Large Blood Vessels Of The Gut Question And Answers
Question 1. Write in detail about the formation, course, tributaries, and relations of portal vein.
Answer:
Portal vVein
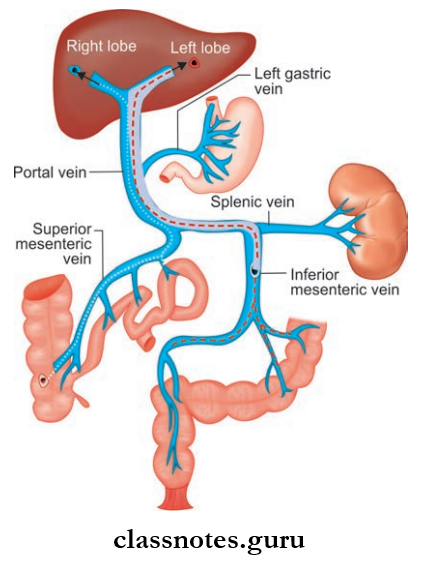
Portal Vein Length: 7.5–8 cm.
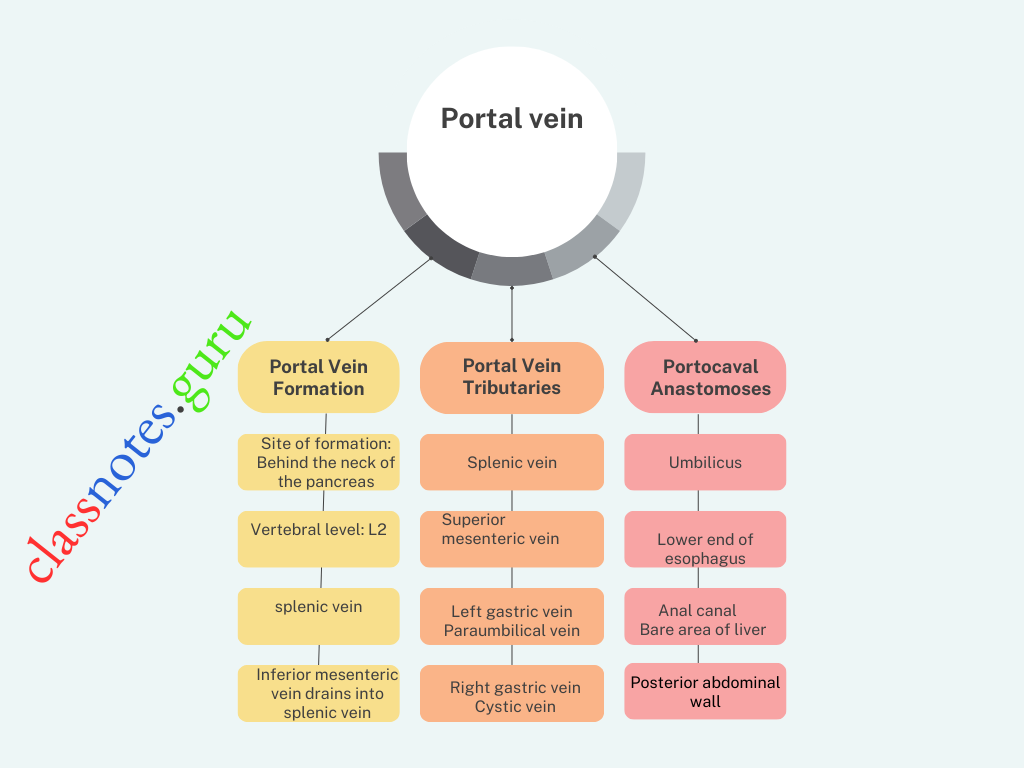
Portal Vein Formation
- Site Of Formation: Behind the neck of the pancreas
- Vertebral Level: L2
- By the union of the superior mesenteric vein and splenic vein.
- Inferior mesenteric vein drains into splenic vein
Read And Learn More: Abdomen And Pelvis
Portal Vein Course:
- Right Branch
- Shorter and wider
- Portal Vein enters right lobe of liver
- Also receives the cystic vein.
