NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 9 Electricity And Circuits Long Question And Answers
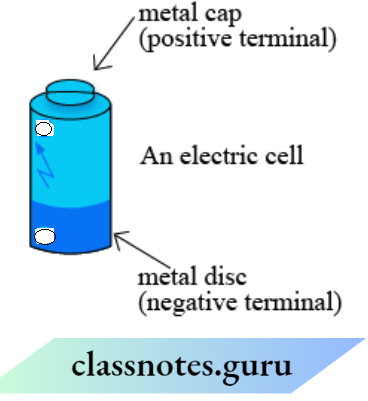
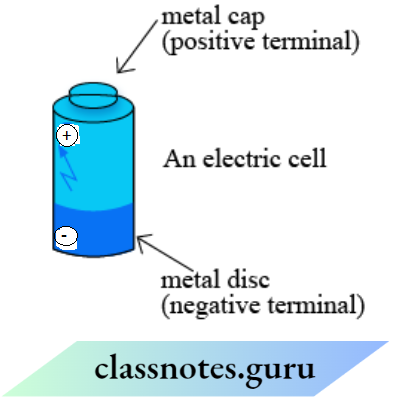
Question 1. The picture shows an electric cell. Fill In the blanks boxes with the correct symbol (+/-) to show the terminals
Answer:
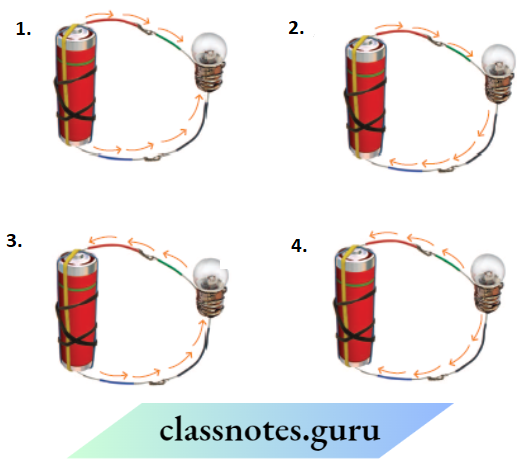
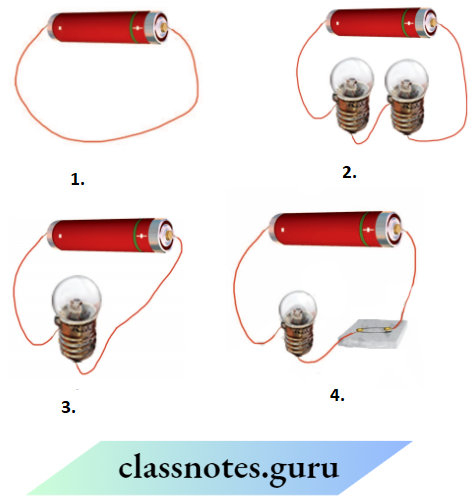
Question 2. Figures 1 and 2, show a bulb connected to a cell in two different ways
- Mention the direction of the current through the bulb in both cases
- Will the bulb glow in both cases?
- Does the brightness of the glowing bulb depend on the direction of current through it?
Read and Learn More Class 6 Science Question And Answers
Answer:
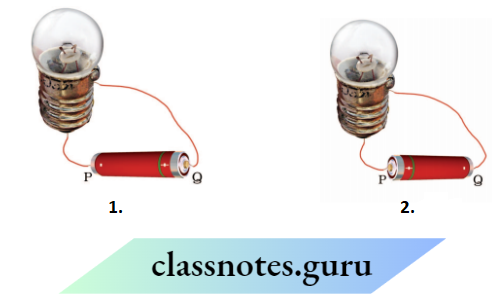
- The direction current will be from Q to P in A and the direction current will be from P to Q in B because the direction of current is always from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the cell or battery.
- Yes, the bulb will glow in both cases because to glow the bulb, we just need to complete the circuit.
- No, the brightness ofthe bulb never depends upon the direction of the current passing through it.

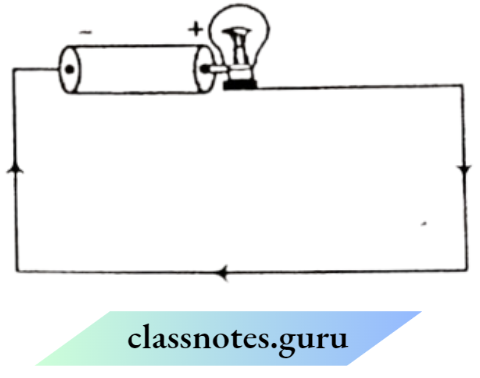
Question 3. Boojho has a cell and a single piece of connecting wire. Without cutting the wire in two, will he be able to make the bulb glow? Explain with the help of a circuit diagram.
Answer:
This can be done by arranging the circuit as in the given
diagram.
One terminal should be connected to the other terminal of the cell directly and the other terminal can be connected using the given wire
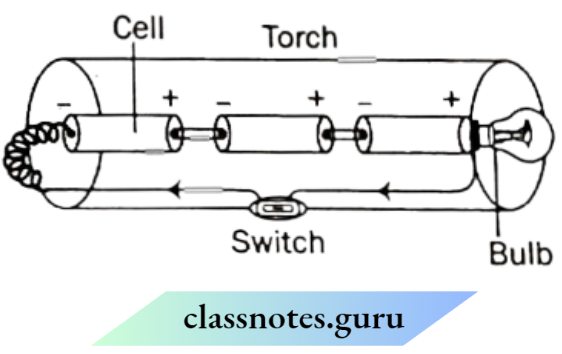
Question 4. A torch requires 3 cells. Show the arrangement of the cells with a diagram inside the torch, so that the bulb glows.
