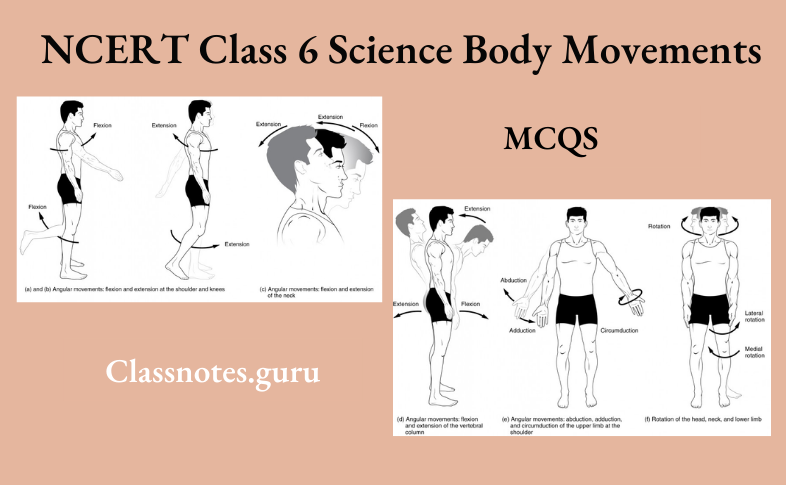
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Getting To Know Plants Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. The plant which cannot be classified as a shrub is
- Jasmine
- Bougainvillea
- Carrot
- Lemon
Answer: 3. Carrot
Question 2. Which one of the following best describes the characteristics of a tree?
- Jasmine
- Bougainvillea
- Carrot
- Cotton
Answer: 2. Bougainvillea
Read and Learn More NCERT Class 6 Science MCQs
Question 3. Which of the following is the correct match between the characteristics of the stem and the category of the plant?
- Weak stem which cannot stand upright- creeper
- Green tender stem-shrub
- Thick, hard stem with branching near the base-tree
- Thick, hard stem with brandies high on the plant-herb
Answer: 1. Weak stem which cannot stand upright- creeper
Question 4. The picture shows a pumpkin. The spreading stems shown to indicate that a pumpkin should be classified as competency
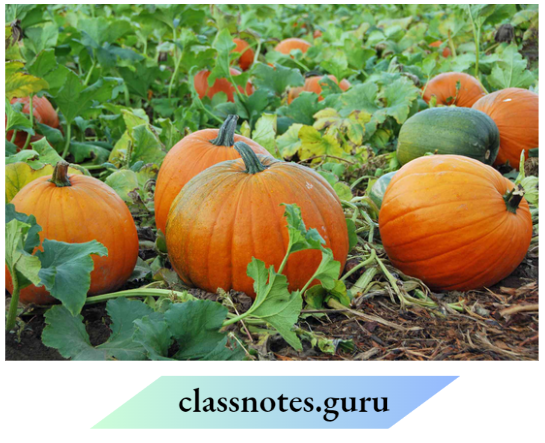

- Herb
- Shru
- Creeper
- Tree
Answer: 3. Creeper
Question 5. The part of the plant which grows towards light and it also transports water, minerals and food.
- Stem
- Roots
- Leaf
- Flower
Answer: 1. Stem
Question 6. Which of the following is not the primary function of the stem?
- Conduction of water
- Photosynthesis
- Formation of branches
- Bears flowers and fruits
Answer: 2. Photosynthesis
Question 7. Which of the following is not a correct match?
- Petiole: attaches the leaf to the stem
- Lamina: green flat part of the leaf
- Margin: gives shape to the leaf
- Veins: transpiration
Answer: 4. Veins: transpiration
Question 8. Which of the following combinations of features would you observe in grass?
- Parallel venation and fibrous root
- Parallel venation and tap root
- Reticulate venation and fibrous root
- Reticulate venation and tap root
Answer: 1. Parallel venation and fibrous root
Question 9. Read the following sentences about photosynthesis.
- Sunlight, carbon dioxide, chlorophyll and water are necessary.
- Oxygen is absorbed.
- Leaves carry out photosynthesis.
- Proteins are made during photosynthesis.
Choose the correct pair of sentences that is true to photosynthesis
- 3 And 4
- 1 And 3
- 2 And 4
- 1 And 4
Answer: 2. 1 And 3
Question 10. Sarita pulled a herb out of the soil and observed that a plant part came out with it. Rohlni was watching the activity and saw some hair-like structures coming out from that part what could be the plant part?
- Flower
- Leaf
- Root
- Stem
Answer: 3. Root
Question 11. Which of the following plants does not have a tap root?
- Marigold
- Mango
- Maize
- Turnip
Answer: 3. Maize

Question 12. Which part of the plant grows in the soil?
- Stem
- Leaf
- Root
- Seed
Answer: 3. Root
Question 13. In the given diagram which part of the flower contains yellow powdery substances?
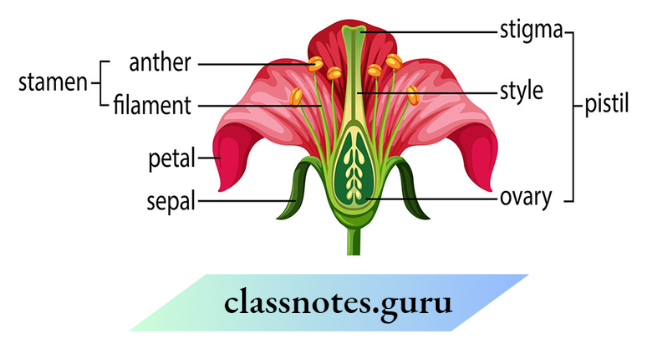
- Ovary
- Filament
- Style
- Anther
Answer: 2. Filament
Question 14. Reproductive parts what characteristics would that plant portion have?
- Presence of stomata
- Presence of stamens and pistil
- Presence of midrib
- Presence of root hairs.
Answer: 2. Presence of stamens and pistil
Question 15. The male parts of the flower are called
- Pistil
- Carpel
- Stamen
- Style
Answer: 3. Stamen
Question 16. Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
- Leaves can only make food when there is light
- Male flowers will develop into fruits
- Roots hold the plant firmly to the ground
- Plants need air, water and sunlight to grow
Answer: 2. Male flowers will develop into fruits
Question 17. Which of the following terms constitutes the female part of the flower?
- Sepals, petals and stamen
- Stigma, style and ovary
- Ovary, stamen and stigma
- Ovary, style and stamen
Answer: 2. Stigma, style and ovary
Question 18. The underground plant part which anchors the plant to the soil is
- Stem
- Internode
- Leaves
- Roots
Answer: 2. Internode
Question 2. What part of the plant do we eat as food in turnip?
- Roots
- Stem
- Flower
- Trunk
Answer: 1. Roots
Question 3. Taproot is found in
- Onion
- Marigold
- Millet
- Wheat
Answer: 2. Marigold
Question 4. Which of the following plants does not have a tap root?
- Mustard
- Maize
- Tulsi
- Balsam
Answer: 2. Maize
Question 5. The lowermost and swollen part of the pistil is catted
- Ovule
- Ovary
- Style
- Filament
Answer: 2. Ovary.