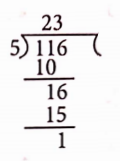Class 6 Maths Chapter 3 Playing With Numbers
Directions: In questions 1 to 14, out of the four options, only one is correct. Write the correct answer.
1 Sum of the number of primes between 16 to 80 and 90 to 100 is
(1) 20
(2) 18
(4) 16
(3) 17
Solution: (3): Prime numbers between 16 to 80 are 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73 and 79.
So, there are 16 prime numbers between 16 to 80.
Also, 97 is the only prime number between 90 to 100.
So, there is only a prime number between 90 to 100.
Required sum = 16 +1 = 17
Read and Learn More Class 6 Maths Exemplar Solutions

2. Which of the following statements is not true?
(1) The HCF of two distinct prime numbers is 1
(2) The HCF of two coprime numbers is 1
(3) The HCF oftwo consecutive even numbers is 2
(4) The HCF of an even and an odd number is even
Solution: (4): The HCF of an even and an odd number is always an odd number.
3. The number of distinct prime factors of the largest 4-digit number is
(1) 2
(3) 5
(2) 3
(4) 11
Solution: (2): The largest 4-digit number is 9999.
Now,

9999 = 3 x 3×11 x101
So, distinct prime factors of 9999 are 3, 11 and 101, i.e., 3 distinct prime factors.
4. The number of distinct prime factors of the smallest 5-digit number is
(1) 2
(2) 4
(4) 8
(3) 6
Solution: (1): The smallest 5-digit number is 10000.
Now,

10000 = 2x2x2x2x5x5x5x5
So, distinct prime factors of10000 are 2 and 5, i.e., 2 distinct prime factors.
5. If the number 7254*98 is divisible by 22, the digit at* is
(1) 1
(2) 2
(3) 6
(4) 0
Solution: (3): 7254*98 is divisible by 22, if it is divisible by both 2 and 11.
Given number is even, therefore it is divisible by 2.
7254*98 is divisible by 11, if (7 + 5 + * + 8) – (2 + 4 + 9) or (20 + *)- 15 or 5 + * is divisible by 11.
The digit at * should be filled by 6.
6. The largest number which always divides the sum of any pair of consecutive odd numbers is
(1) 2
(2) 4
(3) 6
(4) 8
Solution:(2): The sum of any pair of consecutive odd numbers comesin the form ofmultiple of 4.
The required largest number is 4.
7. A number is divisible by 5 and 6.It may not be divisible by
(1) 10
(3) 30
(2) 15
(4) 60
Solution: (4): The LCM of 5 and 6 is 30.
And 30 is divisible by 10, 15 and 30 but not by 60.
8. The sum of the prime factors of 1 729 is
(1) 13
(2) 19
(4) 39
(3) 32
Solution: (4): We have,
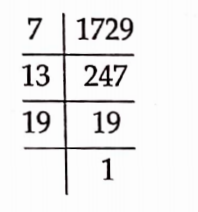
The prime factors of 1729 = 7 x 13 x 19.
The sum of the prime factors of 1729 = 7+ 13 +19 = 39
9. The greatest number which always divides the product of the predecessor and successor of an odd natural number other than 1, is
(1) 6
(2) 4
(3) 16
(4) 8
Solution: (2): Since the odd natural numbers other than1 are 3, 5, 7, 9 and so on.
Now, the predecessor and successor of 3 are 2 and 4 respectively, and their product is 2×4 = 8
Similarly, the predecessor and successor of 5 are 4 and 6 respectively and their product is 4 x 6 = 24 and so on.
Thus, the above shows that the greatest number which always divides the product of the predecessor and successor of an odd natural other than 1 is 4.
10. The number of common prime factors of 75, 60,105 is
(1) 2
(2) 3
(3) 4
(4) 5
Solution: (1): We have,
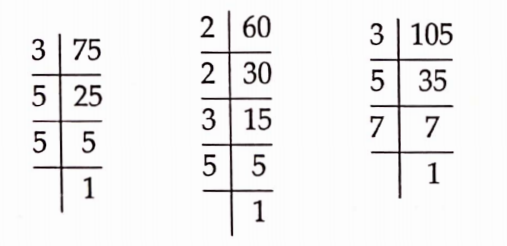
75 = 3 x 5 x 5
60 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 5
105 = 3 x 5 x 7
The common prime factors of 75, 60 and 105 are 3 and 5 i.e., 2 in number.
11. Which of the following pairs is not coprime?
(1) 8,10
(3) 1,3
(2) 11, 12
(4) 31,33
Solution: (1): 8 and 10 are not co-prime numbers.
Their common factor other than 1 is 2
12. Which of the following numbers is divisible by 11?
(1) 1011011
(2) 1111111
(3) 22222222
(4) 3333333
Solution: (3): The difference of the sum of digits of 22222222 at even and odd places is 0. It must be divisible by 11.
13. LCM of10, 15 and 20 is
(1) 30
(2) 60
(4) 180
(3) 90
Solution: (2): We have,

