Anti-Epileptic Drugs Important Notes
1. Anti-Epileptic Drugs Types of seizures and drugs used in it
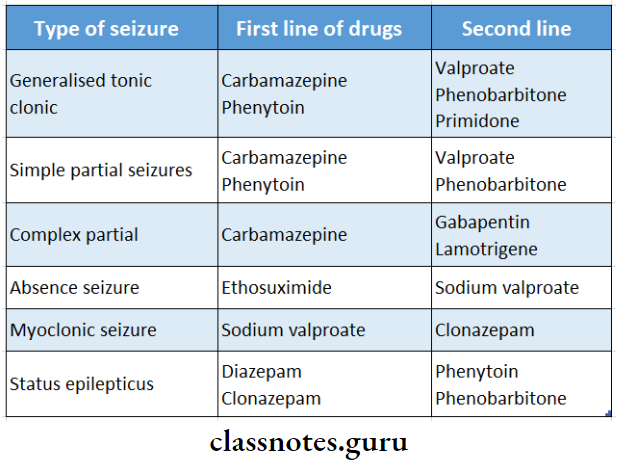
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question and Answers
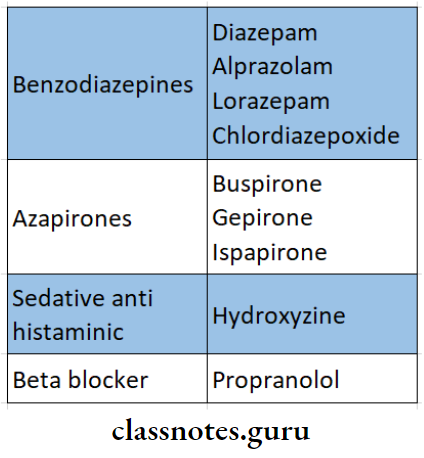
2. Anti-Epileptic Drugs Classification of anti-anxiety drugs
3. Anti-Epileptic Drugs Phenytoin
- It is the drug of choice for grand mal epilepsy and generalized seizures
- Adverse effects
- Insomnia, headache, giddiness
- Gingival hyperplasia
- Produces fetal hydantoin syndrome in pregnancy characterized by deft lip and palate and microcephaly
- Hirsutism
- Megaloblastic anaemia
- Used to treat digitalis-induced ventricular arrhythmias
Antiepileptic drugs questions and answers
4. Anti-Epileptic Drugs Carbamazepine
- Used in
- Temporal lobe epilepsy
- Grand mal epilepsy
- Trigeminal neuralgia
5. Anti-Epileptic Drugs Diazepam
- Useful in
- Acute pain
- Anxiety
- Status epileptics
- Has a high therapeutic index
- Dose: 2-5 mg BID
Anti-Epileptic Drugs Long Essays
Question 1. Classify the drugs used in epilepsy. Write the mechanism of action and adverse effects of diphenylhydantoin sodium.
Answer:
Anti-Epileptic Drugs:
- Anti-epileptic drugs are used during epilepsy.
Anti-Epileptic Drugs Classification:
- Barbiturate – phenobarbitone, mephobarbitone.
- Deoxybarbiturate – primidone.
- Hydration – Phenytoin, mephenytoin.
- Iminostilbene – Carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine.
- Succinimide – Ethosuximide.
- Aliphatic carboxylic acid – valproic acid.
- Benzodiazepine s- Clonazepam. Diazepam.
- Phenyltriazine – Lamotrigine.
- Cyclic – GABA analogue – Gabapentin, pregabalin.
- Newer drugs – Vigabatrin, topiramate.
Diphenylhydantoin/Phenytoin sodium:
- It is a major antiepileptic drug.
Diphenylhydantoin/Phenytoin sodium Mechanism of action:
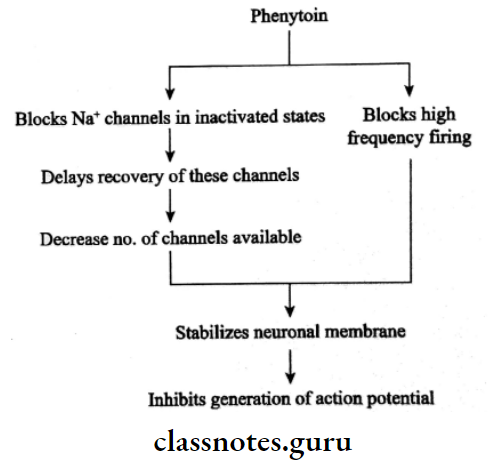
Diphenylhydantoin/Phenytoin sodium Adverse effects:
1. At therapeutic doses:
- Gum hypertrophy – is common in younger patients.
- Nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, anorexia.