Answer:
The arrangement of the bulb should be such that the positive terminal of a battery touches the base of the bulb. When switched ON, bulb will glow.
Question 5. Explain why they would not glow in the arrangement
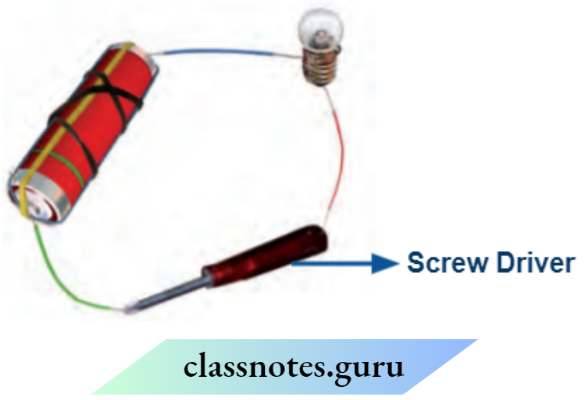
Answer:
Here, we must check two phenomena. One is the usage of conductors and the other is insulators which can stop the flow of electric current.
We observe that one end of the screwdriver is made up of metal and the other is made up of an insulator. Thus, electric current starts through one end but stops at the other end, and hence, current cannot flow through it. Thus, the bulb will not glow.
Question 6. Complete the drawing shown In the figure to Indicate where the free ends of the two wires should be joined to make the bulb glow

Answer:
To complete the circuit, we must join the one end of the wire with the free end of the cell. The other end of the wire must be connected to the bulb. Now, the bulb will glow.
Question 7. Paheli connected two bulbs to a cell as shown In the figure

She found that the filament of bulb B was broken. Will the bulb A glow in this circuit? Give reason.
Answer:
No, the bulb will not glow in the circuit because the filament of the bulb B is broken and current will not flow in the whole circuit, i.e. the circuit is broken or incomplete.
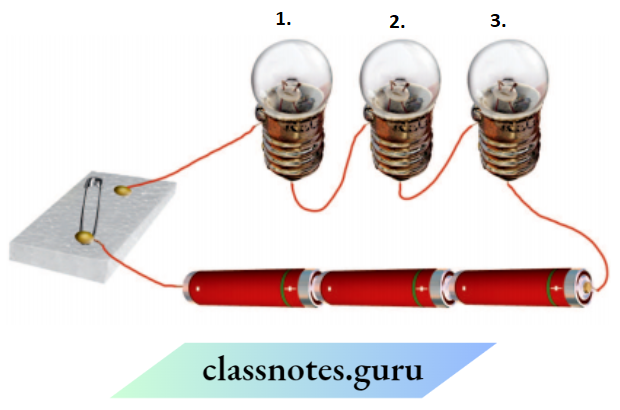
Question 8. In which of the following circuits 1, 2, and 3 given in the figure, the cell will be used up very rapidly?

Answer:
The cell will be used up rapidly in A because all the current will discharge through the wire very rapidly as any appliance is not connected between the positive and negative terminals.
Question 9. Will the bulb glow in the circuit shown in the figure? Explain
Answer:
As in the given circuit diagram, it seems that the switch is open, i.e. there is an air gap between the connecting wires, so the circuit is not complete and the bulb will not glow.
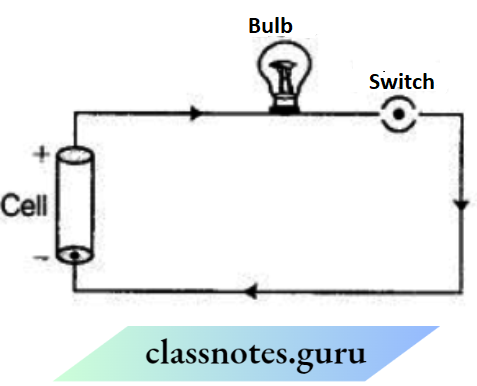
Question 10. You are provided with a bulb, a cell, a switch, and some connecting wires. Draw a diagram to show the connections between them to make the bulb glow.
Answer:
The complete circuit diagram, so that the bulb glows is given below
Question 11. Which of the following arrangements 1, 2, 3and 4 given In the figure should not be set up? Explain why,
Answer:
Arrangement A should not be a set-up because both the terminals of the electric cell connect directly without a switch and bulb, which causes chemicals in the cell used up rapidly.
Question 12. The diagram shows an electric circuit.
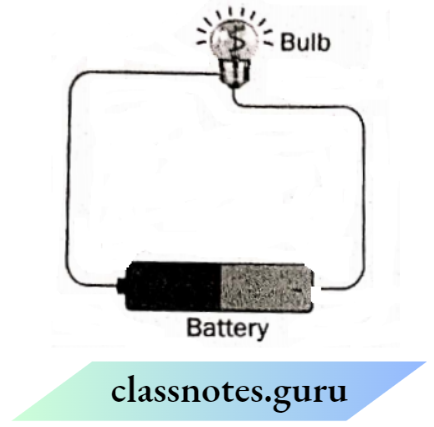
1. What will happen, if another battery is added to the circuit?
Answer: The bulb will glow more brighter
2. What is the direction of the flow of electric current in the circuit? Use small arrows to show the direction in the picture.
