NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Light Shadows And Reflections Long Question And Answers
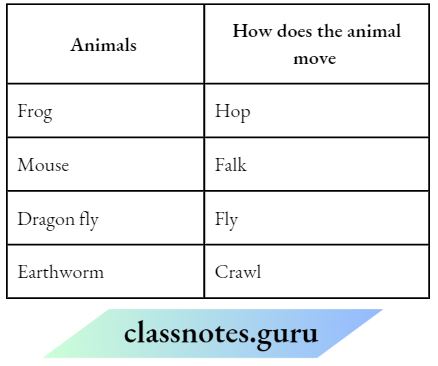
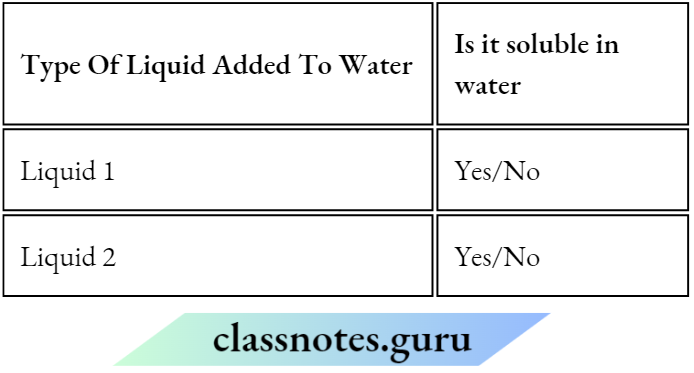
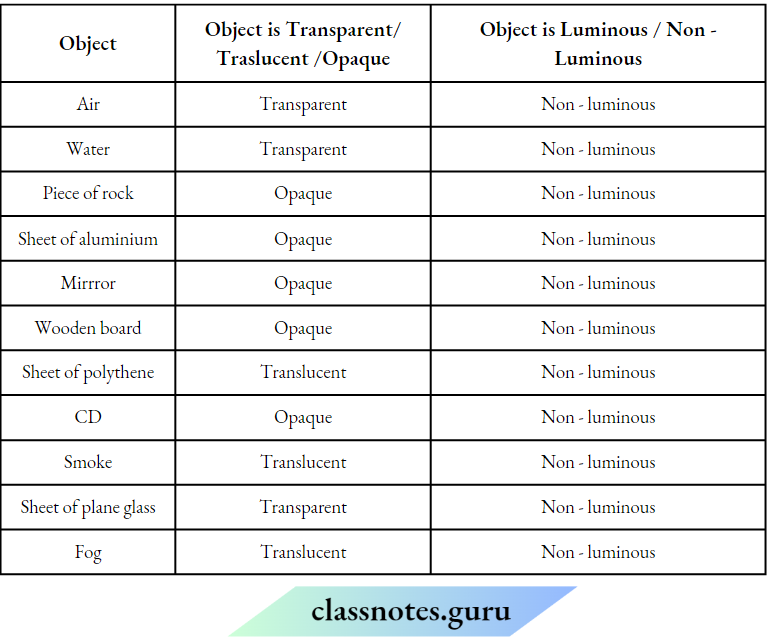
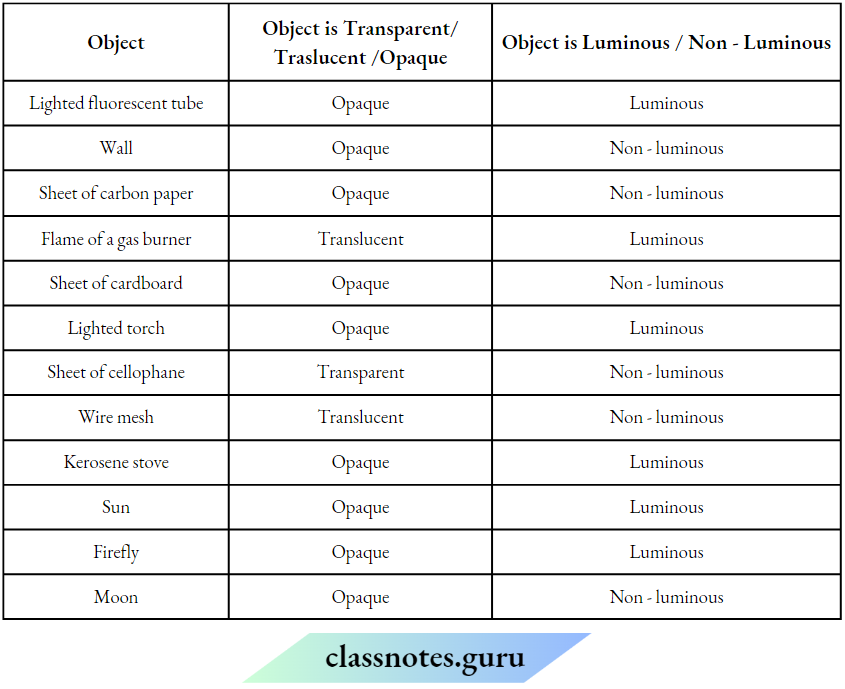
Question 1. Classify the objects or materials given below as opaque, transparent translucent anti-luminous or voluminous. Air, water, a piece of rook, a sheet of aluminium, n mirror, a wooden board, a sheet of polythene, a CD, smoke, a sheet of plane glass, fog, a piece of rod hot Iron, an umbrella, a lighted fluorescent tube, a wall, a sheet of carbon paper, the flame of a gas burner, a sheet of cardboard, a lighted torch, a shoot of cellophane, a wire mesh, kerosene stove, sun, firefly, moon.
