Drugs And Cough And Bronchial Asthma Important Notes
1. Drugs used in bronchial asthma
- Bronchodilators
- Sympathomimetics
- Selective β2 agonists
- Short-acting – salbutamol, Terbutaline
- Longer acting – salmeterol
- Non-selective agents – adrenaline, aminophylline
- Methylxanthines – Heophylline, aminophylline
- Anticholinergics – ipratropium bromide, atropine
- Sympathomimetics
- Anti-inflammatory
- Systemic – glucocorticoids, hydrocortisone, prednisolone
- Inhalational – beclomethasone, triamcinolone
- Mast cell stabilizer – disodium cromoglycate
- Leukotriene receptor antagonists – Montelukast
- Anti – IgE antibody – Omalizumab
Bronchial asthma questions and answers
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question and Answers
2. Drugs causing bronchospasm
- ACE inhibitors
- Aspirin and other NSAIDs
- Beta-blockers
- Cholinergic drugs
- Bulk-forming laxatives
- Quinine
- Morphine
3. Ipratropium bromide
- It is an anticholinergic drug
- Produces slower response
- Used for regular prophylactic use
4. Mechanism of adrenergic as a bronchodilator
- Stimulation of β2 receptor
- Increased cAMP formation in bronchi muscle cells
- Relaxation of bronchi
5. Salbutamol
- It is β2 receptor agonist
- Safer than adrenaline and isoprenaline in the treatment of asthma
- Uses
- In acute exacerbation of asthma
- COPD
- For short-term relief of bronchoconstrictor
Bronchial asthma short notes with Q&A
Drugs And Cough And Bronchial Asthma Short Essays
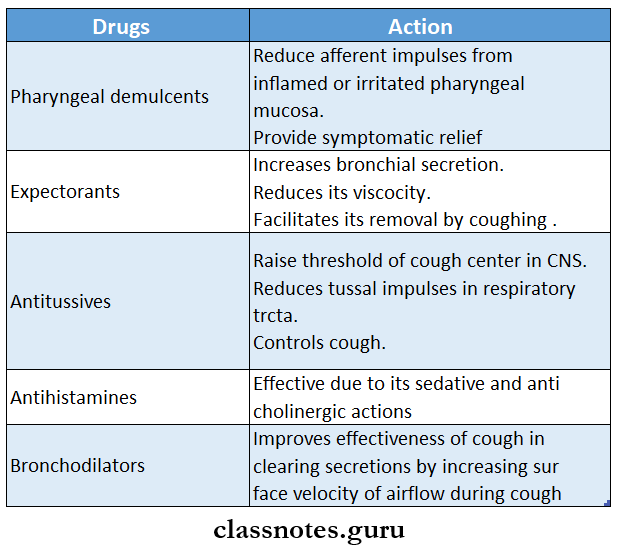
Question 1. Mention two drugs used to suppress dry cough
Answer:
Drugs Used To Suppress Dry Cough:
1. Pharyngeal demulcents
- Lozenges
- Cough drops
- Glycerine
2. Expectorants
- Bronchial secretion enhancers
- Sodium or potassium citrate
- Potassium iodide
- Balsum of tolu
- Mucolytic
- Bromhexine
- Acetylcysteine
3. Antitussives
- Opioids
- Codeine
- Pholcodine
- Non Opioids
- Noscapine
- Dextromethorphan
- Antihistamines
- Chlorpheniramine
- Diphenhydramine
- Promethazine
Bronchial asthma important questions for exams
4. Adjuvant Antitussives
- Bronchodilators- Salbutamol, terbutalin
Question 2. Noscapine
Answer:
- Noscapine is a natural opium alkaloid
- It is a potent Antitussive
- It is highly effective and safe
