Structure Of Matter And Principle Of Adhesion Important Notes
1. Contact Angle
- It is an angle formed by the adhesive with the adherent at their interface
- The less the contact angle the more the wettability and spreadability
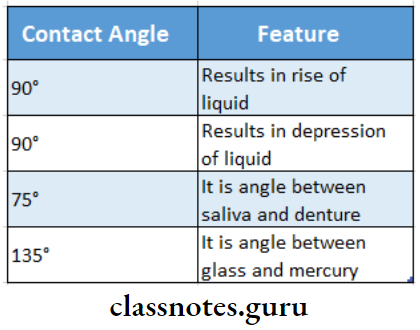
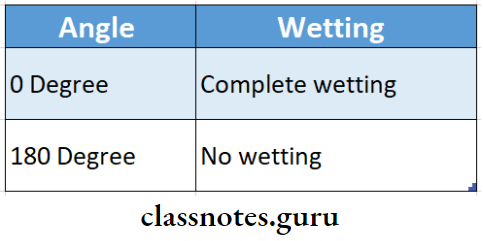
2. Wetting
- To produce adhesion the liquid must flow easily over the entire surface and adhere to the solid
- This feature is known as wetting
Read And Learn More: Dental Materials Question and Answers
3. Surface Tension/ Surface Energy
- Wetting and adhesion are directly related to the surface energy of adhesives
- The surface energy of many restorative materials is higher when compared to that of tooth
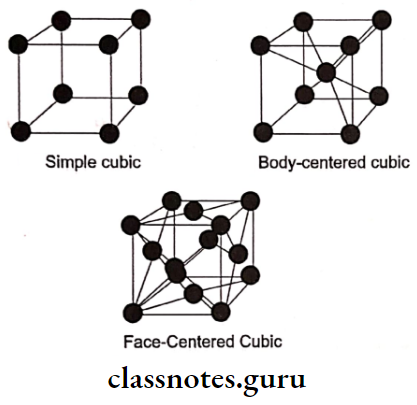
4. Space Lattice
- Space Lattice can be defined as any arrangement of atoms in space in which every atom is situated similarly to every other atom.
- Space Lattice may be the result of primary or secondary bonds
- There are 14 possible types
Structure Of Matter In Dentistry
Structure Of Matter And Principle Of Adhesion Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Space lattice?
Answer:
Space Lattice Synonym: Crystal structure
Synonym Definition:
- A space lattice can be defined as any arrangement of atoms in space such that every atom is situated similarly to every other atom.
- It may be the result of primary or secondary bonds.
Space Lattice Types: The type of space lattice is defined by the length of each of the three unit cell edges and the angles between the edges
There are 14 possible lattice types or forms
- Simple cubic space lattice
- It is the most commonly used form
- In it, the position of atoms is located at the points of intersection of three sets of parallel planes called crystal planes
- Other types are
- Body-centered cubic
- Face-centered cubic
- Rhombohedral
- Orthorhombic
- Monoclinic
- Triclinic
- Tetragonal
- Simple hexagonal
- Closed packed hexagonal
- Rhombic
Adhesive Bonding In Dental Materials
Question 2. Mechanical bonding.
Answer:
Mechanical Bonding: Attachment between the two substances is achieved by mechanical bonding or retention
Mechanical Bonding Applications
1. Non-dental applications
- Mechanical bonding is achieved by the use of screws, bolts, or undercuts
2. Dental applications
- It is involved in the penetration of the adhesive into the microscopic irregularities in the surface of the substrate
- Micromechanical bonding is a type of mechanical bonding that is used in dentistry
- This type is used for
- Retention of a cast restoration
- Mechanical bonding of the cementing agent improves retention of the casting over the tooth surface
- Resin restorative material
- Resins are not capable of adhering to the tooth surface
- Thus before its insertion, the enamel Is treated with phosphoric add called the acid etched technique
- By this minute pores are produced over the enamel surface into which resin flows and provides retention
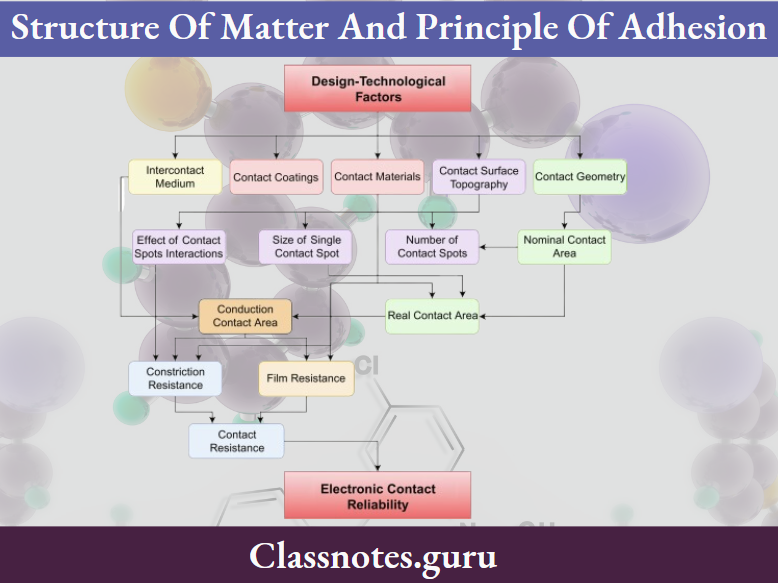
Question 3. Contact angle?
