Disease Of The Hepatobiliary System Important Notes
- Hepatic Carcinoma
- Hepatic Carcinoma is cancer of the liver
- Hepatic Carcinoma Etiology
- Hepatitis B and C
- Cirrhosis of liver
- Wilsons disease
- Haemochromatosis
- Estrogen and androgen
- Anabolic steroids
- Alcohol
- Hepatic Carcinoma Clinical Features
- Yellow skin
- Bloating from fluid in the abdomen
- Easy bruising
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea, vomiting
- Fatigue
- Polycythemia
- Hypoglycaemia
- Hypercalcemia
- Liver Abscess
- It is a pus-filled mass inside the liver
- Liver Abscess Etiology
- Portal vein bacteremia
- Systemic bacteremia
- Ascending cholangitis
- Penetrating trauma
- Direct extension from focus of infection
- Liver Abscess Clinical features
- Jaundice
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea, vomiting
- Dark urine
- Clay-colored stools
- Fever with chills
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Weakness
- Jaundice
- The yellow pigmentation of the skin, mucous membrane & deeper tissues due to increased bilirubin levels in blood is called jaundice
- It occurs when the bilirubin level exceeds 2 mg%
- Jaundice Types:
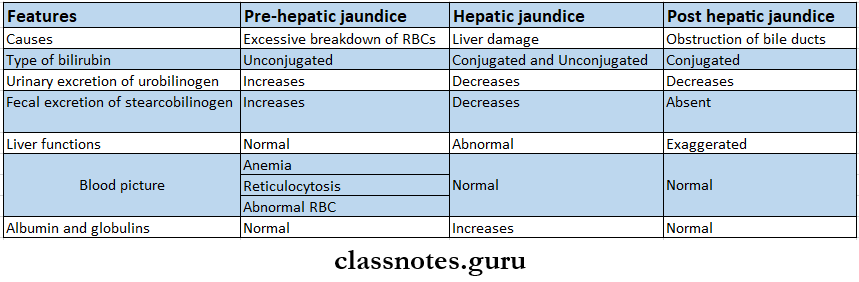
- Cirrhosis Of The Liver – Features
- Jaundice
- Hepatomegaly
- Ascites
- Spider telangiectasia
- Loss of libido
- Gynaecomastia
- Bruises, epistaxis
- Portal hypertension
- Clubbing
- Ascites
- It is an abnormal collection of fluid in the peritoneum
- Clinical features
- Abdominal enlargement
- Stretching sensation
- Low back pain
- Indigestion
- Heart bum
- Dyspnoea or tachypnoea
- Abdominal or inguinal hernia
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Ascitic Fluid In Different Diseases
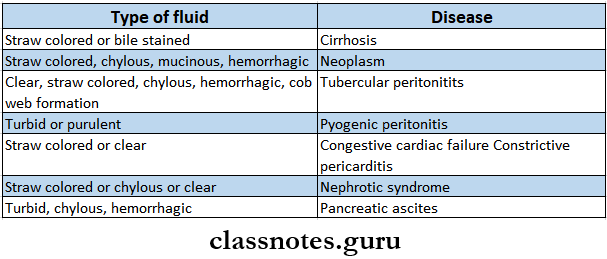
- Hepatic Encephalopathy
- It is a neuropsychiatric syndrome caused by liver disease
- Precipitating factors
- Infection
- Hypokalaemia
- Constipation
- GI bleeding
- Dehydration
- Drug
- Trauma
- Hepatomegaly
- Hepatomegaly Cause
- Hepatomegaly Vascular
- Congestive cardiac failure
- Hepatic vein thrombosis
- Hemolytic anemia
- Hepatomegaly Bile duct obstruction
- Stone
- Tumour
- Hepatomegaly Infiltrative
- leukemia
- Lymphoma
- Fatty liver
- Fat storage disease
- Amyloidosis
- Hepatomegaly Vascular
- Hepatomegaly Cause
Read And Learn More: General Medicine Question and Answers
- Parasitic
- Malaria
- Kala-azar
- Hydatid disease
- Inflammatory
- Hepatitis
- Typhoid fever
- Tumor
- Rare
- Polycystic disease of the liver
- Parasitic
- Types Of Liver Enlargement