- It may cause bronchoconstriction due to the release of histamine
- It acts by inhibiting the cough center In the medulla
Noscapine Use:
- Cough suppressant
Noscapine Adverse Effects:
- Nausea
- Headache
Noscapine Dose:
- 15-30 mg 6 hourly
BSc Nursing bronchial asthma questions
Question 3. Disodium cromoglycate
Answer:
- Disodium cromoglycate is a synthetic derivative
- It belongs to a group of antiasthmatic drugs
- It is administered as an aerosol through metered dose inhaler
Disodium cromoglycate Mechanism of Action:
- Inhibits degranulation of mast cells
- Inhibits the release of inflammatory mediators
- Inhibits the release of cytokines
- Depresses neuronal reflexes
Disodium cromoglycate Adverse Effects:
- Throat irritation
- Cough
- Rarely bronchospasm and allergic reactions
Disodium cromoglycate Uses:
1. Prophylactic in bronchial asthma
- It is used for longer periods in mild to moderate asthma
- 2 puffs, 3-4 times daily
2. Allergic rhinitis
- Used as a nasal spray to produce symptomatic improvement
3. Allergic conjunctivitis
- Used as eyedrops
- 1-2 drops, 3-4 times daily
Treatment of bronchial asthma questions
Question 4. Salbutamol
Answer:
- Salbutamol is a sympathomimetic drug
- It is fast acting bronchodilator
- The onset of action-1-5 min
- Duration of action- short
Salbutamol Actions:
- Bronchodilator
- Relaxation of the pregnant uterus
- Dilatation of blood vessels supplying the skeletal muscles
- Promote peptic glycogenolysis and uptake of potassium
Salbutamol Uses:
- In bronchial asthma- 100-200 meg every 6 hours through metered dose inhaler
- To delay premature labor
- In hyperkalemia
Salbutamol Adverse Effects:
- Tachycardia, palpitation
- Muscle tremors
- Tolerance
- Restlessness, nervousness
- Throat irritation
- Ankle edema
- Hyperglycaemia, hypokalaemia
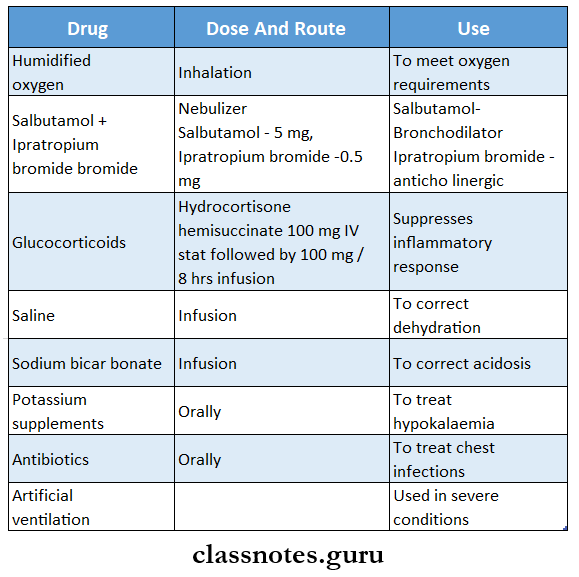
Question 5. Pharmacotherapy of status asthmatics
Answer:
Treatment of status asthmaticus is as follows:
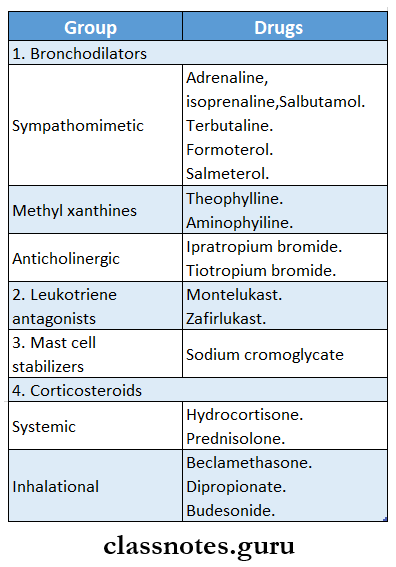
Question 6. Mention three groups of drugs used in bronchial asthma with an example.
Answer:
Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma:
Question 7. Write the rationale for using any one drug for asthma.
