Growth And Development
Definition
1. Growth
- According to Todd, growth refers to an increase in size
2. Development
- It is naturally occurring unidirectional changes in the life of an individual from its existence as a single cell to its elaboration as a multifactorial unit terminating in death
Read And Learn More: Pedodontics Short Essays Question And Answers
Growth And Development Important Notes
1. Growth Theories
- Genetic theory by Brodie
- Proposed that genes control all the factors of growth and development
- Sutural theory by Sicher
- Proposed that sutures cause most of craniofacial growth
- Cartilaginous theory by Scott
- It states that the determinant of craniofacial growth is by the growth of cartilage
- Functional matrix theory by Melvin Moss
- It is divided into a functional matrix and a skeletal unit
- Van Utnborg concept
- Suggested five factors that control growth
- Intrinsic genetic factors
- Local epigenetic factors
- General epigenetic factors
- Local environmental factors
- General environmental factors
- Suggested five factors that control growth
2. Functional matrix theory
- Functional matrix
- It consists of teeth, organs, glands, muscles, nerves, and vessels
- It is divided into
- Periosteal matrix
- All nonskeletal units adjacent to skeletal units
- Capsular matrix
- Neurocranial capsule – sandwiched between skin and dura mater
- Orofacial capsule – surrounds and protects or nasopharyngeal space
- Skeletal unit
- Comprised of bone, cartilage or tendon
- It consists of micro skeletal unit and macro skeletal unit
Growth And Development Short Essays
Question 1. Functional matrix theory.
Answer:
- Melvin Moss combined sutural theory and cartilaginous theory and introduced this concept
Hypothesis:
- It claims that the origin, form, position, growth, and maintenance of all skeletal tissues and organs are always secondary, compensatory, and necessary responses to chronologically and morphologically prior events or processes that occur in specifically related non-skeletal tissues, organs or functioning spaces
Components:
- Skeletal Unit
- Microskeletal
- Macroskeletal
- Functional Matrix
- Periosteal Matrices
- Capsular Matrices
Skeletal Unit:
- All skeletal tissues associated with a single function are called the skeletal unit
- When a bone is comprised of several contagious skeletal units, it is termed as “Micro skeletal unit” Example. Maxilla, Mandible
- When adjoining portions of a number of neighboring bones are united to function as a single cranial component, termed as “Macro skeletal unit” Example. Calvarium
Functional matrix:
- Consists of muscle, glands, nerves, vessels, fat, teeth, and functional spaces
- Divided into
- Periosteal matrices
Acts directly and act upon skeletal units
↓
Transformation in their size and shape
↓
Resulted due to bone deposition and resorption
- Capsular matrices
- Acts indirectly and passively on bone
- Expansion of capsule
- Results growth of bones within it
- Example. Growth of facial bones due to the expansion of the oro-facial capsule
- Capsular matrices
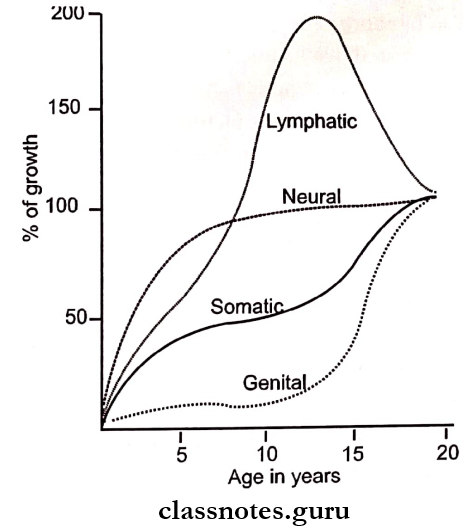
Question 2. Scammon’s Growth Curve.
Answer:
It indicates that the growth of different tissues are different at different age.
Body tissues are classified into 4 types:
1. Lymphoid tissue:
- It proliferates rapidly in late childhood and reaches 200% of adult size
- It is for the protection of children against infection
- At the age of 18, this tissue undergoes involution.
2. Neural tissue:
- It grows very rapidly and reaches adult size by 6-7 years of age.
- Later very little growth occurs.
- This facilitates the intake of further knowledge.
3. General tissue:
- This exhibit an “S” shaped curve.
- Rapid growth occurs up to 2-3 years of age.
- This is followed by a slow growth between 3-10 years.
- After the tenth year, a rapid phase occurs up to 18-20th years.
4. Genital tissue:
- It consists of reproductive organs
- They show negligible growth until puberty
- They grow rapidly at puberty reaching adult size
Growth And Development Viva Voce
- Functional matrix theory by Malvin Moss explains the origin, form, position, growth, and maintenance of all skeletal tissues and organs
- Van Limb org’s theory emphasizes on five factors that control growth i.e. intrinsic genetic factors, local and general epigenetic factors, and local and genetic environmental factors
- Chondro-cranial growth is mainly controlled by intrinsic genetic factors
- Sutural and periosteal growth is governed by non genetic environmental factors