Answer:
Question 13. Sanjay saw a sign on an electric pole.
Answer:
1. What should Sanjay never do?
- Play in a park near the pole
- Touch the pole with bare hands
- Park a bicycle in front of the pole
- Walk on the footpath near the pole
Answer: 2. Touch the pole with bare hands
2. What makes the human body conduct electricity?
Answer:
The human body contains various ions like sodium ion, potassium ion, chloride ions, etc., which tend to conduct electricity. Thus, it makes the human body conduct electricity.
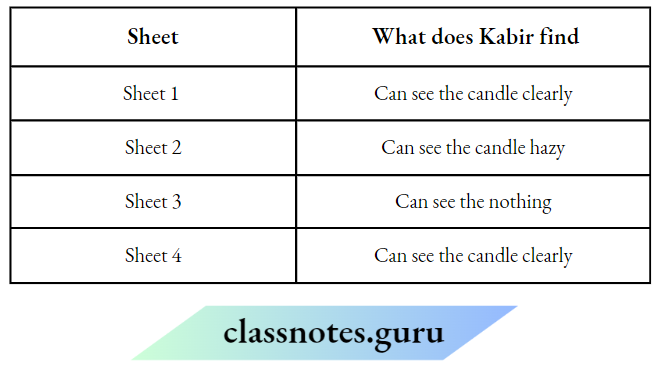
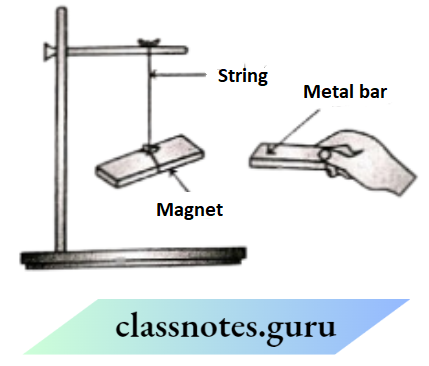
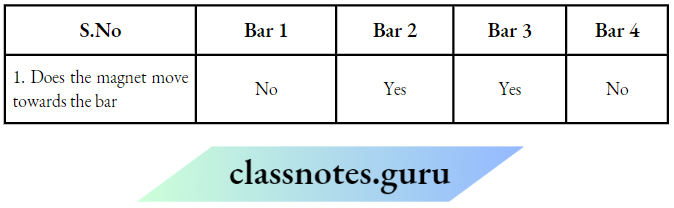
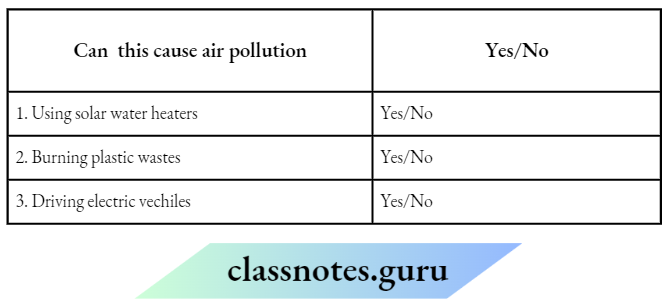
Question 14. Neeraj designed an electric circuit as shown below
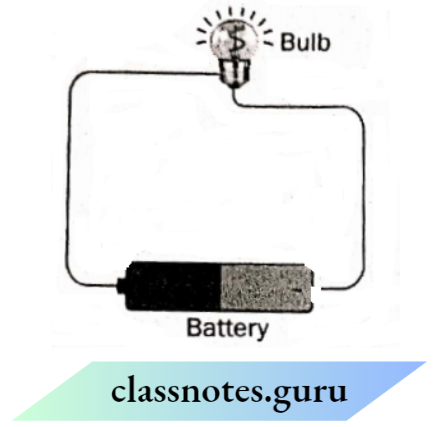
He filled the gap in the circuit with four different objects, one at a time.
The table shows Neeraj’s findings:
