Class 6 Maths Chapter 12 Ratio And Proportion
Question 1. The ratio of books to 20 books is
- 2:5
- 5:2
- 4:5
- 5:4
Solution: (1): The ratio of 8 books to 20 books
= 8 books: 20 books
⇒ \(=\frac{8}{20}=\frac{2}{5}=2: 5\)
Question 2. The ratio of the number of sides of a square to the number of edges of a cube is
- 1:2
- 3:2
- 4:1
- 1 :3
Solution: (4) : Required ratio = \(\frac{\text { Number of sides of a square }}{\text { Number of edges of a cube }}=\frac{4}{12}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{1}{3}=1: 3\)
Read and Learn More Class 6 Maths Exemplar Solutions
Question 3. A picture is 60 cm wide and 1.8 m long. The ratio of its width to its perimeter in the lowest form is
- 1:2
- 1:3
- 1:4
- 1:8
Solution:
(4) : Width of the picture = 60 cm and length of the picture = 1.8 m = 1.8 x 100 cm = 180 cm
Primetor of the picture = 2* (180 + 60) cm
= 2 x 240 cm = 480 cm
The required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Width of the picture }}{\text { Perimeter of the picture }}\)
⇒ \(\frac{60 \mathrm{~cm}}{480 \mathrm{~cm}}=\frac{1}{8}=1: 8\)
Question 4. Neelam’s annual income is ₹ 288000. Her annual savings amount to ₹ 36000. The ratio of her savings to her expenditure is
Solution:
- 1:8
- 1:7
- 1:6
- 1:5
Solution: (2):
Given
Neelam’s annual income =₹ 288000
Her savings =₹ 36000
Her expenditure = Annual income – Savings
= ₹ 288000- ₹ 36000 =₹ 252000
The required ratio = \(=\frac{\text { Savings }}{\text { Expenditure }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{₹ 36000}{₹ 252000}=\frac{1}{7}=1: 7\)
Question 5. The mathematics textbook for Class VI has 320 pages. The chapter’symmetry’runs from page 261 to page 272. The ratio of the number of pages of this chapter to the total number of pages of the book is
- 11: 320
- 3: 40
- 3: 80
- 272: 320
Solution: (3):
Given
The mathematics textbook for Class VI has 320 pages. The chapter’symmetry’runs from page 261 to page 272.
Total number of pages = 320
The number of pages of the chapter ‘symmetry’ = 272- 261 +1 = 12
The required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Number of pages of chapter ‘symmetry’ }}{\text { Total number of pages of the book }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{12}{320}=\frac{3}{80}=3: 80\)
Question 6. In a box, the ratio of red marbles to blue marbles is 7: 4. Which of the following could be the total number of marbles in the box?
- 18
- 19
- 21
- 22
Solution: (4):
Given
In a box, the ratio of red marbles to blue marbles is 7: 4.
Since the sum of the given ratio is 7 + 4 = 11 and from the given options, only 22 is Divisible by 11.
Option (D) is correct.
Question 7. On a shelf, books with green covers and those with brown covers are in the ratio 2 : 3. If there are 18 books with green covers, then the number of books with brown covers is
- 12
- 24
- 27
- 36
Solution:
Given
On a shelf, books with green covers and those with brown covers are in the ratio 2 : 3. If there are 18 books with green covers
(3): Let the number of green cover and brown cover books be 2x and 3x respectively. Since, the number of green cover books = 18
⇒ 2x = 18
⇒ \( x=\frac{18}{2}=9\)
The number of brown cover books = 3×9 = 27
Question 8. The greatest ratio among the ratios 2 : 3, 5: 8, 75:121 and 40: 25 is
- 2 : 3
- 5: 8
- 75: 121
- 40: 25
Solution: (4): we have \(2: 3=\frac{2}{3}, 5: 8=\frac{5}{8}, 75: 121=\frac{75}{121}\) and \(40: 25=\frac{40}{25}\)

The LCM of 3, 8, 121 and 25 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 5 x 5x11x11 = 72600
Making the denominator of each ratio equal to 72600, we get
⇒ \(\frac{2}{3}=\frac{2 \times 24200}{3 \times 24200}=\frac{48400}{72600}\)
⇒ \(\frac{5}{8}=\frac{5 \times 9075}{8 \times 9075}=\frac{45375}{72600}\)
⇒ \(\frac{75}{121}=\frac{75 \times 600}{121 \times 600}=\frac{45000}{72600}\)
⇒ \(\frac{40}{25}=\frac{40 \times 2904}{25 \times 2904}=\frac{116160}{72600}\)
On comparing the numerator of the above ratios, we get \(\frac{40}{25}\) is the greatest ratio, i.e., 40: 25 is the greatest ratio among the given ratios.
