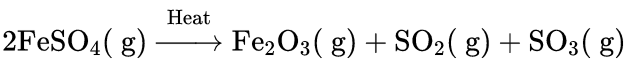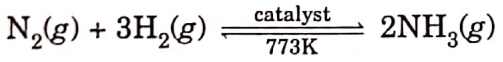NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions And Equations Long Question And Answers
Question 1.
1. What is rancidity? Mention any two ways by which rancidity can be prevented.
2.
- Why is respiration considered an exothermic reaction?
- Define the terms—oxidation and reduction.
- Identify the substance that is oxidised and reduced in the reaction:
CuO(s) + Zn(s) → Cu(s) + ZnO(s)
Answer:
1. The process in which the taste and smell of food get spoiled is called rancidity. It happens due to oxidation.
Prevention from rancidity:
- Antioxidants are added to fatty acids to prevent oxidation, e.g., chips are packed in the presence of nitrogen gas which prevents spoilage by oxidation.
- Food should be kept in an airtight container in the refrigerator.
2.
- This is because heat is evolved during respiration.
- Oxidation is a process in which O2 is added or H2 is removed or loss of electrons takes place. Reduction is a process in which H2 is added or O2 is removed or a gain of electrons takes place.
- Zn is getting oxidised, and CuO is getting reduced.
Chemical Reactions and Equations NCERT Class 10 Science Solutions
Read and Learn More Class 10 Science Solutions
Question 2.
1. 2 g of ferrous sulphate crystals are heated in a boiling tube.
- State the colour of ferrous sulphate crystals both before heating and after heating.
- Name the gases produced during heating.
2. Give reasons for the following:
- All decomposition reactions are endothermic reactions.
- The colour of copper sulphate solution changes when an iron nail is dipped in it.
- Respiration is an exothermic reaction.
Answer:
1.
- Before heating- Pale green. After heating- Brown or reddish brown.
- SO2 and SO3
2.
- Decomposition reactions require energy either in the form of heat, light or
electricity for breaking down the reactants or energy is absorbed. - Iron has displaced copper from the copper sulphate solution to form iron sulphate
which is light green. Fe is more reactive than copper. - During digestion, food (rice, potatoes etc.) containing carbohydrates are broken down to form glucose. This glucose combines with oxygen in the cells of our body and provides energy. Since energy is given so it is an exothermic.

Question 3.
1. Write one example for each decomposition reaction
- Electricity
- Heat
- Light
2. Which of the following statements is correct and why copper can displace silver from silver nitrate and silver can displace copper from copper sulphate solution
Answer:
1.
- 2H2O → (Electricities)→ 2H2(g) +O2
- CaCO3 → (Heat) → CaO+CO2
- 2AgBr → (Sunlight) → 2Ag +Br2
2. Copper can displace silver from AgNO3 because copper is more reactive than Ag,
Example: Cu + 2AgNO3(aq)→ Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2Ag (s)
NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations Summary
Question 4.
- Define corrosion.
- What is corrosion of iron called?
- How will you recognise the corrosion of silver?
- Why corrosion of iron is a serious problem?
- How can we prevent corrosion?
Answer:
- Define Corrosion: The process in which metals break down gradually by the action of air, moisture or a chemical on their surface.
- Rusting of iron.
- By the development of a black coating on silver.
- Even- year enormous amount of money is spent to replace damaged iron.
- Paint, or galvanisation, or electroplating.
Question 5. A metal nitrate ‘A’ on heating gives yellowish brown coloured metal oxide along with brown gas ‘B ‘and a colourless gas ‘C’ Aqueous solution of ‘A’ on reaction with potassium iodide forms a yellow precipitate of compound ‘D’. Identify ‘A, B, C, and D Also identify the types of h reactions. The metal present in ‘A’ is used in the alloy which is used for soldering purposes.
Answer:
Metal nitrate A is Pb(NO3)2.
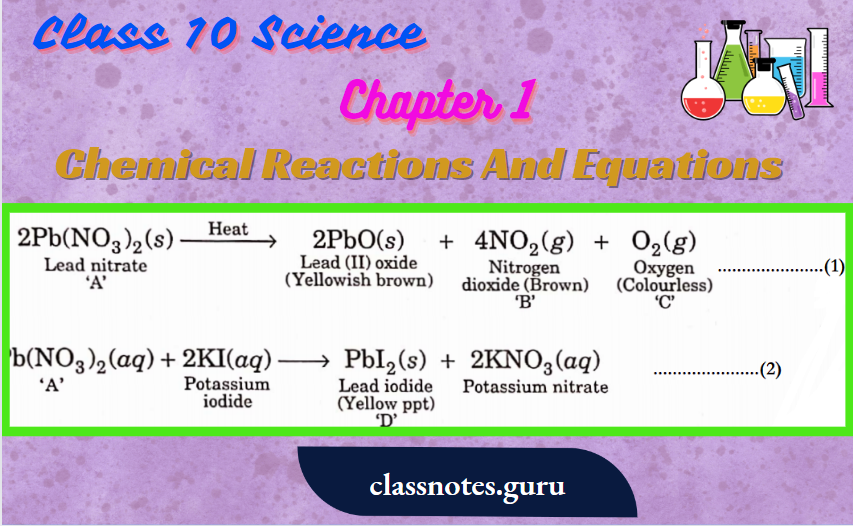
A’ is lead nitrate, ‘B’ is nitrogen dioxide, ‘C’ is oxygen and ‘D’ is lead.