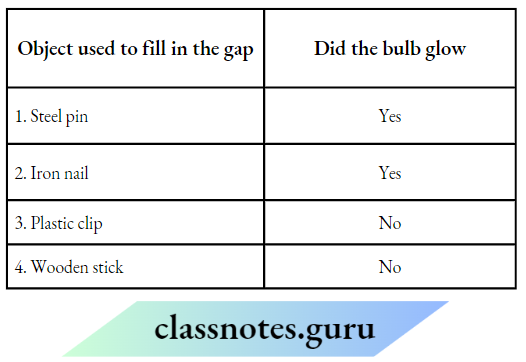
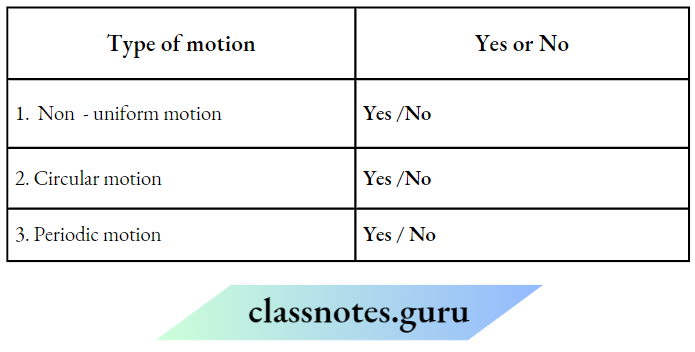
1. Which question can be answered through Neeraj’s activity?
Choose Yes or No for the correct response:
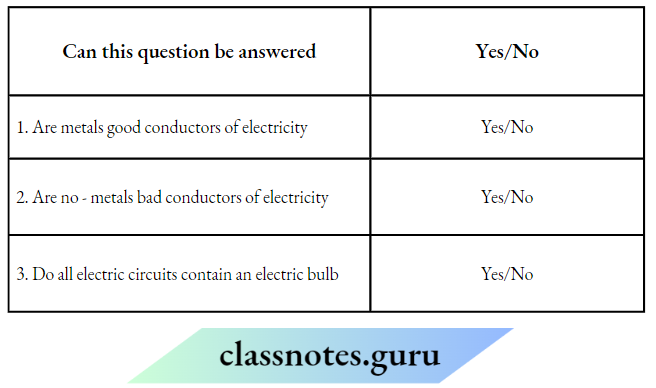
Answer:
1. Yes
2. yes
3. No
2. Which safety measures must Neeraj follow during the activity?
- Wear an apron
- Wear a face mask
- Wear a pair of goggles
- Wear a pair of rubber gloves
Answer: 4. Wear a pair of rubber gloves
3. Neeraj repeated the activity using the same four objects. This time the bulb did not glow for any of the four objects. What could be the most likely reason for this?
Answer:
- The circuit may not be properly connected.
- The bulb may be fused. Or Chemicals in cells are used up
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 9 Electricity And Circuits Short Question And Answers
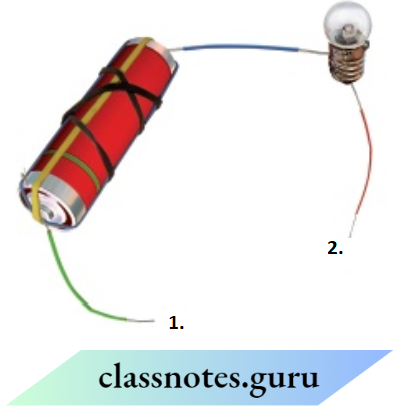
Question 1. Paheli has another arrangement of the cell and the bulb. Will the torch bulb glow in the following arrangement?
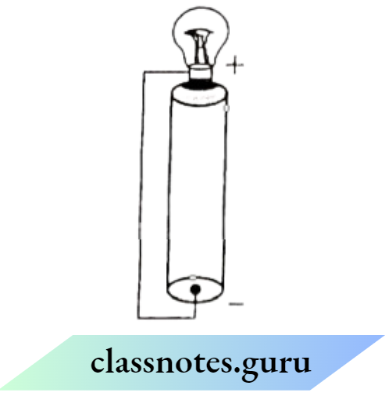
Answer:
The bulb is connected to the cell directly at one terminal and the other terminal is connected to the negative of the cell with a wire. So, the bulb will glow.
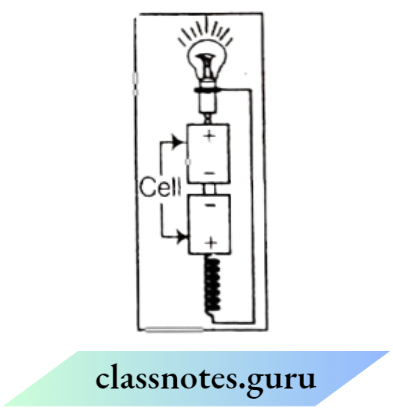
Question 2. Boojho has drawn the inside structure of the torch as shown In the figure. When we close the switch, the circuit Is completed and the bulb glows. Can you draw a red line on the figure indicating the complete circuit?
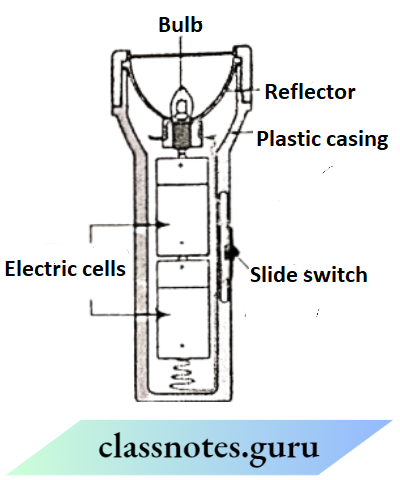
Answer:
Question 3. What is the purpose of using an electric switch? Name some electrical gadgets that have switches built Into them.
Answer:
The switch is a simple device that is used to either break the electric circuit or to complete it. With the help of a switch, we can use an appliance according to our desire. The switches used in the lighting of electric bulbs and other devices in the homework are on the same principle.
Some electrical gadgets that have switches built into them are as follows:
- Torch
- Table fan
- Television set
- Radio
- Electric iron
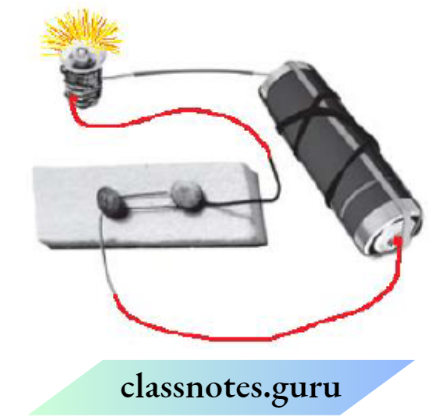
Question 4. Would the bulb glow after completing the circuit shown If Instead of the safety pin, we use an eraser?
