Diseases Of Bone And Joints Important Notes
- Fibrous Dysplasia Definition: It is an idiopathic condition, in which an area of normal bone is gradually replaced by abnormal fibrous connective tissue, which then again undergoes osseous metaplasia, and eventually the bone is transformed into a dense lamellar bone.
- Fibrous Dysplasia Classification:
- Monostotic – Only one bone is involved
- Polyostotic – More than one bone is involved
- Jaffe’s type -Polyostotic along with cafe-au-lait-skin pigmentation
- Albright syndrome – characterized by polyostotic fibrous dysplasia, cafe-au-lait skin pigmentation, and endocrine disturbances
- Diseases Of Bone And Joint Features
- Cafe au lait pigmentation of skin
- Unilateral swelling of the jaw
- Precocious puberty
- Egg crackling of the cortex of the bone is present
- Later ground glass appearance is seen
- Maxillary lesions causes obliteration of maxillary sinus
- Spindle-shaped fibroblasts are arranged in a whorled pattern
- Fibrous Dysplasia Classification:
- Paget’s disease
- It is characterized by excessive and abnormal remodeling of bone
- Affects the adult skeleton
- Patients suffer from deafness, blindness, and facial paralysis
- There is a progressive enlargement of the skull and maxilla because of which the patient has to change the hats and dentures frequently
- Cherubism
- Manifests by the age of 3-4 years
- Painless symmetric swelling of the mandible or maxilla occurs
- Results in chubby face appearance
- The deciduous teeth shed prematurely and numerous teeth are absent
- X-ray shows numerous unerupted teeth floating in cyst-like spaces
- Cleidocranial dysplasia
- it is characterized by abnormalities of the skull, shoulder girdle, jaws, and teeth
- Skull – delayed closure of sutures and wormian bones
- Shoulder – partial or complete absence of clavicles
- Teeth – prolonged retention of deciduous and delayed eruption of permanent
- Numerous supernumerary teeth are found in the mandibular premolar and incisor areas
- Blue sclera Is seen In
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Marfan syndrome
- Cherubism
- Ehlers Danlos syndrome
- Osteopetrosis
- Fetal rickets
- Normal infants
- Marfan’s syndrome
- Long thin extremities
- Hyperextensibility of joints
- Spidery fingers
- Arachnodactyly
- Bifid uvula
- CVS complications
- Albright’s syndrome
- Precocious puberty
- Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
- Cafe-au- lait pigmentation
- Down syndrome
- It occurs due to trisomy 21
- Features
- Hypermobility
- Macroglossia
- Flat face
- Large anterior fontanelle
- Sexual underdevelopment
- Cardiac abnormalities
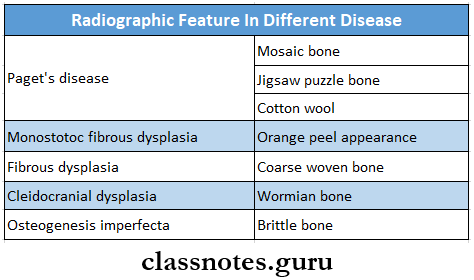
- Cotton wool appearance is seen in
- Paget’s disease
- Chronic sclerosing diffuse osteomyelitis
- Fibrous dysplasia
- Cemento-osseous dysplasia
- Radiographic features in different disease
Serum affine phosphatase is elevated In- Malignancy
- Abscess of Ihrer
- Amyloidosis
- Leukemia
- Sarcoidosis
- Pierre Robin syndrome
- Features
- Micrognathia
- Geffc palate
- Glossoprosis
- Features
- Diseases with cafe-Au lait spots are
- Albright syndrome
- Yon Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis
- Bloome’s syndrome
- Fanconi’s syndrome
- Cowden’s syndrome
- Tuberculosis sclerosis
- Watson’s syndrome
- Ataxia telangiectasia
Diseases Of Bone And Joints Short Question And Answer
Question 1. Classify the diseases of TMJ. Write etiology and clinical features of ankylosis
Answer:
Classification of Diseases of Temporomandibular Joint:
- Disorders due to extrinsic factors
- Masticatory muscle disorders
- Myofunctional pain dysfunction syndrome
- Myositis
- Problems due to trauma
- Traumatic arthritis
- Fracture
- Internal disc derangement
- Tendonitis
- Masticatory muscle disorders
- Disorders due to intrinsic factors
- Trauma
- Dislocation
- Fracture
- Internal disc displacement
- Anterior disc displacement with reduction
- Anterior disc displacement without reduction
- Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Juvenile arthritis
- Infantile arthritis
- Developmental defects
- Agenesis
- Hypoplasia
- Hyperplasia
- Ankylosis
- Neoplasm
- Benign
- Malignant
- Trauma
Read And Learn More: Oral Pathology Questions and Answers
Ankylosis: Ankylosis means stiff joint
Ankylosis Etiology:
- Trauma
- Congenital
- Infections- osteomyelitis
- Inflammation- Osteoarthritis
- Systemic diseases-typhoid
- Measles
- Prolonged trismus
Ankylosis Types:
- False or true ankylosis
- Extra articular or intra articular
- Fibrous or bony
- Unilateral or bilateral
- Partial or complete
Ankylosis Clinical Features:
- Unilateral ankylosis
- Deviation of the chin on the affected side
- The fullness of the face on the affected side
- Flatness on the unaffected side
- Crossbite
- Angle’s class 2 malocclusion
- Condylar movements absent on the affected side
- Bilateral ankylosis
- Inability to open mouth
- Neck chin angle reduced
- Class 2 malocclusion
- Protrusive upper incisors
- Multiple carious teeth
Question 2. Enumerate bone disorders affecting the jaws. Describe the pathogenesis, clinical features, radiographic appearance, and histopathology of fibrous dysplasia.