Answer:

Classification of objects or materials Is given as below:
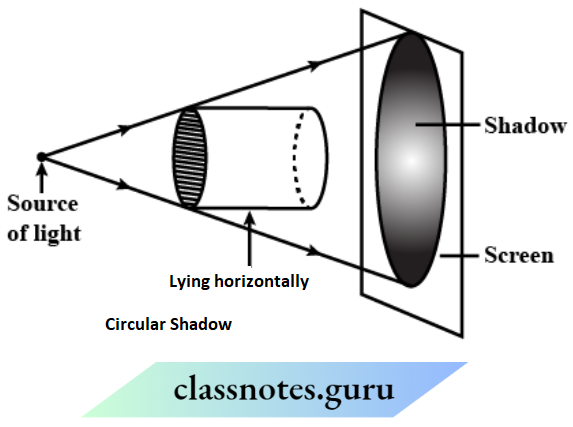
Question 2. Can you think of creating a shape that would give a circular shadow, if held in one way and a rectangular shadow, if held in another way?
Answer:
Yes, many things could give a circular shadow if held in one way and a rectangular shadow, if held in another way
Read and Learn More Class 6 Science Question And Answers
Example:
A cylindrical object, a pencil, a candle, etc
1. Getting a circular shadow of a candle (which is cylindrical), when it is laid down horizontally position.
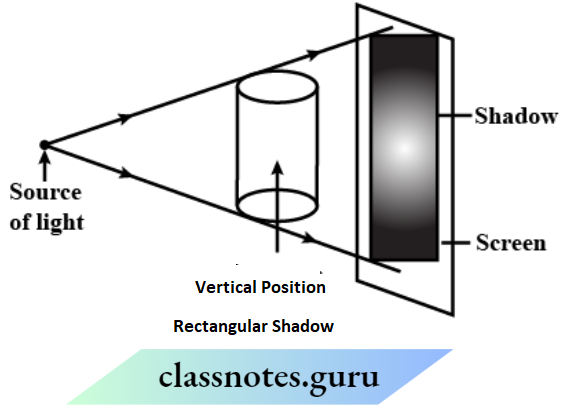
2. Getting a rectangular shadow of a candle, when it is in standing or vertical position.
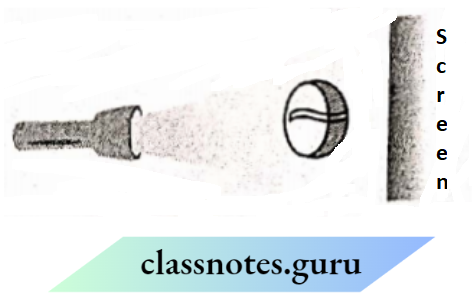
Question 3. A student had a ball, a screen and a torch in working condition. He tried to form a shadow of the ball on the screen by placing it in different positions. Sometimes, the shadow was not obtained. Explain.
Answer:
Sometimes, the shadow of the object (ball) may not be formed because of improper arrangement. It may happen that the direction of the torchlight is not towards the screen. The shadow will be formed.
Question 4. A football match Is being played at night In a stadium with floodlights ON. You can see the shadow of a football kept on the ground but cannot see its shadow when it Is kicked high In the air. Explain.
Answer:
The shadow of the object cannot be caught, if the screen and the object are very far from each other. This is the same case, the shadow of the football cannot be seen on the ground when it is kicked high in the air. This happens because if we take the object away and away from the screen, the image becomes smaller and smaller and a time comes when it disappears from the screen.
Question 5. A sheet of plywood, a piece of muslin cloth and that transparent glass, all of the same size and shape were placed at A one-by-one in the arrangement. Will the shadow be formed in each case? If yes, then how will the shadow on the screen be different in each case? Give reasons for your answer.

Yes, the shadow will be formed in all the cases but in all
the cases, the darkness of the shadow will be different.
- Most ofthe light in the case of the transparent sheet will pass through the glass, so the darkness of shadow will be very low.
