Diseases Of The Respiratory System Short Essays
Question 1. Complications of pneumonia
Answer:
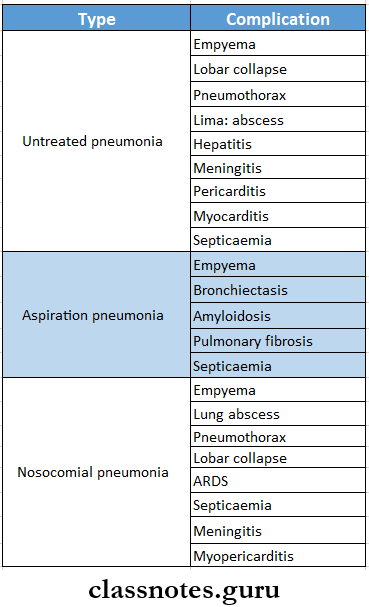
Complications Of Pneumonia
Question 2. Treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis
Answer:
Pulmonary Tuberculosis Principles
- To administer multiple drugs
- To add atleast 2 new drugs in case of failure
- To provide safest and most effective therapy shortest period of time
- To ensure compliance to treatment
Pulmonary Tuberculosis Drugs
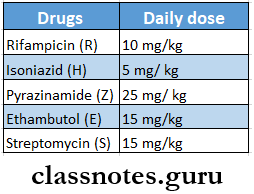
- Anti-tubercular drugs that are used for treating it are as follows:
- Four or three drugs are choosen from the drugs meant for first-line treatment for new cases
- Response to treatment is assessed by
- Gain in body weight
- Improved appetite
- Improvement in general health – Fall in ESR
- Conversion of sputum from positive to negative
- Primary or secondary resistance to drugs may develop when patient consume the drugs in irregular dose or take the drugs irregularly
- In such cases, second-line drugs are used
- Drugs:
- PAS (Paraminosalicyclic acid) – 5 g BID orally
- Ethionamide – 0.75 -1 g/day orally
- Capromycin – 0.75-1 g IM daily
- Cycloserine – 0.75-1 g/ day orally
- Ciprofloxacin – 500-750 mg BID orally
- Ofloxacin – 400 mg BID
Respiratory Diseases Short Notes
Question 3. Four causes of clubbing
Answer:
Clubbing:
- Clubbing is enlargement of the distal segment of fingers and toes due to an increase in soft tissues
Clubbing Causes:
- Disorders of heart
- Cyanotic heart disease
- Subacute bacterial endocarditis
- Disorders of lung
- Suppuration of lung
- Bronchiectasis
- Lung abscess
- Suppurative pneumonia
- Tumors of lung
- Mesothelioma
- Primary lung cancer
- Metastatic lung cancer
- Suppuration of lung
- Disorder of GI tract and liver
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Regional ileitis
- Ulcerative colitis
- Malabsorption syndrome
- Cirrhosis of liver
- Malignancy of liver
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Hereditary or idiopathic
Read And Learn More: General Medicine Question and Answers
Question 4. Mantouxtest
(or)
Tuberculin test
Answer:
Mantouxtest
- Mantouxtest is a routinely used method for tuberculin testing
Mantouxtest Method:
- 0.1 ml of purified protein derivative, PPD containing 5 TU( tuberculin unit) is injected intradermally into flexor ascept of forearm
- It is given between layers of the skin
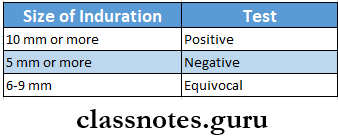
- The site is examined after 48-72 hours for induration
Result:
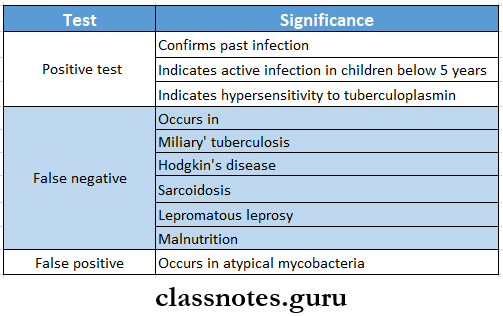
Mantouxtest Significance:
Question 5. Lung abscess
Answer:
Lung Abscess
- Lung abscess is collection of purulent material in a localised necrotic area of lung parenchyma
Etiopathogenesis:
- Infection without obstruction
- Aspiration of nasopharyngeal contents
- Involvement of various organisms like staphylococcus, Kleibsella, gram-negative and anaerobic organisms
- Formation of abscess
- Metastatic spread of infection
- Obstruction with or without infection
- Bronchus obstruction due to tumor, foreign body, lymph node
- Bronchial collapse
- Abscess formation
Lung Abscess Clinical Features:
- High-grade fever with chills and rigors
- Pleuritic chest pain
- Dry cough
- Presence of copious purulent discharge
- Haemoptysis
- Weight loss, anorexia
- Empysema
common respiratory disorders short essay
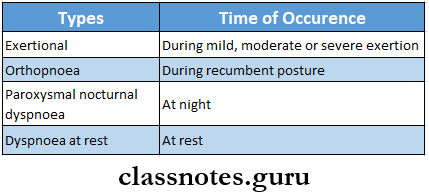
Question 6. Dyspnoea
Answer:
Dyspnoea Definition:
- Dyspnoea is abnormal and uncomfortable breathing which makes the patient aware of it
Etiology:
- Cardiac causes
- Cyanotic congenital heart disease
- Left ventricular failure
- Systemic hypertension
- Chronic thromboembolism
