Sterilization And Disinfection Important Notes
1. Disinfection:
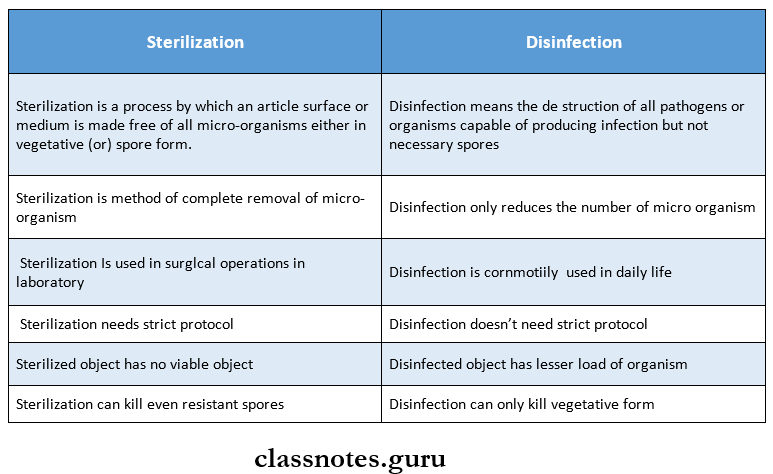
- It is the destruction or removal of all pathogenic organisms or organisms capable of giving rise to infection
2. Sterilization Controls:
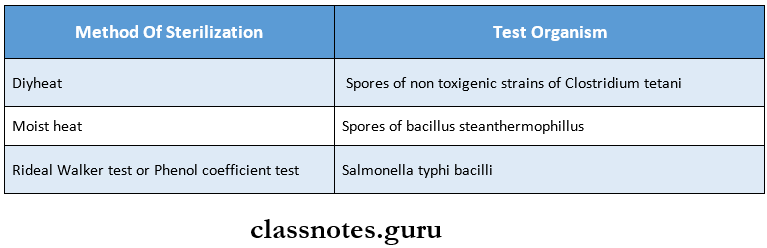
Read And Learn More: Microbiology Question and Answers
Sterilization And Disinfection Long Essays
Question 1. Define Sterilization. Describe An Autoclave.
Answer:
Sterilization Definition:
- Sterilization is a process by which an article surface or medium is made free of all micro-organisms either in vegetative (or) spore form.
Autoclave:
- Autoclaving is the process of sterilization by saturated steam under high pressure above 100°C temperature.
Sterilization And Disinfection Questions And Answers
Autoclave Principle:
- Water boils when its vapor pressure equals that of the surrounding atmosphere
- When the atmospheric pressure is raised then the boiling temperature is also raised
- At normal pressure, water boils at 100° C but when the pressure inside a closed vessel increases, the temperature at which water boils also increases
Components of Autoclave:
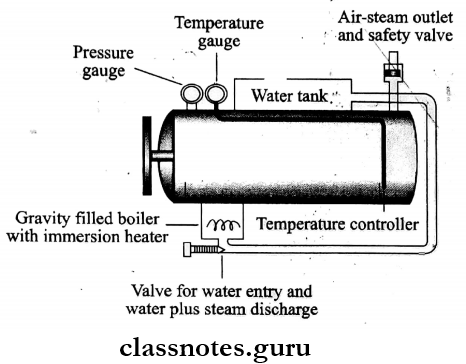
- Autoclave is a modified pressure cooker (or) boiler.
- It consists of a vertical (or) horizontal cylinder made up of gunmetal (or) stainless steel in a supporting sheet iron case.
- The lid has screw clamps and is made airtight by an asbestos washer.
- Structures present in the lid are
- Discharge tap – for air and steam
- A pressure gauge
- Safety valve.
- Heating is generally done by electricity.
Autoclave Procedure:

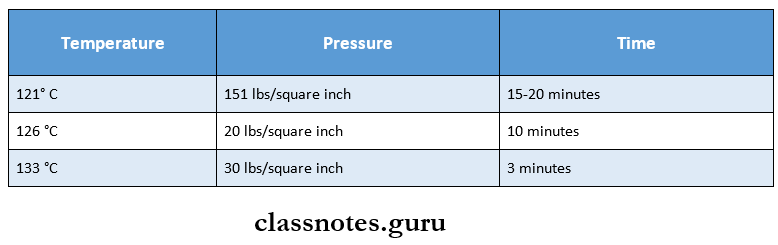
Sterilization Conditions:
Question 2. Write moist heat sterilization and dry heat method of sterilization.