- Is decomposition reaction and
- Is a double displacement reaction (Precipitation reaction
NCERT Solutions Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations Questions and Answers
Question 6. Translate the following statement into chemical equations and then balance them.
- Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia.
- Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in the air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
- Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate.
- Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
- Aluminium chloride reacts with ammonium hydroxide to form a gelatinous white precipitate of aluminium hydroxide and a salt of ammonium chloride.
Answer:
1. \(3 \mathrm{H}_2(g)+\mathrm{N}_2(g) \Longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{NH}_3(g)\)
2. \(2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}(g)+3 \mathrm{O}_2(g) \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{SO}_2(g)+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(g)\)
3. \(3 \mathrm{BaCl}_2(a q)+\mathrm{Al}_2\left(\mathrm{SO}_4\right)_3(a q) \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{AlCl}_3(a q)+3 \mathrm{BaSO}_4(s) \)
4. \(2 \mathrm{~K}(s)+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(l) \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{KOH}(a q)+\mathrm{H}_2(g) \)
5. \( \mathrm{AlCl}_3(a q)+3 \mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{OH}(a q) \longrightarrow \mathrm{Al}(\mathrm{OH})_3(s) \downarrow+2 \mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{Cl}(a q)\)
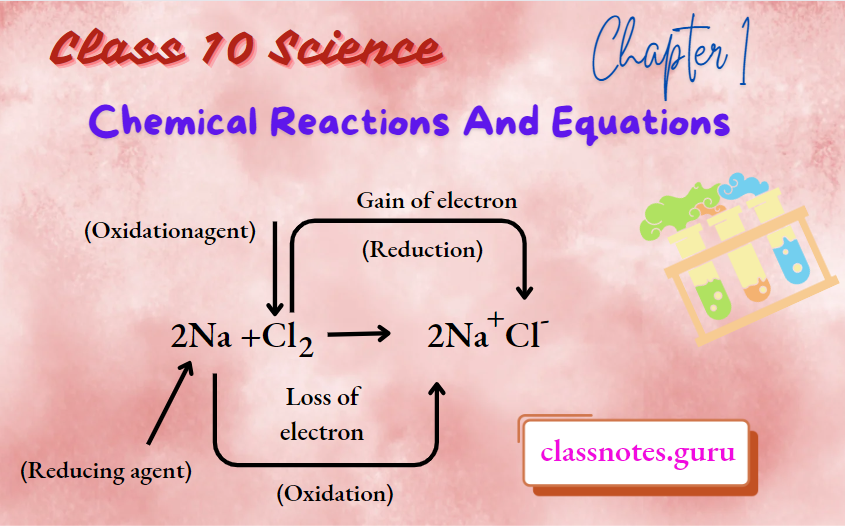
Question 7. Give reasons why:
- Sodium acts as a reducing agent while chlorine acts as an oxidising agent in the following reactions: 2Na(s)+Cl2 (g)→ 2 NaCl(s)
- White-coloured silver chloride turns grey when kept in sunlight.
- Why is the decomposition reaction called the opposite combination reaction?
Answer:
1. Sodium reduces chlorine atoms to chloride ions, therefore it acts as a reducing agent while chlorine oxidises sodium atoms to sodium ions, therefore, it acts as an oxidising agent
2. This is due to the decomposition of silver chloride into silver and chlorine by light.
3. In a decomposition reaction, one substance [compound] splits to give two or more simpler substances [elements or compounds] whereas in a combination reaction, two or more substances [elements or compounds] combine to form a single substance. Due to this reason, a decomposition reaction is called the opposite of a combination reaction.
Question 8. Observe the given figure and answer the following questions:
- Write the complete balanced reaction for the above.
- Write the type of reaction involved.
- Is there any precipitate formed?
- If any precipitate formed, write the colour of the precipitate.
Answer:
1. Na2SO4(ag) + BaCl2(aq) →2NaCl(aq) + BaSO4(s)↓ (White precipitate)
2. Double displacement reaction
3. Yes.
4. White precipitates of barium sulphate is formed.

NCERT Solutions Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations Questions and Answers
Question 9. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions and identify the type of reaction in each case.
- Nitrogen gas is treated with hydrogen gas in the presence ofa catalyst at 773K to form ammonia gas.
- Sodium hydroxide solution is treated with acetic acid to form sodium acetate and water.
- Ethanol is warmed with ethanoic acid to form ethyl acetate in the presence of
concentrated H2SO4 - Ethene is burnt in the presence ofoxygen to form carbon dioxide, and water and releases heat and light.
Answer:
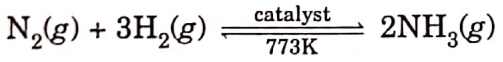
Example of a combination reaction.
2. NaOH(aq) + CH3COOH(aq) → CH3COOH(aq) + H2O(l)
Example of neutralisation reaction as well as double displacement reaction.
3. C2H5OH(l) + CH3COOH(Z) → H+ → CH3COOC2H5 (l) + H2O(Z)
Example of displacement reaction/Esterification
4. 2CH3– CH3(g) + 7O2→ 4CO2 + 6H2O + Heat
Example of combustion reaction.
