Working Length Determination Important Notes
- Methods for determing working length
- Radiographic
- Grossman formula
- Ingle’s method
- Weine’s method
- Kutler’s method
- Radiographic grid
- Xeroradiography
- Digital radiography
- Subtraction radiography
- Non-radiographic
- Digital tactile sense
- Paper point method
- Electronic Apex locators
- Radiographic
- Grossman’s method
- An instrument is placed in the root canal and a radiograph is taken
- By measuring the length of radiographic images of both the tooth and measuring instrument as well as actual length of the instrument, the clinician can determine the actual length of the tooth by formula
∴ \(\frac{\text { Actual length of tooth }}{\text { Actual length of instrument }}=\frac{\begin{array}{c}
\text { Apparent length of } \\
\text { tooth in radiograph }
\end{array}}{\begin{array}{c}
\text { Apparent length of } \\
\text { instrument in radiograph }
\end{array}}\)
- Apex locators

Endodontic Working Length Determination
Working Length Determination Long Essays
Question 1. Mention various methods to determine working length and describe any one in detail.
Answer.
Working Length Determination
Various Methods To Determine Working Length And Describe Any One In Detail
Working Length: The distance from a coronal reference point to a point at which canal preparation and obturation should terminate.
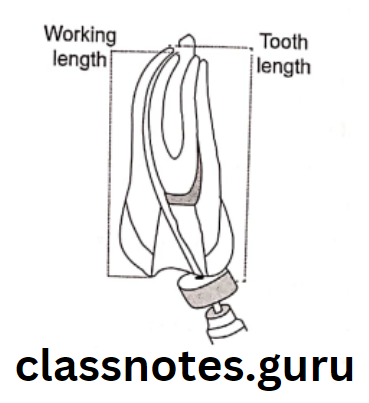
Methods:
- Radiographic:
- Grossman formula
- Ingle’s method
- Weine’s method
- Kutler’s method
- Radiographic grid
Read And Learn More: Endodontics Question and Answers
- Xeroradiography
- Digital radiography
- Subtraction radiography
- Non-radiographic
- Digital tactile sense
- Paper point method
- Electronic Apex locators
- Radiographic Method:
Method:
- The Rule For Subtraction:
- No resorption – 1mm
- Bone resorption – 1.5mm
- Bone and root resorption – 2mm
- Advantages:
- The following can be viewed
- Anatomy of tooth
- Curvature of canal
- Relationship with adjacent structures
- The following can be viewed
- Disadvantages:
- Observation variation
- Superimposition
- Two-dimensional view
- Time-consuming
- Radiation exposure
- The Rule For Subtraction:
- Grossman Method:
\text { Apparent length of } \\
\text { tooth in radiograph }
\end{array}}{\begin{array}{c}
\text { Apparent length of } \\
\text { instrument in radiograph }
\end{array}}\)
- Kuttler’s Method:
- Narrow canal – 10-15 no. file
- Average – 20-25 no. file
- Wide – 30-35 no file
Radiographic Grid: Millimeter grid superimposed on radiograph
- Endometric Probe:
Working Length In Endodontics
Working Length Determination Short Essays
Question 1. Nonradiographic methods for working length determination.
Answer.
Non Radiographic Methods
- Non Radiographic Methods Non Radiographic Methods Paper Point Method:
Steps:- Introduce paper-points inside the apex
- Leave it for 1 min
- Remove paper point
- Observe it
- When paper point penetrates the periodontium, the paperpoint will be wet
- Measure the length of dry part
Disadvantages: - Incorrect determination
- Can be easily curved
- Non Radiographic Methods Tactile Method:
- Introduce the file till it stops
- Mark the level with stopper
- Take smaller file
- Introduce it into canal
- Repeat steps and compare it with larger file
- Steps are repeated till 2 files measure same length
- Non Radiographic Methods Apical Periodontal Sensitivity:
- Introduce smallest file into canal
- It may go deeper and file slip very easily
- At this moment the patient feel pain
- This means file reaches periodontal tissues
Apical Periodontal Sensitivity Advantages: - Doesn’t require special devices
- Cheaper
- Very quick method
- Easy to perform
Apical Periodontal Sensitivity Disadvantages: - Incorrect
- Destroys periodontal tissues
- Apex Locators:
Apex Locators Uses:- As adjacent to radiograph
- Used to locate apical constriction or CDJ or apical foramen
Apex Locators Components: - Lip clip
- File clip
- Electronic devices
- Cord connecting them
Apex Locators Advantages: - Use for pulp vitality
- Objective
- Accurate
Apex L - ocators Disadvantages:
- Over estimated
- Problematic in immature apex
- Inaccurate in cases of
- Presence of pulp tissue in canal
- Blockage
- Narrow file
- Low battery
Apex Locator In Endodontics
Question 2. Electronic Apex Locaters.
Answer.
Electronic Apex Locaters Uses:
- As adjacent to radiograph
- Used to locate apical constriction or CDJ or apical foramen
Electronic Apex Locaters Components:
- Lip clip
- File clip
- Electronic devices
- Cord connecting them
Working Length Determination
Electronic Apex Locaters Advantages:
- Use for pulp vitality
- Objective
- Accurate
Electronic Apex Locaters Disadvantages:
- Over estimated
- Problematic in immature apex
- Inaccurate in cases of
- Presence of pulp tissue in canal
- Blockage
- Narrow file
- Low battery
Contradictions: Patient with cardiac pacemakers.