Answer:
Bone Disorders Affecting the Jaws:
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Osteopetrosis
- Fibrous dysplasia
- Cheruhism
- Mandibulofaci dysostosis
- Pierre Robin malformation
- Achondroplasia
- Chondroectodermal dysplasia
- Cleidocranial dysplasia
- Down’s syndrome
- Marfan syndrome
- Infantile cortical hyperostosis
Fibrous Dysplasia:
- Fibrous dysplasia is a skeletal developmental anomaly of the bone-forming mesenchyme that manifests as a defect in osteoblastic differentiation and maturation
Fibrous Dysplasia Pathogenesis:
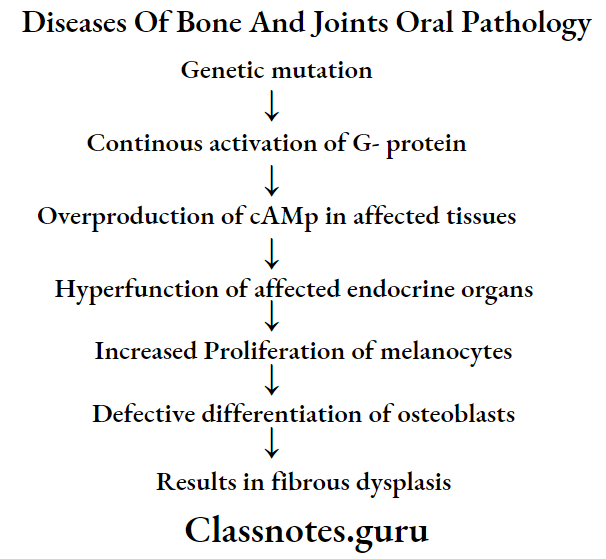
Fibrous Dysplasia Types:
- Monostotic form
- Polyostotic form
- Jaffe’s type
- Albright syndrome
Fibrous Dysplasia Clinical Features:
- Age- Occurs in the first and second decade of life
- Sex- common in females
- Site involved
- Skull
- Facial bones
- Clavicles
- Pelvic bones
- Long bones-femur, tibia, humerus
- Skeletal lesions
- Unilateral distribution of lesions
- Swelling on the affected side
- Recurrent bone pain
- Cessation of growth
- Pathological fractures
- Skin lesions
- Cafe-au- Jail pigmentations
- It consists of irregularly, pigmented, light brown, flat, melanotic spots
- Oral manifestations
- Slow enlarging, painless, unilateral swelling of the jaw
- Facial deformity
- Expansion and distortion of cortical plates,
- Displacement of regional teeth
- Disturbances in teeth eruption
- Severe malocclusion
- Maxillary lesions lead to Exophthalmos, proptosis, and nasal obstruction
- Mandibular protuberance
- Precocious puberty
- Premature vaginal bleeding
- Breast development
- Presence of axillary and pubic hairs at the age of 2-3 years
Fibrous Dysplasia Radiographic Features:
- Initially, it produces unilocular or multilocular radiolucent areas in bone
- Expansion and distortion of cortical plates occurs
- Displacement of teeth
- The egg-cell crackling of the cortex of the bone is present
- Later a classical ground glass or orange peel appearance of bone is seen
- The margin of the lesion blends with the surrounding normal bone
- Mandibular lesions cause bulging of the US inferior border
- Narrowing of periodontal ligament
- Thinning of lamina dura
- Maxillary lesions causes obliteration of maxillary sinus
Fibrous Dysplasia Histopathology:
- Monostatic fibrous dysplasia
- Consists of proliferating fibroblasts in the stroma of interlacing collagen fibers
- Trabeculae of bone are multiple, coarse, irregular, and immature
- This produces a Chinese letter pattern
- Spheroidal areas of calcification are seen
- Presence of giant cells
- At the margin, the lesion blends with the surrounding bone
- Gradually the amount of cellularity decreases and the amount of bone tissue increases
- There is remodeling of woven bone
- Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
- Areas of fibrous metaplasia within flat and tubular bones
- Well defined lesions
- Rich in spindle-shaped fibroblasts arranged in a whorled pattern
- Presence of giant cells
- Collagen fiber bundles lack orientation
Question 3. Enumerate the osteodystrophies. Write in detail about Paget’s disease of bone.