Answer:
Moist Heat Sterilization:
- Moist heat kills micro-organisms by
- Denaturation and coagulation of proteins.
- Methods of sterilization may be used at different temperatures as follows.
1. At A temperature Below 100°C.
- Pasteurization Of Milk: Two Types Of Method
- Holder method – 63°C for 30 min
- Flash method – 72°C for 15 – 20 seconds
- Organisms like mycobacterium and brucellae are killed.
- Inspissation:
- Inspissator is used.
- The slow solidification of serum (or) egg is carried out at 80°C temperature for 30 minutes daily on 3 consecutive days.
- Vaccine Bath:
- Bacterial vaccines are sterilized in special vaccine baths at 60°C for one hour.
2. At A Temperature 100°C
- Boiling:
- Boiling for 10 to 30 min may kill most of vegetative forms but not spores.
- Glass syringes, and rubber stoppers can be sterilized
- Tyndallisation:
- Steam at 100°C for 20 minutes on 3 successive days is used.
- Also known as intermittent sterilization.
- The first exposure kills all vegetative forms
- In the interval between the heating, the remaining spores germinate into vegetative forms, which are killed on subsequent heating.
- Egg serum, and sugar-containing media can be sterilized.
- Steam Steriliser At 100°C For 90 Minutes.
- Koch’s (or) Arnold’s steam sterilizer is used.
- Usually used for media that are decomposed at high temperatures.
3. At A Temperature Above 100°C.
- Autoclave:
- In this method material for sterilization is exposed to 121°C for 15 – 20 min at 15 lbs per square inch
- Autoclave is used for culture media, rubber materials, syringes, and dressings
Dry Heat Sterilization:
The following procedures are under dry heat
Red Heat
- Inoculating wires (or) loops, tips of forceps, and needles are held in the flame of a Bunsen burner till they become red hot
Flaming
- Glass slides, and scalpels are passed through bunsen flame without allowing them to become red hot
Incineration
- By this method infective material is reduced to ashes by burning.
- Solid dressings, animal carcasses, bedding, and pathological materials are dealt with in this method.
Hot Air Oven:
- Most widely used dry heat method of sterilization.
- Sterilization requires 160°C for 2 hours.
- Glasswares, surgical instruments, and chemicals can be sterilized.
Question 3. Classify sterilization. Write briefly about chemical methods of sterilization.
Answer:
- Sterilization Classification:
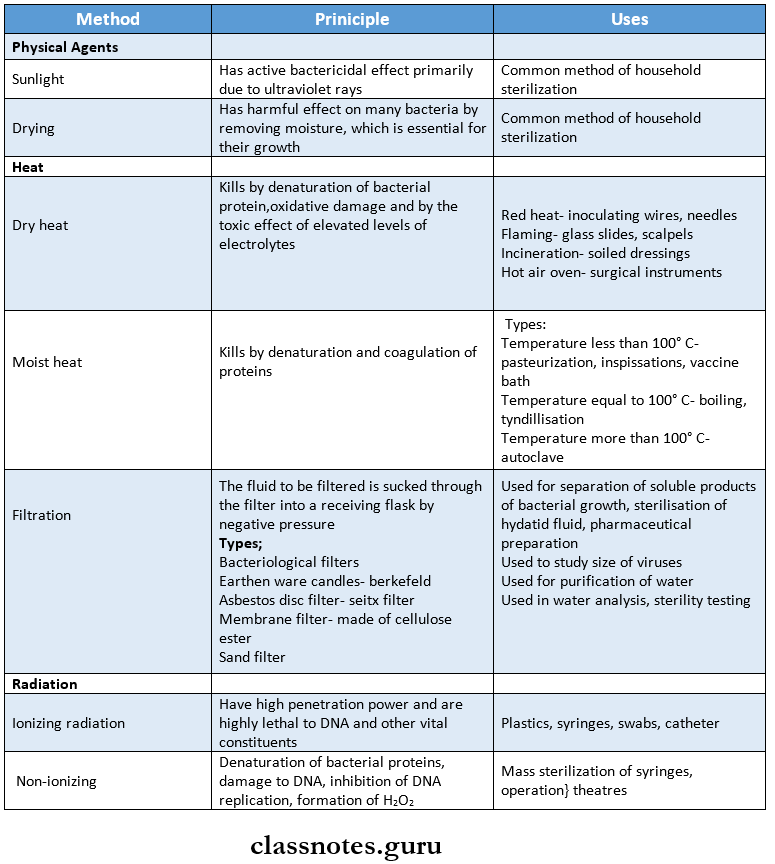
- Physical methods:
- Sunlight
- Heat
- Dry heat
- Moist heat
- Filtration
- Radiation.