Abdominal Blood Vessels Anatomy MCQs
- Left Branch
- Longer and narrower
- Portal Vein enters left lobe of liver
- Portal Vein gives branches to caudate and quadrate lobes
- Portal Vein receives paraumbilical veins
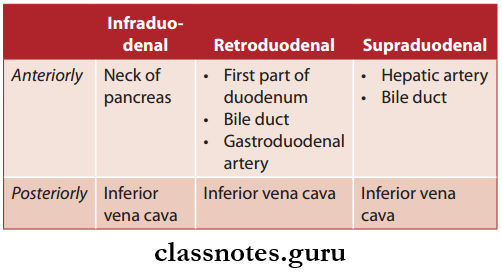
Based On Its Course, The Portal Vein Can Be Divided Into Three Parts:
- Infraduodenal part
- Retroduodenal part
- Supraduodenal part
Portal Vein Relations
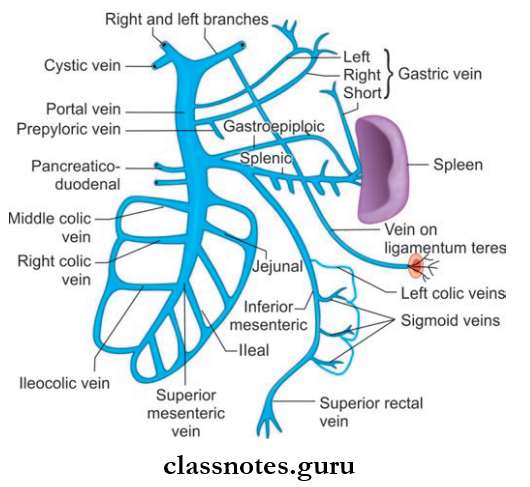
Portal Vein Tributaries
- Splenic vein
- Superior mesenteric vein
- Left gastric vein
- Right gastric vein
- Superior pancreaticoduodenal vein
- Cystic vein
- Paraumbilical vein.
Pelvic Blood Vessels Important Questions
Question 2. What is portocaval anastomoses or portosystemic anastomoses?
Answer:
Portocaval Anastomoses
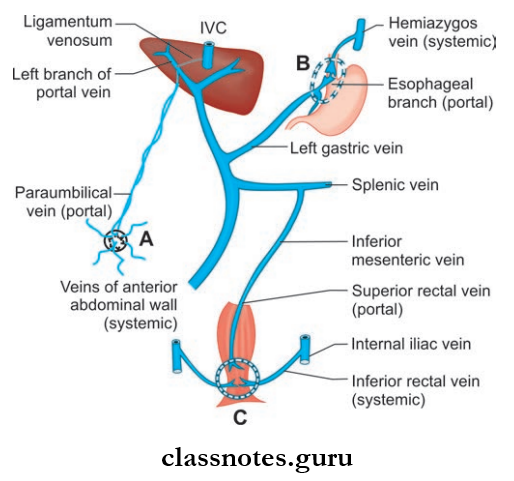
- There are many sites in the abdominal cavity, where there is anastomoses between the portal and systemic venous systems
- The communicants act as important routes of collateral circulation in cases of portal obstruction Important sites of portal caudal anastomoses is described below.
Portocaval Anastomoses Or Portosystemic Anastomoses Applied Anatomy: In portal obstruction, veins around the umbilicus get distended, called as caput medusae.
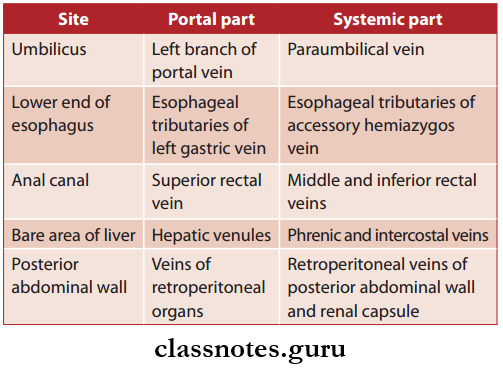
- Umbilicus
- The left branch of two portal vein anastomoses with paraumbilical veins (systemic)
- The paraumbilical vein receives superficial veins of the anterior abdominal wall.
- Lower End Of Esophagus: Esophageal tributaries of left gastric vein (portal) anastomose with esophageal tributaries of accessory hemiazygos vein (systemic)
- Anal Canal: Superior rectal vein (portal) anastomoses with middle and inferior rectal veins (systemic)
- Bare Area Of Liver: Hepatic venules (portal) anastomoses with phrenic and intercostal veins (systemic)
- Posterior Abdominal Wall: Veins of retroperitoneal organs (portal) anastomoses with retroperitoneal veins of the posterior abdominal wall and renal capsule (systemic).
