Oral Medicine Red And White Lesions Definitions
1. Oral Submucous Fibrosis
- An insidious chronic disease affecting any part of the oral cavity and sometimes the pharynx.
- Although occasionally preceded by and /or associated with vesicle formation, it is always associated with juxtaepithelial inflammation reaction followed by fibroelastic changes of lamina propria with epithelial atrophy leading to stiffness of oral mucosa and causing trismus and inability to eat
2. Leukoplakia
- Leukoplakia is a whitish patch or plaque that cannot be characterized, clinically or pathologically, as any other disease and which is not associated with any other physical or chemical causative agent except the use of tobacco.
3. Premalignant Lesions
- Premalignant Lesions are defined as morphologically altered tissue in which cancer is more likely to occur than its apparently normal counterparts
4. Premalignant Conditions
- Premalignant Conditions is defined as a generalized state or condition associated with a significantly increased risk for cancer development.
5. Erythroplakia
- Erythroplakia is a red patch or plaque in the oral mucosa which cannot be characterized clinically or pathologically as any other condition and which has no apparent cause
Red Lesions Classifications
- Inflammatory Conditions:
- Inflammation associated with traumatic injury
- Mechanical- cheek biting, ill-fitted denture
- Chemical- aspirin, formoterol
- Thermal- hot food, hot beverages
- Radiation- mucositis
- Infection
- Bacterial
- Scarlet fever
- Gonococcal stomatitis
- Vincent infection
- Fungal
- Atrophic candidiasis
- Angular cheilitis
- Viral
- Measles
- Herpes simplex infection
- Herpes zoster
- Herpangina
- Chickenpox
- Allergic
- Pyogenic granuloma
- Giant cell epulis
- Pregnancy tumour
- Congenital:
- Hemangioma
- Sturge-Weber syndrome
- Median rhomboid glossitis
- Geographic tongue
- Vascular Diseases:
- Purpura
- Polycythemia
- Agranulocytosis
- Leukaemia
- Dermatological:
- Pemphigus
- Erythema multiforme
- Steven Johnson’s syndrome
- Lichen planus
- Psoriasis
- Other Diseases:
- Uremic stomatitis
- Diabetes stomatitis
- Scurvy
- Pernicious anaemia
- Premalignant And Malignant Lesions:
- Atrophic leukoplakia
- Erythroplakia
- Carcinoma in situ
- Kaposi’s sarcoma
White lesions Classifications
- Variation In Structure And Appearance Of Normal Mucosa
- Leukoedema
- Fordyce’s granules
- Linea alba
- White Lesion With Precancerous Potential
- Leukoplakia
- Erythroplakia
- Lupus erythematous
- Carcinoma in situ
- Lichen planus
- White Lesion Without Precancerous Potential
- Traumatic lesions
- Focal epithelial dysplasia
- White sponge nevus
- Stomatitis nicotine
- Hairy leukoplakia
- Non-Keratotic Lesion
- White hairy tongue
- Burns
- Pemphigus
- Desquamative gingivitis
- Candidiasis
- Koplik’s spots
3. Premalignant Lesions:
- Leukoplakia
- Erythroplakia
- Mucosal changes associated with smoking habits
- Carcinoma in situ
- Bowen’s disease
- Actinic keratosis
4. Premalignant Conditions:
- Oral submucous Fibrosis
- Syphilis
- Sideropenic dysplasia
- Dyskeratosis congenital
5. Lupus Erthymetosis
- Leukoplakia:
- Homogenous leukoplakia
- Ulcerative leukoplakia
- Nodular or speckled leukoplakia
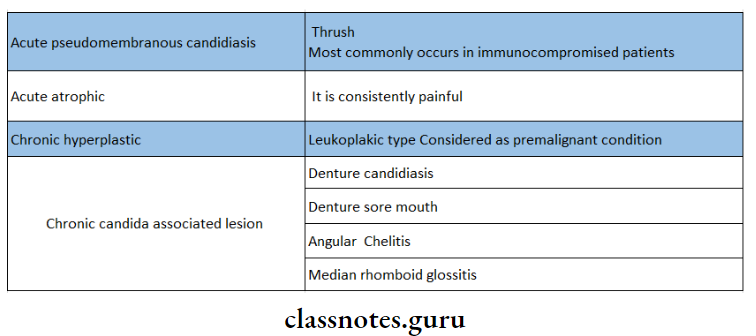
6. Candidiasis:
- Acute
- Acute pseudomembranous candidiasis