- Also, most ofthe light in the case of muslin cloth will be reflected, so the shadow will be darker than the transparent sheet.
- While in the case of plywood, all the light would be stopped completely by the plywood. So, the darkness strength will be highest in this case
Question 6. A mug was placed between a torch and a screen. The picture shows the shadows of the cup at different positions of the cup.
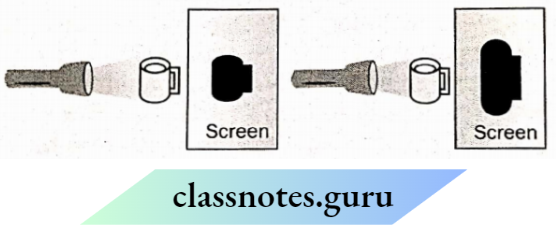
Choose Yes or No for the correct response:
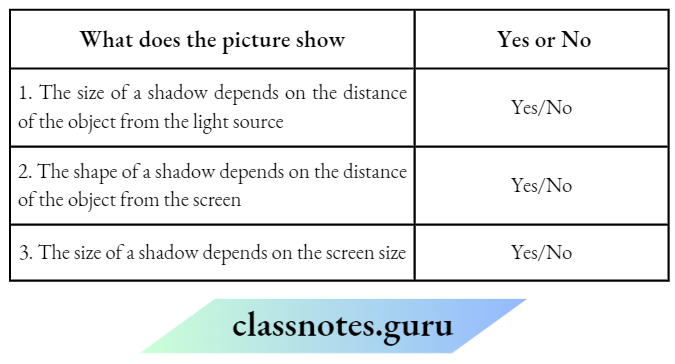
Answer:
1. Yes
2. No
3. No
Question 7. Suggest a situation where we obtain more than one shadow of an object at a time
Answer:
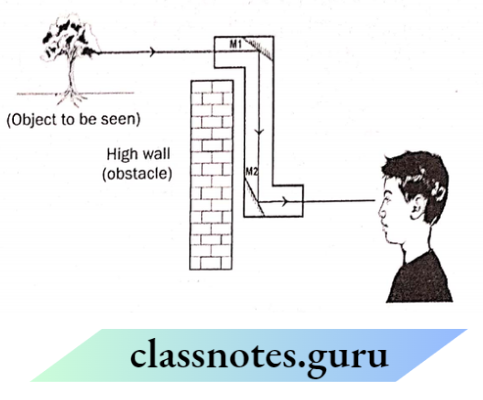
Place the object in front of a mirror and put the light source behind the object. The image/shadow will be formed by the object as well as the image of the object by the mirror.
Question 8. A torch Is placed at two different positions A and B one by one as shown in the figure
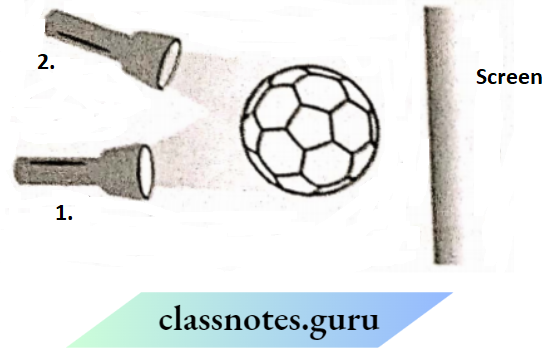
The shape of the shadow obtained In two positions Is shown in the given figure.

Choose the position of the torch and the shape of the shadow of the ball.
Answer:
Position A of the torch will form image 1 Position 2 ofthe torch will form the image of the football.
Question 9. It was a bright sunny day. Rajat was returning from school. He was tired. He sat under a tree covered with a very large number of leaves. There were tiny gaps between the leaves that light could pass through them. He saw bright circular patches of light on the ground under the tree. Suddenly, there was a loud noise of an aeroplane in the sky and he rushed to see the aeroplane. He was surprised to see that there was no shadow of the aeroplane on the ground. He was puzzled because he had studied that when there is sun and an opaque object, the shadow is formed on the screen.
Answer:
1. What are the bright patches on the ground? Explain In a brief to Rightnt about the patches of light under the tree.
Answer:
These bright patches are the pinhole images of the sun. When sunlight passes through the leaves of a tree, the gaps between the leaves act as the natural pinhole ” camera. Thus, it forms the bright patches of light under the tree.
2. In what way are Images formed by such holes different from shadows?
- Shadows are colourful but Images are always black.
- Shadows are erect but Images are Inverted,
- Shadows are Inverted but Images are erect.
- Shadows are real but Images are not real.
