Diseases Of The Nervous System Short Essays
Question 1. Status epilepticus
Answer:
Status Epilepticus
- Status Epilepticus is a condition in which a series of seizures occur in the patient without regaining consciousness in between successive attacks
Status Epilepticus Precipitating Factors:
- Sudden withdrawal of drugs
- Irregular use of anti-convulsants
- following intracranial pathology
Status Epilepticus Management:
- Loosen clothes around neck
- Maintain airway
- Administration of high concentration of oxygen
- Diazepam 10-20 mg IV over 1-5 minutes
- Monitor BP, ECG, and blood gases
- Diazepam 10 mg IV repeat once after 15 minutes
- Start infusion drip of phenytoin, 18 mg/ kg at the rate of 50 mg/min
- If seizure are not controlled, start infusion drip of chloromethiazol 4 0.5-1.2 g/hour
- If seizures are not still controlled start 4 drip of thiopentone sodium 20 mg/kg 4 at 50-100 mg/min
Diseases of the nervous system short essays
Read And Learn More: General Medicine Question and Answers
Question 2. Anti-epileptic drugs
Answer:
Anti-Epileptic Drugs Classification:
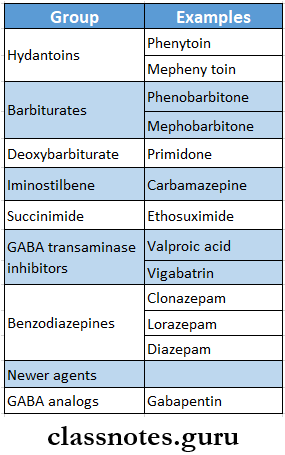
Anti-Epileptic Drugs – Mechanism Of Action:
- Blockade of sodium channels
- Prolongation of their inactive state
- Blockade of low threshold calcium current in the thalamic neurons
- Enhancing GABA-mediated inhibition
Question 3. Trigeminal neuralgia
Answer:
Etiology:
- Pathological
- Dental pathosis
- Traction on divisions of trigeminal nerve
- Ischaemia
- Aneurysm of internal carotid artery
- Environmental
- Allergic
- Irritation to the ganglion
- Secondary lesions
Trigeminal Neuralgia Clinical Features:
- Age: Around 35 years
- Sex: Common in female
- Site: Right lower portion of the face, usually unilateral
- Duration: Few seconds to few minutes
- As time passes duration between the cycles decreases
- Nature: stabbing or lancinating
- Aggravating Factors: Activation of TRIGGER ZONES
- These are Vermillion border of lip, around the eyes, ala of nose
Interference With Other Activities:
- Patient avoids shaving, washing face, chewing, brushing, as these may aggrevate pain
- These lead to poor lifestyle
- Extreme Cases: leads to FROZEN OR MASK-LIKE FACE
Trigeminal Neuralgia Management:
1. Medical
- Carbamazepine: initial dose: 100mg twice daily until relief is achieved
- Dilantin: 300-400mg in single or divided doses
- Combination Therapy: Dilantin + carbamazepine
2. Surgical
- Injection of alcohol in gasserian ganglion
- Nerve avulsion: Performed on lingual, buccal or mental nerve
- Part of nerve is sectioned
- Electrocoagulation of gasserian ganglion: diathermy is done
