Drugs Used In Psychiatric Disorders Important Notes
1. Classical antipsychotic drills – block dopamine D2 receptors
- Chlorpromazine
- Halo peridot
- Zudopenthixol
- Thioridazine
2. Atypical antipsychotic drugs – block 5-HT2 and D4 receptors
- Clozapine
- Olanzapine
- Risperidone
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question and Answers
3. Disorders Adverse effects of antipsychotic drugs
Psychiatric drugs questions and answers
4. Anti-anxiety drugs
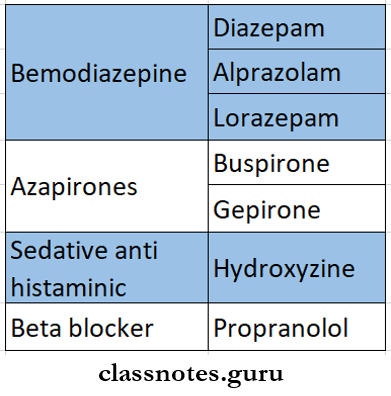
5. Oxazepam
- It is preferred in elders and in patients with liver disease
- Duration of action is short
- Used mainly in short-lasting anxiety
6. Migraine
- Drugs used for its treatment
- Mild – simple analgesics + antiemetic
- Moderate – NSAIDs combination
- Severe – ergot alkaloids + antiemetic + prophylaxis
- Drugs used for prophylaxis
- Propranolol
- Amitriptyline
- Flunarizine
- Valproate
- Methysergide
7. Chlorpromazine
- It belongs to the phenothiazine
- Exhibit antipsychotic action by blocking dopaminergic receptors in CNS
- They are also potent antiemetics
8. Antidepressants
- Act by inhibiting the uptake of biogenic amines like noradrenaline, serotonin, and dopamine
- They are
- Tricyclic compounds – Imipramine, Amitriptyline
- MOA inhibitor – Isocarboxazid, Phenelzine
Antipsychotic drugs pharmacology questions
Drugs Used In Psychiatric Disorders Short Essays
Question 1. Chlorpromazine.
Answer:
Chlorpromazine is phenothiazine with an aliphatic side chain.
Chlorpromazine Mechanism of action:
- Chlorpromazine has potent dopamine D2 receptor-blocking action.
- It also blocks Dl, D3, and D4 receptors.
Chlorpromazine Actions:
1. Chlorpromazine CNS effects.
- In normal individuals.
- Reduces motor activity.
- Produces drowsiness.
- Reduces initiative.
- In psychotic individuals.
- Reduces irritational behavior, agitation, and aggressiveness.
- Normalises sleep.
- Other actions.
- Cortex – lowers the seizure threshold.
- Hypothalamus – decreases gonadotropin secretion.
- Basal ganglia – Acts as a dopamine antagonist
- Brain stem- depresses vasomotor reflexes.
- CTZ – Act as antiemetic.
2. Chlorpromazine Autonomic nervous system.
Chlorpromazine has anticholinergic properties.
3. Chlorpromazine CVS
Has a myocardial depressant effect
4. Chlorpromazine Local anesthesia – Has local anesthetic effect.
5. Chlorpromazine Kidney – depresses ADH secretion.
Chlorpromazine Uses:
- Schizophrenia.
- Mania.
- Organic brain syndrome.
- As antiemetic.
- Hiccough.
- Anxiety.