Answer: 2. Shadows are erect but Images are Inverted,
3. Why could Rajat not find any shadow of the aeroplane on the ground?
- The object was very small
- The object was transparent
- There was no screen on which a shadow could form
- The screen was very far from the object
Answer: 4. The screen was very far from the object
Question 10. The question assesses the learner’s understanding of the formation of shadows. Once upon a time, In a Jungle, lived a wolf. One day, he decided to leave his cave and go out and play. On his way, he saw a shadow of a giant figure. He was scared. He was about to run but then realised that It was a shadow of a tree. He started laughing.
He moved on and played with his friends. When he returned to his cave, the sun had started to set. The setting sun casts shadows on everything everywhere, so the setting sun casts a wolf’s shadow as well. He was extremely happy with his dark figure on the ground. The wolf admired himself, “Why should I run away from the lion? I bet, If I go and growl at him, he will tremble In fear and ask me to be the king.”
Suddenly he saw a lion not far away from where the wolf was standing. He made his way to the lion. When he came near the lion, he growled with all his might. “ I shall rule this Jungle.” The lion laughed at the wolf, and then the lion roared. And before the wolf knew it, he became the lion’s meal. The foolish wolf didn’t know that the sun was playing a trick with him.
Answer:
1. Discuss in brief any two characteristics of a shadow that are shown in the story given above.
Answer:
- Shadows do not tell the exact shape of the object.
- Shadows do not tell the exact size of the object
2. At what time of the day will wolf’s shadow be the longest?
- 11:00 am
- 12:00 pm
- 03:00 pm
- 05:30 am
Answer: 4. 05:30 am
3. In which direction was the shadow of the wolfpointing, on his way back to his cave?
- East
- North
- South
- West
Answer: 1. East
4. Name the property of light that is responsible for the formation of the shadow of an object
Answer: Rectilinear propagation of light
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Light Shadows And Reflections Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Observe the picture given In the figure. A sheet of some material Is placed at position P, still the patch of light is obtained on the screen. What Is the type of material of this sheet?
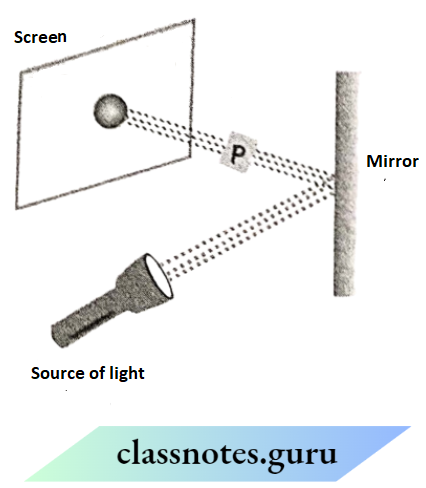
Answer:
The material is transparent glass because only it can pass the light through it completely and the image will be formed at the same place.
Question 2. Look at the given figure.
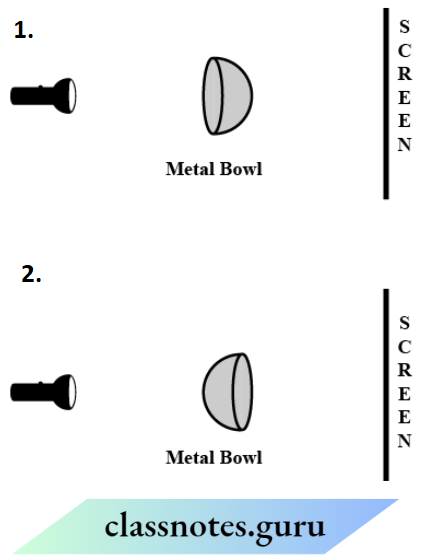
Question 3. State three conditions to observe a shadow.
Answer:
The three conditions for observing a shadow are
- A source of light should be there.
- An opaque object should be there.
- A screen should be there.
Question 4. You have three opaque strips with very small holes of different shapes. If you obtain an image of the sun on a wall through these holes, will the Image formed by these holes be the same or different?
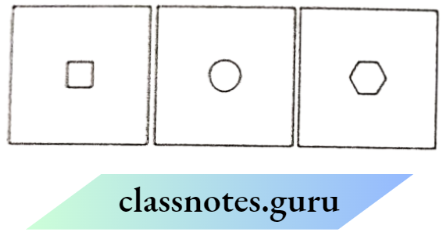
Answer:
The image of the sun will remain the same, still if we use different types of holes because the holes will act as pinhole cameras and light moves in a straight path.
Question 5. State some of the properties of light.
Answer:
Some of the properties of light which can be stated as follows:
- Light is a form of energy.
- It travels in a straight line.
- For an opaque object, light casts a shadow.
Question 6. Differentiate between a luminous and non-luminous object.
Answer:
Luminous objects are those objects which emit the light of their own
Example: The stars, the sun, burning candles, etc. Non-luminous objects are those objects which do not emit light of their own, e.g. blackboard, moon, earth, ground. etc
Question 7. You are given a transparent glass sheet. Suggest any two ways to make It translucent without breaking It.