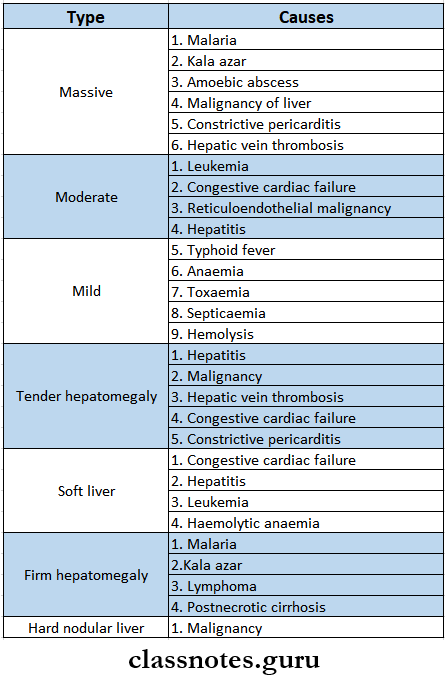
- Splenomegaly
- Splenomegaly Causes
- Infection
- Bacterial – endocarditis, tuberculosis
- Viral – hepatitis, AIDS
- Protozoal – malaria
- Spirochaetal – syphilis
- Fungal – Histoplasmosis
- Inflammatory
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Sarcoidosis
- Congestive splenomegaly
- Portal hypertension
- Hepatic vein thrombosis
- Pericardial effusion
- Hemolytic disorders
- Spherocytosis
- Thalassaemia
- Infiltrative diseases
- Amyloidosis
- Acute leukemia
- Miscellaneous
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Idiopathic
- Sarcoidosis
- Infection
- Splenomegaly Causes
Hepatobiliary diseases short essay
Disease Of The Hepatobiliary System Short Essays
Question 1. Hepatitis A.
Answer:
Hepatitis A
It is caused by the Hepatitis A virus.
Hepatitis A Mode of Transmission:
- Faeco-oral route.
- Contaminated water and milk.
- Blood transfusion.
- Homosexual activity.
Hepatitis A Clinical Features:
- Incubation period 15-45 days.
- Prodromal symptoms – Anicteric phase.
- Icteric phase.
- Recovery phase.
Hepatitis A Investigations:
- Serum transaminases – Rises.
- Serum bilirubin – Rises (5 – 20 mg %)
- Leucocytosis, neutropenia.
- Prothrombin time – normal or prolonged.
- Scrum alkaline phosphatase – normal.
- Urine urobilinogen – Increased.
- Bile salts and bile pigments – Appears in urine.
- Ultrasound – shows an enlarged liver.
Hepatitis A Treatment:
- Bed rest.
- High protein and high carbohydrate intake.
- 4 glucose administration. n Avoid hepatotoxic drugs.
- Use of H2 blockers and antacids.
Question 2. Hepatitis E.
Answer:
Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E is caused by hepatitis E virus.
Hepatitis E Etiology:
- Poor hygiene and sanitation.
- Mode of transmission – Faeco – oral route.
Hepatitis E Clinical Features:
- Incubation period – 3 – 8 weeks.
- Hepatitis E does not progress to chronicity.
Hepatitis E Diagnosis:
- Detection of anti-HEV antibodies,
- IgM – during the early phase.
- IgG – after recovery.
Liver disease short essay questions
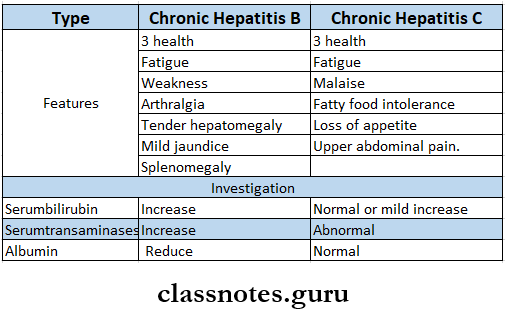
Question 3. Chronic active hepatitis.
Answer:
Chronic active hepatitis
Chronic hepatitis is defined as any hepatitis lasting 6 months or longer.
Chronic active hepatitis Causes:
- Infective.
- Hepatitis B, C, and D.
- Toxic.
- Drugs – alpha – methyldopa, isoniazid.
- Alcohol.
- Metabolic.
- Hemochromatosis.
- Wilson’s disease.
- Other
- Autoimmune hepatitis.
Question 4. Discuss the etiology and clinical features of ascites.