The LCM of 10, 15 and 20 is 2x2x3x5=60
14. LCM of two numbers is 1 80. Then which of the following is not the HCF of the numbers?
(1) 45
(2) 60
(3) 75
(4) 90
Solution:(3): We have,
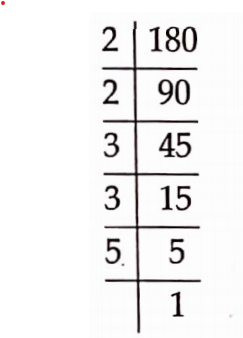
The factors of 180 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 x 5
75 does not divide 180
75 can not be the HCF of the numbers whose LCM is 180.
Directions: In questions 15 to 32 state whether the given statements are true (T) orfalse (6).
15. Sum of two consecutive odd numbers is always divisible by 4.
Solution: True
16. If a number divides three numbers exactly, it must divide their sum exactly.
Solution: True
17. If a number exactly divides the sum of three numbers, it must exactly divide the numbers separately.
Solution: False
18. If a number is divisible both by 2 and 3, then it is divisible by 12.
Solution: False
Since, a number is divisible by both 2 and 3 implies that it is also divisible by 6.
19. A number with three or more digits is divisible by 6, if the number formed by its last two digits (i.e., ones and tens) is divisible by 6.
Solution: False
A number is divisible by 6 if the number is divisible by both 2 and 3.
20. A number with 4 or more digits is divisible by 8, if the number formed by the last three digits is divisible by 8.
Solution: True
21. If the sum of the digits of a number is divisible by 3, then the number itself is divisible by 9.
Solution: False
If the sum of the digits of a number is divisible by 3, then the number it self is divisible by 3.
22. All numbers which are divisible by 4 may not be divisible by 8.
Solution: True
Since, 12 is divisible by 4 but not by 8.
23. The Highest Common Factor of two or more numbers is greater than their Lowest Common Multiple.
Solution: False
HCF of two or more numbers is smaller than their LCM.
24. LCM of two or more numbers is divisible by their HCF.
Solution: True
25. LCM of two numbers is 28 and their HCF is 8.
Solution: False
The LCM of two numbers i.e., 28 is not divisible by their HCF, i.e., 8.
Their HCF cannot be 8.
26. LCM of two or more numbers may be one of the numbers.
Solution: True
27. HCF of two or more numbers may be one of the numbers.
Solution: True
28. Any two consecutive numbers are coprime.
Solution: True
The common factor of any two consecutive numbers is 1.
29. If the HCF of two numbers is one of the numbers, then their LCM is the other number.
Solution: True
The product of two numbers =HCF * LCM.
30. The HCF of two numbers is smaller than the smaller ofthe numbers.
Solution: False
Since, HCF of two numbers is less than or equal to the smaller of the numbers.
31. The LCM of two numbers is greater than the larger ofthe numbers.
Solution: False
Since, LCM of two numbers is greater than or equal to the larger of the numbers.
32. The LCM of two coprime numbers is equal to the product ofthe numbers.
Solution: True
33. A number is a _________ of each ofits factor.
Solution: Multiple
34.__________ is a factor of every number.
Solution:1
35. The number of factors of a prime number is_______
Solution: 2
36. A number for which the sum of all its factors is equal to twice the number is called a___________ number.
Solution: Perfect
37. The numbers having more than two factors are called___________
Solution: Composite
38. 2 is the only__________
Solution: Prime
39. Two numbers having only 1 as a common factor are called___________numbers.
Solution: Co-prime
40. Number of primes between 1 to 100 is_______.
Solution: 25 : Prime numbers between I to 100,are 2. 3, 5. 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47. 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97.
So, there are 25 primes between 1 to 100.
41. If a number has ________in ones place, then it is divisible by 10.
Solution: 0
42. A number is divisible by 5, if it has____________ or in its ones place.
Solution: 0, 5
43. A number is divisible by________if it has any of the digits 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8 in its ones place. 1,1,1
Solution: 2
44. If the sum of the digits in a number is a __________ of 3, then the number is divisible by
Solution: Multiple
45. If the difference between the sum of digits at odd places (from the right) and the sum of digits at even places (from the right) of a number is either 0 or divisible by_____________, then the number is divisible by 11.
Solution: 11
46. The LCM of two or more given numbers is the lowest of their common________.
Solution: Multiple
47. The HCF of two or more given numbers is the highest of their common____________.
Solution: Factors
48. Find the LCM of 80, 96, 125, 160.
Solution: We have,