Answer:
Osteodystrophies: Osteodystrophies are disorders of bone other than neoplastic and inflammatory conditions
Osteodystrophies Classification:
- Fibro-osseous lesions
- Fibrous dysplasia
- Periapical cementitious dysplasia
- Focal cementitious dysplasia
- Giant cell lesions
- Cheru be
- Central giant cell granuloma
- Peripheral giant cell granuloma
- Developmental disorders of bone
- Metabolic disorders of bone
- Brown’s tumor
- Miscellaneous
- Rickets
- Osteomalacia
Paget’s Disease: It is a bone disorder characterized by excessive, tin- coordinated phases of bone resorption and subsequent deposition of new bone in the same area
Paget’s Disease Clinical Features:
- Age- fifth, sixth, seventh decade of life
- Sex- common in males
- Sites involved
- Weight-bearing areas- vertebral column, femur
- Skull
- Pelvis
- Sternum
- Common in maxilla than mandible
- Present as deep and aching bone pain
- Bilateral swelling of the involved bone
- Bowing deformity of weight-bearing areas
- Results in monkey-like stance
- Waddling gait
- Involvement of facial bones is referred to as dementia- sis ossa
- Headache
- Deafness, blindness
- Facial paralysis
- Enlargement of skull
- Bowing of legs
- The increased localized temperature of the skin
Paget’s Disease Histopathology:
- The initial stage shows osteoclastic bone resorption
- Bone is replaced by highly vascularised cellular connective tissue
- Osteoclasts are larger and multinucleated
- The later stage shows the deposition of new lamellar bone by osteoblast cells
- Fatty bone marrow is replaced by fibrous stroma
- Bone resorption and deposition produce prominent reversal and resting lines
- The irregular pattern of such lines produces a jigsaw- puzzle or mosaic pattern
- The affected bone is thick, sclerotic
- Obliteration of the medullary cavity occurs
- Chronic inflammatory cells and dilated blood capillaries are present
Paget’s Disease Radiographic Features:
- Initially, there is the presence of radiolucent areas in the affected bone
- In the next stage, involved bone shows haphazardly arranged newly formed bone in radiolucent areas
- This produces the cotton wool appearance
- The radiopacity of lesions increases due to increased osteosclerosis
- Prognathic and pagetoid mandible
- Obliteration of maxillary sinus
- Hypercementosis of tooth
- Loss of lamina dura
- Obliteration of periodontal ligament space
- Root resorption
Question 4. Clinical features of monostotic fibrous dysplasia
Answer:
Monostotic Fibrous Dysplasia: It is a form of fibrous dysplasia that involves single-bone
Monostotic Fibrous Dysplasia Clinical Features:
- Common in children and young adults
- Painless swelling of the jaw
- Common in mandible
- The protuberance of its inferior border
- Misalignment or displacement of regional teeth
- The overlying mucosa is intact
- Maxillary lesions involve the maxillary sinus, the floor of the orbit, and the zygomatic process
- There is a bulging of canine fossa
Question 5. Cleidocranial dysplasia
Answer:
Cleidocranial dysplasia
It is a hereditary disorder characterized by abnormal growth of the bones in the face, skull, and clavicles with a tendency for the failure of tooth eruption
Cleidocranial dysplasia Clinical Features:
- Absence or hypoplasia of one/ both clavicles
- Hypermobility of shoulder joints
- Elongated frontal and occipital skull plates
- Underdeveloped entire mid-face
- Delayed closure of fontanelles
- High and narrow arched palate
- Underdeveloped paranasal sinuses
- Photophobia
- Multiple unerupted and impacted teeth
Cleidocranial dysplasia Radiographic Features:
- Open sutures
- Open fontanelles
- Partial/complete loss of clavicles
- Multiple impacted teeth
- Thin roots of teeth
Question 6. Etiopathogenesis and Histopathology of cherubism
Answer:
Cherubism: It is a rare benign hereditary condition characterized by bilaterally symmetrica] enlargement of the mandible
Cherubism Etiopathogenesis:
- It results due to
- Anomalous development of bone
- Latent hyperparathyroidism
- Hormone dependent neoplasm
- Trauma
- Disturbance in the development of bone-forming mesenchyme
Cherubism Histopathology:
- The presence of numerous multinucleated giant cells
- Stroma consists of a large number of spindle-shaped fibroblasts
- Numerous small vessels and capillaries are present
- They are lined by endothelial cells and perivascular cuffing
- Advanced lesions show
- Increase in fibrous tissue
- Decrease in giant cells
- Formation of new bone
Question 7. MPDS
Answer:
MPDS
- It is a disorder characterized by facial pain limited to mandibular function, muscle tenderness, joint sounds, absence of significant organic and pathologic changes in TMJ
- It may be due to functional derangement of dental articulation, psychological state of mind, or physiological state of the joint
- Coined by Laskin
MPDS Etiology:
- Extrinsic factors
- Occlusal disharmony
- Trauma
- Environmental influences
- Habits
- Intrinsic factors
- Internal derangement of TMI
- Anterior locking of disc
- Trauma
MPDS Features:
- Unilateral preauricular pain
- Dull constant sound
- Muscle tenderness
- Clicking noise
- Altered jaw function
- Absence of radiographic changes
- Absence of tenderness in ext. auditory meatus
MPDS Management:
- Reassurance
- Soft diet
- Occlusal correction: 7 ‘R’s
- Remove-extract the tooth
- Reshape grind the occlusal surface
- Reposition orthodontically treated
- Restore conservative treatment
- Replace by prosthesis
- Reconstruct TMJ surgery
- Regulate control habits
- Isometric exercises
- Opening and closing of mouth 10 times a day
- Medicaments
- Aspirin: 0.3-0.6 gm/ 4 hourly
- NSAIDS: for 14-21 days
- Pentazocine: 50 mg/ 2-3 times a day
- Heat application
- It increases circulation
- Diathermy
- Causes heat transmission to deeper tissues
- LA injections
- 2% lignocaine into trigger points
- Steroid injection
- As anti-inflammatory
- Anti-anxiety drugs
- Diazepam-2-5 mg * 10 days
- TENS
- Acupuncture
Question 8. Cherubism
Answer:
Cherubism
It was described by Jones in 1933
Cherubism Classification:
- Based on the severity and location of the lesion
- Grade 1- Affects Minus of the mandible
- Grade 2- Affects ramous and body of the mandible and maxillary tuberosity
- Grade 3 – after maxilla ami mandible entirely
Cherubism etiology:
- Autosomal dominant trail latent hyperparathyroidism
- Trauma
- Disturbance in bone-forming mesenchymal
Cherubism Clinical Features:
- Age and sex- 2-3 years males are affected
- Site-angle of mandible bilaterally
- Bilateral, painless, symmetrical swelling giving a chubby appearance
- Swelling is firm to hard in consistency
- Maxillary swelling causes pressure over the floor of the orbit
- Due to this, pupils turn upwards giving a “heavenward look”
- Difficulty in speech, deglutition, mastication, and respiration
- Limited jaw movements
- Expansion and widening of alveolar ridge
- Flattening of palatal vault
- Chronic lymphadenopathy
- Malocclusion
Question 9. Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Answer:
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
It is a genetically transmitted disease of bone characterized by defective matrix formation and lack of mineralization
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Clinical Features:
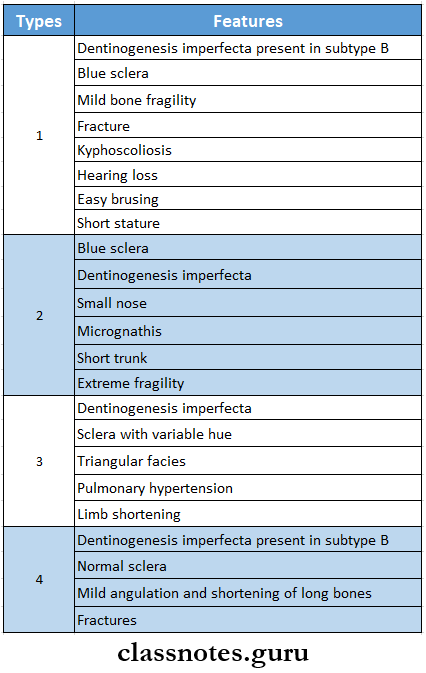
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Oral Manifestations:
- Large head
- Frontal bossing
- Maxillary hypoplasia
- Bulbous crowns of teeth
- Class 3 malocclusion
- Severe attrition of deciduous teeth
- Multiple impacted permanent teeth
- Increased incidence of osteomyelitis
Question 10. Osteopetrosis
Answer:
Osteopetrosis
- It is also known as marble disease
- It is a rare bone disorder characterized by increased bone density
Osteopetrosis Clinical Features:
- Decreased bone marrow activity leading to anemia, leukopenia, and pancytopenia
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Deafness, blindness, and facial paralysis due to narrowing of cranial foramina
- Defective enamel formation
- Short roofs
- Pathological fractures
- Increased incidence of osteomyelitis
Question 11. Blue sclera
Answer:
Blue sclera
- Blue sclera is due to unusually transparent or thin sclera which causes increased visibility of choroids
