Diseases Of The Nervous System Important Notes
- Bell’s Palsy
- Bell’s Palsy is idiopathic paralysis of facial nerve
- Etiology
- Rheumatic – Cold
- Ischaemia
- Immunological
- Viral
- Clinical features
- Pain in post auricular region
- Sudden onset
- Unilateral loss of function
- Loss of facial expression
- Absence of wrinkling
- Inability to close eye
- Watering of eye
- Inability to blow
- Obliteration of nasolabial fold
- Loss of taste sensation
- Hyperacusis
- Slurring of speech
- Grand Mal Epilepsy
- Phases
- Prodromal phase
- Aura
- Tonic and clonic phase
- Postictal phase
- Phases
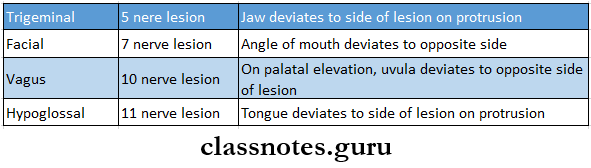
- Nerve Lesion
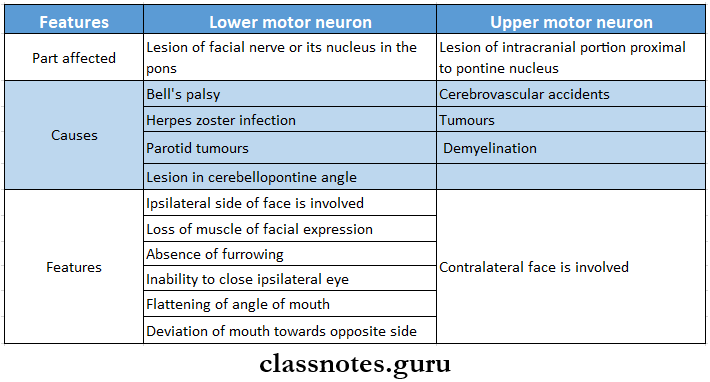
- lower Motor Neuron v/s Upper Motor Neuron
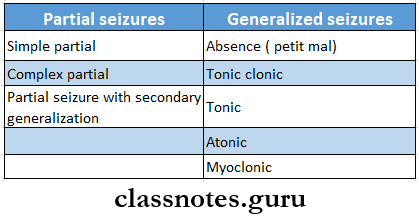
- Types Of Seizures
- Pyogenic Meningitis
- Etiology
- Cram negative bacteria
- Croup B streptococci
- Listeria monocytogenes
- H. influenza
- N. meningitides
- M. tuberculosis
- Drug of choice – ceftriaxone
- Etiology
- Features Of Horner’s Syndrome
- Miosis
- Ptosis
- Anhydrosis
- Enophthalmos
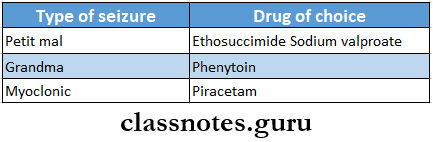
- Drug Of Choice In Different Seizures
- Disorders Of Basal Ganglia
- Parkinson’s disease
- Wilson’s degeneration
- Chorea
- Athetosis
- Parkinsonism
- Parkinsonism is a syndrome consisting of akinesia and bradykinesia, rigidity, and tremors
- Anticholinergics are used for it
- Migraine
- Migraine is characterized by an episodic hemicranial or unilateral throbbing headache and is often associated with nausea, vomiting, and visual disturbances. It is the most common vascular headache
- Causes pain of the face and jaws
- Occurs due to vasoconstriction of intracranial vessels followed by vasodilation
- Status Epilepticus
- Status Epilepticus is a condition in which a series of seizures occur in the patient without regaining consciousness in between successive attacks
- Precipitating factors
- Sudden withdrawal of drugs
- Irregular use of anticonvulsants
- Following major intracranial pathology
- Treatment
- Immediate treatment
- Rest the patient on the bed
- Loosen the clothes
- Maintain airway
- Administration of high concentration of 02
- Administration of 20-25 ml dextrose
- Transfer the patient to ICU
- Immediate treatment
- Late treatment
- Diazepam 10 mg IV repeat once only after 15 min
- Lorazepam 4 mg IV repeated after 10 min
- If the patient does not respond then drip of phenytoin 15 mg/kg at the rate of 50 mg/min
- If still not controlled then 4 drip of thiopentone sodium 20 mg/kg at 50-100 mg/min.

Diseases of the nervous system important notes
Read And Learn More: General Medicine Question and Answers
- Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Occurs due to paralysis of the trigeminal nerve
- Clinical features
- Site: right lower portion of the face, usually unilateral
- Duration: a few seconds to a few minutes
- As time passes duration between the cycles decreases
- Nature: stabbing or lancinating
- Aggravating Factors: activation of TRIGGER ZONES
- These are the Vermillion border of the lip, around the eyes, ala of nose
- Interference with other activities:
- The patient avoids shaving, washing face, chewing, and brushing, as these may aggravate pain
- These lead to a poor lifestyle
- Extreme cases: leads to “FROZEN OR MASK-LIKE FACE”
- Syncope
- Syncope refers to generalized weakness of muscles, loss of postural tone, inability to maintain an erect posture, and loss of consciousness
- Syncope Causes
- Decreases cerebral perfusion
- Inadequate vasoconstrictor mechanism
- Hypovolemia
- Reduction of venous return
- Reduced cardiac output
- Arrhythmias
- Cerebrovascular disturbances
- Noncirculatory causes
- Hypoxia
- Prolonged bed rest
- Hypoglycaemia
- Anaemia
- Anxiety neurosis
- Hyperventilation
- Decreases cerebral perfusion
- Syncope Types
- Vasovagal syncope
- Postural hypotension with syncope
- Micturition syncope
- Cardiac syncope
- Carotid sinus syncope
- Cough syncope
- Syncope of cerebrovascular disease
- Petit Mal Epilepsy
- Typically seen in children
- It is brief, and lasts only for seconds
- They may left unnoticed by the people
- Later it may develop into tonic-clonic seizures in adulthood
Neurology quick revision notes
Occurs Due To Developmental Abnormality Of Neuronal Control
- Babinski’ Sign
- Extension of the great toe with fanning of other toes is called Babinski’s sign
- Headache
- Classification
- Migraine headache
- Tension type of headache
- Cluster headache
- Miscellaneous headache
- Traumatic headache
- Headache due to vascular causes- hematoma
- Headache due to nonvascular causes- due to increased pressure
- Headache due to substance abuse- alcohol
- Headache due to systemic infection
- Headache due to metabolic disorders
- Headache due to referred pain- from the ear, etc.
- Cranial neuralgia- trigeminal neuralgia
- Unclassified headache
- Classification
