Removable Partial Dentures Definitions
- Removable Partial Denture: Any prosthesis that replaces some teeth in a partially dentate arch is called a removable partial denture. It can be removed from the mouth and replaced at will
- Direct Retainer: It is defined as “A clasp or attachment placed on an abutment tooth to hold a removable denture in position
- Indirect Retainer: It is defined as “a part of a removable partial denture which assists the direct retainers in preventing displacement of distal extension denture bases by functioning through lever action on the opposite side of the fulcrum”.
- Major Connector: It is defined as “A part of a removable partial denture which connects the components on one side of the arch to the components on the opposite side of the arch”
- Minor Connector: It is defined as “The connecting link between the major connector or base of a removable partial denture and other units of the prosthesis, such as clasps, indirect retainers, and occlusal rests”.
- Rest: “It is defined as “A rigid extension of a fixed or removable partial denture which contacts a remaining tooth or teeth to dissipate vertical or horizontal forces.”
- Denture Base: It is defined as “that part of a complete or removable partial denture which rests upon the basal seat and to which teeth are attached”.
- Surveyor: An instrument used in the construction of removable partial dentures to locate and delineate contours and relative positions of abutment teeth and associated structures
- Retentive Arm: “A flexible segment of a removable partial denture which engages an undercut on an abutment and which is designed to retain the denture”
- Reciprocal Arm: “A clasp arm or other extension used on a removable partial denture to oppose the action of some other part or parts of the prosthesis”
- Reciprocation: It is defined as the means by which one part of a prosthesis is made to counter the effect created by another part
- Stress Breaker: A device that relieves the abutment teeth of all or part of the occlusal forces
- Interim Removable Denture: “A transitional denture may become an interim denture when all of the natural teeth have been removed from the dental arch”.
- Immediate Partial Denture: “A complete removable partial denture constructed for insertion immediately following the removal of natural teeth”
- Guiding Planes: “Two or more vertically parallel surfaces of abutment teeth so oriented as to direct the path of placement and removal of removable partial denture”
- Survey Line: “A line drawn on a tooth or teeth of a cast by means of a surveyor for the purpose of determining the positions of the various parts of a clasp or clasps”.
- Height Of Contour: A line encircling a tooth designating its greatest circumference at a selected position.
- Internal Attachment: “A retainer, used in removable partial denture construction, consisting of a metal receptacle and a closely fitting part: the former is usually contained with the normal or expanded contours of the crown of the abutment tooth and the latter is attached to a pontic or the denture framework”.
- Fulcrum Line: “An imaginary line around which a partial denture tends to rotate.”
Removable Partial Dentures Notes
Read And Learn More: Prosthodontics Question And Answers
Removable Partial Dentures: Important Notes
1. Kennedy’s Classification:
- Kennedy’s Class 1:
- Bilateral edentulous areas located posterior to the remaining natural teeth
- There are two edentulous spaces located in the posterior region without any teeth posterior to it.
- Kennedy’s Class 2:
- The unilateral edentulous area located posterior to the remaining natural teeth
- There is a single edentulous space located in the posterior region without any teeth posterior to it.
- Kennedy’s Class 3:
- Unilateral edentulous area with natural teeth anterior and posterior to it.
- It indicates a single edentulous area that does not cross the midline of the arch
- Kennedy’s Class 4:
- Single Bilateral Edentulous area located anterior to the remaining natural teeth
- It crosses the midline of the arch
- Teeth are present only posterior to the edentulous arch
- Kennedy’s Class 5:
- The edentulous area is bounded anterior and posteriorly by natural teeth
- Kennedy’s Class 6:
- Edentulous area in which the teeth adjacent to the space are capable of total support of the required prosthesis
RPD Prosthodontics Guide
2. Applegate’s Rules:
- Rule one – Classification should follow rather than precede extractions that might alter the original classification
- Rule two – If the third molar is missing and not to be replaced, it is not considered in the classification
- Rule three – If the third molar is present and is used as an abutment, it is considered in the classification
- Rule Four – If the second molar is missing and not to be replaced, it is not considered in the classification
- Rule Five – The most posterior edentulous area or areas always determine the classification
- Rule Six – Edentulous areas other than those, that determine the classification, are referred to as modification spaces and are designated by their number
- Rule Seven – The extent of the modification is not considered, only the number of additional edentulous spaces is considered
- Rule Eight – There can be no modification areas in class 4.