- It is seen in
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Marfan syndrome
- Cherubism
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- Osteopetrosis
- Fetal rickets
- Normal infants
Question 12. Leontiasis ossa
Answer:
Leontiasis ossa
The involvement of facial bones in Paget’s disease is known as leontiasis ossa
Leontiasis ossia Features:
- Progressive enlargement of the maxilla
- Widening of alveolar ridges
- Loosening of teeth
- Flattening of palate
- Mouth remains open
- In edentulous patients, there is difficulty in wearing dentures
Question 13. Albright’s syndrome
Answer:
Albright’s syndrome Features:
- Common in females
- It is a severe form of fibrous dysplasia involving nearly all the bones in the body
- It is accompanied by pigmentations of the skin and endocrine disorders
- Endocrine disorders
- Precocious puberty
- Goitre
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Cushing’s syndrome
- Acromegaly
- Skin lesions
- These are coffee with milk color spots
- There is an irregular flat area of increased skin pigmentation
- Vaginal bleeding occurs
- Long bones are frequently affected
Question 14. Marfan’s syndrome
Answer:
Marfan’s syndrome
It is a hereditary syndrome
Marfan’s Syndrome Clinical Features:
- Long, thin extremities resembling spider fingers
- Hyperextensibility of joints
- Habitual dislocations
- Kyphosis
- Aortic regurgitation
- Cardiac aneurysm
- Mitral valve prolapse
- Myopia, cataract
- Retinal detachment
- Psychological trauma
Marfan’s Syndrome Oral Manifestations:
- Long and narrow face
- High arched palate
- Bifid uvula
- Presence of multiple odontogenic cysts
- Malocclusion
- Temporomandibular joint dysarthrosis
Question 15. Mandibulofacial dysostosis
Answer:
Mandibulofacial dysostosis
It is a hereditary- disease characterized by defects in structures derived from 1st and 2nd branchial arches
Mandibulofacial dysostosis Clinical Features:
- Malformation of the external ear- the absence of an external auditor canal, deformity in the middle and internal ear
- Antimongoloid palpebral fissures
- Coloboma of the outer portion of lower eyelids
- Hypoplasia of the mandibular body and zygoma
- Narrow face and depressed cheek
- Results in bird-face appearance
- Crowding and malocclusion of teeth
- High arched palate
- Atypical hair growth
- Parotid hypoplasia
- Narrowing of larynx and trachea
- Difficulty in speech and respiration
Question 16. Serum alkaline phosphatase
Answer:
Serum alkaline phosphatase
- Alkaline phosphatase occurs in many tissues of the body, especially in osteoblasts
- It is elevated in
- Malignancy
- Abscess of liver
- Amyloidosis
- Leukemia
- Sarcoidosis
Question 17. Pierre Robin syndrome
Answer:
Pierre Robin syndrome
It is a hereditary disease
Pierre Robin syndrome Features:
- Mandibular micrognathia giving bird face appearance
- Downward and backward placement of tongue
- Difficulty in breathing, airway maintenance, feed- ind and speech
- Malocclusion of teeth
- Presence of multiple missing teeth or supernumerary teeth
- Absence of TMJ
- Mongolism
- Congenital heart defects
- Hydrocephaly, microcephaly
- Mental retardation
- Psychological trauma
Question 18. Cotton wool appearance
Answer:
Cotton wool appearance
- Cotton wool appearance is a radiographic feature of Paget’s disease
- In the later stage of the disease, new bone is formed in the present radiolucent areas
- It results from thickened, disorganized trabeculae which lead to areas of sclerosis in previously lucent areas of bone
- These areas are poorly calcified
Question 19. Peaud orange radiographic appearance
Answer:
Peaud orange radiographic appearance
- It is seen in the later stage of fibrous dysplasia
- Initially, there is the presence of unilocular or multi-locular radiolucent areas
- Later quite opaque areas develop due to delicate trabeculae
- This results in a proud orange or orange peel appearance
- It is not well-circumscribed
- Its margins blend with the surrounding bone
Question 20. Down syndrome
(or)
Trisomy 21
Answer:
Down syndrome
- Down’s syndrome/trisomy 21/mongolism affects approximately 1 in 1000 births.