Question 10. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions and identify the type of reaction in each case.
- In thermit reaction, iron (III) oxide reacts with aluminium and gives molten iron and aluminium oxide.
- Magnesium ribbon is burnt in an atmosphere of nitrogen gas to form solid magnesium nitride.
- Chlorine gas is passed in an aqueous potassium iodide solution to form a potassium chloride solution and solid iodine.
- Ethanol is burnt in the air to form carbon dioxide, water and releases heat.
Answer:
1. Fe2O3(s) + 2Al(s)- Al2O3(S) + 2Fe(Z) + Heat
Displacement reaction/Redox reaction
2. 3Mg(s) + N2(g) – Mg3N2(s)
Combination reaction
3. 2KI(aq) + Cl2(g) – 2KCl(aq) + I2(s)
Displacement reaction
4. C2H5OH(l) + 3O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) + Heat
Redox reaction/Combustion reaction
NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations Key Concepts
Question 11. During the reaction of some metals with dilute, hydrochloric acid following changes were made:
- Silver metal does not show any change.
- The temperature of the reaction mixture rises when aluminium (Al) is added.
- The reaction of sodium metal is found to be highly explosive.
- Some bubbles ofa gas are seen when lead (Pb) is reacted with the acid.
- Explain these observations giving suitable reasons.
Answer:
1. Silver is below hydrogen in the reactivity series so it cannot displace hydrogen when reacted with acid.
2. The reaction of Al with dilute HC1 is exothermic
2Al + 6 HCl→ 2AlCl3 + 3H2 + Heat
3. Sodium is a very reactive metal. It reacts with hydrochloric acid to form NaCl and H2 with the evolution of heat too. H2 gas produced catches fire immediately.
4. Lead is slightly more reactive and displaces hydrogen from acid very slowly and to a small extent. Hence, only bubbles of H2 can be seen
PbCl2 + 2HCl → PbCl2 + H2 (g)
Question 12. Write a balanced chemical equation for each ofthe following reactions and also classify them.
- Lead acetate solution is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid to form lead chloride and acetic acid solution.
- Ca(OH)2(aq)
- A piece of sodium metal is added to absolute ethanol to form sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas.
- Iron (3) oxide on heating with carbon monoxide gas reacts to form solid iron and liberates carbon dioxide gas.
- Hydrogen sulphidegas reacts with oxygen gas to form solid sulphur and liquid water.
Answer:
Pb (CH3COO)2 + 2HCl→PbCl2 + CH3 COOH; Double displacement reaction
2Na + 2C2H5OH→ 2C2H5ONa + H2; Displacement reaction
Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2 ; Redox reaction
2H2 S + O2 – 2S + 2H2O; Redox reaction
Question 13. Balance the following chemical equations and identify the type of chemical reaction.
1. \(\mathrm{Mg}(s)+\mathrm{Cl}_2(g) \longrightarrow \mathrm{MgCl}_2(s) \)
2. HgO(s)→ (Heat)→ Hg(l)+O2(g)
3. Na(s)+S(s)→ (Fuse)→ Na2S(s)
4. \( \mathrm{TiCl}_4(l)+\mathrm{Mg}(s) \longrightarrow \mathrm{Ti}(s)+\mathrm{MgCl}_2(s)\)
5. \(\left(\text { e) } \mathrm{CaO}(s)+\mathrm{SiO}_2(s) \longrightarrow \mathrm{CaSiO}_3(s)\right. \)
6. H2O2(l)→(UV) → HO2(l)+O2(g)
Answer:
1. \(\mathrm{Mg}(s)+\mathrm{Cl}_2(g) \longrightarrow \mathrm{MgCl}_2(s)\)(Balanced) – Combination reaction
2. 2HgO(s)→ (Heat)→ 2Hg(l)+O2(g)- Decomposition reaction
3. 2Na(s)+S(s)→ (Fuse)→ Na2S(s) – Combination reaction
4. \(\mathrm{TiCl}_4(l)+2 \mathrm{Mg}(s) \longrightarrow \mathrm{Ti}(s)+2 \mathrm{MgCl}_2\) – Displacement reaction
5.\(\mathrm{CaO}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{SiO}_2(\mathrm{~s}) \longrightarrow \mathrm{CaSiO}_3(\mathrm{~s})\) – Combination reaction
6. 2H2O2(l)→(UV) → 2HO2(l)+O2(g) – Decomposition reaction
Chemical Reactions and Equations NCERT Class 10 Science Explanation and Notes
Question 14. On heating a blue-coloured powder of copper (II) nitrate in a boiling tube, copper oxide(black), oxygen gas and a brown gas X are formed.
- Write a balanced chemical equation ofthe reaction.
- Identify the brown gas X evolved.
- Identify the type ofreaction.
- What could be the pH range of the aqueous solution ofthe gas X?
Answer:
1. Balanced chemical equation
2Cu(NO3)2(s) →(Heat) → 2CuO (s) + O2(g) + 4NO2(g)
2. The brown pas X evolved is nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
3. This is a decomposition reaction.
4. Nitrogen dioxide dissolves in water to form an acidic solution because it is an oxide of non-metal. Therefore, pH of this solution is less than 7.
