probing of gingival cer-vice
Epidemiology Of Gingival And Periodontal Diseases Short Essays
Question 1. Plaque Index.
Answer:
Selected tooth
- Surfaces: Distofacial, facial, mesiofacial and lingual
- Site: Cervical third of the tooth
Plaque Index Scoring:
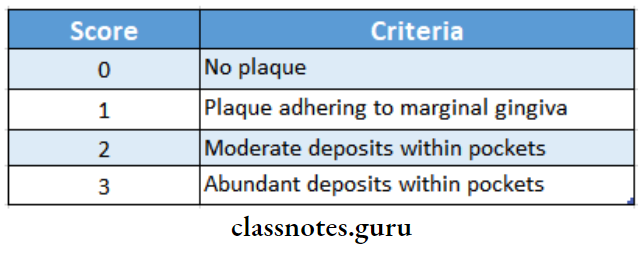
Plaque Index Calculation:
- Per tooth-Score/4
- Per person – Score per tooth/No. of teeth
Question 2. OHI-S by Greene and Vermillion.
Answer:
- The oral hygiene index-simplified was described by John C. Greene and Jack R. Vermillion in 1964
Tooth Examined:
- 16/17, 11, 26/27
- 46/47,31 36/37
Surfaces: Facial of 16/17, 11, 26/27, 36/37 Lingual of 31
Sites:
- D1-S – Incisal third to gingival third
- C1-S Distal gingival crevice subgingivally from dis- tal to medial contact
Scoring: For D1-S:
- 0-No debris
- 1-Debris covering 1/3rd of tooth surface
- 2-Debris covering more than 1/3rd and less than 2/3rd of tooth surface
- 3-Debris covering more than 2/3rd of tooth surface
For CI-S:
- O-No calculus
- 1-Supragingival calculus covering 1/3rd of tooth surface
- 2-Supragingival calculus covering more than 1/3rd but less than 2/3rd of tooth surface
- 3-Supragingival calculus covering more than 2/3rd of the tooth surface, heavy bands of subgingival
calculus also present
Calculation:
- OH1 – S = D1-S+C1-S
Interpretation:
- Good – 0.0 to 1.2
- Fair – 1.3 to 3.0
- Poor – 3.1 to 6.0
Question 3. Russel’s Periodontal Index.
Answer:
By Russell Al.
Teeth examined:
All
Surfaces:
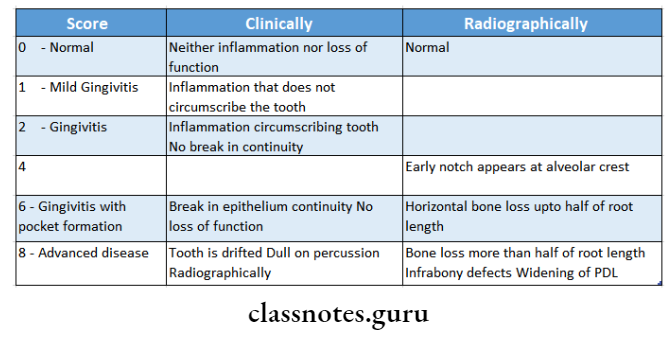
Interpretation:
- 0-0.2 – Normal
- 0.3-0.9 – Simple Gingivitis
- 0.7-1.9 – Beginning of destructive disease
- 1.6-5.0 – Established destructive disease
- 3.8-8.0 – Terminal disease
Question 4. Gingival Index – by Loe and Stillness.
Answer:
- Teeth Examined: All or selected
Surfaces:
- Distal facial papillae
- Facial margin
- Mesial facial papillae
- Lingual margin
Scoring:
- 0-No inflammation
- 1-Mild inflammation, no bleeding on probing
- 2-Moderate inflammation, and bleeding on probing
- 3-Severe inflammation
Calculation:
- Per tooth-Score/4
- Per person\( -\frac{\text { TotalScore }}{\text { Total teeth examined }}\)
Interpretation:
- 0.1-1.0 – Mild gingivitis
- 1.1-2.0 – Moderate gingivitis
- 2.1-3.0 – Sever gingivitis
Question 5. CPITN.
Answer:
Objectives:
- Mild gingivitis Moderate gingivitis Severe gingivitis
- To survey and evaluate periodontal treatment needs Identify actual and potential problems posed by periodontal diseases both in the community and in the individual
Teeth examined: Ten specified index teeth are
- 17-16 11 26-27
- 47-46 31 36-37
Scoring:
- Code X – When only one tooth or no teeth are present in the sextant
- Code 0 – Healthy periodontium
- Code 1 – Bleeding on probing
- Code 2 – Calculus present
- Code 3 – Pocket of 4-5 mm
- Code 4 – Pocket of more than 6 mm
Treatment Needs:
- TN-0 -No treatment
- TN-1 -Improvement of personal oral hygiene
- TN-2 -Professional scaling
- TN-3 Complex treatment involving deep scaling, root planning, and complex procedures
Question 6. Incidence and prevalence.