- Diplopia, ataxia, nystagmus.
- Peripheral neuropathy on prolonged use.
- Hypersensitivity.
- Endocrine disorders – hirsutism, acne, hyperglycaemia, decreased release of ADH, osteomalacia, hypocalcaemia.
- Megaloblastic anaemia, pancytopenia, neutropenia.
- Teratogenicity – causes foetal hydantoin syndrome.
2. At high doses.
- Prominent cerebellar and vestibular effects.
- Drowsiness, hallucinations, mental confusion, delirium, altered behaviour.
Antiepileptic drugs MCQs
Question 2. Enumerate antiepileptic drugs. Mention the actions of phenytoin sodium. How do you manage a case of convulsion precipitated during tooth extraction?
Answer:
Anti-epileptic drugs:
Phenytoin sodium:
- It is a major anti-epileptic drug.
Phenytoin sodium Actions:
- It has CNS actions.
- Anti-seizure.
- Effective against generalised tonic-clonic seizures and partial seizures.
- Doesn’t cause generalised CNS depression.
Management of convulsion precipitated during tooth extraction:
1. Drugs used.
- Diazepam 10 mg IV bolus injection followed by fractional doses every 10 min or slow infusion titrated to control the fits. Or.
- Phenobarbitone 100 – 200 mg 1M/1V or.
- Phenytoin 25 mg/min. IV.
2. Maintain patent airway, oxygen, fluid and electrolyte balance, BP, cardiac rhythm, and care of unconsciousness.
Question 3. Mention the clinical uses of dilantin sodium.
Answer:
Uses of dilantin sodium:
- In generalised tonic-clonic seizures.
- In simple and complex partial seizures.
- Status epilepticus – 25 mg/min, slow IV. Used as an alternative to diazepam.
- Trigeminal neuralgia – second choice of drug, next to carbamazepine.
- Used in digitalis-induced cardiac arrhythmia – 100 mg IV every 10 min or 100 – 200 mg orally 2 – 6 hourly followed by 400 mg/day for maintenance.
Anti-Epileptic Drugs Short Essays
Question 1. Sodium valproate.
Answer:
Sodium valproate is a broad-spectrum anticonvulsant drug.
Sodium valproate Mechanism:
1. Enhances the level of GABA by.
- Increasing its synthesis.
- Decreasing its metabolism.
2. Blocks Na+ channels.
- Delays its recovery from inactivated states.
3. Decreases low threshold Ca++ current in the thalamus.
Sodium valproate Uses:
- In absence seizures – drug of choice.
- Adjuvant drug for generalized tonic-clonic seizures, simple and complex partial seizures.
- Myoclonic and atonic seizures.
- As a mood stabilizer in bipolar mood disorders.
- Tried as a prophylactic measure in migraine.
Sodium valproate Adverse Effects:
- GIT symptoms – nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain.
- CNS symptoms – Ataxia, drowsiness, tremors. Sedation.
- Rashes, alopecia, curling of hair, increased bleeding.
- Rarely fulminant hepatitis.
- Teratogenicity-neural tube-defects in newborns.
Question 2. Enlist the advantages and disadvantages of tone sodium.
Answer:
Thiopentone sodium:
- It is ultra short-acting thiobarbiturate.
Thiopentone sodium Advantages:
- Highly soluble in water.
- Produces unconsciousness within 15-20 sc.
- Highly lipid soluble.
Thiopentone sodium Disadvantages:
- Poor analgesic.
- Weak muscle relaxant.
- Produces CNS depression.
- Causes respiratory depression.
- Required to prepare freshly every time.
- Extravasation of solution causes intense pain, necrosis and gangrene.
Antiepileptic drugs classification
Question 3. Phenytoin sodium in grand mal epilepsy.
Answer:
Phenytoin prolongs the inactivated state of the voltage-sensitive neuronal Na+ channel and it also governs the refractory period of the neurons.
- As a result, high-frequency discharges are inhibited with little effect on normal low-frequency discharges.
- It has a stabilizing influence on the neuronal membrane and thus prevents repetitive detonation.
- This stabilizing influence consists of a synchronous and unusually large depolarization over which action potentials are superimposed.
- At high doses.
- Reduces Caz+ influx.
- Inhibits glutamate.
- Facilitates GABA responses.
- Prevents intracellular accumulation of Na+ occurring during repetitive firing.
- Therefore, phenytoin sodium is used in grand mal epilepsy.
Question 5. BDZ (benzodiazepines) as anticonvulsants.
Answer:
- Benzodiazepine have useful anticonvulsant property
Benzodiazepine Mechanism of Action:
- Inhibits GABA metabolism
- Enhances GABA-mediated inhibition
- At large doses, high-frequency discharges are inhibited
Anti-Epileptic Drugs Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Phenobarbitone.