Question 15. Give the characteristic tests for the following gases
- CO2
- SO2
- O2
- H2
Answer:
- CO2 gas turns lime water milky when passed through.
- SO2 gas when passed through an acidic KMnO4 solution (purple) turns
colourless. - The evolution of oxygen (O2) gas during a reaction can be confirmed by bringing a burning candle near the mouth ofthe test tube containing the reaction mixture.The intensity of the flame increases because oxygen supports burning.
- H2 gas burns with a pop sound when a burning candle is brought near it.
Chemical Reactions and Equations NCERT Class 10 Science Explanation and Notes
Question 16. What happens when a piece of
- Zinc metal is added to copper sulphate solution1?
- Aluminium metal is added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
- Silver metal is added to copper sulphate solution?
Also, write the balanced chemical equation if the reaction occurs.
Answer:
1. Zinc being more reactive than copper displaces copper from its solution and a solution of zinc sulphate is obtained
⇒ \(\underset{\text { Zinc }}{\mathrm{Zn}(s)}+\underset{\text { Copper sulphate(Blue) }}{\mathrm{CuSO}_4(a q)} \longrightarrow \underset{\text { Zinc sulphate(Colourless) }}{\mathrm{ZnSO}_4(a q)}+\underset{\text { Copper }}{\mathrm{Cu}(s)}\)
2. Aluminium being more reactive displaces hydrogen from dilute hydrochloric acid solution and hydrogen gas is evolved.
⇒ \(\underset{\text { Aluminium }}{2 \mathrm{Al}(s)}+\underset{\text { Hydrochloric acid}}{6 \mathrm{HCl}(a q)} \longrightarrow \underset{\text { Aluminium chloride}}{2 \mathrm{AlCl}_3(a q)}+\underset{\text { Hydrogen }}{3 \mathrm{H}_2(g)}\)
3. Silver metal being less reactive than copper cannot displace copper from its salt solution. Therefore, no reaction occurs
⇒ \(\underset{\text { Silver }}{\mathrm{Ag}(s)}+\underset{\text { Copper sulphate }}{\mathrm{CuSO}_4(a q)}\) → No reaction
Question 17. What happens when zinc granules are treated with a dilute solution of H2SO4, HCl, HNO3, NaCl and NaOH? Also, write the chemical equations if a reaction occurs.
Answer:
The reaction of Zn granules with
1. Dilute H2SO4
Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq)→ ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
2. Dilute HCl
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq)→ ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
3. Dilute HNO3
4 Zn(s) + 10HNO3 (aq) → 4Zn(NO3)2(aq) + 5 H2O(l) + N2O(g)
4. NaCl solution
Zn(s) + NaCl (aq ) → No reaction
5. NaOH solution
Zn(s) + 2NaOH(ag)→ Na2ZnO2(aq)( Sodium zincate) + H2(g)
NCERT Solutions for Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science
Question 18. On adding a drop of barium chloride solution to an aqueous solution of sodium sulphite, a white precipitate is obtained
- Write a balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved.
- What other name can be given to this precipitation reaction?
- On adding dilute HCl to the reaction mixture, the white precipitate disappears. Why?
Answer:
1. Balanced chemical equation
⇒ \(\underset{\text { Sodium sulphate }}{\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{SO}_3(a q)}+\underset{\text { Barium chloride }}{\mathrm{BaCl}_2(a q)} \longrightarrow \underset{\text { Barium sulphite }}{\mathrm{BaSO}_3(s)}+\underset{\text { Sodium chloride }}{2 \mathrm{NaCl}(a q)}\)
2. This reaction is also known as a double displacement reaction.
3. BaSO3 is a salt ofa weak acid (H2SO3), therefore dilute acids such as HCl decompose barium sulphite to produce sulphur dioxide gas which has the smell of burning sulphur
⇒ \(\underset{\text { Barium sulphite }}{\mathrm{BaSO}_3(s)}+\underset{\begin{array}{c}
\text { Hydrochloric } \\
\text { acid }
\end{array}}{2 \mathrm{HCl}(a q)} \longrightarrow \underset{\begin{array}{c}
\text { Barium } \\
\text { chloride }
\end{array}}{\mathrm{BaCl}_2}+\underset{\text { Water }}{\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}}+\underset{\begin{array}{c}
\text { Sulphur } \\
\text { dioxide }
\end{array}}{\mathrm{SO}_2(g)}\)
BaCl2 is soluble in water, hence white precipitate disappears.
Question 19. You are provided with two containers made up of copper and aluminium. You are also provided with solutions of dilute HCl, dilute HNO3, ZnCl2, and H2O. In which of the above containers these solutions can be kept?
Answer:
1. When solutions are kept in a copper container
⇒ Dilute HCl
Copper does not react with dilute HCl. Therefore, it can be kept.
⇒ Dilute HNO3
Nitric acid acts as a strong oxidising agent and reacts with copper vessels, therefore cannot be kept.
⇒ ZnCl2
Zinc is more reactive than copper (Cu) therefore, no displacement reaction occurs and hence can be kept.
⇒ H2O
Copper does not react with water. Therefore, can be kept.
2. When solutions are kept in aluminium containers
⇒ Dilute HCl
Aluminium reacts with dilute HCl to form its salt and hydrogen is evolved.
