Post-Insertion Problems Long Essays
Question 1. Discuss post-insertion problems and their management.
(or)
Discuss post-insertion problems in edentulous patients using complete dentures. Enumerate the reasons for it and their management
Or
Post-insertion instructions and problems encountered in complete dentures.
Answer:
Instructions for Insertion And Removal:
The patient is taught to insert and remove the denture along the path of insertion
Maintenance Of Prosthesis:
- Patients are taught to clean their dentures regularly
- Cleansers used are:
- Chemicals: Chlorhexidine
- Ultrasonic cleaner
- Soaking & brushing the denture
- Avoid hard brushing
- Avoid excessive flossing
Read And Learn More: Prosthodontics Questions And Answers
Night Wear Of Prosthesis:
- Avoid nightwear or dentures
- Allowed to wear only in Brussels
- Report to the dentist if the denture causes any irritation, even after 24 hours.
- The patient is asked to read newspapers or novels loudly during the 1st 24 hours to adapt to the denture.
Post Insertion Problems in Complete Dentures
Post Insertion Problems: Post insertion is
- Direct Sequelae
- Indirect Sequelae
Direct Sequelae:
1. Denture Stomatitis:
Denture Stomatitis is the pathological reaction of the palatal portion of the denture-bearing mucosa
- Denture Stomatitis Types:
- Type 1: Localized simple infection
- Type 2: Erythematous type
- Type 3: Granular type
- Denture Stomatitis Etiology:
- Candida albicans
- Denture Stomatitis Predisposing Factors:
- Local factors:
- Dentures
- Xerostomia
- High-carbohydrate diet
- Use of broad-spectrum antibiotics
- Smoking
- Systemic factors:
- Old age
- Diabetes mellitus
- Nutritional deficiency
- Immune defect
- Malignancy
- Local factors:
- Denture Stomatitis Management:
- 0.2-2% chlorhexidine
- Removal and cleaning of dentures after every meal
- Avoid wearing dentures
- Polishing of denture
- Administration of antifungal drugs
- Surgically: Elimination of crypts, by cryosurgery
Complete Denture Complications After Insertion
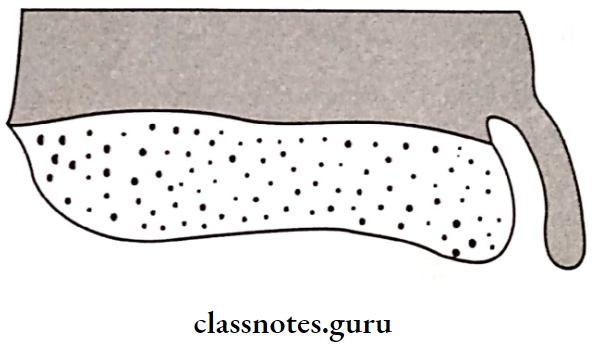
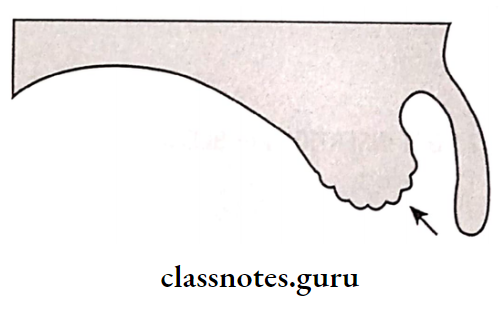
2. Flabby Ridge: Replacement of bone by fibrous tissue
- Site: Anterior part of maxilla
- Effect: Poor support for the denture
- Flabby Ridge Causes:
- Excessive load overdenture
- Unstable occlusal conditions
- Flabby Ridge Management:
- Surgical removal
3. Denture Irritation Hyperplasia:
- The hyperplastic reaction of the mucosa over the borders of the denture
- Denture Irritation Hyperplasia Cause: Trauma due to unstable dentures
- Denture Irritation Hyperplasia Features:
- Deep ulceration
- Fissuring
- Inflammation
- Denture Irritation Hyperplasia Management:
- Surgical excision
- Correction of dentures
4. Burning Mouth Syndrome:
Burning sensation in the structures in contact with the dentures without any visible change in the mucosa
- Burning Mouth Features:
- Pain in the morning
- Dry mouth
- Persistent altered taste
- Generalized symptoms
- Burning Mouth Etiology:
- Irritation by ill-fitting dentures
- Constant masticatory activity, Excessive friction on the mucosa
- Candidal infection
- Nutritional deficiency
- Xerostomia
- Medication
- Burning Mouth Management:
- Counseling
- Repair of ill-fitted dentures

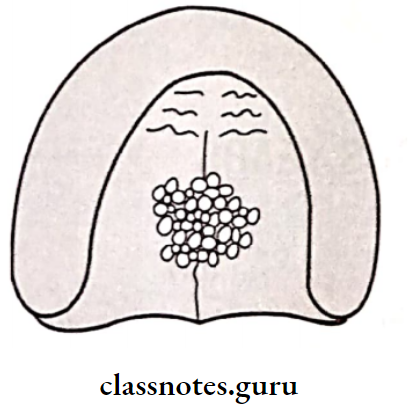
5. Gagging:
The gag reflex is a normal, healthy defense mechanism to prevent foreign bodies from entering the trachea
- Gagging Causes:
- Over-extended denture borders