Answer:
Ascites: Abnormal collection of fluid in peritoneum e c.tll< d ascites.
Ascites Etiology:
- Systemic causes.
- Nephrotic syndrome.
- Cirrhosis of liver
- Hypoproteinaemia.
- Congestive cardiac failure.
- Malignancy of the liver.
- Local causes.
- Peritonitis
- Tuberculosis.
- Pancreatitis.
Ascites Clinical Features:
- Abdominal enlargement.
- Stretching sensation
- Low back pain
- Indigestion, heartburn
- Dyspnoea or tachypnoea.
- Abdominal or inguinal hermia.
- Hepatosplenomegaly.
Question 5. Complications Of Hepatitis B
Answer:
Complications Of Hepatitis B
- Cirrhosis of liver
- Liver cancer
- Liver failure
- Chronic renal diseases
Gallbladder diseases short notes
Question 6. Obstructive jaundice – investigation.
Answer:
Obstructive jaundice – investigation
- Hemoglobin level – normal.
- Bile Salts and bile pigment.
- Present in urine
- Absent in stools
- Bilirubin – raised, conjugated.
- Serum cholesterol – raised.
- Serum alkaline phosphate – raised
- Serum transaminase – mildly raised.
- USG – shows dilatation of intrahepatic and extra-hepatic biliary system.
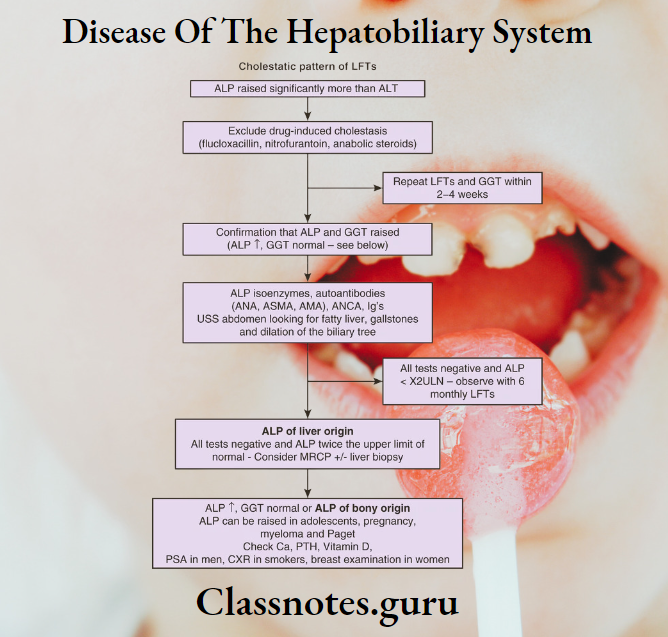
Question 7. Hepatomegaly.
Answer:
Hepatomegaly
Enlargement of the liver is called hepatomegaly.
Hepatomegaly Causes:
- Vascular changes.
- Congestive cardiac failure.
- hepatic vein thrombosis
- hemolytic anemia.
- Bile duct obstruction
- Due to stone, tumour.
- Infiltrative causes.
- leukaemia.
- Lymphoma
- Fatty liver
- Amyloidosis.
- Parasitic infection.
- Malaria
- Kala-azar
- Amoebic liver abscess
- Inflammatory disease
- hepatitis
- Typhoid fever.
- Tumors
- Primary or secondary in River.
Hepatic failure short essay
Question 8. Tender hepatomegaly – causes.
Answer:
Tender Hepatomegaly Causes:
- Hepatitis
- Malignancy
- Hepatic vein thrombosis
- Congestive cardiac failure
- Constrictive pericarditis.
Question 9. Hepatitis B – prevention.
Answer:
Hepatitis B – prevention
Two HBV vaccines are available.
- Recombivax HB
- Engerix – B
- 3 injections of it are administered over six months.
Hepatitis B – Prevention Recommended For:
- All infants at birth
- Children – 18 years or above who have not been vaccinated previously.
- Anyone who is undergoing treatment for sexually transmitted disease.
- Injection drug users.
- People with chronic liver diseases
- Residents and staff for developmentally disabled individuals.
- Hemodialysis patients.
- People living with HIV.
Question 10. Hepatitis C.
Answer:
Hepatitis C
Caused by hepatitis C, RNA virus.
Hepatitis C Route of Transmission:
- Blood transfusions.
- 4 drug user
- Sexual transmission.