Answer:
Contact Angle Definition:
The angle formed at the interface of the adhesive and adherend is known as the contact angle.
Contact Angle Significance:
- Contact angle determines the extent to which an adhesive wets the surface of an adherend.
- If the adhesive forces are stronger than cohesive, no angle is formed
- If the adhesive remains as a drop and doesn’t spread, the contact angle will be higher
- The smaller the contact angle between an adhesive and an adherend, the better the ability of the adhesive to flow
- It is used to measure wettability.
Dental Adhesion Mechanisms
Question 4. Surface Tension?
Answer:
Surface Tension Definition: The increase in energy on the surface per unit area is referred to as surface tension.
Surface Tension Synonym:
Surface energy
Surface Tension Reason:
The Energy at the surface of a solid is greater than in its interior because
1. Inside a lattice
- All the atoms are equally attracted to each other
- The interatomic distance arc equal
- Energy is minimal.
2. But at the surface of the lattice
- Atoms are not equally attracted in all directions
- There is only force from the inside of the lattice pulling the outermost atoms inwards.
- This creates tension on the outer surface.
Question 5. Wetting agent?
Answer:
Wetting Agent Definition:
A wetting agent is a surface-active substance that reduces the surface tension of a liquid to promote wetting or adhesion.
Wetting Agent Synonym: It is also called a surfactant.
Wetting Agent Significance:
- To improve the wettability of the set Impression material by gypsum-water mixture, a wetting agent is added.
- It ensures the good surface quality of the gypsum model
Factors Affecting Adhesion In Dentistry
Question 6. Adhesion
Answer:
Adhesion Definition:
- A molecular or atomic attraction between two contacting surfaces promoted by the Interfacial force of attraction between molecules or atoms of two different species is called adhesion.
- The material that is used to cause bonding is known as adhesive and the material to which it adheres is called the adherend.
Adhesion Types: Adhesion may occur by chemical or mechanical adhesion or both.
Adhesion Applications:
1. Restorative procedures
- Incomplete adhesion of restorative materials to the tooth structure results in leakage of the material 1 causing secondary caries
2. Prosthodontic procedures
- Retention of dentures occurs due to adhesion between dentures and saliva and between saliva and soft tissue
3. Periodontal aspects
- Plaque and calculus adhere to the tooth structure
Question 7. Interatomic bonds.
Answer:
Interatomic Bonds The interatomic bonds are classified into primary and secondary bonds
Primary Bonds: They are chemical In nature
Primary Bonds Types:
- Ionic Bonds: It is a simple bond that occurs due to the mutual attraction of positive and negative charges
- Covalent Bonds: In covalent bonding, two valence electrons are shared by adjacent atoms
- Metallic Bond: It is the primary bond occurring between metal atoms
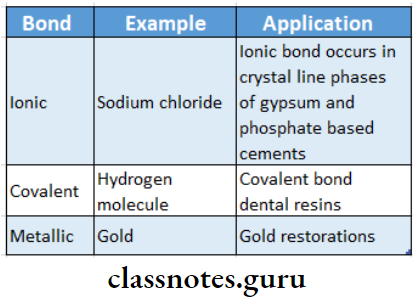
Secondary Bonds
- Hydrogen Bonds: Occurs in water molecules between an oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms
- Van der Walls forces
- It is due to the formation of a dipole
- These are weak forces
Adhesive Bonding In Dental Materials
Question 8. Chemical adhesion
Answer:
Chemical Adhesion
- A molecular or atomic attraction between two contacting surfaces promoted by the interfacial force of attraction between molecules or atoms of two different species is called adhesion.
- Types of adhesion – mechanical and chemical
- Chemical adhesion occurs due to primary and secondary bonds
1. Primary Bonds
- Ionic bonds
- Covalent bonds
- Metallic bonds
2. Secondary Bonds
- Hydrogen bonds
- Van der Walls forces