- It is the most common chromosomal disorder and is the commonest cause of mental retardation.
Down syndrome or Trisomy 21 Etiology:
- Late maternal age
- Nondisjunction of chromosome 21 during an early stage of embryogenesis.
Down Syndrome or Trisomy 21 Clinical Features:
- Epicanthal folds and flat facial profile,
- Slanting eyes produce a mangoloid appearance.
- Hands are short with a transverse single palmar crease.
- Abnormalities of ears, trunk, pelvis, and phalanges
- Cardiac malformations
- Congenital malformations are common and quite disabling
- Risk of developing acute leukemia, especially megakaryocytic leukemia.
Down syndrome or Trisomy 21 Oral Manifestation:
- Deficient maxilla- class 3 relation,
- Open mouth,
- Large tongue,
- Caries free teeth due to excess salivation.
Question 21. Brown tumor
Answer:
Brown tumor
- The brown tumor is also known as hyperparathyroidism
- It is an endocrine disorder occurring due to an excess of circulating parathyroid hormone
Brown tumor Types:
- Primary hyperparathyroidism
- Occurs due to tumour of glands
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism
- Occurs in response to hypocalcemia
- Tertiary hyperparathyroidism
- Occurs after long-standing secondary hyperparathyroidism
Brown Tumour Clinical Features: Age and sex- common in middle-aged women
- Classic triad
- Kidney stones
- Bone resorption
- Duodenal ulcers
- Renal symptoms
- Renal calculi
- Hematuria
- Back pain
- Psychological symptoms
- Emotionally unstable
- GIT symptoms
- Anorexia
- Nausea, vomiting
- Skeletal
- Bone pain
- Pathologic fractures
- Bone deformities
- Hypercalcaemia
- Generalised symptoms
- Muscle weakness
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Insomnia
- Headache
- Polydipsia and polyuria
- Oral manifestations
- Intraoral and extraoral swelling
- Gradual loosening of teeth
- Drifting and loss of teeth
- Malocclusion
Question 22. Philadelphia chromosome
Answer:
Philadelphia chromosome
- Philadelphia chromosome is the translocation of chromosomal material from chromosome 22 to chromosome 9
- It is seen in leukemic patients
Question 23. Cafe au lait spots
Answer:
Cafe au lait spots
- Cafe-au-lait spots are pigmented macules
- They are arranged in linear or segmental patterns near the midline of the body
Diseases with Cafe-Au-Lait Spots are:
- Albright syndrome
- Von Recklinghausen’s neurofibromatosis
- Bloome’s syndrome
- Fanconi’s anaemia
- Cowden’s syndrome
- Tuberculosis sclerosis
- Watson’s syndrome
- Ataxia telangiectasia
Diseases Of Bone And Joints Viva Voce
- Pathognomic feature of osteogenesis imperfecta is blue sclera
- Ankylosis means stiff joint
- Cotton wool appearance is seen in Paget’s disease
- Ground glass appearance is seen in monostotic fibrous dysplasia
- Mosaic bone and jigsaw puzzle appearance is seen in Paget’s disease
- Chinese letter appearance is seen in Monostotic fibrous dysplasia
- The brown tumor occurs due to an excess of circulating parathyroid hormone
- Philadelphia chromosome is the translocation of chromosomal material from chromosome 22 to chromosome 9