Therefore, if cannot be kept.
2Al + 6HCl→ 2 AlCl3 + 3H2
⇒ Dilute HNO3
Aluminium gets oxidised by dilute HN03 to form a layer of A1203 and can be kept
⇒ ZnCl2
Aluminium being more reactive than zinc can displace zinc ions from tho solution.
Therefore, the solution cannot ho kept.
2Al + 3ZnCl2→ 2AlCl3 + 3Zn
⇒ H2O
Aluminium does not react with cold or hot water. Therefore, water can be kept.
Aluminium is attacked by steam to form aluminium oxide and hydrogen
2Al(s) + 3H2O →Al2O3(s) + 3H2(g)
NCERT Solutions for Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science
Question 20. Translate the following statement into a chemical equation and then balance the equation: Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in the air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
Answer:
By observing the products, water (H2O) and sulphur dioxide (SO2), we can conclude that only oxygen from the air reacts with hydrogen sulphide (H2S).
Hydrogen sulphide + Oxygen
The skeletal equation for the reaction is:
⇒ \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}+\mathrm{O}_2 \longrightarrow \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{SO}_2\)
If we observe the equation we find that H and S atoms are equal on both sides of the equation. To balance O atoms multiply O2 by \(\frac{3}{2}\) becomes 3 on each side of the equation.
⇒ \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}+\frac{3}{2} \mathrm{O}_2 \longrightarrow \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{SO}_2\)
To make the coefficients whole numbers, multiply the above equation by 2.
⇒ \(2 \times \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}+\frac{3}{2} 3 \mathrm{O}_2 \longrightarrow \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{SO}_2\)
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}+3 \mathrm{O}_2 \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+2 \mathrm{SO}_2\)
In the above equation, there are 4 atoms of hydrogen, 2 atoms of sulphur and 6 atoms of oxygen on each side of the equation. Hence, the equation is balanced.
Question 21. The equation for the oxidation of ammonia is: NH3 + O2 → N+ H2O, Rewrite the equation in a balanced form.
Answer:
The skeletal equation is
NH3 + O2 → N2 + H2O
NH3 contains a maximum number of atoms, so the atoms present in it are balanced first.
Multiply NH3 by 2 to balance N atoms.
2NH3 + O2 →N2 + H2O
Multiply H2O by 3 to balance H atoms.
2NH3 + O2 → N2 + 3H2O
Oxygen is balanced last of all. To balance oxygen atoms multiply O2 by \(\frac{3}{2}\)
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{NH}_3+\frac{3}{2} \mathrm{O}_2 \longrightarrow \mathrm{N}_2+3 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Since all the coefficients should be whole numbers, multiply the above equation by 2 in order to convert all the coefficients to whole numbers.
⇒ \(2 \times 2 \mathrm{NH}_3+\frac{3}{2} \mathrm{O}_2 \longrightarrow \mathrm{N}_2+3 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
4NH3 + 3O2 → 2N2 + 6H2O
This is a balanced equation. There are 4 nitrogen atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms and 6 oxygen atoms on each side of the equation.
Question 22. Translate the following statement into a chemical equation and then balance the equation: Carbon disulphide burns in air to give carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide.
Answer:
Carbon disulphide + Oxygen (from air)-» Carbon dioxide + Sulphur dioxide
The skeletal equation for the reaction is
CS2 +O2→ CO2+ SO2
Multiply SO2 by 2 to balance sulphur atoms.
CS2 +O2 →CO2 + 2SO2
Carbon atoms are already balanced.
To balance oxygen atoms multiply O2 by 3 so that each side of the equation has 6 oxygen atoms.
CS2 + 3O2 → CO2 + 2SO2
This is a balanced equation. It has 2 sulphur atoms, 6 oxygen, atoms and 1 carbon atom on each side of the equation
Question 23. When copper (2) oxide is heated with hydrogen, copper metal and water are according to the equation: CuO + H2 →Cu + H2O
In this reaction, identify:
- The substance which undergoes oxidation
- The substance which undergoes reduction
- The oxidising agent
- The reducing agent
Answer:
1. Here, H2 changes to H2O This involves addition ofoxygen. Hence, H2 is oxidised to water.
2. In this reaction, CuO changes to Cu. This involves the removal of oxygen i.e., reduction.
Thus, Copper(2) oxide, CuO is reduced to Cu.
3. Here, CuO brings about the oxidation of H2 by supplying oxygen. Hence, CuO is, an oxidising agent.
4. H2 brings about a reduction of CuO. Hence, H2 is, a reducing agent.
Class 10 Science Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations Practice Questions
Question 24. Give differences between displacement and double displacement reactions.
Answer:
Displacement reactions:
1. In these reactions, a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its salt solution.
In these reactions, a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its salt solution.
2. These reactions are usually slow and take longer time for their completion.
3. During these reactions usually change of colour takes place. e.g.,
⇒ \(\mathrm{Fe}(s)+\underset{\text { Blue }}{\mathrm{CuSO}_4(a q)} \longrightarrow \underset{\text { Light green }}{\mathrm{FeSO}_4(a q)}+\mathrm{Cu}(s)\)
Double displacement reactions:
In these reactions, there is an exchange of ions between two reactants.
These reactions are usually fast and take place instantaneously.