Question 9. There are ‘b’ boys and ‘g’ girls in a class. The ratio of the number of boys to the total number of students in the class is: 20
- \(\frac{b}{b+g}\)
- \(\frac{g}{b+g}\)
- \(\frac{b}{g}\)
- \(\frac{b+g}{b}\)
Solution: (1) :
Given
There are ‘b’ boys and ‘g’ girls in a class. The ratio of the number of boys to the total number of students in the class is: 20
Total number of students = number of boys + number of girls = b+g
The required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Number of boys }}{\text { Total number of students }}\)
⇒ \(\frac{b}{b+g}\).
Question 10. If a bus travels 160 km in 4 hours and a train travels 320 km in 5 hours at uniform speeds, then the ratio of the distance travelled by them in one hour is
Solution:
- 1: 2
- 4: 5
- 5: 8
- 8: 5
Solution: (3):
Given
If a bus travels 160 km in 4 hours and a train travels 320 km in 5 hours at uniform speeds
Distance travelled by bus in 4 hours = 160 km
Distance travelled by bus in 1 hour \(=\frac{160}{4} \mathrm{~km}=40 \mathrm{~km}\)
Distance travelled by train in 5 hours = 320 km
Distance travelled by train in1 hour \(=\frac{320}{5} \mathrm{~km}=64 \mathrm{~km}\)
The required ratio = \(\frac{40 \mathrm{~km}}{64 \mathrm{~km}}=\frac{5}{8}=5: 8\)
Question 11. 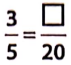
Solution:
To get the missing number, we consider the fact that 4 * 5 = 20, i.e., we get 20 when we multiply 5 by 4. This indicates that to get the missing number, 3 must also be multiplied by 4.
When we multiply, we have, 3 x 4 = 12
Hence, the ratio is \(\frac{12}{20}.\)
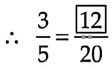
Question 12. 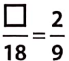
Solution:
To get the missing number, we consider the fact that 9 * 2 = 18, i.e., when we multiply 9 by 2 we get 18. This indicates that to get the missing number, 2 must also be multiplied by 2.
When we multiply, we have, 2×2 = 4
Hence, the ratio is \(\frac{4}{18}.\)
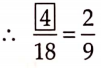
Question 13. 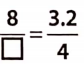
Solution:
To get the missing number, we consider the fact that 3.2 x 2.5 = 8, i.e., when we multiply 3.2 by 2.5 we get 8. This indicates that to get the missing number, 4 must also be multiplied by 2.5.
When we multiply, we have, 4 x 2.5 = 10
Hence, the ratio is \(\frac{8}{10}.\)
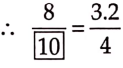
Question 14. 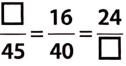
Solution:
To get the missing number, we consider the fact that 40 x 1.125 = 45, i.e., when we multiply 40 by 1.125 we get 45. This indicates that to get the missing number of the first ratio, 16 must also be multiplied by 1.125.
When we multiply, we have, 16 * 1.125 = 18.
Hence, the first ratio is \(\frac{18}{45}\)
Similarly, to get the third ratio we multiply both terms of the second ratio by 1.5.
Hence, tine third ratio is \(\frac{24}{60}\)
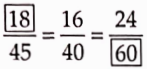
Question 15.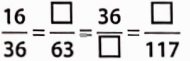
Solution:
To get the missing number, we consider the fact that 36 x 1.75 = 63, i.e., we get 63 when we multiply 36 by 1.75. This indicates that to get the missing number of the second ratio, 16 must also be multiplied by 1.75.
When we multiply, we have, 16 * 1.75 = 28
Hence, the second ratio is \(\frac{28}{63} \text {. }\)
Similarly, to get the third ratio we multiply both terms of the first ratio by 2.25
Hence, the third ratio is \(\frac{36}{81} \text {. }\)
And to get the fourth ratio we multiply both terms of the first ratio by 3.25.