Answer:
Since the eraser is an insulator that means it is a bad conductor of electricity. So, conduction of electric current is not possible, Thus, if instead of the safety pin, an eraser is used, the bulb will not glow.
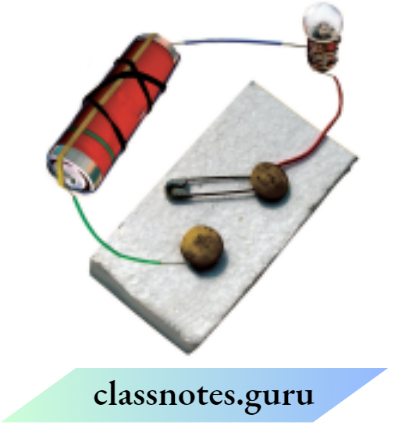
Question 5. Would the bulb glow in the circuit?

Answer:
In the given figure, the bulb will not glow because the two terminals of the connecting wire of the cell are connected to the same terminal of the bulb.
Question 6. Using the conduction tester on an object, It was found that the bulb begins to glow. Is that object a conductor or an insulator? Explain.
Answer:
As we have found using a conduction tester on an object, the bulb begins to glow which is possible only when electric current flows through it. We know that electric current flows only through the conductors. Thus, the object is a conductor that allows electric current to pass through it.
Question 7. Why should an electrician use rubber gloves while repairing an electric switch at your home? Explain.
Answer:
An electrician should use rubber gloves while repairing an electric switch because rubber is an insulator that does not allow an electric current to pass through it. Thus, it prevents his body from getting electric shocks. On the other hand, the human body is a conductor of electricity, so it is necessary to prevent it from electric shocks.
Question 8. The handles of the tools like screwdrivers and pliers used by electricians for repair work usually have plastic or rubber covers on them. Can you explain, why?
Answer:
As we know, the human body is a good conductor of electricity. So, it is necessary to prevent it from electric shocks. On the other hand, plastic and rubber are insulators that do not allow electricity to pass through them, Hence, electricians use screwdrivers and pliers that have plastic or rubber covering on them for repairing work
Question 9. When the chemicals in the electric cell are used up, the electric cell stops producing electricity. The electric cell is then replaced with a new one. In case of rechargeable batteries (such as the type used in mobile phones, cameras, and inverters), they are used again and again. How?
Answer:
A rechargeable battery has such chemicals which after use can be restored by passing a suitable current in the opposite direction to the rechargeable batteries, so it can be used again and again.
Question 10. Briefly explain the components present inside the cell.
Answer:
The cell consists of a carbon rod present at the center of the zinc container. By the side, a metal cap is present which is a positive terminal, and opposite to that is a metal disc which is a negative terminal.
Question 11. Why do bulbs have two terminals?
Answer:
The bulb has two terminals because it is connected to the terminals of a cell or a battery so that current passes through the filament.
Question 12. Discuss briefly that how the switch works,
Answer:
A device that is used to close or open a circuit is known as a switch, so when we open the switch, there exists an air gap that does not allow the current to pass through it. On the other hand, when it is closed, then there is not any existence of a gap between the wires and therefore in this way, it conducts electricity.
Question 13. An electric bulb is connected to a cell through a switch as shown in the figure. When the switch Is brought in the ON position, the bulb does not glow. What could be the possible reasons for it? Mention any two of them.
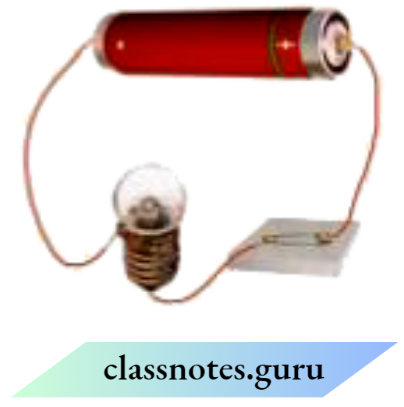

The possible reasons why the even at switching ON position bulb is not glowing are
- The cell may be discharged.
- The filament wire of the bulb may be broken.
Question 14. A torch is not functioning, though contact points In the torch are in working condition. What can be the possible reasons for this? Mention any three.
Answer:
The possible reasons for the not functioning of the torch may be
- The torch bulb may be fused.
- The cell may be discharged.
- The connecting wires may be broken up
Question 15. Pallavi is preparing a torch in her house with her friend Radhika. But even after completing the circuit, the bulb didn’t glow Radhika advised her to check the correct sequence of cells used
State the values reflected by Radhika here. Explain what can be the reason for not glowing the bulb.
- Radhika has good knowledge of electrical circuits and its uses. She is also cooperative with her friends.
- There may be an incorrect sequence of cells that is used by her.
Question 16. As we know, silver is the best conductor of electricity instead of this we use copper and aluminum. Why?
Answer:
Among copper, silver, and aluminum, we use copper and aluminum for household wires because copper and aluminum are much cheaper than silver. It is also heavier than copper and aluminium.
Question 17. Sita is operating a base electric wire so that its electric iron can be used safely. Her friend Vimlesh advised her not to do so without plastic gloves. Mention the values that Vimlesh shows here. A plastic glove is an insulator or conductor.