Classification:

Question 3. EDTA
Answer.
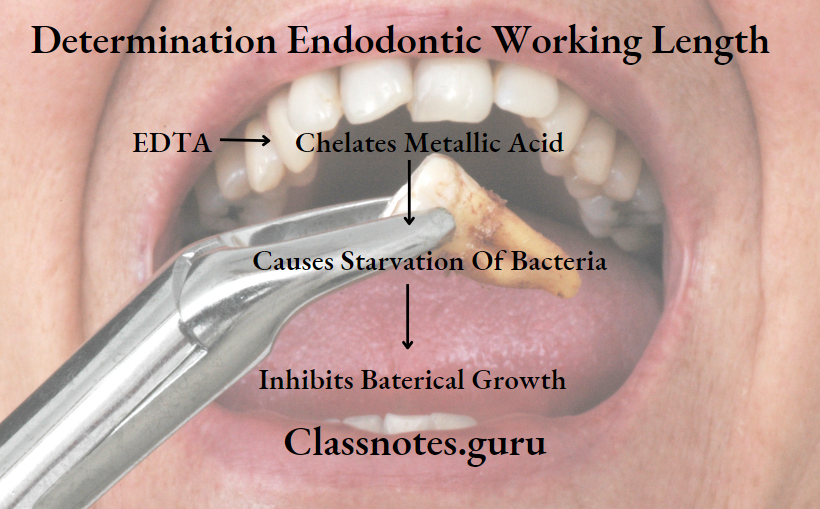
EDTA
EDTA is chelating agent
EDTA Properties:
- The effect depends on its concentration
- Non-toxic
- Optimal cleansing and shaping of canals
EDTA Functions [HELS]:
- Hold debris in suspension
- Emulsification
- Lubrication
- Smear layer removal
EDTA Mechanism:
EDTA Uses:
- Time saver
- Easier Manipulation of Instruments
- Dissolve dentin
- Enlarges canals
EDTA Forms:
- EDTAT
- EDTA-C
- Rc Prep
- R.EDTA
Root Canal Working Length Methods
Question 4. Sodium Hypochlorite.
Answer.
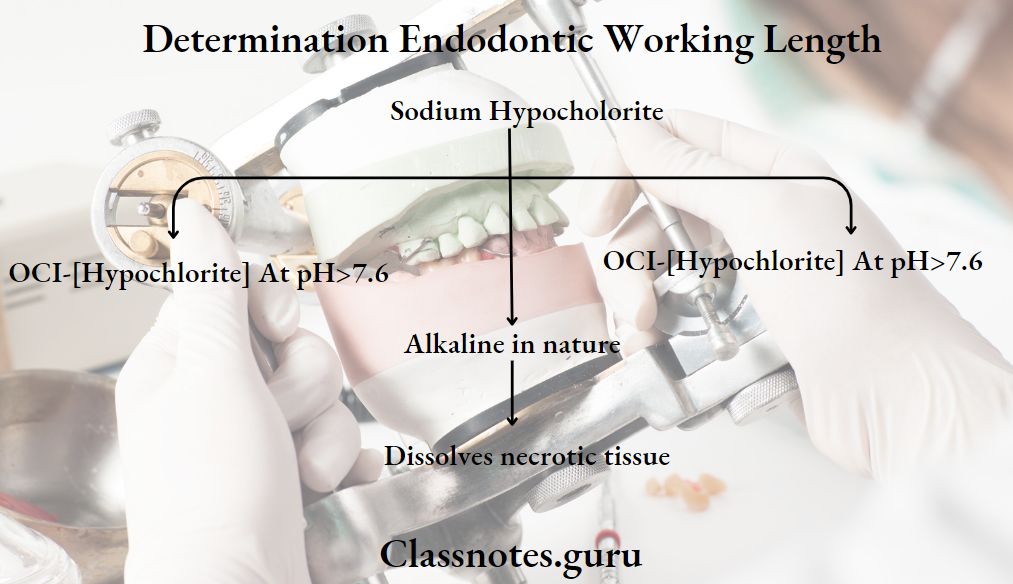
Sodium Hypochlorite
- Sodium Hypochlorite a clear, pale, green-yellow liquid
- Strong odor of chlorine
- Easily miscible with water
- Decomposes by light
Sodium Hypochlorite Mechanism:
Factors Affecting Sodium Hypochlorite Activity:
- Sodium Hypochlorite Activity Increases:
- Volume of solution
- Heating of solution
- Time of contact
- Sodium Hypochlorite Activity Decreases:
- Storage time
- EDTA
Advantages: - Dissolve tissue
- Antibacterial and bleaching action
- Lubricate canal
- Economical
Disadvantages: - High surface tension
- Irritate tissue
- Irritate eyes
- Causes inflammation of the gingiva
- Bleaches clothes
- Bad odour and taste
- Corrosive to instruments
Sodium Hypochlorite Activity Combine With:
Working Length Determination
- Calcium hydroxide
- EDTA
- Chlorhexidine
Radiographic Determination Of Working Length
Working Length Determination Short Answers
Question 1. Apex locators – generations.
Answer.
Apex Locators – Generations

