Drugs Used In Periodontal Therapy Short Essays
Question 1. Why antibiotics are not routinely used in periodontal therapy?
Answer:
Periodontal therapy:
Periodontal Therapy Uses Of Antibiotics:
- Reduce/eliminate bacteria
- Retards bone loss
- Reduce/Eliminate the need for surgery
- Useful in aggressive periodontitis
Read And Learn More: Periodontics Question and Answers
periodontal therapy Not Used Routinely:
- Despite the above use, systemic administration is not recommended routinely as
- It produces systemic effects
- Disturbs the functioning of various systems of the body, such as GIT
- Certain drugs are contraindicated in certain conditions like pregnancy
- Besides, this systemic administration is useless unless there is plaque and calculus removal.
- The presence of a thick band of calculus prevents the penetration of the drug into the site
- Thus, it is used only as an adjunctive.
Question 2. Tetracycline in periodontics
Answer:
- Tetracycline are widely used drugs in the treatment of periodontal diseases
Tetracycline in Periodontics Clinical Use:
- It is used as an adjunct in the treatment of localized aggressive periodontitis
- A contains is a frequent microorganism associated with localized aggressive periodontitis and is tissue invasive, Therefore mechanical removal of calculus and plaque from root surfaces may not eliminate this bacterium from periodontal tissues
- Systemic tetracycline in conjunction with scaling and root planning can
- Eliminate tissue bacteria
- Arrest bone loss
- Suppresses A.a. comitans
- Allows mechanical removal of root surface deposits and elimination of pathogenic bacteria from within tissues
Tetracycline in periodontics Actions:
- Has the ability to concentrate in periodontal tissues
- Inhibits growth of A.a. contains
- Exerts anti-collagenase effect
- Inhibits tissue destruction
- Aids in bone Regeneration
Tetracycline in periodontics Dose:
- 250 mg Qid
Tetracycline in Periodontics Side Effects:
- GI disturbances
- Photosensitivity
- Hypersensitivity
- Increased blood urea nitrogen
- Dizziness, headache
- Blood dysplasias
- Tooth discoloration in children
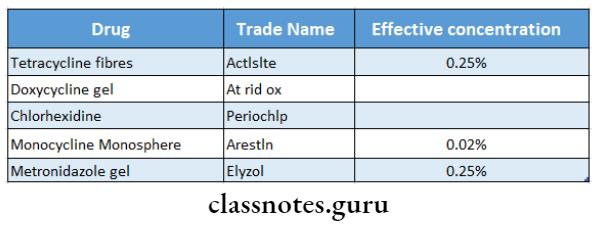
Question 3. LDD (Local Drug Delivery).
Answer:
LDD Advantages:
- Greater concentrations of drug at the site
- Slow release of drug
- Direct effect on the area
- Reduced systemic effects
LDD Contraindications:
- Allergic to drug
- Children below 10 years
LDD Drugs Used:
Question4. Methods of Delivery.
Answer:
1. Keye’s technique:
- Apply slurry of sodium bicarbonate and hydrogen peroxide over tooth brush
- Tooth brushing
Limitation: Does not reach periodontal pocket
2. Root Bio-modification:
- Application of root conditioner during surgery
Methods of Delivery Effects:
- Prevents long junctional epithelium
- Improves healing
Methods of Delivery Agents Used:
- Tetracycline
- Citric acid pH1
- Fibronectin
3. Irrigation:
Methods of Delivery Types:
- Home Irrigation
- Supra gingival
- Subgingival
- Marginal
- Professional Irrigation
- It delivers medicament into the periodontal pockets via irrigation devices
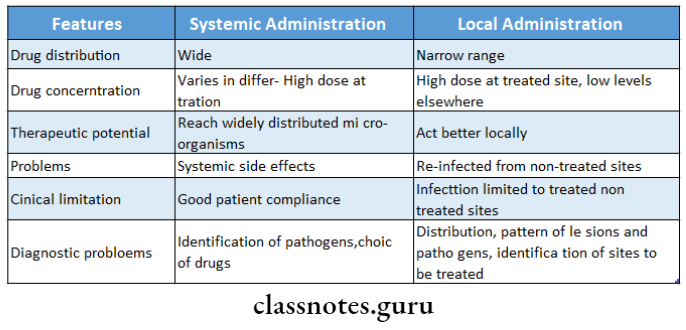
Question 5. Compare local and systemic drug delivery systems.