Answer:
Vimlesh is intelligent and has good knowledge of current and its hazards. A plastic glove is an insulator. It does not conduct electricity.
Question 18. With the help of a labeled diagram, explain the structure and function of a torch.
Ans.
An electric torch is a device which is used as a lamp. It has two or more than two cells, a bulb, and a switch.
So, when we slide the switch (ON position) of the electric torch, the circuit becomes complete and the bulb starts glowing, while on the sliding switch back OFF position, the circuit gets broken and the bulb goes off.
Question 19. If we touch a bare wire and we are in contact with the earth, then we can get an electric shock and if we are standing above a plastic or dry wood chair, then even on touching the bare wire, we will not get any electric shock. Explain why.
Answer:
Current can only flow through a body if it gets the way to pass through it. In the case of the earth, it gets the way from bare wire to your body to the earth. In the case of plastic chairs or dry wood chairs, it doesn’t get the way to flow. So, you don’t get any electric shock
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 9 Electricity And Circuits Very Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Mention the way through which an electric cell can produce electricity.
Answer: A chemical reaction is a way through which an electric cell can produce electricity.
Question 2. Give the name of a portable electric lamp that works on cells.
Answer: A torch is a portable electric lamp that works on cells.
Question 3. What does the positive terminal of dry cells consist
Answer: The positive terminal of the dry cell consists of carbon.
Question 4. Name the glowing part of an electric bulb.
Answer: The glowing part of an electric bulb is its filament.
Question 5. When you switch ON the torch, which part of the bulb glows?
Answer: When you switch ON the torch, the filament part ofthe bulb glows
Question 6. The electric cell and the bulb both have two terminals. Explain why?
Answer: The electric cell and the bulb both have two terminals, that ther e will be a path for the flow of electricity in a complete circuit.
Question 7. A fused bulb does not glow. Why?
Answer: A fused bulb does not glow because in a fused bulb, the filament of the bulb burns up and the connection is broken or incomplete, so the current cannot flow.
Question 8. What Is the advantage of using a switch in a circuit?
Answer: The advantage of using a switch is to either make or break the electric circuit.
Question 9. Name the device which is used to break an electric circuit.
Answer: Switch
Question 10. Define switch.
Answer: A simple device that is used to either break the electric circuit or to complete it, is known as an electric switch.
Question 11. Paheli wanted to glow a torch bulb using a cell. She could not get connecting wires instead she got two strips of aluminum foil. Will she succeed? Explain how.
Answer: Yes, she will succeed because aluminum is a conductor of electricity, it will complete the electrical circuit and the bulb will glow.
Question 12. We should use plastic gloves for operating electrical devices. Explain why.
Answer: To avoid electric shocks, we should use plastic gloves for operating electrical devices.
Question 13. State whether electricity can pass through glass. If not, then explain the reason.
Answer: Electricity cannot pass through glass because it is an insulator.
Question 14. What are the purposes for which you use electricity?
Answer: We use electricity for many purposes to make our tasks easier. For example, we uses electricity to operate pumps that lift water from wells or ground level to the rooftop tank.
Question 15. Where does the torch get electricity from?
Answer: Electric cells are kept inside the torch so, it provides electricity.
Question 3. Did you notice the positive (+) sign and a negative (-) sign marked on the electric cell?
Answer: The sign (+) represents the positive terminal and the sign (-) represents the negative terminal of an electric cell.
Question 16. What Is inside the glass case of the bulb?
Answer: Filament is inside the glass case of a bulb.
Question 17. Why do electric bulbs and electric cells have two terminals?
Answer: A circuit can be completed only when there is both a positive and negative terminal such that current flows.
Question 18. Mention what type of materials can be used in electric circuits, so that the current can pass through them.
Answer: Mention what type of materials can be used in electric circuits, so that the current can pass through them such as metals (aluminum, copper, iron, etc).
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 9 Electricity And Circuits Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. The thin wire that gives off light in an electric bulb is called _____________
Answer: Filament
Question 2. Cell that can be recharged is called _____________
Answer: Secondary cell
Question 3. A bulb is glowing in an electric circuit, that means it is a _____________ circuit.
Answer: Closed
Question 4. _____________ makes the human body to conduct electricity.
Answer: Ions
Question 5. Chemicals used in electrical cell are_____________
Answer: Ammonium chloride and zinc chloride
Question 6. An electric cell converts chemical energy into _____________
Answer: Electrical energy
Question 7. A power station provides us _____________
Answer: Electricity
Question 8. The electric cell and bulb have_____________ terminals.
Answer: Two
Question 9. In bulb_____________ glows.
Answer: Filament
Question 10. A complete circuit contains bulb _____________ and _____________
Answer: Switch And Cell
Question 11. A device which makes or breaks the circuit is called _____________
Answer: Switch
Question 12. Materials that allow electricity to pass through them are called
_____________
Answer: Conductors
Question 13. The handle of an electrician’s screwdriver is made up of _____________
Answer: Insulator
Question 14. Materials that do not allow electricity to pass through them are called_____________
Answer: Insulators
Question 15. A device which is used to break an electric circuit is called ________________
Answer: Switch
Question 16. An electric cell has ________________ terminals.
Answer: Two
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 9 Electricity And Circuits True/False
Question 1. A cell is a device that can produce current.
Answer: True
Question 2. A car battery contains many cells.
Answer: True
Question 3. The combination of two or more cells is called a circuit.