Answer:
A transparent sheet can be made translucent for two days
- By rubbing it on the ground and making jt rough.
- By polishing It, not completely but partially-
- By applying oil, grease or butter to It,
Question 8. Why does a rubber ball cast a shadow, while a glass doesn’t?
Answer:
The rubber ball is an opaque object, so it does not allow to pass the light through it, that’s why It casts a shadow but glass is a transparent object, so it passes the light completely through it that’s why it does not cast a shadow,
Question 9. Can an object form two or more shadows at the same time? If so, how?
Answer:
Yes, an object can form two or more shadows at the same time. If an object is lit up from more than one direction by light, we can have more than one shadow,
Question 10. What will be the colour of a shadow formed in red light?
Answer:
The colour of a shadow does not depend on the colour of light. Shadow shows the absence of light at any dance, so the colour of shadow always be black,
Question 11. In the given figure, a flower made of thick coloured paper has been pasted on the transparent glass sheet, What will be the shape and colour of the shadow seen on
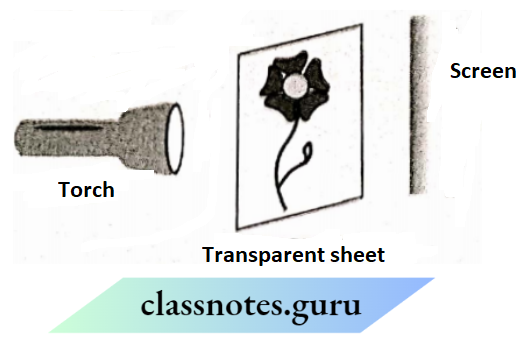
Answer:
The shape of the flower on the screen will be the same as that of the flower but the shadow of the flower is black,
Question 12. On a sunny day, does a bird or an aeroplane flying high In the sky cast Its shadow on the ground? Under what circumstances, can we see their shadow on the
Answer:
No, they do not cast any shadow on the ground because they are so high. They can cast shadows only, if they are at some lower height, i.e. if they are near to the ground, we can see their shadows.
Question 13. Three Identical towels of red, blue and green colour are hanging on a cloth line In the sun. What would be the colour of the shadows of these towels?
Answer:
Shadow does not change by changing the colour of the object. Shadow will always show the absence of light at that place. So, the shadow colour will remain the same in all the cases. Thus, the shadow of all the towels is black
Correct the following statements.
- The colour of the shadow of an object depends on its colour.
- Transparent objects allow light to pass through
Answer:
- The colour ofthe shadow of an object does not depend on its colour.
- Transparent objects allow light to pass through them completely.
Question 14. Rearrange the boxes given below to make a sentence that helps us to understand opaque objects.

Answer:
The rearrangement of the given boxes is shown as below

The above rearrangement implies a sentence, i.e. opaque objects make shadows
Question 15. In a completely dark room, if you hold up a mirror in front of you. Will you see a reflection of yourself in the mirror?
Answer:
No, because reflection is the phenomenon in which light rays are sent back to show the image after reflecting by mirror. If there is no source of light, no image will be formed and hence, we cannot see the image of ourselves or any other object unless a light source is there.
Question 16. A student covered a torch with a red cellophane sheet to obtain red light. Using the red light, she obtains a shadow of an opaque object. She repeats this activity with green and blue light. Will the colour of the light affect the shadow? Explain.
Answer:
Shadow is just an absence of light in that place. Shadow is not affected by the colours of the object because the amount of light is preventing from passing will remain the same. The shadow is affected by the shape of the object only. If the object is large, the shadow will be large and vice-versa
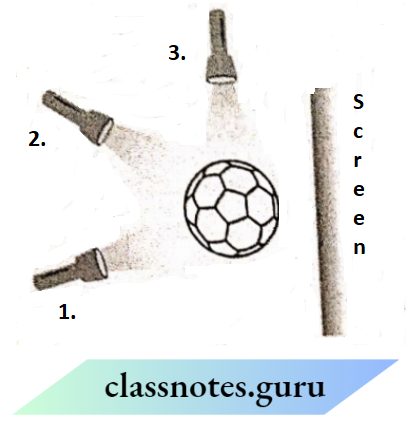
Question 17. Three torches A, B and C shown in the figure are switched ON one by one. The light from which of the torches will not form a shadow of the ball on the screen?

Answer:
The light from torch C will not form a shadow or screen because light travels in a straight path and will form the shadow on the same path from which it is coming.
Question 18. Differentiate between a shadow and an image
Answer:
The dark patch of light is known as a shadow which is formed when there is an opaque object in the path of light. While an image is the reflection of light. By seeing the image, we can identify the object but the shadow can mislead us from the actual object.