During these reactions usually, precipitates are formed, e.g.,
AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq)→ AgCl(s)(White Precipitate)↓+ NaNO3(aq)
Question 25. Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them.
- Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia.
- Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in the air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
- Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate.
- Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas
Answer:
1. H2(g) + N2(g) → NH3(g)
Balanced equation: 3H2 (g) + N2(g)- 2NH3(g)
2. H2S(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l) +2 SO2(g)
Balanced equation: 2H2S(g) + 3O2(g) → 2H2O(l) +2 SO2(g)
3. BaCl2(aq) + Al2(SO4)3(aq)→AlCl3 (aq) + 3 BaSO4(s)
Balanced equation: 3BaCl2(aq) + Al(SO4)3(aq)→ 2AlCl3(aq) + 3BaSO4(s)
4. K(s) + H2O(l) → KOH(aq) + H2(g)
Balanced equation: 2K(s) + 2H2O(l) — 2KOH(aq) + H2(g)
Question 26. Balance the following chemical equations:
1. \(\mathrm{HNO}_3+\mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_2 \longrightarrow \mathrm{Ca}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
2. \(\mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \longrightarrow \mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
3. \(\mathrm{NaCl}+\mathrm{AgNO}_3 \longrightarrow \mathrm{AgCl}+\mathrm{NaNO}_3\)
4. \(\mathrm{BaCl}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \longrightarrow \mathrm{BaSO}_4+\mathrm{HCl}\)
Answer:
Balanced equations are as follows:
1. \( 2 \mathrm{HNO}_3+\mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_2 \longrightarrow \mathrm{Ca}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \)
2. \(2 \mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \longrightarrow \mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
3. \(\mathrm{NaCl}+\mathrm{AgNO}_3 \longrightarrow \mathrm{AgCl}^2+\mathrm{NaNO}_3 \text { (already balanced) } \)
4. \(\mathrm{BaCl}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \longrightarrow \mathrm{BaSO}_4+2 \mathrm{HCl}\)
Question 27. Write the balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case.
1. Potassium bromide (aq) + Barium iodide (aq) → Potassium iodidei (aq) + Barium, bromides)
2. Zinc carbonate(s)→ Zinc oxide (s) + Carbon dioxide
3. Hydrogen (aq)+ Chlorine→ Hydrogen chloride(aq)
4. Magnesium(s) + Hydrochloric acid (aq)
Magnesium chloride(aq) + Hydrogen(aq)
Answer:
1. 2KBr(aq) + Bal2(aq)→ 2KI(aq) + BaBr2(s)
Type of Reaction: Double displacement reaction
2. ZnCOg(s)→ ZnO(s) + CO2(g)
Type of Reaction: Decomposition reaction
3. H2(g) + Cl2(g) — 2HCl(g)
Type of Reaction: Combination reaction
4. Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq)→ MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Type of Reaction: Displacement reaction
Chemical Reactions and Equations: NCERT Class 10 Science Solutions
Question 28.
1. Write the essential condition for the following reaction to take place:
2AgBr → 2Ag + Br2 Write one application of this reaction.
2. Complete the following chemical equation of a chemical reaction:
2FeSO4 → (Heat)→ Fe2O3+……….+……….
3. What happens when water is added to quick lime? Write chemical equation
Answer:
1. 2 AgBr → (Sunlight)→ 2Ag+Br
This reaction is used in photography
2. 2 FeSO4 →(Heat) → FeO+SO2+SO3
Slaked lime is formed with a hissing sound and a lot of heat is evolved.
⇒ \(\mathrm{CaO}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_2+\text { Heat }\)
Question 29. A zinc plate was put into a solution of copper sulphate kept in a glass container. It was found that the blue colour of the solution gets fader and fader with time. After a few days when the zinc plate was taken out of the solution, several holes were observed in it
- State the reason for changes observed on the zinc plate.
- Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Answer:
1. This is because zinc has displaced copper from CuSO4. Zinc metal has been used to form zinc sulphate, therefore, a number of holes were observed.
2. \(\mathrm{Zn}(s)+\underset{\text { Blue }}{\mathrm{CuSO}_4(a q)} \longrightarrow \underset{\text { Colourless }}{\mathrm{ZnSO}_4(a q)}+\mathrm{Cu}(s)\)
Question 30. The following diagram displays a chemical reaction. Observe and answer the following questions:
- Identify the type of chemical reaction that will take place and define it. How will the colour ofthe salt change?
- Write the chemical equation ofthe reaction that takes place.
- Mention one commercial use of this salt.
Answer:
1. Photochemical decomposition reaction. The reaction in which a compound breaks down into simple substances in the presence of light is called a photochemical decomposition reaction. The colour of salt will change from white to grey.
2. 2AgCl(s) → (Sunlight) → 2Ag(s)+Cl(g)
3. Silver chloride is used in photography
Question 31. A, B, and C are are three elements which undergo chemical reactions according to the following equation:
A2O3 + 2B→ B2O3 + 2A
3CSO4 + 2B→ B2(SO4 )3 + 3C
3CO + 2A → A2O3 + 3C
Answer the following questions with reasons:
- Which element is the most reactive?
- Which element is the least reactive1?
- What are the types of reactions listed above?
Answer:
- B as B displaces both A and C from their solution.
