Psychological Development And Behaviour Management Important Notes
1. Theories of child psychology

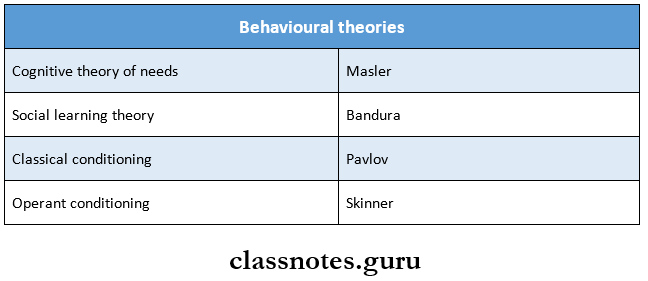
2. Behavioural theories
Read And Learn More: Pedodontics Short Essays Question And Answers
3. Mahler’s theory
- It is divided into 3 stages
- Normal autistic phase 01 years
- Normal symbiotic phase 4 weeks to 4 years
- Separation individualization phase 536 months
4. Operant conditioning
- According to this theory, the consequence of behavior itself acts as a stimulus and affects the future behavior
- There are 4 types of operant conditioning by Skinner
- They are
- Positive reinforcement
- Negative reinforcement
- Omission
- Punishment
5. Cognitive theory
- It is based on how children and adolescents think and acquire knowledge
- According to Piaget, the environment does not shape child behavior but the child and adult actively seek to understand the environment
6. Hierarchy of needs
- According to Masler, the needs of the person are arranged in a hierarchy and as one general type of need is satisfied, another higher-order need will emerge
- The desires from most biological needs to the more psychological ones become more important only after basic needs have been satisfied
7. Behavioural management techniques
1. Nonpharmacological techniques
- Communication
- It is of 2 types verbal and nonverbal
- The voice that is used should be constant and gentle
- The tone of voice can express empathy and firmness
- Nonverbal is by body language and smiling. Eye contact, by touching the child or by giving a hug
- Behavior shaping
- Desensitization
- It involves teaching the patient how to induce a state of deep muscle relaxation and describing imaginary scenes relevant to his fear
- Modeling
- Introduced by Bandura
- Here the child is allowed to observe one or more individuals who demonstrate positive behavior in a particular situation
- Contingency management
- The presentation or withdrawal of reinforces is termed as contingency management
- Reinforces always increase the frequency of a behaviour
- Behavior management
- Audio analgesia
- An auditory stimulus such as pleasant music has been used to reduce stress and also to reduce the reaction to pain
- Biofeedback
- It involves the use of certain instruments to detect certain physiological processes such as BP associated with fear
- Voice control
- It is the modification of intensity and pitch of one’s own voice in an attempt to dominate the interaction between the dentist and child
- It is used in conjunction with some form of physical restraints and the Home technique
- Hypnosis
- Humor
- It helps to elevate the mood of the child which helps the child to relax
- Coping
- It is the mechanism by which a child copes up with the dental treatment by establishing a close or trusting relationship with the doctor or nurse
- Relaxation
- Implosion theory
- It mainly comprises of Home, physical restraints, and voice control
- Aversive conditioning
- It is a safe and effective method
- Parental consent is required prior to its use
- Two methods used for it are HOME and physical restraints
2. Pharmacological techniques
- Premedication
- Conscious sedation
- General anesthesia
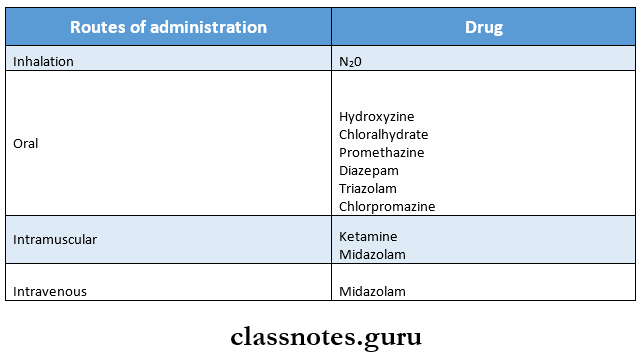
8. Drugs used for behavioral management
9. Home
- It is Hand Over Mouth Exercise
- Introduced by Evangeline Jordan
- Indications
- 3-6 years of age
- A child who can understand simple verbal commands
- A healthy child displaying uncontrolled behavior
- Contraindications
- Children under 3 years of age
- Handicapped/ immature/ frightened child
- Physical, mental, and emotional handicaps
10. Tell, Show, Do technique