Retroperitoneal Organs
- Duodenum
- Ascending colon
- Descending colon
Table Showing Site And Vessels Of Portocaval Anastomoses:
Vascular Anatomy Of Abdomen And Pelvis Viva Questions
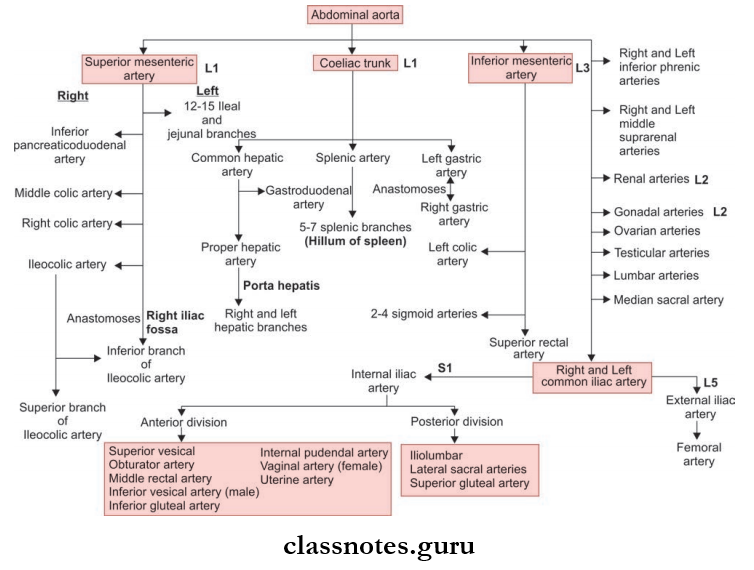
Question 3. Write a note on the internal iliac artery.
Answer:
Internal Iliac artery
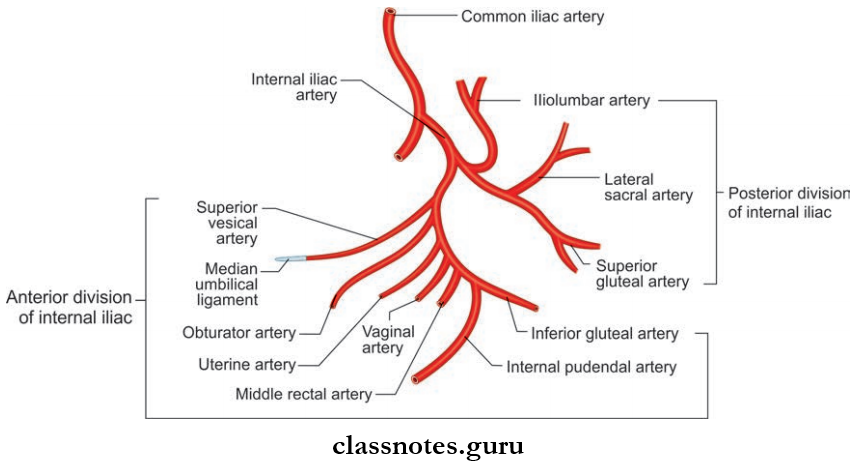
Smaller terminal branch of common iliac artery
Internal Iliac Artery Course:

Internal Iliac Artery Relations:
- Anteriorly
- Ureter
- Uterine tube
- Ovary
- Posteriorly
- Sacroiliac joint
- Lumbosacral trunk
- Internal iliac vein
- Medially
- Peritoneum
- Laterally
- External iliac vein
- Obturator nerve
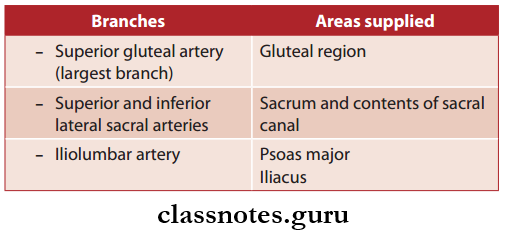
Branches Of Anterior Division Internal Iliac Artery And Areas Supplied:
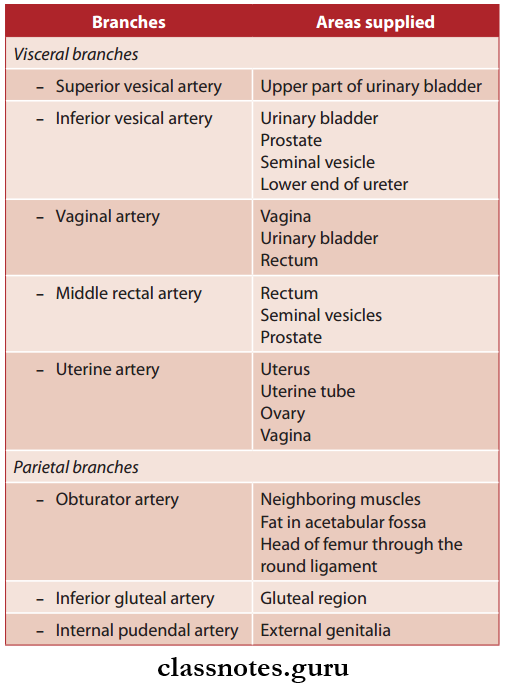
Branches Of Posterior Division Internal Iliac Artery And Areas Supplied:
Abdominal Aorta And Its Branches Questions
Question 4. Write a note on the celiac trunk.