Answer: False
A combination of two or more cells is called a battery
Question 4. Dry cell converts electrical energy into chemical energy
Answer: False
Dry cell converts the chemical energy into electrical energy
Question 5. When the filament of a bulb gets broken, it is termed as fused.
Answer: True
Question 6. The filament is a thin wire that gives off the light.
Answer: True
Question 7. The filament of a bulb is made up of aluminum.
Answer: False
The filament of a bulb is made of tungsten.
Question 8. A closed circuit is known as a switch ON.
Answer: True
Question 9. Saltwater is a good conductor of electricity.
Answer: True
Question 10. Handles of electrical appliances are made up of insulators.
Answer: True
Question 11. The metal cap in an electric cell acts as a positive terminal.
Answer: True
Question 12. An electric bulb has three terminals.
Answer: False
Question 13. Electric currents do not flow through metals.
Answer: False
Question 14. Mark True or False for the following statements
Answer: True
Question 15. Electric current can flow through metals.
Answer: False
As jute is an insulator and hence, current cannot pass through it. Thus, in a circuit, we need conductors through which electric current can pass.
Question 16. Instead of metal wires, a jute string can be used to make a circuit.
Answer: False
As thermocol is an insulator, thus electric current cannot pass through it
Question 17. Electric current can pass through a sheet of thermocol
Answer: False
As thermocol is an insulator, thus electric current cannot pass through it
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 9 Electricity And Circuits Assertion-Reason Questions
The following questions consist of two statements Assertion and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- A is true but R is false
- A is false but R is true.
Question 1.
Assertion (A): The Plastic coating of connecting wires should be removed before making circuits.
Reason (R): Plastic is an insulator, it does not allow electric current to flow through it.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Plastic coating should be removed before making the circuit, if not removed, then it does not allow current to pass through it