- Introduced by Addleson
- Effective in children more than 3 years of age
- First, the dentist tells the child what is going to be done in simple words
- Second the dentist demonstrates the exact procedure to the child
- Finally, the dentist performs the procedure exactly as it was described and demonstrated
- Indications
- Children more than 3 years of age
- Fearful child
- First visit
11. N2O sedation
- Contraindications:
- COPD
- Asthma
- Respiratory infection
- Sickle cell anaemia
- Otitis media and epilepsy
12. Types of physical restraints
- Active performed by dentists/ parents/ staff
- Passive by restraining device
13. Stages of development according to cognitive theory
- Sensorimotor stage 0-2 years
- Preoperational stage 2-6 years
- Concrete operation stage 7-12 years
- Formal operation stage 11-15 years
Psychological Development And Behaviour Management Long Essays
Question 1. Explain Psychological development of a child according to Sigmund Freud.
Answer:
Sigmund Freud gave a psychoanalytical theory explaining the psychological development of a child. He describes 6 psychosexual stages and at each stage he included the development of sexual desires.
Sigmund Freu Stages:
- Oral Stage
- It is a dependent stage where the infant depends on adults to fulfill his needs
- But if the child’s needs are not fulfilled he develops a negative and aggressive behavior
- Anal Stage
- During this stage, maturation of neuromuscular control occurs
- The child obtains a sense of control over its voluntary functions, a sense of independence.
- If it fails, the child develops abnormal behavior like stubbornness.
- Urethral Stage:
- It is a transitional stage between the anal and a phallic stage
- The child obtains and is satisfied with the control over its urinary sphincter
- If it fails to develop, the child becomes competitive
- Phallic Stage:
- Period 3rd5th year of life
- Development of Oedipus complex and Electra complex where the young boys are attracted towards mother, while girls are attracted towards her father respec¬tively.
- The child has unusual sexual feelings for the opposite sex
- He carries out his sexual activities without any embarrassment
- Latency Stage:
- This stage ends in puberty
- A child develops a well-balanced control over his desires
- The child adapts to the changing environment
- Lack of this behavior results in immature behavior of the child.
- Genital Stage:
- Period 1113 years to adulthood
- The child realizes the sense of maturity, sense of individuality, sense of ability to reproduce, and sense of independence.
- The child develops social environment by communicating and interacting with the surrounding
- The child accepts the social expectations and lives according to it.
Question 2. Define behavior management. Discuss in detail nonpharmacological techniques of behavior management.
(or)
What is behavioral management, describe in detail the techniques employed in treating an apprehensive 4 years old child.
Answer:
Definition:
- Behavior management is defined as the means by which the dental health team effectively and efficiently performs dental treatment and thereby instills a positive dental attitude.
Non Pharmacological Techniques
1. Communication: This can be used in both cooperative and uncooperative child
Non-Pharmacological Techniques Types:
- Verbal by speech:
- Using kind words
- With a friendly nature
- Nonverbal:
- Smiling face
- Eye contact
- Giving a hug
- Touching the child
- Combination:
2. Behavior Shaping:
It is the procedure which slowly develops behavior by reinforcing a successive approximation of the desired behavior until the desired behavior comes into being.