Question 19. Using a pinhole camera, a student observes the image of two of his friends standing In sunlight wearing yellow and red shirts, respectively. What will be the colours of the shirts In the Image?
Answer:
The colours of the shirts will remain the same. We see them on the screen because the pinhole camera forms the images of the object having the same colour but upside down. So, a yellow shirt will form a yellow image and a red shirt will form a red image.
Question 20. Explain the reason of using a silver glass as a mirror.
Answer:
As we know, the silvered glass surface is very smooth and shiny as well. So, this type of surface helps in forming a clear image. Silvering makes it shiny and this shiny surface in turn helps in increasing the reflection.
Question 21. Which of these questions can be answered by a scientific study?
Choose Yes or No for the correct response:
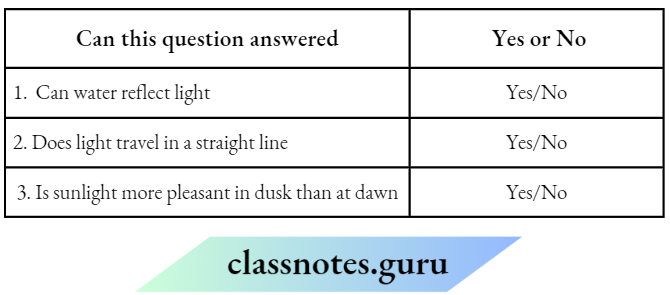
Answer:
1. Yes
2. Yes
3. No
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Light Shadows And Reflections Very Short Question And Answers
Question 1. How do you think, we see objects? Page go
Answer: We see an object when light is reflected from it into our eyes, which enables us to see,
Question 2. Suppose you go Inside a completely dark room, Are you able to see any object in the room?
Answer: In a dark room, there is no light inside it, So, we are not able to see any object in the room,
Question 3. Do you observe your shadow In a dark room or at night, when there is no light?
Answer: No, we cannot observe any shadow without any source of light.
Question 4. Do you observe a shadow, when there is Just a source of light and nothing else in a room?
Answer: No, we cannot see the shadow without any opaque object.
Question 5. Does the picture seen in the pinhole camera show the colour of the object on the other side?
Answer:
The image formed by a pinhole camera is inverted compared to the object. The image formed by the pinhole camera has the same colour as the object.
Question 6. Is the formation of shadows and pinhole images possible only if light moves In a straight path?
Answer: Yes.
Question 7. Which form of energy enables us to see the things around us?
Answer: Light is a form of energy which enables us to sec the things around us.
Question 8. As we know, the moon appears to be bright at night. Does It mean that It Is a luminous object?
Answer: The moon doesn’t produce its light, the brightness of the moon is due to the reflection of the light of the sun. So, it is not a luminous object.
Question 9. Mention the name of an object which does not allow the light to pass through It.
Answer: The name of an object which does not allow the light to pass through is an opaque object
Example: Wood, Brick wall etc,
Question 10. Mention the name of an object which partially allows c the light to pass through It.
Answer: The object which partially allows the light to pass through it is translucent
Example: Wax paper.
Question 11. Name the things other than a source of light and opaque objects required to see the shadow.
Answer: A screen like cardboard, wall and ground is required to see the shadow
Question 12. If you can see the faint glow of a lighted torch through an object, but not the torch Itself, then what kind of the substance is it opaque, translucent or transparent?
Answer: If we can see the faint glow of the torch, but are unable to view the torch Itself, then such an object is classified as translucent.
Question 13. The shadow of a flying aeroplane cannot be seen on the Earth. Explain, why.
Answer: The shadow of a flying aeroplane cannot be seen on Earth because the distance between the object and the screen is too Far.
Question 14. Will there be any difference In the shadow formed on
Answer: No, there will not be any difference because the length and breadth of an object are the same in both cases.
Question 15. If an object is of two different colours, then what will be the colour of the shadow?
Answer: If an object is of two different colours, then the colour of the shadow will always be black.
Question 16. Concerning the direction of the source of light, what is the direction of shadow?
Answer: In respect to the direction of the source of light, the direction of the shadow is always opposite to it.
Question 17. Does the colour of the shadow depend upon the colour of the object?
Answer: No, the colours of the shadows are the same for different colours of objects, it is always black. Some portion of the shadow may be grey.
Question 18. Mention the type of image which is formed in a pinhole camera.
Answer: The inverted and real image is formed in a pinhole camera
Question 19. Through which pipe, we can see the candle, straight pipe or curved pipe?
Answer: As the light travels in a straight line path, so we can see the candle through a straight pipe.
Question 20. Give the name of two instruments which show that light travels in a straight line.
Answer: The pinhole camera and periscope are the two instruments which show that light travels in a straight line.
Question 21. What kind of image cannot be obtained on the screen?
Answer: An image which cannot obtained on the screen is virtual.