The LCM of 80, 96, 125 and 160 is = 2x2x2x2x2x3x5x5x5 = 12000
49. Find the LCM of 160, 170 and 90.
Solution: We have,
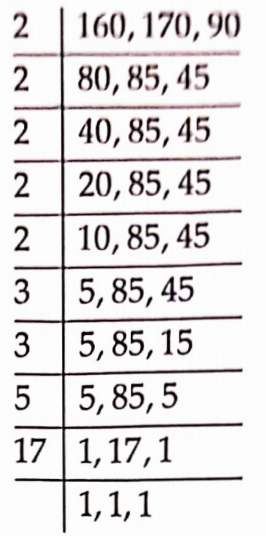
The LCM of 160, 170 and 190
=2x2x2x2x2x3x3x5x17
= 24480
50. Determine the sum of the four numbers as given below:
(1) successor of 32
(2) predecessor of 49
(3) predecessor of the predecessor of 56
(4) successor of the successor of 67
Solution:
Since, successor of32is 33, predecessor of 49 is 48, predecessor of the predecessor of 56 is 54 and successor of the successor of 67 is 69.
The required sum = 33 + 48 + 54 + 69 = 204
51. Determine the least number which when divided by 3, 4 and 5 leaves remainder 2 in each case.
Solution: We have,
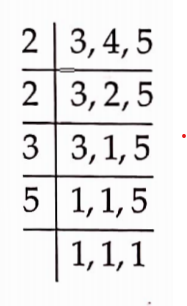
Since, the LCM of 3, 4 and 5 is 2 x 2 x 3 x 5 = 60.
The required number is 60 + 2 = 62
So, 62 is the least number which when divided by 3, 4 and 5 leaves remainder 2 in each case.
52. A merchant has 120 litres of oil of one kind, 180 litres of another kind and 240 litres of a third kind. He wants to sell the oil by filling the three kinds of oil in tins of equal capacity. What should be the greatest capacity of such a tin?
Solution:
Given:
merchant has 120 litres of oil of one kind, 180 litres of another kind and 240 litres of a third kind. He wants to sell the oil by filling the three kinds of oil in tins of equal capacity.
A merchant has 3 kinds of oil with different quantities like 120 litres, 180 litres and 240 litres
Since, he wants lo soli the oil by filling the three kinds of oil in tins of equal capacity, so the greatest capacity of such a tin is the HCF of 120, 180 and 240.

Now, 120 = 2x2x2x3x5
180 = 2x2x3x3x5
240 = 2x2x2x2x3x5
The required greatest capacity of a tin
= (2 x 2 x 3 x 5) litres
= 60 litres
The greatest capacity of a tin = 60 litres
53. Find a 4-digit odd number using each of the digits 1, 2, 4 and 5 only once such that when the first and the last digits are interchanged, it is divisible by 4.
Solution: By using the digits 1, 2, 4 and 5 only once, we get a 4 digit odd number 4521.
When we interchanged its first and last digits we get a new number, i.e., 1524 which is divisible by 4.
Thus, the required number is 4521.
54. Using each of the digits 1, 2, 3 and 4 only once, determine the smallest 4-digit number divisible by 4.
Solution: By using the digits 1, 2, 3 and 4 only once, the smallest 4-digit number which is divisible by 4 is 1324.
55. Fatima wants to mail three parcels to three village schools. She finds that the postal charges are 20, 28 and 36, respectively. If she wants to buy stamps only of one denomination, what is the greatest denomination of stamps she must buy to mail the three parcels?
Solution:
Given
Fatima wants to mail three parcels to three village schools. She finds that the postal charges are 20, 28 and 36, respectively.
The postal charges to mail three parcels are 20, 28 and 36 respectively.
Also, Fatima wants to buy stamps only of one denomination.
So, to find the greatest denomination of stamps, we find the HCF of 20, 28 and 36.
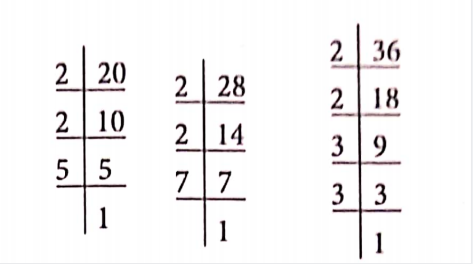
Now, 20 = 2 x 2 x 5
28 = 2 x 2 x 7
36 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 3
The HCF of 20, 28 and 36 is 2×2 = 4
So, ? 4 is the greatest denomination of stamps, she must buy to mail the three parcels.
56. Three brands A, B and C of biscuits are available in packets of 12, 15 and 21 biscuits respectively. If a shopkeeper wants to buy an equal number of biscuits, of each brand, what is the minimum number of packets of each brand, he should buy?
Solution:
Given
Three brands A, B and C of biscuits are available in packets of 12, 15 and 21 biscuits respectively. If a shopkeeper wants to buy an equal number of biscuits, of each brand
A shopkeeper has three brands A, B and C of biscuits are available in packets of 12, 15 and 21 biscuits respectively.
Also, a shopkeeper wants to buy equal number of biscuits of each brand for that we need to find the LCM of 12, 15 and 21.

