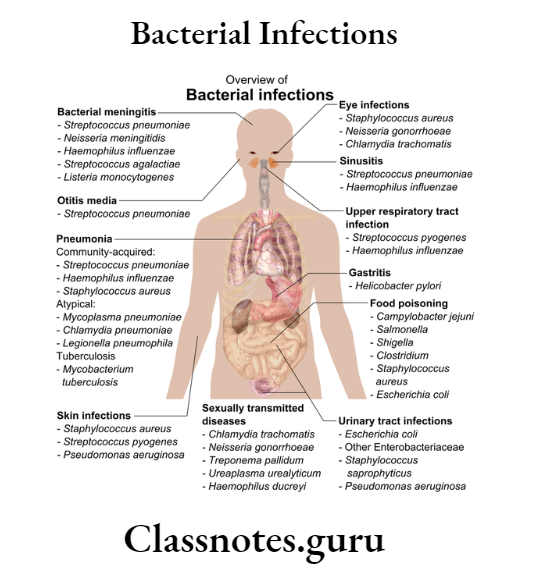
Oral Medicine Bacterial Infections Important Notes
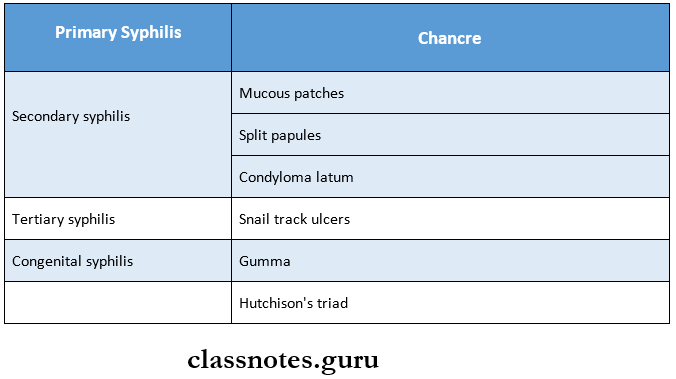
1. Important Features Of Different Stages Of Syphilis
2. Hutchison’s Triad
- Mulberry molars and notched incisors
- Interstitial keratitis
- 8th nerve deafness
3. Actinomycosis
- It commonly Involves the cervicofacial region
- There Is the development of multiple abscesses which drain through the skin
- Pus contains sulfur granules
4. Scarlet Fever
- Caused by a hemolytic type of streptococci
- Appears as a bright skin rash
- Small papule erupts through these rashes
- The tongue exhibits a white coating at the fungiform papilla that projects above the surface
- Known as strawberry tongue
- Later the coating is lost and the tongue becomes red and smooth called raspberry tongue
Read And Learn More: Oral Medicine Question and Answers
5. Tuberculosis
- Primary tuberculosis of the skin is called lupus vulgaris
- Primary oral tuberculosis is associated with regional lymphadenopathy mostly involving submandibular and cervical implodes
- It involves gingiva
- Present as diffuse, nodular, or papillary proliferation of gingival tissues
- Secondary oral tuberculosis can affect any site but the most common tongue and palate
- Present as superficial or deep, irregular painful ulcer
6. Psoriasis With Monro Abscess Is Seen In
- Benign migratory glossitis
- Psoriasis
- Reiter’s syndrome
7. Snail Track Ulcers Are Seen In
- Secondary syphilis
- Pyostomatitis vegetans
Oral Medicine Bacterial Infections Short Essays
Question 1. Congenital syphilis.