Hepatitis C Clinical Features:
- Incubation period – 45 – 50 days.
- Insidious in onset.
- Produces moderate hepatitis.
- Occurs in all age groups.
- It leads to.
- Vasculitis.
- Arthritis
- Glomerulonephritis.
- Cryoglobulinaemia.
- Its chronicity leads to
- Cirrhosis of liver
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Liver failure.
Question 11. Complications of cirrhosis of the liver.
Answer:
Complications Of Cirrhosis Of The Liver
- Portal hypertension
- Hepatic
- encephalopathy
- Hepatorenal syndrome.
- Hepatic cell carcinoma.
- Fulminant septicaemia.
- Fatal bleeding.
- Peritonitis.
Question 12. Portal hypertension.
Answer:
Complications Of Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Complications Of Cirrhosis Of The Liver is defined as prolonged elevation of portal venous pressure above normal levels.
Portal Hypertension Causes:
- Prehepatic causes.
- Portal vein thrombosis.
- Intrahepatic causes.
- Cirrhosis.
- Congenital hepatic fibrosis.
- Drugs.
- Sarcoidosis.
- Secondaries in the liver.
- Post hepatic causes.
- Budd-Chiari syndrome
- Right heart failure.
Portal Hypertension Clinical Features:
- Haemetemesis or malena.
- Ascites,
- Splenomegaly.
- Fetor hepaticus.
- Chronic hepatic encephalopathy.
Portal hypertension short essay notes
Question 13. Hepatic encephalopathy.
Answer:
Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatic Encephalopathy is a syndrome of mental and neurological features that occur in patients with long-standing cirrhosis with or without portal hypertension.
Hepatic Encephalopathy Clinical Features:
- Impaired celebration.
- Moderate to severe jaundice.
- Fetor hepaticus.
- Flapping tremors.
- Cirrhosis.
- Portal hypertension.
- Fever
- Tachycardia.
- Hyperventilation.
- Hypotension.
Question 14. Spider nevi.
Answer:
Spider Nevi is one of the features occurring due to arteriolar changes induced hyperestrogenism.
- They are dilated central arterioles with radiating small vessels.
Spider Nevi Parts Involved:
- Parts drained by superior vena cava.
- Head
- Neck
- Upper limbs
- Front and back of the chest.
- Size: Varies from 1- 2 mm to 1 – 2 cm in diameter.
- Seen In:
- Cirrhosis of liver
- Chronic hepatic dysfunction.
Question 15. Splenomegaly-causes.
Answer:
Splenomegaly-Causes
- Infective disorders.
- Bacterial – Endocarditis, tuberculosis, septicaemia.
- Viral – Hepatitis, AIDS.
- Protozoal malaria.
- Spirochaetal – syphilis.
- Fungal – Histoplasmosis.
- Inflammatory disorders.
- Rheumatoid arthritis, sarcoidosis.
- Congestive splenomegaly.
- Portal hypertension.
- Hepatic vein thrombosis.
- Pericardial effusion.
- Hemolytic disorders.
- Spherocytosis, thalassemia.
- Infiltrative diseases.
- Amyloidosis.
- Gaucher’s disease
- Aclucleukemia.
- Miscellaneous.
- Iron deficiency anemia.
- Idiopathic
- Sarcoidosis.
VIVA VOCE
- Glucose is stored in the liver in the form of glycogen
- The liver utilizes amino acids for endogenous protein synthesis and plasma protein synthesis
- Conjugation of unconjugated bilirubin occurs in liver cells with the help of glucuronyltrans- phrase
- Kupffer cells are derived from blood monocytes and have immunological functions
- Normal bilirubin level – 0.3-1.0 mg/dl
- Normal alkaline phosphatase level – 25-115 U/L
- Normal acid phosphatase level – 1-5 U/l
- The normal prothrombin time index is 100%
- Transudative ascites is seen in cirrhosis of the liver
- Blood-stained ascites are seen in malignant infiltration of the peritoneum
- Milky ascites is seen in ductal obstruction
- Exudative ascites are seen in TB, malignancy, and hepatic vein obstruction
- Serum bilirubin level more than 2.5 mg/dl leads to jaundice
- Potassium-sparing diuretics are used in ascites
- Budd Chiari syndrome occurs from occlusion of the hepatic vein
- Collection of fluid more than 300 ml in the peritoneum leads to ascites