Answer:
The Rationale of Using Sympathomimetic Drugs in Bronchial Asthma:
- Sympathomimetic drugs like adrenaline have the following mechanism
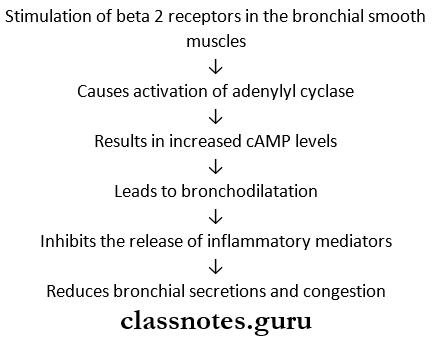
- It has a rapid onset and a short duration of action
- Hence it is used in acute asthmatic attacks as an aerosol
Short and long essay on bronchial asthma
Drugs And Cough And Bronchial Asthma Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Aminophylline
Answer:
- Aminophylline is one of the methylxanthines
Aminophylline Mechanism of Action:
- Enhances cAMP levels
- Causes bronchodilatation
- Inhibits the release of inflammatory mediators
Aminophylline Actions:
- CNS stimulant
- CVS stimulant
- Relaxes smooth muscles
- Mild diuretic
- Enhances secretion of acid and pepsin in the stomach
- Inhibits the release of inflammatory mediators
Aminophylline Uses:
- Bronchial asthma and COPD
- Apnea in the premature infant
Aminophylline Adverse Effects:
- Dyspepsia, vomiting, nervousness, tremor, delirium, hypotension, arrhythmia, and convulsions
Question 2. Nasal decongestants.
Answer:
- Nasal decongestants stimulate the alpha receptors and cause vasoconstriction in the nasal mucous membrane and relieve nasal congestion
Drugs Used As Nasal Decongestants:
- Naphazoline
- Pseudoephedrine
- Phenylephrine
- Imidazole
Nasal decongestants Use:
- Allergic rhinitis
- Common cold
- Sinusitis
Nasal decongestants Adverse Effects:
- Atrophic rhinitis
- Anosmia
- Local irritation
Bronchial asthma causes, symptoms, and treatment Q&A
Question 3. The rationale for using Salbutamol in bronchial asthma
Answer:
- Salbutamol is used in asthma to reduce cardiac side effects
- Inhaled Salbutamol produces bronchodilatation within 5 min
- Its action lasts for 2-4 hours
- It is the most effective, convenient, and relatively safe
- Hence it is used to terminate the attacks of asthma.
Question 4. Beclomethasone
Answer:
- Beclomethasone is long acting glucocorticoid
Beclomethasone Mechanism of Action:
- Suppresses inflammatory response to antigen-antibody reaction
- Reduces mucosal edema and hyper irritability
Beclomethasone Uses:
- Prophylactic use to prevent acute attacks of asthma
- Prevent bronchial hypersensitivity
- Controls the symptoms
Beclomethasone Available As:
- Nasal spray- For allergic rhinitis
- Ointment- For skin and mucous membrane
Beclomethasone Dose:
- Beclate inhaler- 50,100,200 microgram
- Metered dose-1-2 puffs 3-4 times a day
Beclomethasone Adverse Effects:
- Hoarseness of voice
- Sore throat
- Oropharyngeal Candidiasis
Bronchial asthma pharmacological treatment questions
Question 5. Ipratropium.
Answer:
- It is a semi-synthetic anticholinergic drug
- Given by inhalation
Ipratropium Uses:
- Bronchial asthma
- COPD
- Inhaled ipratropium – used as a prophylactic agent
- Nebulized ipratropium mixed with salbutamol – used in refractory asthma
Nursing interventions in bronchial asthma
Question 5. Name four bronchodilators.
Answer:
- Sympathomimetics – adrenaline, isoprenaline, salbutamol
- Methyl xanthine – theophylline, aminophylline
- Anticholinergic – ipratropium bromide, tiotropium bromide