- Unstable occlusal conditions
- Systemic conditions
- Alcoholism, smoking
- Gagging Features:
- Causes the displacement of the denture
- Triggered by tactile stimulation of the soft palate, the posterior part of the tongue, and the fauces
- Gagging Site:
- Posterior part of the maxillary denture
- Distolingual part of mandibular denture
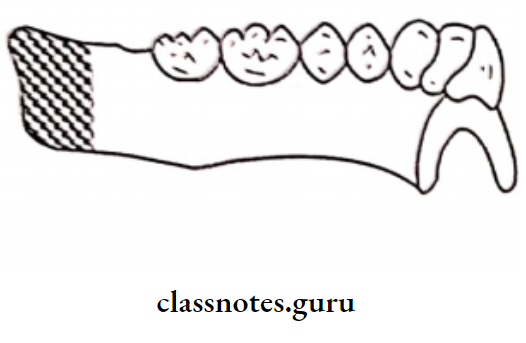
- Gagging Treatment: Limiting the posterior extension of the dentures
Denture Insertion Follow-Up Guide
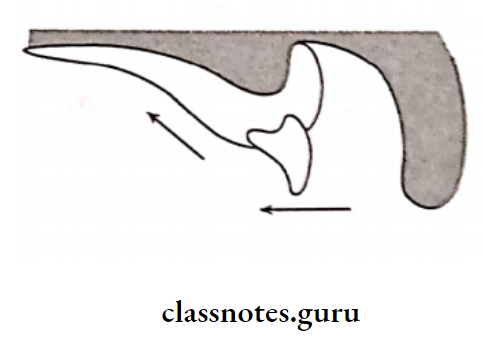
6. Residual Ridge Resorption:
- Residual ridge resorption is alveolar remodeling that occurs due to a change in the functional stimulus of bone tissue
- Residual ridge resorption is a chronic progressive change in the bone structure, which results in severe impairment in the fit & function of the prosthesis
- Residual Ridge Resorption Cause: Excessive forces over non-stress bearing areas, causing activation of osteoclasts
- Residual Ridge Resorption Clinical Features:
- Decreased depth and width of the sulcus
- Decreased vertical dimension at occlusion
- Reduced lower facial height
- Anterior rotation of mandible
- Increase in relative prognathism
- Increased mandibular arch
- Decreased maxillary arch
- Effects support, stability & retention of dentures
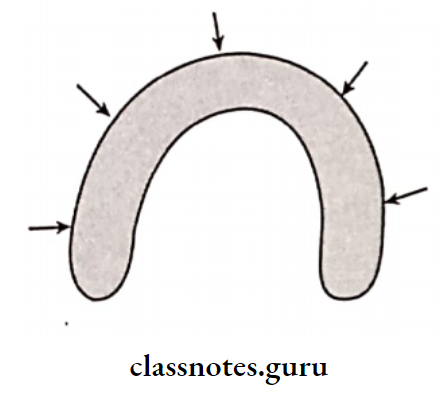
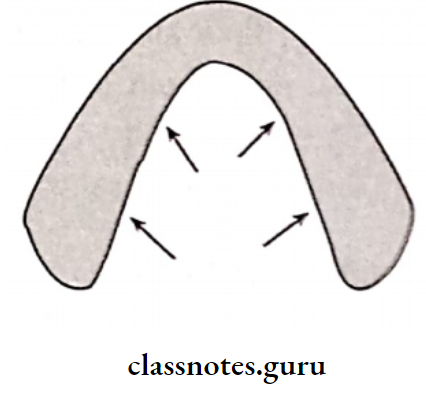
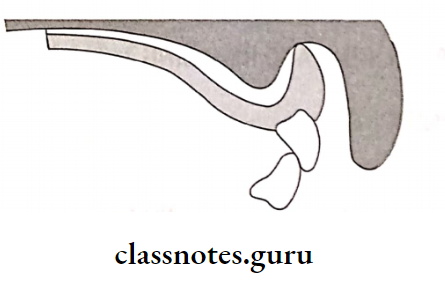
- Residual Ridge Resorption Treatment:
- Ridge augmentation to increase the height of the ridge
- Vestibuloplasty to increase the depth of the sulcus
Common Denture Problems and Solutions
Indirect Sequel:
1. Atrophy Of Masticatory Muscles:
- Masticatory efficiency depends on the skeletal forces
- This force decreases with age
- Besides, denture wearers do not use their muscles to their maximum function
- Due to poor usage, atrophy of the muscle occurs
- Common Muscles Affected: Medial pterygoid and masseter
- Muscle Management:
- Use of an overdenture
- Use of implants
2. Nutritional Deficiencies:
- Causes Of Malnutrition:
- Poor general health
- Poor absorption
- Catabolic disturbance
- Anorexia
- Reduced salivary secretion
Nutritional Deficiencies Management:
- Intake of a protein-rich diet
- Encouraging patients to have good, nutritious food
- It helps in the initial retention of the denture, increasing the psychological comfort of the patient
Prosthodontics Notes on Denture Adjustment
Post Insertion Problems Short Essays
Question 1. Denture adhesive.
Answer:
Denture Adhesive Composition:
- Basic Ingredients:
- Carbonyl methylcellulose
- Vegetable gum
- Example: Tragacanth
- Vinyl methyl ether
- Polyethylene oxide
- Polyvinyl pyrrolidone
- Gantrez salts
- Cationic polyacrylic amide polymers
- Coloring agents-red dye
- Flavouring agents-menthol
- Wetting agents
- Preservatives-sodium borate
- Plasticizers- mineral oil
- Dispersion agents-magnesium oxide
- Denture Adhesive Indications:
- Improve the retention and stability of the dentures
- To stabilize trial dentures
- For handicapped patients
- To provide a psychological sense of security
- To simplify the insertion for patients
- As an adjunct to the maxillary prosthesis
- Denture Adhesive Contraindications:
- Patients with ill-fitting dentures
- In medication-induced xerostomia
- In worn-out dentures
- As a substitute for a recliner
- In patients with an inability to clean dentures
- In immediate dentures
- In case of allergy to components of the adhesive