- Acute atrophic candidiasis
- Chronic
- Chronic atrophic candidiasis
- Denture stomatitis
- Median rhomboid glossitis
- Angular cheilitis
- ID reaction
- Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis
- Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis
- Familial CMC
- Localized CMC
- Diffused CMC
- Candidiasis endocrinopathy syndrome
Oral Medicine Red And White Lesions Important Notes
1. TNM Staging
- It is staging of malignancy which measures 3 major parameters of cancer
- T- size of the tumour
- N- lymph node involvement
- M- distant metastasis
- T- Primary tumour
- Tx– Primary tumour cannot be assessed
- T0– No evidence of primary tumour
- Tis– carcinoma in situ e Tl- Tumour size- 2 cm or less in diameter
- T2– Tumour size- 2-4 cm in diameter
- T3– Tumour size- more than 4 cm in diameter
- T4– Tumour invades adjacent structures
- N- Regional lymph node
- Nx– Regional lymph node cannot be assessed
- N0– No regional lymph node metastasis
- N1– Metastasis in the single ipsilateral lymph node, 3 cm or less in dimension
- N2– Metastasis in the single ipsilateral lymph node, more than 3 cm but less than 6 cm
- N2a– Metastasis in the single ipsilateral lymph node, 3-6 cm in dimension
- N2b– Metastasis in multiple ipsilateral lymph nodes, not more than 6 cm
- N2c– Metastasis in bilateral or contralateral lymph nodes, not more than 6 cm
- N3- Metastasis in the lymph node, more than 6 cm in dimension
- M- Distant metastasis
- Mx– The presence of distant metastasis cannot be assessed
- M0– No distant metastasis
- M1– Presence of metastasis
2. Histological Features Of Lichen Planus
- Sawtooth appearance of recipes
- Liquefaction degeneration of the basal layer
- Presence of Civatte bodies
- Characteristic band of T-lymphocytes and histiocytes
- Hyperparakeratosis and Hyperorthokeratosis
- Thickening of the granular layer
3. Lichenoid Reactions
- They are drug-induced
- Has the same histological features as lichen planus
- It resolves promptly when the offending drug is eliminated
- Drugs producing it are
- Antihypertensives
- NSAIDs
- Penicillamine
- Rapwnr
- Ketoconazole
- Tetracycline
- Sulfamethoxazole
- Oral hypoglycaemic drugs,
4. Grmspan Syndrome
- Diabetes melli-uv
- Lichen planus
- Hypertension
5. Nevus
- It is x congenital, developmental tumour-like malformation of skin and mucous membrane
- It is composed of nevus cells
- The nevus cells are situated within the Conner tier tissue and are not in contact with surface epithelium
- The common mole is an intradermal mole
- In junctional nevus, the epithelium is thin and irregular and shows roll crossing the junction and growing down- into the connective tissue
6. White Sponge Nevus
- Described by Cannon
- Follows hereditary pattern
- Die oral lesions are widespread
- Appears as thickened and folded or corrugated with s-.ft or spongy texture
- Has a peculiar white opah scent hue
- Removed by gentle rubbing without bleeding
7. Leukoedema
- Mostly occurs bilaterally
- Involves the buccal mucosa along the occlusal line in the bicuspid and molar region
- Resembles early leukoplakia
- Disappears on stretching
8. Types Of Candidiasis
9. Id Reaction
- It is due to an allergic response to Candida antigens
- Patients develop vesicula popular rash due to allergy
- Lesions will resolve with treatment of Candida infection