Means:
- Desensitization:
- Developed by Joseph Wolpe
- It is a procedure which teaches a child gradually desired behavior by introducing stimuli from less threatening objects to more threatening objects
- Modeling:
- Introduced by Bandura
- It makes the patient to observe other child patients or models to develop the desired behavior
- The model should initiate the same situation
- Live models, if used, it should involve a person who has a greater impact on the child like siblings, parents, etc.
- Contingency management:
- It modifies the child’s behavior by introducing/withdrawing the reinforce
- Types Of Reinforcement:
- Positive toys, patting back
- Negative withdrawal of the mother
3. Behavioral management:
- Audio Analgesia:
- The use of mild, soft music in the dental clinic reduces a child’s anxiety
- Biofeedback:
- This method uses various means of investigation like blood pressure that detect the level of anxiety
- Humor:
- This relieves the anxiety of the child
- Simultaneously, transmits essential information
- Coping:
- Measures like friendliness, support, and reassurance are used to master and reduce the stresses of patients.
- A child may totally accept the stressful condition or may keep thinking about the procedure in his mind at the same time, he is calm.
- Voice control:
- Modification of intensity of voice is done to obtain desired behavior from the child
- Dentists should have adequate knowledge of changing the tone from gentle to firm.
- Relaxation:
- It is time-consuming
- It involves a series of exercise which is taught to the child
- Children need to perform it at least 15 minutes per day
- Hypnosis:
- It is an altered state of consciousness
- Creates heightened suggestibility to obtain the desired behavior
- Implosion therapy:
- It involves the administration of a combination of various means to such that the child has no other choice but to cope up with the situation
- Aversive conditioning:
- It is a safe and effective method
- Use to manage extremely negative behavior
- It involves
- Home
- Physical restraints
Question 3. Classify theories of child psychology. Discuss in detail the cognitive theory of child psychology.
Answer:
Theory of child psychology Classification:
1. Psychodynamic theories:
- Psychosexual theory by Sigmund Freud
- Psychosocial theory by Erik Erikson
- Cognitive theory by Jean Piaget
2. Theories of learning and development of behaviour:
- Hierarchy of Needs by Maslow
- Social learning theory by Bandura
- Classical conditioning by Pavlov
- Operant Conditioning by Skinner
3. Margaret and Mahler’s theory of development Cognitive Theory:
- Proposed by Jean Piaget
- It involves three functional variants
- Assimilation: The child observes anything in the environment and tries to recognize it and relate it to the previous experiences
- Accommodation: Here the child develops new strategies or concepts due to the changing concepts.
- Equilibrium: The child carries out adjustments in the basic assumptions.
Cognitive Theory Stages:
- Sensorimotor stage (Birth18 months)
- During this stage, the child relies on seeing, touching, sucking
- The child uses their senses to learn things
- Preoperational stage (18 months7years)
- Preconceptual stage (18 months 4 years)
- Intuitive period (47 years)-During this child’s thinking is self-centered or egocentric
- Concrete operational stage (712years):
- The child develops reasoning power
- He organizes his thoughts comprehensively
- Formal operational stage (1213 years):
- The child develops an ability to solve a problem
Cognitive Theory Merits:
- It is a comprehensive theory
Cognitive Theory Demerits:
- It underestimates a child’s ability
- Underestimates environmental role
- Overestimates age differences.
Question 4. Define behavior science and behavior management. Discuss factors affecting child’s behavior.
Answer:
Definition:
1. Behavior Science:
- It is the science which deals with the observation of behavioral habits of man and lower animals in various physical and social environment.
2. Behavior Management:
- It is defined as the means by which the dental team effectively and efficiently performs dental treatment and thereby instills a positive dental attitude.
