Oral Medicine Dermatological Diseases Important Notes
1. Various Findings Of Dermatological Diseases
2. Ectodermal Dysplasia
- It is congenital dysplasia of ectodermal structures
- Manifested as hypohidrosis, hypotrichosis and hypodontia
3. Pemphigus
- Histological Features:
- There is a formation of vesicles or bullae intraepithelial just above the basal layer producing suprabasal split c
- Intercellular bridges in suprabasal layers disappear due to edema resulting in acantholysis
- Clumps of degenerating cells are found in vesicular areas called Tzanck cells
4. Scleroderma – Features
- Stiff and broad-like tongue
- Lips become rigid
- Microstomia
- Dysphasia
- Inability to open and close mouth
- Extreme widening of PDL
Read And Learn More: Oral Medicine Question and Answers
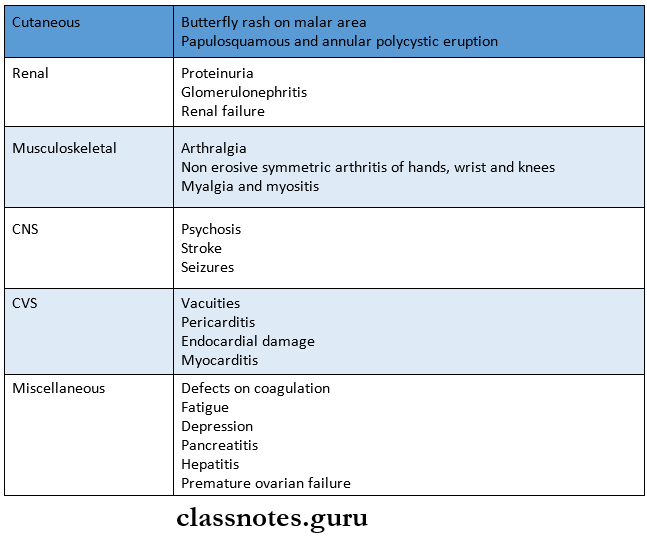
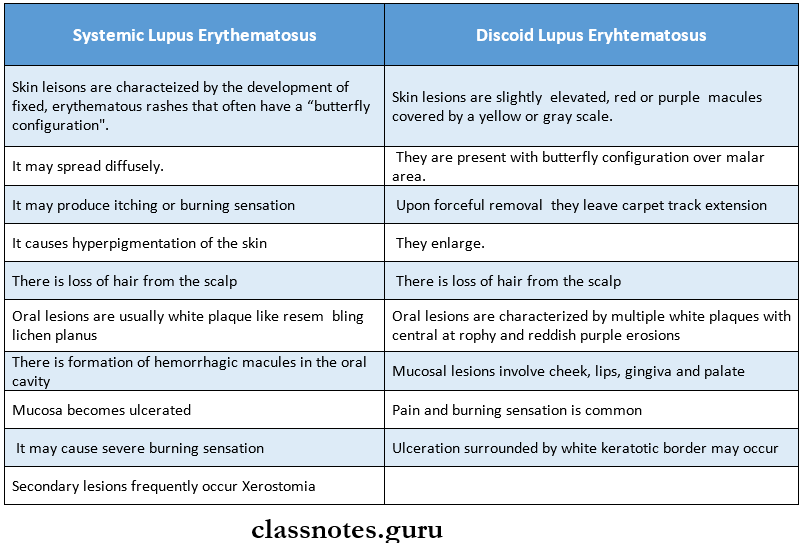
5. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- It is a multisystem inflammatory disorder
6. Steven Johnson Syndrome
- Severe bullous form of erythema multiforme involving the skin, eyes, oral cavity, and genitalia
7. Nikolsky’s Sign
- Loss of epithelium due to rubbing resulting in raw sensitive surface
- Seen in
- Pemphigus
- Familial benign chronic pemphigus
- Epidermolysis bullosa
8. Tzanck Cells
- They are multinucleated giant cells of epithelial origin
- Seen in
- Herpes
- Pemphigus
9. Bulla Are Seen In
- Intraepithelial Bulla
- Herpes simplex Herpes zoster Chicken pox Pemphigus
- Familial benign pemphigus
- Epidermolysis bullosa
- Oral lesions of eiythema multiforme
- Subepithelial Bulla
- Pemphigoid
- Bullous pemphigoid
- Bullous lichen planus
- Dermatitis herpetiformis
- Epidermolysis bullosa
- Skin lesions of erythema multiforme.
Oral Medicine Dermatological Diseases Short Essays
Question 1. Lupus Erythematosus.
Answer:
Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus Erythematosus is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the destruction of tissue due to the deposition of autoantibodies and immune complexes within it
Lupus Erythematosus Types:
Lupus Erythematosus Generalized symptoms
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Dysphagia
- Depression
- Splenomegaly
- Lymphadenopathy
- Leucopenia
- Arthritis
- Sjogren’s syndrome
- Raynond’s phenomenon
- Scleroderma
- Pemphigoid
- Pemphigus
- Erythema multiforme
Lupus Erythematosus Investigations:
- Anti-nuclear antibodies are present
- Anti-DNA antibodies are present
- Polyclonal hyperactivity of the B lymphocytes
- Decrease in the number of suppressor cells
- Leucopenia
- Thrombocytopenia
- Hemolytic anemia
- Hypergammaglobulinemia
- Profuse proteinuria
- Direct immunofluorescence
- It reveals deposition of IgG, IgA, and IgM in the base¬ment membrane zone
- Indirect immunofluorescence
- It reveals circulating auto-antibodies
Lupus Erythematosus Management:
- Systemic steroids are given
Question 2. Nikolsky’s Sign
Answer:
Nikolsky’s Sign is the diagnosis of pemphigus vulgaris
- It is demonstrated by applying gentle pressure over the bullae
- This results in the spreading of the lesion to the adjacent intact surface
- Contacting an intact surface after pressing the lesion will result in the formation of a new lesion
Oral Medicine Dermatological Diseases Short Answers
Question 1. Koplik’s spots.