Question 22. In a completely dark room, if you hold up a mirror in front of you, will you see a reflection of yourself in the mirror?
Answer: To see a thing, there must be light which reaches after reflection from the object to our eyes. In a dark room there is no light, so we are not able to see our faces.
Question 23. What makes us see ourselves, when we stand in front of a competency-based queue?
Answer: Light coming from our body is reflected by the mirror and reaches our eyes which enables us to see ourselves when we stand in front of it.
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Light Shadows And Reflections Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. Sun is a __________________ object.
Answer: Luminous
Question 2. Objects that do not emit light of their own are known as _____________ objects.
Answer: Non-luminous
Question 3._____________ material passes light partially.
Answer: Translucent
Question 4. Rubber is_____________but glass is _____________
Answer: Opaque, Transport
Question 5. Shadows are formed by_____________object.
Answer: Opaque
Question 6. Pinhole camera forms_____________image.
Answer: Inverted
Question 7. When light rays fall on the mirror, it _____________
Answer: Reflects
Question 8. _____________ propagation is the property of light that is, responsible for the formation of the shadow of an object.
Answer: Rectilinear
Question 9._______________ are the objects which partially allow the light to pass through them.
Answer: Translucent objects
Question 10. Dark patches formed, when an opaque object comes in the path of light are known as
Answer: Shadow
Question 11. Pinhole images are………in nature.
Answer: Inverted
Question 12. Light always moves in the path.
Answer: Straight
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Light Shadows And Reflections True / False
Question 1. Moon is a luminous object.
Answer: False
The moon is a non-luminous object because it does not emit the light of their own
Question 2. Non-luminous objects emit the light of their own.
Answer: False
Non-luminous objects do not emit the light of their own as luminous objects emit the light of their own
Question 3. Rubber is a translucent object.
Answer: False
Rubber is an opaque object
Question 4. Images are similar to shadows.
Answer: False
Images are different from shadows
Question 5. Shadow is formed by a transparent object.
Answer: False
Shadow is always formed by opaque objects.
Question 6. The shadow of an object at noon is longer than its shadow in the evening.
Answer: False
At noon, the sun is directly above the objects and the sun’s rays fall vertically on the body, thus the shadow is very short or negligible at noon as compared to the evening.
Question 7. The shadow of a coloured object is always black.
Answer: True
Question 8. Light travels in a straight line.
Answer: True
Question 9. A pinhole camera produces a diminished image.
Answer: False
A pinhole image can be smaller or bigger than the object depending on the distance of the object from the pinhole camera
Question 10. The mirror does not change the direction of light that falls on it.
Answer: False
Mirror changes the direction of light falling on it
Question 11. Translucent objects can cast shadows.
Answer: True
Question 12. Pinhole camera works on the principle of rectilinear propagation of light.
Answer: True
Question 13. Fresh water does not reflect the light rays.
Answer: False
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Light Shadows And Reflections Assertion-Reason Questions
The following questions consist of two statements Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- A is true but R is false
- A is false but R is true.
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Glass allows only some of the light to pass through it.
Reason (R): Glass is a transparent material.
Answer: 4. A is false but R is true.
Glass is a transparent material. It allows them to pass H the light completely through it
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Only opaque objects form shadows.
Reason (R): A shadow is formed in the opposite, direction as that of the light source.
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
An opaque object forms a shadow because these objects do not allow light to pass through them. The shadow is formed on the opposite side of the source oflight
Question 3.
Assertion (A): We can see through the transparent materials.
Reason (R): Transparent materials do not pass the light falling on them.
Answer: 3. A is true but R is false
We can see through transparent materials because it allows passing the light completely through it
Question 4.
Assertion (A): We can see the shadow of the flying aeroplane and the flying birds.
Reason (R): The shadow of flying aeroplanes and flying birds can be possible only when they are very close to the ground.
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
It is possible to see the shadow of flying aeroplanes and flying birds when they are very close to the ground
Question 5.
Assertion (A): A pinhole camera is a device which forms inverted images.
Reason (R): The pinhole camera is based on the principle that light always moves in a straight path.
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 6.
Assertion (A): Opaque objects are used to form shadows.