Answer:
Phenobarbitone is an important drug used in epilepsy.
- It inhibits the neurotransmitter’s action by enhancing the GABA receptors thus facilitating them to open chloride ion channels.
- It raises the seizure threshold and thus prevents epileptic attacks.
- It is preferred due to its efficacy and low cost.
Phenobarbitone Uses:
- Generalized tonic-clonic seizures.
- Partial seizures.
Question 2. Carbamazepine.
Answer:
Carbamazepine is anti-epileptic drug.
Carbamazepine Uses:
- Epilepsy – generalized tonic-clonic seizure and partial seizures.
- Neuralgia – trigeminal and glossopharyngeal neuralgia.
- Manic depressive illness and acute mania.
- Chronic neuropathic pain.
Carbamazepine Adverse effects:
- Dose-related neurotoxicity – sedation, dizziness vertigo, diplopia and ataxia.
- GIT disturbance, vomiting, diarrhoea.
- Hypersensitivity reactions – rashes, photosensitivity agranulocytosis, aplastic anaemia.
- Minor foetal abnormalities.
Question 3. Sodium valproate.
Answer:
Sodium valproate Uses:
- In absence seizures – drug of choice.
- Adjuvant drug for generalized tonic-clonic seizures, simple and complex partial seizures.
- Myoclonic and atonic seizures.
- As a mood stabilizer in bipolar mood disorders.
- Tried as a prophylactic measure in migraine.
Sodium Valproate Adverse Effects:
- GIT symptoms-nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain.
- CNS symptoms – Ataxia, drowsiness, tremors. Sedation.
- Rashes, alopecia, curling of hair, increased bleeding.
- Rarely fulminant hepatitis.
- Teratogenicity – neural tube defects in newborns.
Antiepileptic drugs: mechanism of action
Question 4. Phenytoin sodium/Dipbenyl hydantoin sodium.
Answer:
Diphenyihydantoin/Phenytoin sodium:
It is a major antiepileptic drug
Diphenyihydantoin/Phenytoin sodium Adverse effects:
1. At therapeutic doses:
- Gum hypertrophy – is common in younger patients.
- Nausea, vomiting epigastric pain, anorexia.
- Diplopia, ataxia, nystagmus.
- Peripheral neuropathy on prolonged use.
- Hypersensitivity.
- Endocrine disorders – hirsutism, acne, hyperglycaemia, decreased release of ADH, osteomalacia, hypocalcaemia.
- Megaloblastic anaemia, pancytopenia, neutropenia.
- Teratogenicity – causes foetal hydantoin syndrome.
2. At high doses.
- Prominent cerebellar and vestibular effects.
- Drowsiness, hallucinations, mental confusion, delirium, altered behaviour.
Question 5. Phenytoin sodium contra-indicated in pregnancy.
Answer:
Phenytoin sodium causes teratogenicity. When taken by the pregnant lady.
- It produces foetal hydantoin syndrome.
- It is characterized by.
- Hypoplastic phalanges.
- Cleft palate.
- Harelip.
- Microcephaly.
Question 6. Adverse effects of Phenytoin.
Answer:
1. Phenytoin At therapeutic doses
- Gum hypertrophy
- Nausea, vomiting epigastric pain
- Diplopia
- Ataxia, nystagmus
- Hypersensitivity
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Endocrine disorders: hirsutism, acne, hyperglycaemia
- Megaloblastic anaemia, pancytopenia, neutropenia
- Teratogenicity
2. Phenytoin At high doses
- Prominent cerebellar and vestibular effects
- Drowsiness, hallucinations, mental confusion, delirium, altered behaviour
Antiepileptic drugs pharmacology questions
Question 7. Name three uses and three adverse effects of Diazepam.
Answer:
Diazepam Uses:
- Status epilepticus
- 5-10 mg IV every 10-15 min upto 30 mg
- IV anaesthesia
- Dose – 0.2-0.5 mg/kg IV
- For conscious sedation
- 1-2 mg IV is given in repeated doses or by slow infusion until the desired level of sedation is achieved
- As sedative and hypnotic
- Centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant
- Combined with analgesic
- As antiepileptic
Diazepam Adverse Effects:
- Drowsiness
- Confusion
- Amnesia
- Impaired motor coordination
- Blurred vision
- Ataxia
- Headache
Question 8. Enlist three adverse effects of Sodium Valproate.
Answer:
- GIT symptoms – nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain
- CNS symptoms – ataxia, drowsiness, tremors, sedation
- Rashes, alopecia, curling of hairs, increased bleeding
- Teratogenicity – neural tube defects in newborns
