Disturbances In Water Electrolyte And Acid Base Balance Important Notes
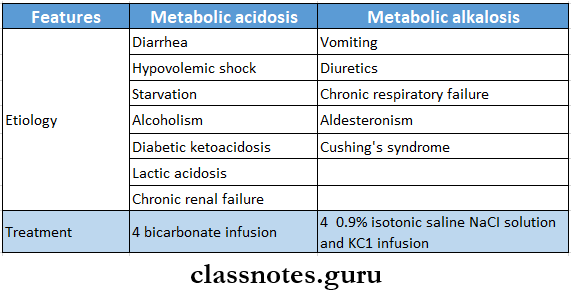
- Metabolic Acidosis And Alkalosis
- Dehydration
- Dehydration is the loss of water from the body
- Clinical features
- Thirst
- Dry mouth
- Dizziness
- Dysphagia
- Muscular weakness
- Oliguria
- Mental confusion
- Hypokalaemia
- Depletion of potassium from the body
- Clinical features
- Generalized muscular weakness
- Depression of tendon reflexes
- Confusion
- Coma
- Paraesthesia
- Muscle stiffness
- Polyuria
- Nocturia
- Hyperkalaemia
- A marked increase in potassium content
- Clinical features
- Cardiac arrest
- Irregular pulse
- Flaccid paralysis
- Abdominal distension
- Hyponatraemia
- Hyponatraemia is the loss of sodium from the body
- Clinical features
- Lassitude
- Hypotension
- Tachycardia
- Reduced skin elasticity
- Apathy
- Weakness
- Coma
- Oliguria
Water and electrolyte balance short note
Disturbances In Water Electrolyte And Acid Base Balance Short Essays
Question 1. Dehydration
Answer:
Dehydration
- Dehydration is the primary water depletion
Read And Learn More: General Medicine Question and Answers
Dehydration Aetiology:
- Decreased intake of water
- Increased loss from the skin
- Increased respiratory loss
- Increased loss in urine
Dehydration Clinical Features:
- Marked thirst
- Muscle weakness
- Dry mouth
- Mental confusion
- Coma
- Intracranial haemorrhage
- Tachycardia
Dehydration Investigations:
- Increased blood urea level
- Raised plasma sodium
- Urine specific gravity of more than 1.010
- Polyuria
Dehydration Treatment:
- Administration of isotonic saline
Question 2. Hypokalaemia
Answer:
Hypokalaemia
- A decrease in the concentration of serum potassium is called hypokalaemia
Hypokalaemia Causes:
- Overactivity of the adrenal cortex
- Prolonged cortisone therapy
- Intravenous administration of potassium-free fluids
- Treatment of diabetic coma with insulin
- Prolonged diarrhoea and vomiting
Read And Learn More: General Medicine Question and Answers
Hypokalaemia Symptoms:
- Irritability
- Muscular weakness
- Tachycardia
- Cardiomegaly
- Cardiac arrest
ECG Changes:
- Flattening of waves
- Inverted T wave
Question 3. Respiratory alkalosis
Answer:
Respiratory Alkalosis
- Excessive loss of carbon dioxide leads to respiratory alkalosis
Aetiology:
- Hysterical overbreathing
- Lobar pneumonia
- Pulmonary embolism
- Meningitis
- Salicylate poisoning
- Hepatic failure
Respiratory Alkalosis Features:
- Fall in partial pressure of carbon dioxide and hydrogen ion concentration
- Decreased plasma bicarbonate level
- Paraesthesia
- Numbness
- Tingling sensation
Respiratory Alkalosis Treatment:
- Elimination of underlying disorder
- Sedation.
Disturbances in electrolyte balance essay
Question 4. Hyperkalaemia
Answer:
Hyperkalaemia
- An increase in the concentration of serum potassium is called hyperkalaemia
Hyperkalaemia Causes:
- Impaired excretion
- Excessive intake
- Tissue breakdown
- The shift of potassium ions out of the cell
Hyperkalaemia Clinical Features:
- Cardiac arrhythmia
- Muscular weakness
- Respiratory depression
Hyperkalaemia Investigations:
- ECG Changes:
- Tall T waves
- Prolongation of PR interval
- Reduced height of P wave
- Prolongation of QRS complex
Hyperkalaemia Treatment:
- Elimination of the underlying cause
- 10 ml of 10% calcium gluconate solution is given intravenously slowly over 5-10 min
- Intravenous administration of glucose along with insulin
- Intravenous administration of 50-100 ml of 8.4% sodium bicarbonate
- Nebulization of beta-agonists
Disturbances In Water Electrolyte And Acid Base Balance Short Answers
Question 1. Hyponatraemia
Answer:
Hyponatraemia
- Hyponatraemia indicates the dilution of body fluids by excess water relative to total solute
Aetiology:
- Increased ECF volume- congestive cardiac failure, nephrotic syndrome, cirrhosis of the liver
- Reduced ECF volume- sweating, vomiting, diarrhoea
- Hyperglycaemia
- Mannitol administration
Hyponatraemia Clinical Features:
- Muscle cramps
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Mental confusion
- Disorientation
- Coma
- Convulsions
Hyponatraemia Treatment:
- Administration of loop diuretics and hypertonic saline
Question 2. Metabolic acidosis
Answer:
Metabolic Acidosis
- Metabolic Acidosis is a reduction in bicarbonate concentration, which leads to a fall in blood pH
Metabolic Acidosis Causes:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Renal failure
- Lactic acidosis
- Severe diarrhoea
- Renal tubular acidosis
Metabolic Acidosis Treatment:
- Hyperventilation of lungs
- This decreases the partial pressure of carbon dioxide
acid-base balance disorders short essay
Question 3. Oral rehydration
Answer:
Oral Rehydration
- Oral rehydration solution is used in patients with diarrhoea to replenish the lost water
Oral Rehydration Composition:
- NaCl -3.5 g
- KCl -1.5 g
- Trisodium citrate -2.9 g
- Glucose -20 2
- Water -1 litre
Oral Rehydration Uses:
- To replace fluids and salts lost from the body during diarrhoea
- To restore and maintain hydration
- Maintain electrolyte and pH balance
- Maintain hydration in patients postsurgically after burns, trauma, and heat stroke