Answer:
Celiac Trunk
- Artery of foregut, since it supplies all the derivatives of foregut in the abdomen
- It is a short vessel
- Length: 1.25 cm
- Celiac Trunk Origin: Arises from the front of abdominal aorta just below aortic opening of the diaphragm
- Celiac Trunk Vertebral Level Of Origin: Between T12 and L1
- Course: Runs forwards and a little to the right and ends by dividing into its three terminal branches
- Celiac Trunk Terminal Branches:
- Left gastric artery
- Common hepatic artery
- Splenic artery
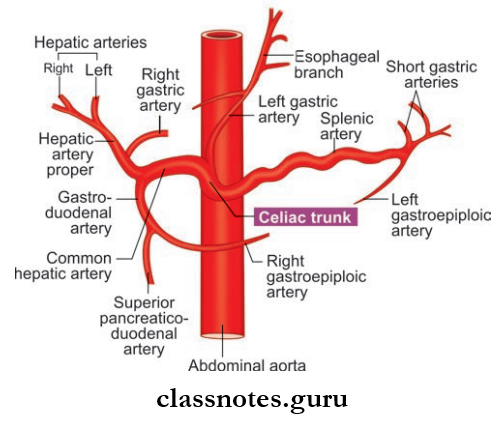
Celiac Trunk Relations:
- Anteriorly: Lesser sac and lesser omentum
- Posteriorly: Abdominal aorta
- Inferiorly: Splenic vein and body of pancreas
- Right: Right crus of the diaphragm, caudate process of the liver, and right celiac ganglion
- Left: Left crus of the diaphragm, cardiac end of the stomach, and left celiac ganglion stomach
- Structures Supplied (Foregut derivatives): The lower end of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum up to the level of opening of the common bile duct, liver, greater part of pancreas, and spleen.
Iliac Arteries And Veins Question Answers
Question 5. Write a note on the Superior Mesenteric Artery
or
Write a note on the SMA Disease
Answer:
Superior Mesenteric Artery
- Artery of the midgut, since it supplies all the derivatives of the midgut
- Origin: In front of the abdominal aorta about 1.25 cm below the origin of the celiac trunk
- Vertebral Level Of Origin: L1
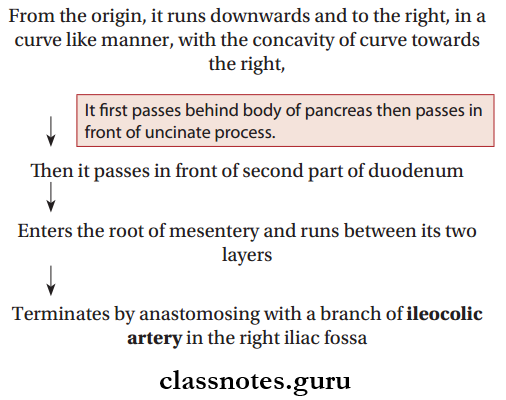
Superior Mesenteric Artery Course:
Superior Mesenteric Artery Relations:
- Anteriorly: Body of pancreas, splenic vein
- Posteriorly: Left renal vein, the uncinate process of the pancreas, the third part of the duodenum, right psoas major, inferior vena cava.