- Pulmonary
- Obstructive diseases
- Bronchial asthma
- Bronchiectasis
- COPD
- Parenchymal lung diseases
- Acute pneumonia
- Pulmonary vascular diseases
- Thromboembolism
- Respiratory muscle diseases
- Severe kyphoscoliosis
- Obstructive diseases
- Cardiopulmonary’causes
- Corpulmonale
- Others
- Metabolic acidosis
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
- Severe anaemia
Dyspnoea Types:
Question 7. Bronchodilators
Answer:
Bronchodilators:
- Various bronchodilators are
- Sympathomimetics
- Adrenaline
- Ephedrine
- lsoprenaline
- Salbutamol
- Terbutaline
- Methylxanthines
- Theophylline
- Aminophylline
- Anticholinergics
- Atropine
- Methonitrate
- Ipratropium bromide
Bronchodilators Actions:
- Improves effectiveness of cough in clearing secretions by increasing surface velocity of airflow during cough
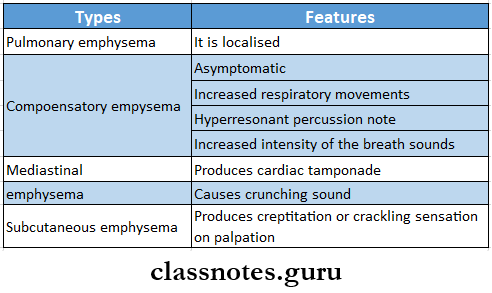
Question 8. Clinical signs of emphysema
Answer:
Clinical signs of emphysema
- Emphysema means inflation or distension with air
EmphysemaTypes:
short answer on respiratory tract diseases
Question 10. Haematemesis- causes and investigations
Answer:
Haematemesis Definition:
- Haematemesis is vomiting of blood
Haematemesis Causes:
- Prolonged and vigorous retching
- Irritation or erosion of the lining of the esophagus or stomach
- Bleeding ulcer located in the stomach, duodenum, or oesophagus
- Vomiting of ingested blood
- Vascular malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract
- Tumours of the stomach or oesophagus
- Radiation poisoning
- Gastroenteritis
- Gastritis
- Peptic ulcer
Haematemesis Management:
- Minimal blood loss
- Administration of proton pump inhibitors like omeprazole
- Blood transfusion
- Significant blood loss
- Resuscitation
- Fluid and/or blood administration
- Use of a cuffed endotracheal tube
Question 11. Aspiration pneumonia
Answer:
- Aspiration pneumonia is the consolidation of the lung in which there is the continued destruction of parenchyma by the inflammatory cells leading to the formation of microabscesses
Aspiration Pneumonia Clinical Features:
- High intermittent fever
- Cough
- Dyspnoea
- Tachycardia
- Restlessness
- Perspiration
- Weight loss
- Digital clubbing
Aspiration Pneumonia Compiicatons:
- Empyema
- Bronchiectasis
- Amyloidosis
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Septicaemia
Aspiration Pneumonia Treatment:
- Oral amoxicillin 500 mg 8 hourly or
- Cotrimoxazole 9960 mg 12 hourly or
- Oral metronidazole 400 mg 8 hourly
- Analgesic for pleuritic pain
- Physiotherapy
- Postural drainage for lung abscess
viral respiratory infections short note
Question 12. BCG vaccination
Answer:
BCG vaccination
- BCG vaccine was prepared by Calmette and Guerin
- BCG vaccination is a live attenuated and freeze-dried vaccine
BCG vaccination Dose and Administration:
- BCG vaccination Dose and Administration is available as a fresh liquid vaccine or in the form of freeze-dried vaccine
- BCG vaccination Dose and Administration is given intradermally in a dose of 0.1 ml soon after birth
BCG vaccination Immune Response:
- Induces a self-limited infection with multiplication and dissemination of the bacillus in different organs and production of small tubercles
- BCG vaccination Immune Response gives rise to delayed hypersensitivity
BCG vaccination Complications:
- Local abscess, indolent ulcer, keloid, confluent lesion, lupoid lesion
- Regional enlargement and suppuration of draining lymph nodes
- Systemic fever, mediastinal adenitis
- Erythema nodosum
BCG vaccination Contraindications:
- In patients with AIDS, eczema, pertussis, measles, and patient on steroids
Role of BCG:
- Makes the disease milder
- Prevents serious forms of disease