- Rhizotomy: Trigeminal sensory root is sectioned
- Newer Technique: TENS
- Low-intensity current is used at high frequency is applied to the skin through electrodes attached by a conduction paste
Short essay on nervous system disorders
Question 4. Etiology and clinical manifestations of depression
Answer:
Etiology
- Depression is a common psychiatric disorder
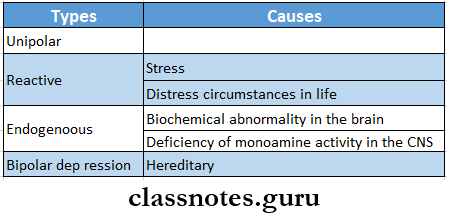
Etiology Clinical Manifestations:
- Emotional symptoms
- Sadness
- Misery
- Hopelessness
- Low self esteem
- Loss of interest
- Suicidal thoughts
- Biological symptoms
- Fatigue
- Apathy
- Loss of libido
- Loss of appetite
- Lack of concentration
- Sleep disturbances
- Symptoms of bipolar depression
- Over enthusiasm
- Overconfidence
- Irritation
- Aggression
Question 5. Petit mal epilepsy
Answer:
Petit Mal Epilepsy
- This form of epilepsy is seen in children
Petit Mal Epilepsy Features:
- Child stops working
- Looks confused
- Stares in space
- May blink or roll up eyeballs
- Fails to respond to verbal commands
- Attack is brief
Petit Mal Epilepsy Diagnosis:
- EEG changes shows spike and wave complexes at a frequency of 3 Hz per second
Question 6. Peripheral neuropathy
Answer:
Peripheral Neuropathy
- Peripheral neuropathy is the disorder of peripheral nerves either sensory, motor, or mixed, symmetrical, and affecting distal parts of limbs
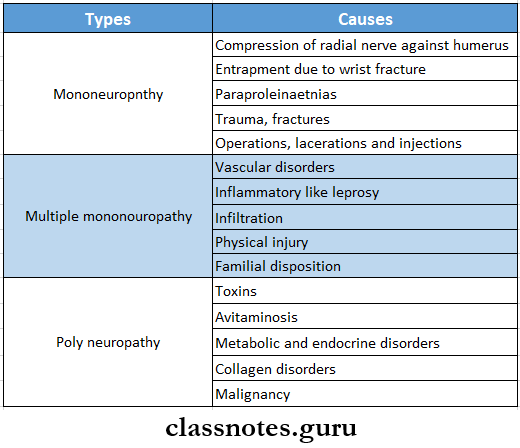
Neurological disorders short essay questions
Question 7. Causes of epilepsy
Answer:
Causes Of Epilepsy
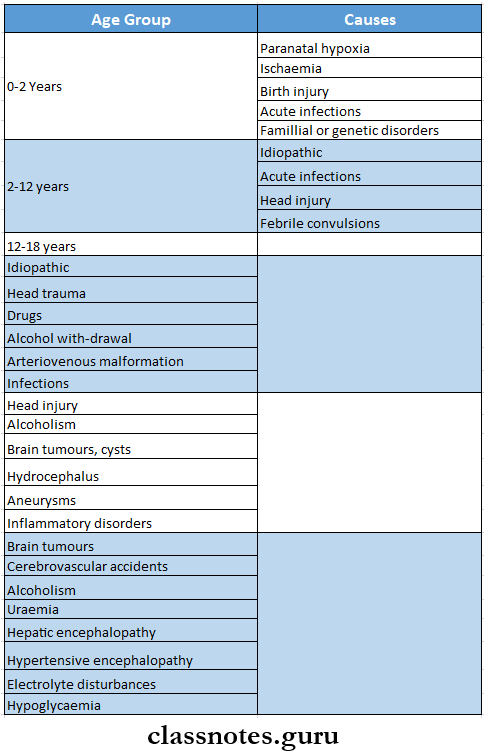
Question 8. Hypertensive encephalopathy
Answer:
Hypertensive Encephalopathy
- Hypertensive encephalopathy is characterized by a very high blood pressure and neurological disturbances including transient abnormalities in speech, vision, paresthesia, disorientation, fits, loss of consciousness, and papilloedema
Hypertensive Encephalopathy Treatment:
- Intravenous sodium nitroprusside-0.3-1 micro- gratn/kg/ min
- Parenteral labetelol- 2 mg/min
- Hydralazine-5-10 mg every 30 min
- Bed rest
- Sedation
- Diuretics
Nervous system diseases short note essays
Question 9. Discuss the differential diagnosis of headache
Answer:
The Differential Diagnosis Of Headache
- Migraine headache
- Tension type of headache
- Cluster headache
- Miscellaneous headache
- Traumatic headache
- Headache due to vascular causes- hematoma
- Headache due to non vascular causes- due to increased pressure
- Headache due to substance abuse- alcohol
- Headache due to systemic infection
- Headache due to metabolic disorders
- Headache due to referred pain- from ear, etc
- Cranial neuralgia- trigeminal neuralgia
- Unclassified headache