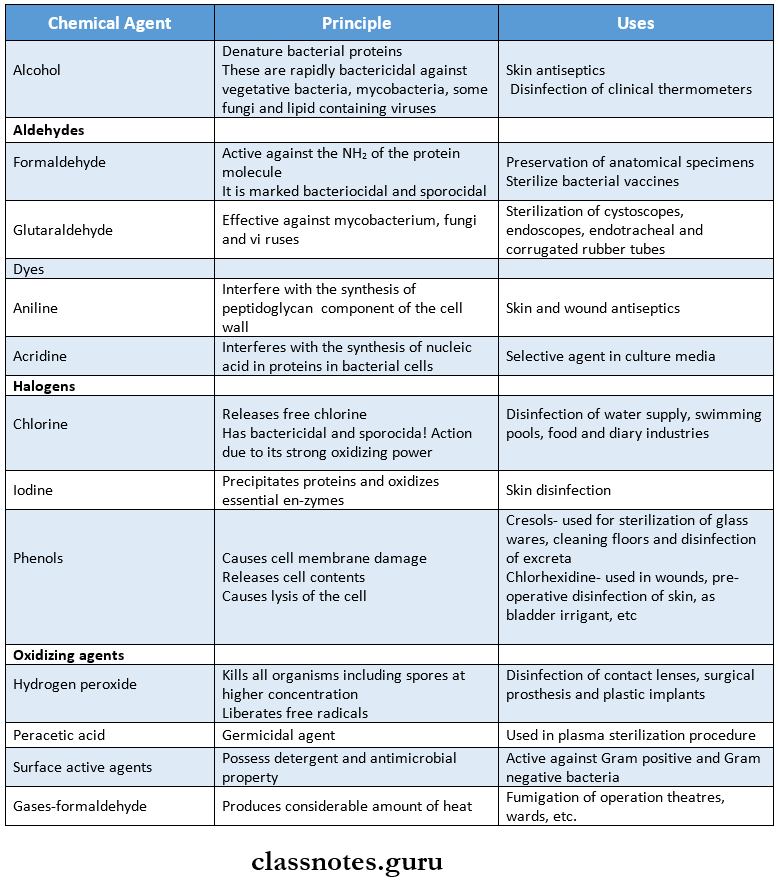
- Chemical Methods:
- Alcohols
- Aldehydes
- Phenols
- Halogens
- Oxidising agents
- Salts
- Surface active agents
- Gases
- Dyes
- Physical methods:
Chemical Methods of Sterilization:
Question 4. Write about physical methods of sterilization
Answer:
Sterilization And Disinfection Questions And Answers
Physical Methods of Sterilization:
Question 5. Define and differentiate sterilization and disinfection.
Answer:
Difference Between Sterilization And Disinfection
Sterilization And Disinfection Short Essays
Question 1. Seitz filter
Answer:
Seitz filter
- Seitz filters are a type of asbestos filter.
- These are made up of asbestos (magnesium silicate)
- The filter disc is supported on a metal mount
- The filter is attached to a vacuum flask through a silicone rubber bung.
- After use the filter disc is discarded.
- These filters have a high absorbing capacity.
Seitz filter Disadvantage:
- The carcinogenic potential of the filters.
Seitz filter Uses:
- To sterilise sera, sugars, and antibiotic solutions
- Sterlisation of hydatid fluid.
- Purification of water.
Question 2. Hot air oven
Answer:
Hot Air Oven
- The most widely used sterilization method by dry beat
About Oven:
- It is electrically heated and is fitted with a fan to ensure adequate and even distribution of hot air in the chamber.
- Thermostat is fitted to maintain the chamber air at a chosen temperature.
Hot Air Oven Temperature And Time:
- 160°C for 2 hours
Hot Air Oven Uses:
- Used for sterilization of
- Glasswares like glass syringes, flasks, and test tubes
- Surgical instruments like scalpels, and scissors.
- Chemicals such as liquid paraffin, and fats.
Hot Air Oven Precautions:
- Should not be overloaded.
- Materials should be arranged in a manner that allows free circulation of air.
- Materials to be sterilized should be perfectly dry.