Reason (R): Opaque objects obstruct the path of light
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
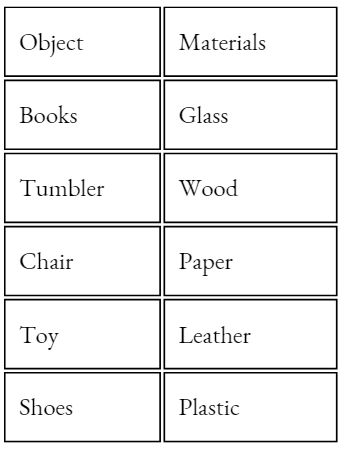
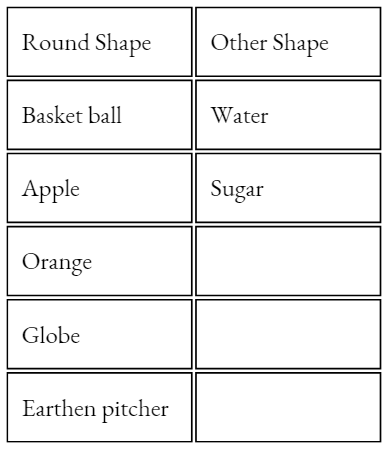
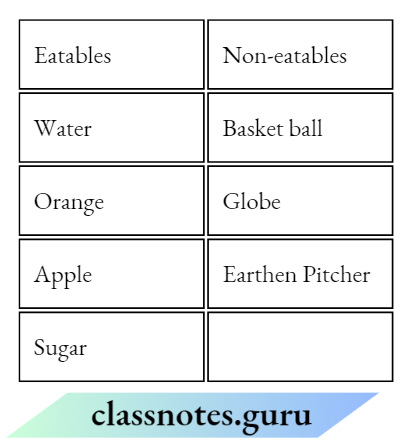
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Light Shadows And Reflections Match The Columns
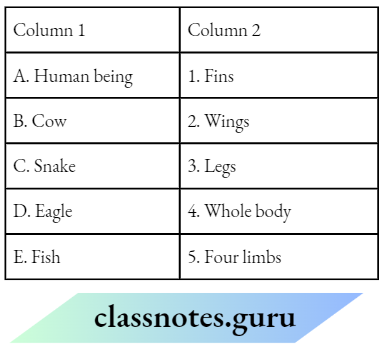
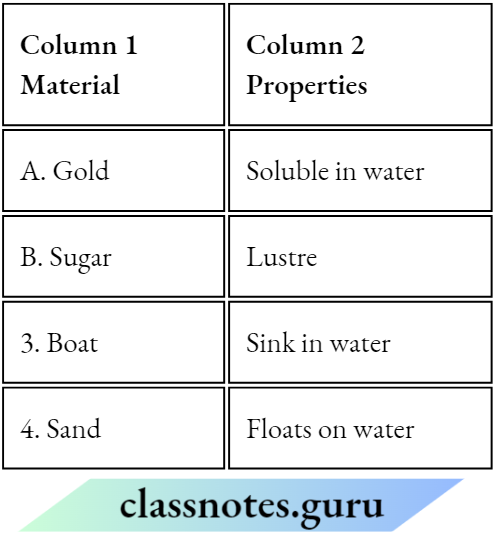
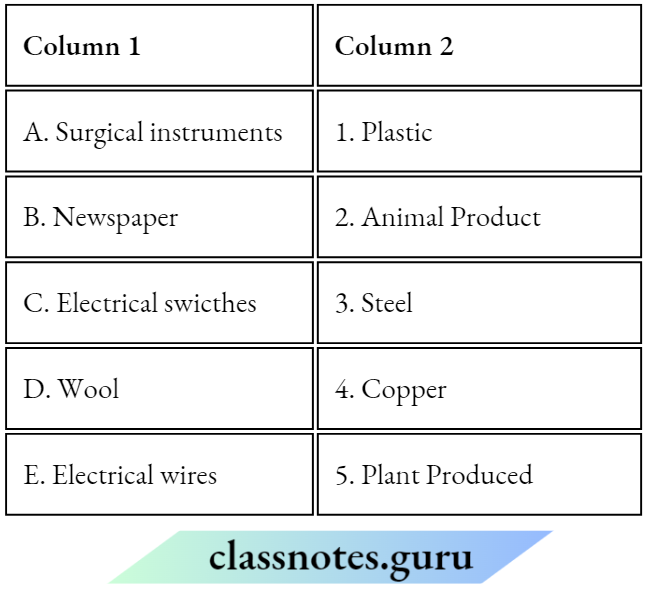
Question 1. Match the Column A with Column B
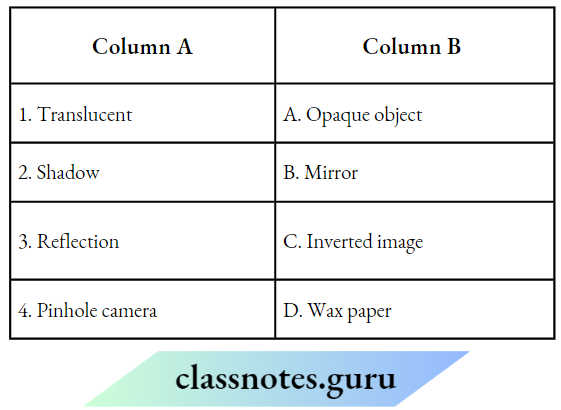
Answer: 1- D, 2- A, 3- B, 4- C