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Electricians are provided with rubber gloves while working on electric poles.
Reason (R): Rubber is a conductor, it does not allow electricity to pass through it and saves from getting electric shock.
Answer: 3. A is true but R is false
Rubber gloves are provided to electricians because rubber is an insulator and this saves them from getting an electric shock
Question 3.
Assertion (A): A fused bulb glows, when it is connected to the cell.
Reason (R): A bulb gets fused, when there is a break in the filament.
Answer: 4. A is false but R is true.
A bulb gets fused, when there is a break in the filament and a fused bulb does not glow when it is connected to the cell.
Question 4.
Assertion (A): The human body does not allow electric current to pass through it.
Reason (R): The materials which allow electric current to pass through it are called conductors
Answer: 4. A is false but R is true.
The human body is a conductor of electricity and conductors are those materials which allow electricity to pass through them
Question 5.
Assertion (A): An electric bulb glows, when electricity passes through its filament.
Reason (R): Filament is made up of aluminum.
Answer: 3. A is true but R is false
Question 6.
Assertion (A): Ocean water is a good conductor of electricity.
Reason (R): The salts present in ocean water make it a good conductor.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
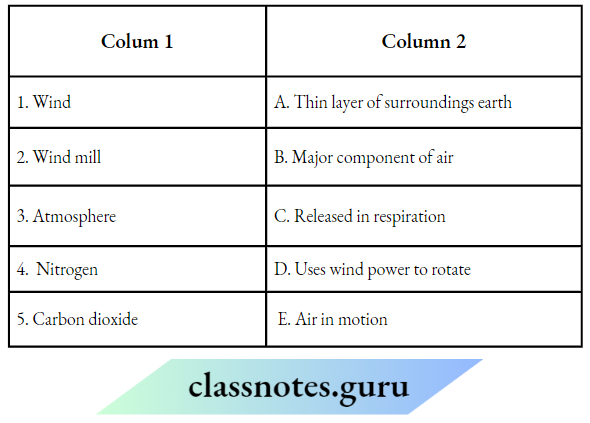
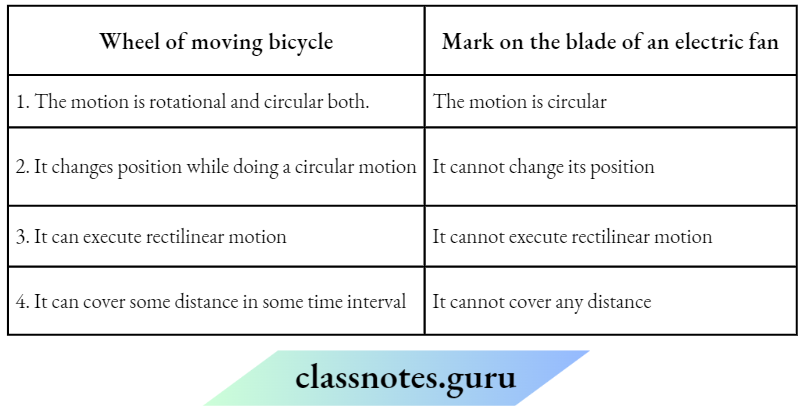
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 9 Electricity And Circuits Match The Columns
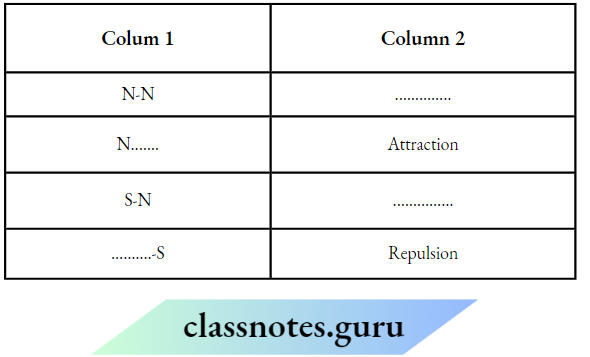
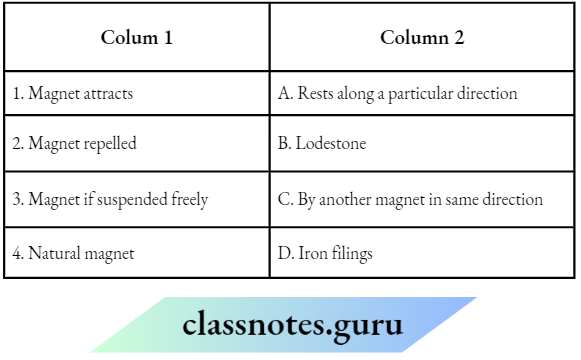
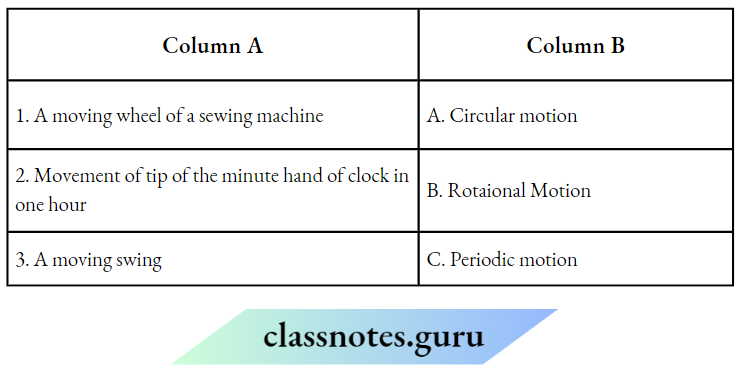
Question 1. Match the Column A with Column B
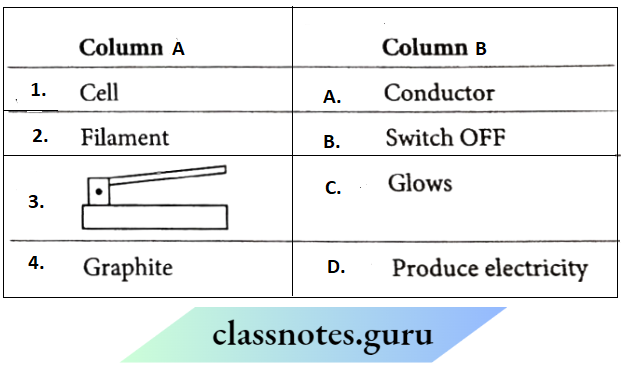
Answer: 1- D, 2- C, 3-2, 4- 1
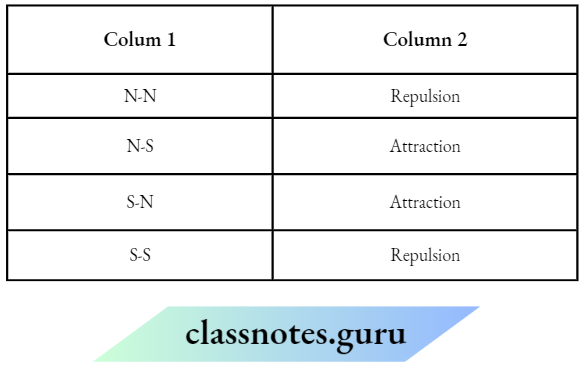
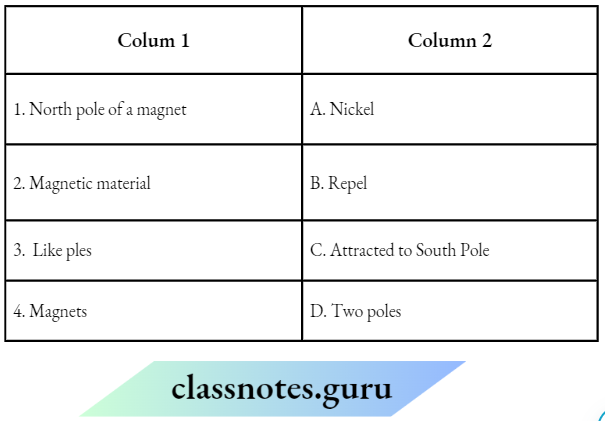
Question 2. Match the Column A with Column B
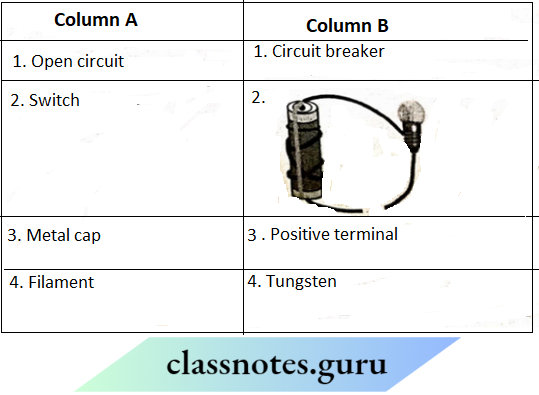
Answer: 1- B, 2- A, 3-C, 4- D