Answer:
Incidence:
- Incidence is defined as the number of new cases of a specific disease occurring in a defined population during a specified period
Incidence Uses:
- Provide a clue for the etiology and pathogenesis of the disease
- Study the distribution of the study
- Control the disease
Incidence Types:
- Episode incidence
- It is the rate of occurrence of new episodes of a discase arising in the population
- Cumulative incidence
- Similar to incidence but the time interval is ex-presses as a fixed period
Prevalence:
- The total number of all individuals who have an attribute or disease at a particular time divided by the population at risk of having the attribute or disease at this point or midway through the period
Prevalence Uses:
- Estimate the magnitude of disease or health problems in the community
- Identify the potential high-risk population
- Useful in administrative and planning purposes like assessing manpower needs in health services
Prevalence Types:
1. Point prevalence:
- Point prevalence is the number of all current cases of a specific disease at one point in time in a defined population
2. Period prevalence:
- Period prevalence is defined as the total number of existing cases of a specific disease during a defined period of time ex- pressed concerning a defined population
Question 7. Describe the possible causes as to why the incidence, and prevalence of periodontal diseases are very high in India.
Answer:
- The prevalence of periodontal disease in India is high due to:
- Low socioeconomic group
- Poor oral hygiene practice
- Greater prevalence in mentally retarded children due to
- Lack of awareness of oral hygiene
- Nutritional deficiency
- Malocclusion
- Oral health habits like bruxism, tongue thrusting, mouth breathing
- Low power of concentration
- Low neuromuscular coordination
- Vegetarian diet
- Hereditary
- Presence of habits like smoking and betel nut chewing
- Evaluate the efficacy of preventive and therapeutic
- Malnutrition
- measures
- Presence of systemic disease
Question 8. Define the index, its uses, and the ideal requirements of an index.
Answer:
Index Definition:
- Numerical values describing the relative status of the population on a graduated scale with definite upper and lower limits designated to permit and facilitate comparisons with other populations that are classified by the same criteria and methods are referred to as index
Index Uses:
- In the case of individual patients
- Provides individual assessment
- Reveals the degree of effectiveness
- Motivates the patient
- Evaluates the progress of treatment
- In the case of research studies
- Determines the baseline data before the introduction of experimental factors
- Measures effectiveness of specific agents for pre-version control and treatment of oral conditions
- Measures effectiveness of devices for personal care
- In community health
- Provides baseline data
- Assesses the needs of a community
- Evaluates the results
Index Ideal Requirements:
- Clarity simplicity
- The examiner should remember the rules of the index clearly
- The index should be simple & easy to apply
- The criteria should be objective
- Validity
- The index should measure what it is intended to measure
- It should correspond to the clinical stages of the disease under study
- Reliability
- The index should be measured consistently at different times & under a variety of conditions
- Quantifiability
- The index should be amenable to statistical analysis so that the status can be expressed by a number
- Sensitivity
- The index should be able to detect small shifts in either direction
- Acceptability
- The use of an index should not be painful or demeaning to the subject
Epidemiology Of Gingival And Periodontal Diseases Short Answers
Question 1. Index.
Answer:
Numerical values describing the relative status of the population on a graduated scale with definite upper and lower limits designated to permit and facilitate comparisons with other populations that are classified by the same criteria and methods
Index Ideal Requisites:
- Clarity, simplicity, and objectivity
- Validity Reliability
- Quantifiability
- Sensitivity
- Acceptability
Question 2. Epidemiology.
Answer:
The study of the distribution and determinants of health-related states or events in specific populations and the application of this study to control health problems.
Epidemiology Principles:
- Exact observation
- Correct interpretation
- Rationale explanation
- Scientific construction
Epidemiology Types:
- Descriptive epidemiology
- Analytical epidemiology
Question 3. Incidence and prevalence.
Answer:
Incidence:
- Incidence is defined as the number of new cases of a specific disease occurring in a defined population during a specified period of time
Incidence Types:
- Point prevalence
- Period prevalence
Question 4. Indices used to measure calculus.
Answer:
- The following are the various indices used to measure calculus
- Calculus surface index
- Calculus surface severity index
- Marginal line calculus index by Muhlemann and Villa
- Volpe-Manhold index
- PDI
- Calculus component of OHI-S
- Calclus component of PDI by Ramfjord
- Probe method of calculus assessment by Volpe and as- sociates
- Calculus surface index by Ennever and co-workers