3. Surveying Tools:
- Analysing rod
- Carbon marker
- Undercut gauge
- Wax Knife
RPD Procedure Explained
4. Indications For Removable Partial Dentures:
- Distal extension
- After recent extractions
- Long-span edentulous arches
- Need for bilateral cross-arch stabilization
- Excessive loss of alveolar bone
5. Components Of Removable Partial Denture:
- Major connector
- Minor connector
- Direct retainer
- Indirect retainer
- Denture base
- Artificial teeth
6. Parts of Surveyor:
- Surveying platform
- Cast holder/surveying table
- Vertical arm
- Horizontal arm
- Surveying arm
- Surveying tools
7. Types Of Major Connectors:
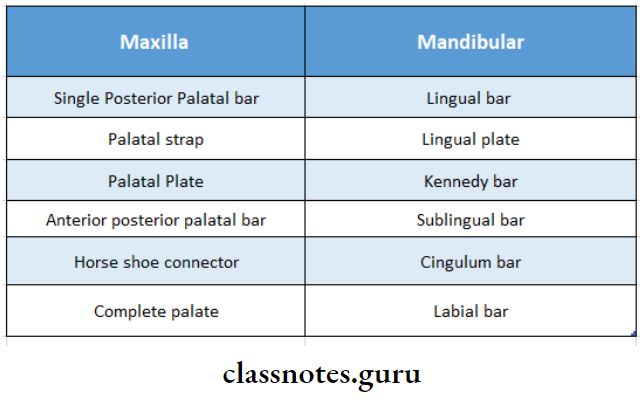
8. Functions Of Minor Connector:
- Joins other units of the prosthesis to the major connector
- Transfers functional stress to the abutment teeth
- Transfers the effect of the retainers, rests, and stabilizing components to the rest of the denture
9. Types Of Minor Co nnectors:
- The minor connector that connects the direct retainer to the major connector
- The minor connector that connects the auxiliary rests to the major connector
- The minor connector that connects the denture base to the major connector
- The minor connector that extends as the approach arm of a bar clasp
10. Parts Of Direct Retainer:
- Retentive arm
- Shoulder
- Rest
- Reciprocal arm
- Body
- Minor connector
11. Functions Of Direct Retainer:
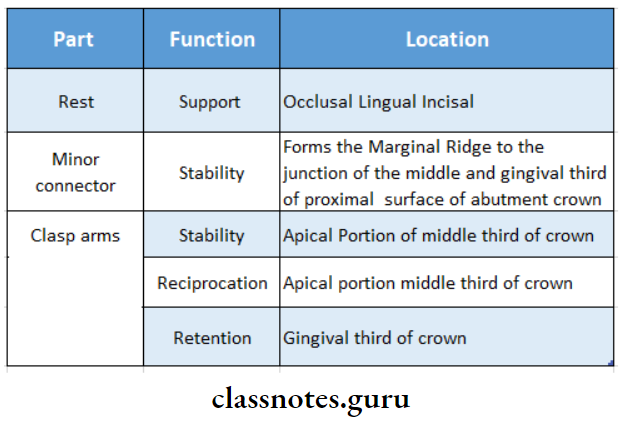
12. Functions Of Reciprocal Arm:
- Acts as an indirect retainer
- Reciprocal Arm can resist the rocking of the denture base
- The Reciprocal Arm provides stability and reciprocation against the retentive arm
- The denture is stabilized against horizontal movement
13. Functions Of Indirect Retainer:
- Indirect Retainer counteracts the lifting forces and stabilizes the denture
- Indirect Retainer counteracts horizontal forces and provides stability and support to the denture
- Indirect Retainer can splint and protect the anterior teeth
- Indirect Retainer may act as an auxiliary rest
- The dislodgement of the indirect retainer suggests the need to reline
14. Types Of Indirect Retainers:
- Auxillary occlusal rest
- Canine rest
- Modification areas
- Direct indirect retention
- Canine extension
- Continuous bar retainer
- Rugae support
- Indirect retention from major connectors
15. Factors Affecting Stability Of The RPD:
- Design of the framework
- Harmonious occlusion
- Relationship of the teeth to the residual ridge
Removable Partial Denture Designs
Viva Voce
- Distal extension partial denture derives support from both the teeth and the residual ridge
- The anteroposterior palatal bar and strap are the most rigid palatal major connectors
- The U-shaped palatal connector is least rigid palatal major connectors
- A partial denture is supported by dual support- soft tissue and tooth support
- In Kennedy’s classification, the deciding factor is the absence of most posterior tooth
- In Kennedy’s classification, the most common arch is class 1
- Totally tooth supported denture is class 3
- In the palatal major connector, relief should always be given for the palatal torus
- Elastomers are best material for taking impressions in RPD
- Guiding planes prepared on enamel surfaces should be flat
- The seat for occlusal rest on the abutment should be on the marginal ridge at 90 degrees to the long axis of the abutment
- The main function of the reciprocal arm is to counteract the forces transmitted by the retentive arm
- The indirect retainer should be placed on the opposite side of the fulcrum line
- The main function of an indirect retainer is to minimize the movement of the denture away from the supporting tissue
- The major connector should be rigid enough to connect the Bilateral components of the removable denture
- The flexibility of major connector causes greatest damage to a partial denture
- The major connector should not terminate on gingival tissue
- In case of large palatal torus, an anteroposterior palatal bar major connector is used
- The outline form of occlusal rest is triangular
- The rest seat for lingual rest is V-shaped
- Incisal rests are frequently seen on mandibular canine
- Lingual rests are commonly used on maxillary canines 23.
- The terminal end of the retentive arm should be placed at a cervical third of the crown
- The relief effect is described by Hanau
- The path of insertion of RPD is preferred to be perpendicular to the occlusal plane
- The encirclement of each clasp is more than 180 degrees 27.
- The easiest clasp to design and construct is a cast circumferential clasp
- Ring clasp is most often indicated in tipped molars