Answer:
Congenital Syphilis
Congenital Syphilis is an infection of the fetus established by the passage of spirochaetes from the mother, through the placenta
Congenital Syphilis Clinical Features:
1. Within the first 2 weeks of life
Congenital Syphilis Features: Rhinitis
- Chronic nasal discharge
- Loss of weight
- Bullae, vesicle formation
- Superficial desquamation with cracking and scaling of reddened soles and palms
- Petechiae, mucous patches
2. Age – After 2 years
Congenital Syphilis Features:
- Interstitial keratitis
- Vascularization of cornea
- 8th nerve deafness
- Arthropathy
- Neurosyphilis
- Anterior tibial bowing
- Higoumenakis sign – Irregular thickening of a sternoclavicular portion of the cheek
Oral Manifestation:
- Postrhagadic Scarring:
- These are linear lesions found around oral and anal orifices.
- These are seen from 3rd- 7th week after birth
- They appear as red or copper-colored linear areas covered with a soft crush
- Syphilitic Rhagades:
- They are radially arranged and perpendicular to the mucocutaneous junction
- Teeth:
- Retarded root resorption of deciduous
- Marring of permanent incisors
- Spacing between cuspid and incisors o Malocclusion and the open bite is present
- The Crown of the molar is irregular
- The occlusal surface appears to be arranged in an agglomerate mass of globules
- Incisor-screw driver shaped
- Constriction of crown towards the incisal edge
- The incisal edge is usually a notch
- Rounding of mesial and distal incisal line angles
- Jaws – Hypoplastic maxilla
- Frontal bossing
- Saddle nose deformity
Congenital Syphilis Management:
- Antibiotics:
- Benzathine penicillin – 2.4 million units/IM
- Aqueous crystalline penicillin
- Tetracycline hydrochloride – 500 mg orally 4 times a day
- Patient allergic to penicillin – Erythromycin 500 mg orally Q1D for 15 days
- Follow up – Repeated examination is to be done at 1, 3, 6, 9,12,18, and 24 months
- Prevention – It can be achieved by subjecting pregnant women to antenatal and post-natal checkups.
Oral Medicine Bacterial Infections Short Answers
Question 1. Chancre.
Answer:
Chancre
- Chancre is one of the clinical findings of primary syphilis
- Incubation period – 3 – 90 days
- Site – Lesion develops at the site of inoculation
- It most frequently occurs on the penis in males and the vulva or cervix in females
Chancre Features:
- The chancre is slightly raised over the surface
- Chancre becomes ulcerated
- Chancre is a non-tender, non-bleeding firm plaque
- Shape – Round and indurated
- Size – Varies from 5 mm to several centimeters
- Edges – Rolled raised edges are seen
- Prognosis – It disappears without treatment after 10 days
Question 2. Hutchison’s Triad.
Answer:
Hutchison’s Triad
- Hutchison’s Triad is a feature of congenital syphilis
- It includes
- Interstitial keratitis – It results from opacification of the corneal surface with resultant loss of vision
- Enamel hypoplasia of permanent incisors and 1st permanent molars
- Eight nerve deafness
Question 3. Split Papule.
Answer:
Split Papule
- Split Papule is a feature of secondary syphilis
- A Split Papule is a double papule that occurs at skin folds and the angle of the mouth
Question 4. Koplik’s spots.
Answer:
Koplik’s Spots
- Koplik’s Spots is one of the important clinical features of measles
- Site: buccal mucosa
- Koplik’s Spots Presentation
- The mucosa becomes inflamed
- Over it, there is the presence of white or white-yellow pinpoint papules
Oral Medicine Bacterial Infections Viva Voce
- Purulent discharge with sulfur granules is characteristic of actinomycosis
- Tuberculosis is also referred as an acid-fast infection
- Scrofula refers to tuberculous involvement of cervical lymph nodes
- Paraesthesia in lips and tongue is found in tertiary syphilis
- Syphilitic rhagades are found in congenital syphilis
- Peg-shaped laterals and mulberry molars are found in congenital syphilis
- Chancre lesions are a characteristic feature of primary syphilis
- Strawberry tongue is a feature of scarlet fever
- A lumpy jaw is seen in actinomycosis
- Sulfur granules are diagnostic of actinomycosis
- Actinomycosis is also called ray fungus