Answer:
Koplik’s Spots
- Koplik’s Spots is one of the important clinical features of measles
- Site: buccal mucosa
- Presentation
- The mucosa becomes inflamed
- Over it, there is the presence of white or white-yellow pinpoint papules
Question 2. Four differences between pemphigus vulgaris and benign mucous membrane pemphigoid
Answer:
Differences Between Pemphigus Vulgaris And Benign Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
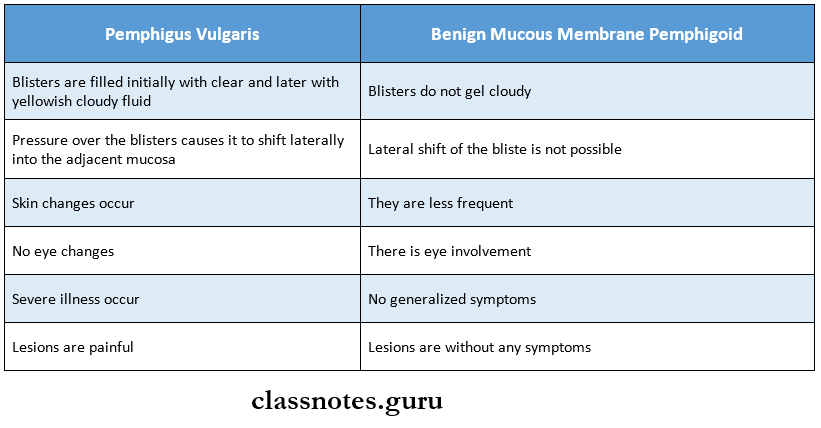
Question 3. Mucous membrane pemphigoid.
Answer:
Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid is a relatively uncommon vesiculobullous lesion
Rare Vesiculobullous Lesion Clinical Features:
- It usually produces mild erosion or desquamation of the gingival tissue
- Vesicles or bullae arise from mucosal areas that have become erythematous earlier
- In severe cases, large vesicles or bullae develop on the palate, cheek, alveolar mucosa, or tongue
- They are quite large
- They persist for several days
- They are often tense and are relatively tough
- Once the bullae rupture, they leave painful, eroded, or ulcerated areas that heal slowly
Question 4. Pemphigus Vegetans.
Answer:
Pemphigus Vegetans
- Pemphigus Vegetans is a common form of pemphigus lesion
Pemphigus Vegetans Types:
- Neumann type
- Hallopean type
Pemphigus Vegetans Clinical Features:
- Flaccid bullae appear
- They become eroded and form vegetation
- It becomes covered by purulent exudates
- It exhibits inflamed borders
- It terminates in pemphigus Vulgaris
Pemphigus Vegetans Oral Manifestations:
- Granular/ cobblestone appearance
- Gingival lesions are lace-like ulcers with purulent sur¬face on a red base or have a granular/ cobblestone appearance
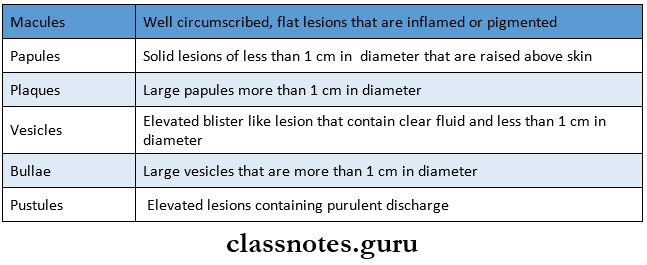
Question 5. Define Vesicle And Pustule.
Answer:
Vesicle:
Vesicles are elevated blisters containing dear fluid that are under 1cm in diameter
Pustule:
Pustule refers to loa raised lesion containing purulent material
Question 6. Target lesions
Answer:
Target Lesions
- Target lesions are a characteristic feature of erythema multiforme
- They appear on extremities
- They are concentric rings resulting from varying shades of erythema giving rise to target, iris, or Bullseye
- They may be purpuric or paler in the center
Question 7. Auspitz sign.
Answer:
Auspitz Sign
- Auspitz Sign is seen in psoriasis
- If the deep scales on the surface of the lesion are removed, one or two tiny bleeding points are often disclosed
- This phenomenon is known as the “Auspitz sign”
Oral Medicine Dermatological Diseases Viva Voice
- Nikolsky’s sign is a feature of Pemphigus
- Monro’s abscess is found in psoriasis
- Cicatricial pemphigoid primarily afr’ettc s
- Bull’s eye lesion is seen in erythema mar
- A butterfly rash is seen in systemic iu sese: (SLE)
- Antinuclear antibodies are a seer. in. SIS
- Kobner’s phenomenon is seen in Pen mar:
- Pemphigus vulgaris shows fish net pates immunofluorescence