Factors Affecting Child’s Behavior:
1. Factors involving the Child
- Growth and Development:
- A child with deficient physical and mental development cannot react to the social expectations
- As a result of rejection by the society to such child, it leads to psychological trauma to the child
- Nutritional factors:
- Increased intake of sugar causes irritable behavior
- Hypoglycaemia causes criminal behavior
- Skipping breakfast leads to impaired performance
- Past dental experiences:
- Any unpleasant experiences are associated with uncooperative behavior
- School environment:
- 50% of a child’s behavior is affected by school
- Teachers as well as seniors influence child’s behavior
- Socioeconomic status:
- High socioeconomic status child develop normally and gets spoilt
- Low socioeconomic status child has tensed behavior
2. Factors involving the Parents
- Home environment:
- All family members one or the other way influ¬ence’s child behavior
- A child’s behavior also depends on the emotional status of the mother during pregnancy
- Family development:
- More parental involvement leads to spoilt behavior of the child
- Maternal behaviour:
- A child’s behavior is influenced by the emotional status as well as the nutritional status of the mother
3. Factors involving the Dentist:
- Dental office environment:
- Make the reception room comfortable
- Provide books for all ages
- Walls, appointment cards and other accessories should be attractive
- Avoid light of instruments or sight of blood
- Effect of dentist’s activity and attitudes:
- Dentists should avoid jerky movements
- He/she should be fluent
- Effect of dentist’s attire:
- The presence of a white colored cloth may evoke a negative behavior
- Presence or absence of parents:
- A mother’s presence is essential for a preschool child, handicapped child
- Mother’s absence for an older child
- Presence of an older sibling:
- An older sibling serves as a role model
Question 5. Define conscious sedation. Describe nitrous oxide-oxygen sedation.
Answer:
Conscious Sedation:
- Definition: A minimally depressed level of consciousness that retains the patient’s ability to maintain an airway independently and respond appropriately to physical stimulation and verbal command
Nitrous Oxide 02 Mixture:
- It is the most widely used form
- Route Inhalation of gas
- The administration of it is carefully titrated to the patient’s need.
Pharmacology:
- With the increase in patient’s anxiety, tidal volume increases from 68 liters
- Nitrous oxide is carried in a free state with less solubil¬ity in blood
- It is a weak anesthetic gas.
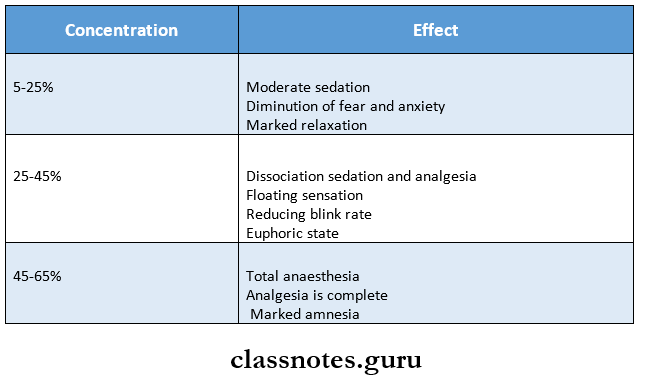
Conscious Sedation: Stages:
Plane 1: Moderate Sedation and Analgesia
- Patient experience:
- Dizziness
- Tingling
- Relaxation
- Impairment of vision and hearing
- Fear and anxiety
Plane 2: Dissociation sedation and analgesia
- Patient feels
- Dissociation from his environment
- Reduced blinking capacity
- But however, the patient responds
Plane 3: Total anesthesia (Analgesia)
- Complete analgesia is achieved with marked amnesia
- It is subdivided into
- Lightest plane
- Samnolent state
- Deepest plane
Plane 4: This results in loss of contact with hazards
Adverse Effects:
- Effects DNA synthesis
- The patient may develop pernicious anemia
Contra-Indications:
- Patient with upper respiratory tract infection
- Pneumothorax
- Pregnancy
Question 6. Define behaviour management. Enumerate fundamentals of management technique and explain aversive conditioning.
Answer:
- Definition: Behavior management is defined as the means by which the dental health team effectively and efficiently performs dental treatment and thereby instills a positive dental attitude.