The LCM of 12, 15 and 21 = 2x2x3x5x7 = 420
Thus, the required number of packets of
brand A =420/12= 35,
brand B =420/15 =28 and
brand C =420/21 = 20
57. The floor of a room is 8 m 96 cm long and 6 m 72 cm broad. Find the minimum number of square tiles of the same size needed to cover the entire floor.
Solution:
Given
The floor of a room is 8 m 96 cm long and 6 m 72 cm broad.
Length of floor of a room = 8 m 96 cm = 896 cm
Breadth of floor of the room = 6 m 72 cm = 672 cm
To find the minimum number of square tiles of same size needed to cover the entire floor, we find the LCM of 896 cm and 672 cm.
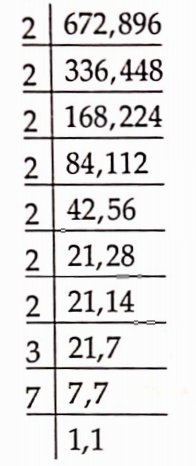
LCM of 672 and 896 is 2 X 2 X 2 x 2 X 2 X 2 X 2 X 3 X 7 = 2688
Number of square tiles =( 2688/672×2688/896)
= 4×3 = 12
58. In a school library, there are 780 books of English and 364 books of Science. Ms. Yakang, the librarian of the school wants to store these books in shelves such that each shelf should have the same number of books of each subject. What should be the minimum number of books in each shelf?
Solution:
Given
In a school library, there are 780 books of English and 364 books of Science. Ms. Yakang, the librarian of the school wants to store these books in shelves such that each shelf should have the same number of books of each subject.
Number of books of English = 780
Number of books of Science = 364
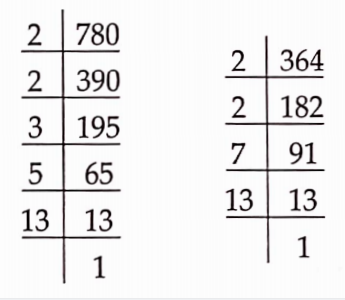
780 = 2x2x3x5x13
364 = 2 x 2 x 7 x 13
The HCF of 780 and 364 = 2 x 2 x 13 = 52
Thus, the minimum number of books in each shelf = 52
59. In a colony of 100 blocks of flats numbering 1 to 1 00, a school van stops at every sixth block while a school bus stops at every tenth block. On which stops will both of them stop if they start from the entrance of the colony?
Solution:
Given
In a colony of 100 blocks of flats numbering 1 to 1 00, a school van stops at every sixth block while a school bus stops at every tenth block.
There are 100 blocks in a colony numbering 1 to 100.
A school van stops at every sixth block and a school bus stops at every tenth block.
We have to find the common stops at which they both stop if they start from a same entrance.
We need to find the LCM of 6 and 10.
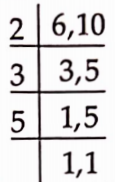
The LCM of 6 and 10 is 2 * 3 * 5 = 30. i.e.
Firstly both will stop at 30th block, then at 60th block and lastly at 90th block.
60. Test the divisibility of following numbers by 11
(1) 5335
(2) 9020814
Solution: (1) We have the difference between the sum of digits at odd places (from the right) and the sum of digits at even places (from the right) of a number 5335 is (5 + 3) = (3 + 5) = 8- 8 = 0, which is divisible by 11.
5335 is divisible by 11.
(2) We have the difference between the sum of digits at odd places (from the right) and the sum of digits at even places (from
the right) of the number 9020814 is (4 + 8 + 2 + 9) -(1 + 0 + 0) = 23-1 = 22, which is divisible by 11.
9020814 is divisible by 11.
61. Using divisibility tests, determine which of the following numbers are divisible by 4?
(1) 4096
(2) 21084
(3) 31795012
Solution: (1) We have, 4096
Since, the last two digits 96 is divisible by 4.
4096 must be divisible by 4.
(2) We have, 21084
Since, the last two digits 84 is divisible by 4.
21084 must be divisible by 4.
(3) We have, 31795012
Since, the last two digits 12 is divisible by 4.
31795012 must be divisible by 4.
62. Using divisibility test determine which of the following numbers are divisible by 9?
(1) 672
(2) 5652
Solution: (1) We have, 672
Since, the sum of all the digits of 672 is 15, which is not divisible by 9.
672 is not divisible by 9.
(2) We have, 5652
Since, the sum of all the digits of 5652 is 18, which is divisible by 9.
5652 must be divisible by 9.