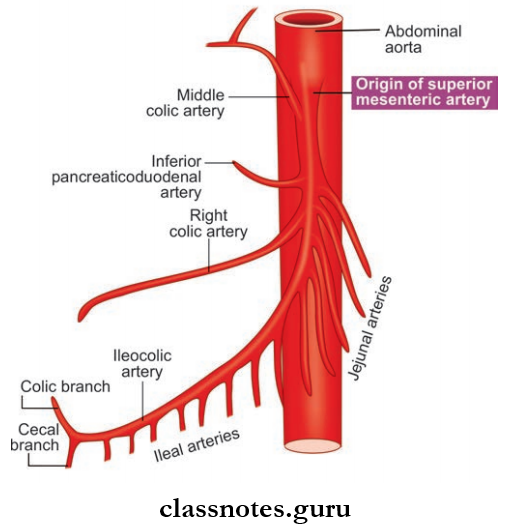
Superior Mesenteric Artery Branches:
- Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery
- Middle colic artery
- Right colic artery
- Ileocolic artery
- 12–15 Jejunal and ileal branches
Structures Supplied (Midgut Derivatives): Duodenum below the opening of the common bile duct, jejunum, ileum, appendix, cecum, ascending colon. Right 2/3rd of transverse colon, lower half of head of the pancreas.
Blood Supply Of Abdominal Organs – Exam Questions
Question 6. Write a note on the inferior mesenteric artery.
Answer:
Inferior Mesenteric Artery
- Artery of the hindgut, since it supplies all the derivatives of the hindgut in the abdomen and also derivatives of the posterior part of the cloaca
- Inferior Mesenteric Artery Origin: Arises from the front of the abdominal aorta about 3–4 cm above the termination of the aorta
- Inferior Mesenteric Artery Vertebral level Of Origin: L3
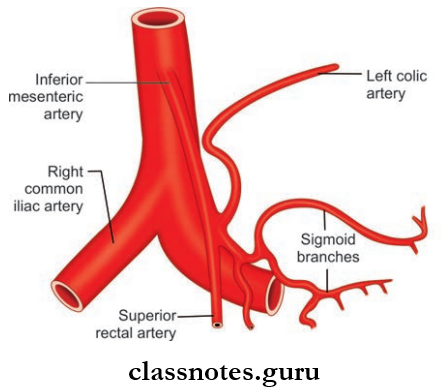
Inferior Mesenteric Artery Course:

Inferior Mesenteric Artery Branches:
- Left Colic Artery
- Sigmoid Arteries: 2–4 in number
- Superior Rectal Artery: Terminal branch.
Inferior Mesenteric Foregut Derivatives: Epithelium of the pharynx, esophagus, stomach, duodenum till ampulla of Vater, respiratory system auditory tube and mucous membrane of the tongue, parenchyma of liver, pancreas, thyroid, parathyroid, etc.
Inferior Mesenteric Midgut Derivatives: Epithelium of the duodenum from the ampulla of Vater to junction of right 2/3rd and left 1/3rd of the transverse colon.
Inferior Mesenteric Hindgut DerivativesP: Mucous membrane of the large intestine from left 1/3rd of the transverse colon to mucocutaneous junction of the anal canal, parenchyma of the prostate, epithelium of urinary bladder, urethra, etc.
Large Blood Vessels Of The Gut Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 1. The bifurcation of the aorta into the common iliac arteries is located at which vertebral level?
- L1
- L2
- L3
- L4
- L5
Answer: 4. L5
Question 2. Which of the following is not a direct branch of celiac trunk?
- Common hepatic artery
- Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery
- Splenic artery
- Left gastric artery
Answer: 2. Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery
Pelvic Circulation And Venous Drainage Questions
Question 3. Which of the following is a branch of the posterior division of the internal iliac artery?
- Uterine
- Umbilical
- Superior gluteal
- Pudendal
Answer: 3. Superior gluteal
Question 4. Inferior mesenteric vein opens into:
- Splenic vein
- Inferior vena cava
- Superior mesenteric vein
- Portal vein
Answer: 1. Splenic vein
Question 5. Which of the following ligaments contains the splenic artery?
- Splenocolic ligament
- Gastrosplenic ligament
- Splenorenal ligament
- Splenophrenic ligament
Answer: 3. Splenorenal ligament