Fundamentals Of Behaviour Management:
- To establish effective communication with the child and the parent
- To gain the confidence of both the child and the parent and make them accept dental treatment
- To teach the child and the parent about the positive aspects of preventive dental care
- To provide a relaxed and comfortable environment for the dental team to work in while treating the child
Aversive Conditioning:
- It is a safe and effective method
- Used for management of extremely negative behavior
- Parental consent must be obtained prior to its administration
- It includes 2 methods
1. Home:
- Hand Over Mouth Exercise
- Introduced by Evangeline Jordan
- In this method, the dentist firmly places his hands over the child’s mouth
- Next, he kindly explains child by being close to the child’s ear
- Once desired cooperation is obtained by the child, he is complimented for his good and cooperative behavior
2. Physical restraints:
- Used as a last resort for uncooperative patients
- The child is seated in the mother’s lap and the child’s movement of head, hands, and feet which shows refusal of treatment, are restricted
Physical restraints: Types:
- Active Without using a restraining device
- Passive With the use of a restraining device
Used Equipment:
- For body:
- Pedi wrap
- Towel and tapes
- For extremities:
- Velcro straps
- Posey straps
- For the head:
- Head positions
- For mouth:
- Mouth blocks
- Mouth props
Question 7. Define behaviour management. Describe Wright’s classification of the behavior of children in the dental clinic. Write in detail about communication as a behavior management technique
Answer:
Behavioral Management:
- Behavior management is defined as the means by which the dental health team effectively and efficiently performs dental treatment and thereby instills a positive dental attitude.
Wright’s Classification:
1. Cooperative
- Cooperative behavior Minimal refusal
- Lacking cooperative ability Seen in preschoolers and handicapped
- Potentially cooperative Patient exhibit inherent fears
Uncooperative:
- Uncontrolled/Hysterical Child shows temper tantrums
- Defiant behavior/obstinate Seen in stubborn children
- A tense cooperative Child accepts the treatment but at the same time is tensed
- Timid/shy Child is shy but cooperative
- Whining type Child keeps on complaining
- Stoic behavior Cooperative without any facial expression
Communication As Behavior Management:
- This can be used in both cooperative and uncoopera¬tive child
Behavioral Management Types:
- Verbal by speech:
- Using kind words
- With a friendly nature
- Nonverbal:
- Smiling face
- Eye contact
- Giving a hug
- Touching the child
- Combination:
Psychological Development And Behaviour Management Short Essays
Question 1. Psychic triad/ld, Ego, Superego.
Answer:
Proposed By Freud
1. Id:
- It is basis of the pleasure principle
- It is a reservoir of desires
- It represents the mental state of the child
- It is present at birth
- The child tries completely to fulfill his desires to obtain immediate pleasure and satisfaction
2. Ego:
- It develops in the 2nd to 6th month of life
- It is based on the reality principle
- The child begins to differentiate between his dreams and his surrounding environment
- The child tries to modify his desires according to the reality
3. Superego:
- It is the restrictions on the individual which prevent him to go wrong
- It includes regulations by the parents, society, and culture
- It creates a feeling of shame and guilt on doing a wrong thing that is against the society
Question 2. Stimulus Response Theory.
Answer:
- It is a form of behavior shaping
- It is a procedure which very slowly develops behavior by reinforcing successive approximations of the desired behavior until the desired behavior is achieved.
- For example, when shaping behavior, the dental assistant or dentist is teaching the child how to behave
- Young children have to be communicative and cooperative
- Gradually the patient adapts to the procedure
Question 3. Modeling.
Answer:
- Introduced by Bandura
- It is a method of behavior modifications
- It reduces the anxiety of the child’s patient by demonstrating the same situation in a less threatening manner
Methods:
- Live models
- Filmed models
- Posters
- Audiovisual aids
Advantage: Doesn’t require any additional equipment
Requirement:
- The selection of the model should be such a person that has a greater impact on the child like siblings, parents, etc.