Drugs used in psychiatric disorders PDF
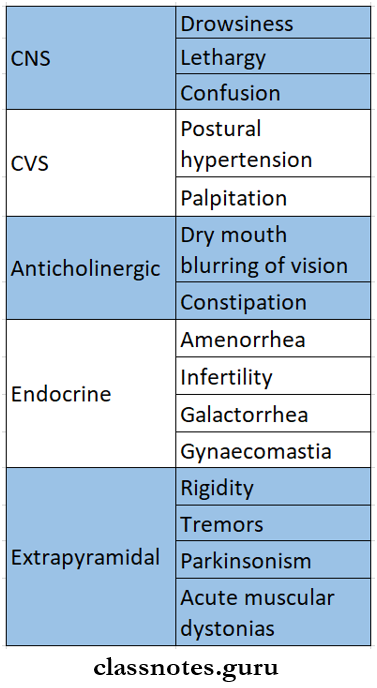
Chlorpromazine Adverse Effects:
1. Chlorpromazine Dose-related.
- CNS effects – drowsiness, lethargy, mental confusion.
- CVS effects – postural hypotension, palpitation.
- Anticholinergic – dry mouth, blurring of vision constipation.
- Endocrine – amenorrhoea, infertility.
- Extrapyramidal disturbances – parkinsonism, acute muscle dystonia, akathisia, malignant neuroleptic syndrome, tardive dyskinesia.
- Others – weight gain, blue pigmentation of skin, corneal ulceration, retinal degeneration, cardiac arrhythmia.
2. Chlorpromazine Hypersensitivity reactions.
- Cholestatic jaundice.
- Skin rashes, urticaria, contact dermatitis
- Agranulocytosis.
Question 2. Classification of antipsychotic drugs.
Answer:
Anti-psychotic drugs/neuroleptics:
These drugs have a therapeutic effect on psychosis.
1. Anti-psychotic drugs Phenothiazines
- Aliphatic side chain – chlorpromazine, trifluoro- magazine.
- Piperidine side chain – thioridazine.
- Piperazine side chain. Trifluoperazine, fluphenazine.
2. Anti-psychotic drugs Butyrophenones
Haloperidol, trifluperiodol, penfluridol.
3. Anti-psychotic drugs Thioxanthenes
Flupenthixol.
4. Anti-psychotic drugs Other heterocyclics
Pimozide, loxapine.
5. Anti-psychotic drugs Atypical antipsychotics
Clozapine, risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine.
Question 3. Neuroleptoanalgesia.
Answer:
Neuroleptanalgesia is a state of analgesia characterized by quiescence, psychic indifference, and intense analgesia without loss of consciousness.
It is obtained by a combination of.
1. Fentanyl – 0.05 mg – short-acting drug.
2. Droperidol – 2.5 mg/ml – rapidly acting drug.
4 – 6 ml of it is infused IV for 10 min.
Neuroleptoanalgesia Advantages:
The patient is drowsy but cooperative.
Neuroleptoanalgesia Adverse Effects:
- Respiratory depression.
- Slight fall in BP and heart rate.
- Extrapyramidal symptoms may be present.
Neuroleptoanalgesia Uses:
- Endoscopies.
- Burn dressing.
- Angiography.
- Diagnostic procedures.
- Minor surgical procedures.
Classification of psychiatric drugs
Drugs Used In Psychiatric Disorders Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Four drugs are used in mental depression.
(or)
Anti-depressants.
Answer:
Anti-depressants Classification:
1. Reversible inhibitors of MAO-A.
Moclobemide, clorgyline.
2. Tricyclic antidepressant
- Na + 5 HT reuptake inhibitors.
- Imipramine, Trimipramine, Amitriptyline.
- Predominantly NA reuptake inhibitors
- Desipramine, nortriptyline.
3. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
Fluoextine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine.
4. Atypical antidepressants.
Trazodone, minaserin, mirtazapine, venlafaxine.
Drug therapy for psychiatric disorders
Question 2. Analeptic drugs.
Answer:
Analeptic drugs are drugs that stimulate respiration and have resuscitative effects in fainting or coma.
Analeptic drugs Uses:
- Hypnotic drug poisoning.
- Suffocation on drowning.
- Respiratory failure due to removal of the hypoxic drive.
- Apnea in premature infants.
Analeptic drugs Adverse Effects:
- Convulsion.
- Postictal depression.