Answer:
Question 6. Metronidazole in periodontal therapy
Answer:
- Metronidazole is a nitroimidazole compound used to treat protozoal infections
Metronidazole Spectrum Of Activity:
- Effective against
- A. contains
- P. gingivalis
- P. intermedia
Metronidazole Uses In Periodontics:
- To treat
- Gingivitis
- Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
- Chronic periodontitis
- Aggressive periodontitis
- A single dose of metronidazole appears in both serum and GCF
- When administered systemically, it reduces the growth of anaerobic flora
- Used as a supplement to rigorous scaling and root planning Subgingival use
- A dental gel containing metronidazole benzoate is used
- It gets converted into an active substance by esterases in GCF
Adverse Effects:
- GIT effects
- Nausea, anorexia, abdominal pain, metallic taste in the mouth, looseness of stool
- Headache, stomatitis, glossitis, dryness of mouth, furry tongue, dizziness, rashes, neutropenia, insomnia
- Prolonged use causes peripheral neuropathy High doses cause convulsions
Drugs Used In Periodontal Therapy Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Advantages of LDD
Answer:
- Greater concentration of drug at the site
- Slow release of drug
- Direct effect on the area
- Reduced systemic effects
Question 2. Periochip
Answer:
- It is a small chip composed of a biodegradable hydrosol-lazed gelatin matrix cross-linked with glyceraldehyde
- It also contains glycerin and water
- 2.5 mg of chlorhexidine is incorporated into it
- It slowly releases chlorhexidine and maintains drug concentration in gingival crevicular fluid for at least 7 days
- Size of chip: 4*5*0.35 mm
Question 3. Keye’s technique
Answer:
- It refers to the application of a slurry of sodium bicarbonate and hydrogen peroxide over the toothbrush
- Tooth brushing of it is done
Keye’s technique Limitation:
It does not reach the periodontal pocket
Question 4. Activity
Answer:
- Among tetracycline-releasing devices, the most widely. It should be selective and effective against micro- used is activity periodontal fiber
- It is a monolithic thread of a biologically inert, non-than retard resorbable plastic copolymer containing 25% tetracycline hydrochloride powder
- The fiber is packed into a periodontal pocket secured with a thin layer of cyanoacrylate adhesive and left in place for 7–12 days
- Due to the continuous delivery of tetracycline, a local concentration of active drug in excess of 1000 mg/l can be. Maintained throughout the period
Activity Effects:
- Decreases pocket depth
- Increases attachment levels
- Decreases bleeding tendency
Question 5. Define antiseptic and antibiotics
Answer:
Antiseptic:
- Antiseptic is an agent that destroys microorganisms and can be used on living tissues
Antibiotics:
- An antibiotic is a chemical substance produced by microorganisms that have the capacity to inhibit the growth or kill another organism in a dilute solution
Question 6. Arestin
Answer:
- Ares tin is a locally delivered, sustained-release form of minocycline microsphere
- It is used for subgingival placement as an adjunct to scaling and root planning
- 2% minocycline is encapsulated into bioresorbable mi- mi-microspheres in a gel carrier
Ares tin Effects:
- Increase in clinical attachment level in patients with pockets of 6 mm or greater
- Reduction in probing depth
- It should destroy microorganisms rather
Question 7. Properties of ideal antibiotics
Answer:
- It should be selective and effective against microorganisms without injuring the host
- It should destroy microorganisms rather than retard their growth
- It should not become ineffective as a result of bacterial resistance
- It should not be inactivated by enzymes, plasma pro- teens or body fluids
- It should quickly reach bactericidal levels in the entire body and be maintained for long periods
- It should have minimal side effects
Drugs Used In Periodontal Therapy Viva Voce
- Metronidazole belongs to nitroimidazole
- The minimum effective concentration of tetracycline needed in GCF is 2-4 μg/m
- The mechanism of action of metronidazole is to disrupt bacterial DNA synthesis
- The mechanism of action of penicillin is it inhibits bacterial cell wall production
- Penicillin is bactericidal
- Pseudomembranous colitis with diarrhea or cramping is a side effect of clindamycin
- All strains of A.a.comitans are susceptible to ciprofloxacin
- The mechanism of action of erythromycin is it inhibits protein synthesis by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit
- Atridox is used for subgingival delivery of doxycycline