- Allow proper time for cooling at least 2 hours especially for glassware to prevent cracking.
- Any inflammable material should not be kept inside the oven.
Sterilisation Control:
- Spore Test:
- Non-toxigenic strains of cltetani are kept inside the oven.
- Spores will be destroyed if sterilization is proper.
- Browns tube with green – color spot is available. The green colour is produced after effective sterilization.
Question 3. Disinfection
(OR)
Antiseptics And Disinfectants
Answer:
Antiseptics And Disinfectants
- Antiseptic is an agent that destroys micro-organisms and contact and can be used on living tissue.
- A disinfectant is used on inanimate objects to detect all pathogenic organisms but not spores.
Disinfection Ideal Requirements:
- Have a wide spectrum of activity.
- Act in the presence of organic matter.
- Have high penetration power and quick action.
- Be safe and easy to use.
- Not cause local irritation.
- Be easily available and cheap.
- Not cause local irritation.
- Be easily available and cheap.
- Not corrode metals.
- Be stable
- Be effective in acidic as well as alkaline conditions
Disinfection Classification:
- Acids – Boric acid, benzoic acid.
- Alcohols – Ethanol, isopropyl alcohol.
- Aldehydes – Formaldehyde, glutraldehyde
- Surfactants – Soaps, cetrimide
- Cetyl pyridinium chloride.
- Phenol Derivatives; Phenol, cresol, Chlorhexidine, Hexachlorophene.
- Halogens: Iodine, Idophores, Chlorine, Chloramines.
- Oxidizing agents: Hydrogen .peroxide, Benzoyl peroxide
- Dyes: Gential violet, Methylene blue.
- Metallic salts: Silver nitrate, Zinc compounds.
Disinfection Uses in Dentistry:
- As a component of mouthwashes [chloroxylenol, chlor-hexidine]
- For gargling [potassium permagnates]
- For root canal therapy [ sodium hypochlorite]
- As gum paints [dequalinium chloride]
Question 4. Tyndallization
Answer:
Tyndallization
- Steam at 100°C for 20 minutes on 3 successive days is used.
- Also known as intermittent sterilization.
- The first exposure kills all vegetative forms
- In the interval between the heating the remaining spores germinate into vegetative forms, which are killed on subsequent heating.
- Egg, serum, and sugar-containing media can be sterilized.
Question 5. Cold sterilization
Answer:
Cold Sterilization
- X-rays, gamma rays, and cosmic rays are ionizing radiations.
- This method is also known as cold sterilization.
- Have high penetration power and are highly lethal to DNA and other vital constituents
- They damage DNA by various mechanisms.
- Used for sterilization of disposable items such as plastic syringes, swabs, and culture plates.
- Gamma rays are commercially used for sterilization.
Sterilization And Disinfection Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Moist heat
Answer:
Moist Heat
- Moist heat is one of the physical methods of sterilization
Moist Heat Principle:
- Kills by denaturation and coagulation of proteins
Moist Heat Types:
- This method may be used at different temperatures as follows:
- Temperature less than 100° C- pasteurization, in- aspirations, vaccine bath
- Temperature equal to 100° C- boiling, tyndillisation
- Temperature more than 100° C- autoclave
Question 2. Autoclave.
Answer:
Autoclave
- It is a method of moist heat sterilization
- It kills the micro-organisms by denaturation and coagulation of proteins
- In this method, material for sterilization is exposed to 121°C for 15-20 min at 15 lbs per square inch
- Uses: Used for sterilization of
- Culture media
- Rubber articles
- Syringes and surgical instruments
- OT gowns, dressing materials
- Endodontic instruments
- Hand instruments
Question 3. Pasteurization
Answer:
Pasteurization
- It is method of moist heat sterilization
- It kills the micro-organisms by denaturation and coagulation of proteins
- Temperature below 100°C is used
- Organisms like mycobacterium, and brucellae are killed by this process
Pasteurization Types:
- Holder method – 63°C for 30 min
- Flash method – 72°C for 15-20 seconds
Sterilization And Disinfection Viva Voce
- A hot air oven is method of dry heat sterilization
- Autoclave is a method of moist heat sterilization
- Rideal Walker test is used to test the efficiency of a disinfectant
- 2% glutaraldehyde is known as CIDEX
- The germicidal effect of sunlight is due to its ultraviolet rays
- Chlorhexidine is most effective against Gram-positive organism
- Ionizing radiation are lethal to DNA