- C as C, is displaced by both A and B.
- Displacement reactions
Question 32. Observe the following diagram and answer the following questions that follow:
- Identify the gases that evolved at the anode and cathode.
- Why are the amounts ofgases collected in the two test tubes not the same volume?
- What type ofreaction is this?
Answer:
1.
- At the anode, oxygen gas is evolved.
- At the cathode, hydrogen gas is evolved.
2. The amounts of gases collected in the two test tubes are of not the same volume because in water, hydrogen and oxygen are present in the ratio of 2: 1 by mass.
3. This reaction is a decomposition reaction.

Question 33. Write the chemical equation of the reaction in which the following changes have taken place with an example of each:
- Change in colour
- Change in temperature
- Formation of precipitate
Answer:
1. Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq)→ Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag
The solution will become blue in colour and shiny silver metal will be deposited.
2. NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O + Heat
The temperature will increase because heat will evolve.
3. Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI (aq)→ Pbl2(s) + 2KNO3(aq)
A yellow precipitate of Pbl2 will be formed.
NCERT Class 10 Science: Chemical Reactions and Equations Detailed Solutions
Question 34. Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer:
A decomposition reaction is considered as the opposite of a combination reaction because in a decomposition reaction, a single substance decomposes to produce two or more substances; whereas in a combination reaction, two or more substances combine to give a single substance.
Examples of decomposition reaction
1. \(\mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{Cl}(\mathrm{s}) \longrightarrow \mathrm{HCl}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{NH}_3(g)\)
2. \(\mathrm{CaCO}_3(\mathrm{~s}) \longrightarrow \mathrm{CaO}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})\)
Examples of combination reaction
1. \(\mathrm{NH}_3($ g $)+\mathrm{HCl}(\mathrm{g}) \longrightarrow \mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{Cl}(\mathrm{s})\)
2. \(\mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{CaO}(\mathrm{s}) \longrightarrow \mathrm{CaCO}_3(\mathrm{~s})\)
Question 35. Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity.
Answer:
Examples of decomposition reaction
1. Decomposition by the use of heat
⇒ \(\mathrm{CaCO}_3(a) → {\text { (Heat) }}→ \mathrm{CaO}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \text {, }\)
2. Decomposition by the use of electricity
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l})→{\text { (Electricity) }} → 2 \mathrm{H}_2(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g})\)
3. Decomposition by the use of light
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{AgCl}(\mathrm{s}) → {\text { (Sunlight) }} → 2 \mathrm{Ag}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{Cl}_2(g)\)
Question 36. What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer:
In displacement reactions, an element displaces or removes another element, whereas in double displacement reactions exchange of ions between the reactants takes place.
Example of displacement reaction:
1. \(\underset{\text { Iron }}{\mathrm{Fe}(s)}+\underset{\text { Copper sulphate }}{\mathrm{CuSO}_4(a q)} \longrightarrow \underset{\text { Iron sulphate }}{\mathrm{FeSO}_4(a q)}+\underset{\text { Copper }}{\mathrm{Cu}(s)}\)
In this, the element iron has displaced copper from its salt solution (copper sulphate).
Example of double displacement reaction:
2. \(\underset{\text { Sodium sulphate }}{\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4(a q)}+\underset{\text { Barium chloride }}{\mathrm{BaCl}_2(a q)} \longrightarrow \underset{\text { Barium sulphate }}{\mathrm{BaSO}_4(s)}+\underset{\text { Sodium chloride }}{2 \mathrm{NaCl}(a q)}\)
In the above reaction, the exchange of ions has taken place, i.e., Na+ ion has replaced Ba2+ and vice versa.
Question 37. Explain the following in terms of gain or loss of oxygen with two examples each.
- Oxidation
- Reduction
Answer:
1. Oxidation: A chemical reaction in which a substance gains oxygen is called oxidation.
For example:
1. 2 Cu +O → (Heat) → 2 CuO
Cu is oxidised to CuO
2. 2 Mg +O → (Burn)→ 2MgO
Mg is oxidised to MgO
2. Reduction: A chemical reaction in which a substance loses oxygen is called reduction.
For examples:
1. ZnO+ C → Zn +CO
ZnO is reduced to Zn
2. CuO +H2 → Cu +H2O
CuO is reduced to MgO
NCERT Class 10 Science: Chemical Reactions and Equations Detailed Solutions
Question 38. Explain the following terms with one example each.
- Corrosion
- Rancidity
Or
What is rancidity? What is corrosion? Mention any two ways by which they can be prevented.
Answer:
1. Corrosion:
Due to the effect of moisture and acids, metals get corroded, i.e., metals particularly iron form a porous layer on the surface and thus get damaged. This effect is called corrosion. Corrosion causes damage to metal articles like car bodies, bridges, iron railings, ships and other substances of daily use. To prevent corrosion iron articles should be regularly painted, done oiling, etc.
2. Rancidity:
Fats and oils in food kept for a long time get oxidised and become rancid and the taste of food changes and causes infection upon eating. This is called rancidity.
To prevent rancidity, antioxidants (which prevent oxidation) are added to foods containing fats and oils. Rancidity can also be prevented by flushing out oxygen with an inert gas like nitrogen.
For example, Packets of food items like chips are flushed with nitrogen so that these can be used even after a long duration.