Question 4. Fear in Dentistry.
Answer:
Fear in an unpleasant emotion/effect consisting of psychophysiological changes in response to realistic threat or danger to one’s own experience
Dentistry Types:
- Innate fear: Fear present since birth
- Objective fears: Acquired by an unpleasant past situation
- Subjective fear: It is parent’s oriented
Features:
- Fear lowers the pain threshold
- Tense muscles
- Anger
- Weakness
- Increased heartbeat
- Urge to urinate
- Dryness of the mouth
- Rapid breathing
- Dilatation of pupils
- Hair standing on end
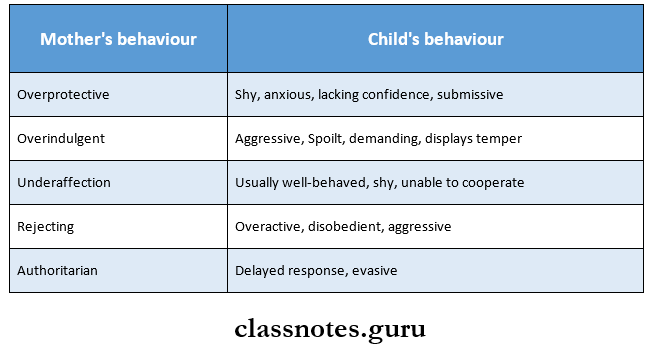
Question 5. Maternal’s influence on child’s psychology.
Answer:
- There is a mother-child interdependency that initiates at infancy and builds well into the preschool period
- Bayley and Schaefer indicate that most of the relevant mother-child relationship fall into two categories
- Autonomy versus control
- Hostility versus love
- Mothers who allowed enough autonomy and expressed affection had children who were friendly and cooperative and those who ignored their children did not have children who exhibited these positive behavioral features
- Highly anxious parents tend to affect their child’s behavior negatively
- The effect is greatest with those under 4 years of age
- Mother-child behavior interactions
Question 6. Home.
Answer:
- It is a technique of aversive conditioning
- It was first described in the 1920s by Dr. Evangeline Jordan
Home Objectives:
- To gain the child’s attention enabling communication with the dentist so that appropriate behavioral expectations can be explained
- To eliminate inappropriate avoidance responses to dental treatment and to establish appropriate learned responses
- To enhance the child’s self-confidence in coping with the anxiety of dental treatment
- To ensure the child’s safety in the delivery of quality dental treatment
Home Technique:
- In this method, the dentist firmly places his hands over the child’s mouth
- Next, he kindly explains child by being close to the child’s ear
- Once desired cooperation is obtained by the child, he is complimented for his good and cooperative behavior
Home Indications:
- In the case of a healthy child who is able to understand and cooperate but who exhibits defiant, obstreperous or hysterical avoidance of behaviour to dental treatment
- For normal children who are hysterical, belligerent
- Used for children with sufficient maturity to understand simple verbal commands
Home Contraindications:
- In children who due to age, disability, medication or emotional immaturity are unable to understand and cooperate
- When it will prevent the child from breathing
Home Variations:
- Hand over mouthairway unrestricted
- Hand over both mouth and nose
- Towel held over mouth only
- Dry towel held over mouth and nose
- Wet towel held over mouth and nose
Question 7. Desensitization.