Question 39. What does one mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Or
Differentiate between exothermic and endothermic reactions? Write one example for each of these reactions in the form of a balanced chemical equation.
Answer:
Exothermic reactions: Chemical reactions in which energy is evolved (or given out) are known as exothermic reactions.
For example:
CO2(s) + O(g) → CO2(g) + 393.7 kJ (ΔH =- 393.7 kJ)
Endothermic reactions:
Reactions in which energy is absorbed are called endothermic reactions. For example.
C(s) + 2S(s) → + CS2 – 92 kJ (ΔH = + 92 kJ)
Question 40. A shiny brown-coloured element ‘X’ on heating in air becomes black. Name the element ‘X and the black-coloured compound formed. (PBQ)
Or
A reddish-brown coloured metal, used in electrical wires, when powdered and heated strongly in an open china dish, its colour turns black. When hydrogen gas is passed over this black substance, it regains its original colour. Based on the above information, answer the following questions:
Answer:
- Name the metal and black-coloured substance formed.
- Write balanced chemical equations for both reactions.
Answer:
Element ‘X’ = Copper (Cu)
Compound = Copper oxide (CuO)
⇒ \(\underset{\text { Brown }}{2 \mathrm{Cu}(s)}+\underset{\text { (from air) }}{\mathrm{O}_2} \longrightarrow \underset{\text { Black }}{2 \mathrm{CuO}}\)
Question 41. Complete the missing components/variables given as x and y in the following reactions.
1. Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(aq)→ Pbl2(x) + 2KNO3(y)
2. Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2 (aq)+ x(s)
3. Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq)→ ZnSO4(x) + H2(y)
4. CaCO3(s)→ (x) → CaO(s)+CO2(g)
Answer:
1. x → Solid(s), y → aqueous (aq)
2. x → 2Ag
3. x → Aqueous(aq) y gas (g)
4. x → heat
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations
Question 42. Which among the following changes are exothermic or endothermic?
- Decomposition of ferrous sulphate
- Dilution of sulphuric acid
- Dissolution of sodium hydroxide in water
- Dissolution of ammonium chloride in water
Answer:
- Endothermic reaction
- Exothermic reaction
- Exothermic reaction
- Endothermic reaction
Question 43. Identify the reducing agent in the following reactions.
- 4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
- H2O + F2→ HF +HOF
- Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
- 2H2+ O2 → 2H2O
Answer:
- Ammonia (NH3)
- Water (H2O) as F2 is getting reduced to HF
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Hydrogen
Question 44. Identify the oxidising agent (oxidant) in the following reactions.
- 2Mg +O2→ 2MgO
- CuSO4 + Zn → Cu + ZnSO4
- V2O5 + 5Ca- →2V + 5CaO
- 3Fe + 4H2O
- CuO + H2→ Cu + H2O
- Pb3O4 + 8HCl 3PbCl2 + Cl2 + 4H2O
Answer:
- O2
- CuSO4
- V2O5
- H2O
- CuO
- Pb3O4
Question 45. A magnesium ribbon is burnt in oxygen to give a white compound X accompanied by the emission of light. If the burning ribbon is now placed in an atmosphere of nitrogen, it continues to burn and forms a compound Y.
- Write the chemical formulae of X and Y.
- Write a balanced chemical equation, whenX is dissolved in water.
Answer:
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
3Mg + N2→ Mg3N2
X is MgO; Y is Mg3N2
MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)2
Question 46. Tarun visited a government hospital to meet his cousin. He saw the medicines in dark bottles were not stored properly. They were not kept away from light and heat. Tarun reported the issue to the medical doctor and was satisfied that all medicines are stored properly.
- Why are some medicines stored in cool places in dark bottles?
- Why do some medicines need cool place1?
- What can we get from this act?
Answer:
- Medicines when kept in sunlight or in high temperatures lose its chemical identity.
- Some medicines if not stored at an appropriate temperature show chemical changes and become dangerous for health.
- Tarun showed his responsibility of well-being.
Question 47. Hunny a student of class 10 visited the house of his uncle Mohit during the summer holidays. He found that all the water taps were rusted. Hunny suggested Uncle to use either chrome-plated or nickel plated taps in place of iron taps. Mohit accepted his suggestion for the future.
- Why did iron taps get rusted?
- Name an antirust solution.
- Name the process involved in the chrome plating or nickel plating.
- Mention the values associated with the above act.
Answer:
- Articles made up of iron readily get rusted when kept in moisture or water.
- Bisphenol
- Electroplating
- Use of scientific knowledge, and help of others.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations
Question 48.
1. Write one example for each ofthe decomposition reactions carried out with the help of:
- Electricity
- Heat
- Sunlight
Give balanced chemical equations in each case.
2. Which of the following statements is correct and why? Copper can displace silver from the solution of silver nitrate and silver can displace copper from the solution of copper sulphate.
Answer:
1.
- Electricity: 2H2O(g)→ (Electric/current )→ 2H2(g) + O2(g)
- Heat: CaCO3(s) → (Heat) → CaO(s) + CO2
- Sunlight: 2AgCl(s) → (Sunlight)→ 2 Ag(s)+Cl2(g)
2. Copper can displace silver from silver nitrate solution because it is more reactive than silver.
Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq)→ Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)