Answer:
- It is form of behavior shaping
- Introduced by Joseph Wolpe
- It is helpful in patients who had unpleasant past experience
- It is done by teaching the child a competing response such as relaxation and then introducing more threatening stimuli
- It is an effective method
- The patient learns to substitute proper and cooperative responses instead of uncooperative response
Question 8. Anxiety v/s fear
Answer:
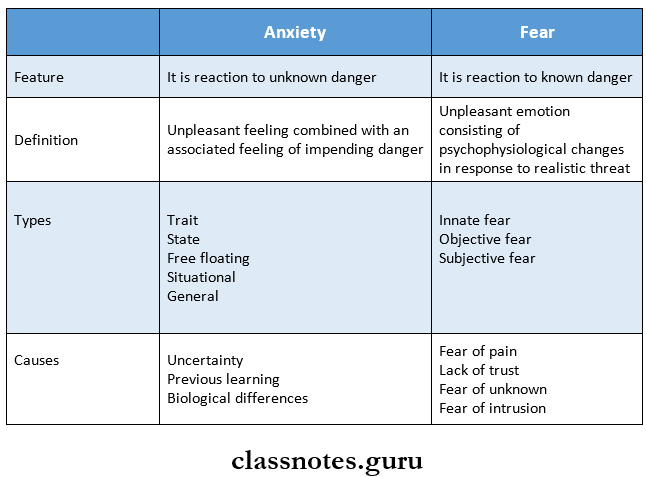
Psychological Development And Behaviour Management Short Answers
Question 1. Frankel Behaviour rating scale.
Answer:
- Definitely negative (- -)
- Child refuses any kind of treatment
- He opposes it by forcefully crying
- Negative (-)
- Reluctant to accept treatment
- Positive (+)
- Accepts treatment
- However, if the patient has any bad past experience, he becomes uncooperative
- Definitely positive (++)
- Very cooperatively accepts the treatment
- Realizes the importance of treatment
Question 2. Voice Control.
Answer:
- It is a form of behavior management
- It includes modification of intensity and pitch of one’s own voice
- Dentists should have adequate knowledge of when and how to change the tone from gentle to firm
- This results to change the patient’s attitude
- The child cooperates to the treatment as well as obeys the dentist.
Question 3. Tell Show Do technique (TSD).
Answer:
Methods of desensitization:
TSD Indications:
- First visit,
- Fearful child
- Apprehensive child
- It is effective in children more than 3 years
Method:
- Tell Explain the treatment procedure to the patient using less threatening manner
- Show Treatment procedure is demonstrated through models
- Do Carry out the treatment
Question 4. Contingent management.
Answer:
- Contigency management technique is based on the operant conditioning theory of BF Skinner
- It is a method of modifying behaviour by presentation or withdrawal of the reinforcers
- These reinforce are the pleasant or unpleasant stimuli mentioned in the operant theory in child psychology
- Contigency management includes:
- Reinforcement of positive or negative
- Omission/ time out
- Punishment
Question 5. Ketamine.
Answer:
- It is an agent used for sedation
- Route Intramuscular
- Dose 10 and 50 mg/ml
Ketamine Indications:
- Dissociative anesthesia
- As an analgesic
Question 6. Subjective fear.
Answer:
- A child develops subjective fear based on somebody else’s experience without actually undergoing dental treatment himself
- Parents may tell the child about an unpleasant or pain-producing situation undergone by them and this fear may be retained in the child’s mind
Question 7. Communication.
Answer:
Basic ways of communication are
1. Verbal communication:
- It is through conversation
- By involving the child in a conversation
- It is best initiated for younger children with com elementary comments followed by questions that elicit an answer other than yes or no
2. Nonverbal communication:
- Body contact is form of it
- The act of placing a hand over the child’s shoulder while sitting on a chair side stool conveys a feeling of warmth and friendship
- Sitting and speaking at eye level allows for friendlier and less authoritative communication
Psychological Development And Behaviour Management Viva Voce
- Oedipus complex describes the desire in young boys to have sexual relations with the mother
- Electra complex describes the development of attrac¬tion in young girls towards their father
- Fear is a reaction to a known danger
- Anxiety is a reaction to unknown danger
- Chloralhydrate is an extremely well-known and widely used drug for conscious sedation
- Head positioner and forearm body support are restraints in uncooperative patients
- Dose of 40% N2O + 60% O2 is commonly used for sedation
- Joseph Wolpe proposed desensitization