Hence, the fourth ratio is \(\frac{52}{117}\)
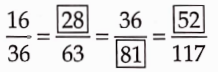
Question 16. \(\frac{3}{8}=\frac{15}{40}\)
Solution: True
We have, \(\frac{15}{40}=\frac{3}{8}\)
Question 17. \(4: 7=20: 35\)
Solution: True
We have, \(20: 35=\frac{20}{35}=\frac{4}{7}=4: 7\)
Question 18. 0.2:5 = 2:0.5
Solution: False
⇒ \(0.2: 5=\frac{0.2}{5}=\frac{2}{50}=\frac{1}{25}\)
⇒ \(2: 0.5=\frac{2}{0.5}=\frac{20}{5}=\frac{4}{1}\)
Since, \(\frac{1}{25} \neq \frac{4}{1}\)
0.2: 5* 2: 0.5
Question 19. 3:33 = 33:333
Solution: False
We have \(3: 33=\frac{3}{33}=\frac{1}{11}\)
⇒ \(\text { and } 33: 333=\frac{33}{333}=\frac{11}{111}\)
Since, \(\frac{1}{11} \neq \frac{11}{111}\)
3: 33 x 33: 333
Question 20. 1 5 m : 40 m = 35 m: 65 m
Solution: False
We have \(15 \mathrm{~m}: 40 \mathrm{~m}=\frac{15}{40}=\frac{3}{8}\)
⇒ \(\text { and } 35 \mathrm{~m}: 65 \mathrm{~m}=\frac{35}{65}=\frac{7}{13}\)
Since,\(\frac{3}{8} \neq \frac{7}{13}\)
15 m : 40 m* 35 m : 65 m
Question 21. 27 cm2: 57 cm2 = 18 cm: 38 cm
Solution: True
We have, 27 cm2: 57 cm2
⇒ \(=\frac{27}{57}=\frac{9}{19}\)
and 18 cm : 38 cm \(=\frac{18}{38}=\frac{9}{19}\)
27 cm2: 57 cm2 = 18 cm : 38 cm
Question 22. 5 kg: 7.5 kg = 7.50:? 5
Solution: False
We have, 5 kg: 7.5 kg
⇒ \(=\frac{5}{7.5}=\frac{50}{75}=\frac{2}{3}\)
and ? 7.50:? 5 =\(\frac{7.50}{5}=\frac{750}{500}=\frac{3}{2}\)
5 kg: 7.5 kg*? 7.50:? 5
Question 23. 20 g : 100 g = 1 metre: 500 cm
Solution: True
We have, \(20 \mathrm{~g}: 100 \mathrm{~g}=\frac{20}{100}=\frac{1}{5}=1: 5\) and 1 metre : 500 cm = 100 cm : 500 cm
⇒ \(=\frac{100}{500}=\frac{1}{5}=1: 5\)
20 g : 100 g =1 metre : 500 cm
Question 24. 1 2 hours: 30 hours = 8 km: 20 km
Solution: True
We have 12 hours : 30 hours = \(=\frac{12}{30}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{2}{5}=2: 5\)
⇒ \(\text { and } 8 \mathrm{~km}: 20 \mathrm{~km}=\frac{8}{20}=\frac{2}{5}=2: 5\)
12 hours: 30 hours- 8 km: 20 km
Question 25. The ratio of 0 kg to 1 00 kg is 1: 1 0
Solution: True
The ratio of 10 kg to 100 kg \(=\frac{10}{100}=\frac{1}{10}=1: 10\)
Question 26. The ratio of 1 50 cm to 1 metre is 1: 1 .5
Solution: False
The ratio of 150 cm to 1 metre = 150 cm : 1 metre = 150 cm : 100 cm
⇒ \(=\frac{150}{100}=\frac{3}{2}=3: 2\)
⇒ \(\text { and } 1: 1.5=\frac{1}{1.5}=\frac{10}{15}=\frac{2}{3}=2: 3\)
Since, 3:2*2:3
150 cm : 1 metre*1 : 1.5
Question 27. 25 kg: 20 g = 50 kg : 40 g
Solution: True
We have, 25 kg : 20 g = 25 * 1000 g : 20 g
⇒ \(=\frac{25000}{20}=\frac{1250}{1}=1250: 1\)
and 50 kg : 40 g = 50 x 1000 g : 40 g
⇒ \(=\frac{50000}{40}=\frac{1250}{1}=1250: 1\)
25 kg : 20 g = 50 kg : 40 g
Question 28. The ratio of 1 hour to one day is 1: 1.
Solution: False
The ratio of1 hour to 1 day =1 hour : 1 day
= 1 hour : 24 hours = \(=\frac{1}{24}=1: 24 \neq 1: 1\)
Question 29. The ratio of 4: 16 is in its lowest form
Solution: False
We have, 4:16 =\(\frac{4}{16}=\frac{1}{4}=1: 4\)
4: 16 is not in its lowest form.
Question 30. The ratio 5: 4 is different from the ratio 4: 5.
Solution: True
We have, 5 : 4 = \(\frac{5}{4} \text { and } 4: 5=\frac{4}{5}\)
5: 4 x 4: 5
Question 31. A ratio will always be more than 1.
Solution: False
A ratio may be less than 1.
Question 32. A ratio can be equal to 1.
Solution: True
Question 33. If b: a = c: d, then a, b, c, d are in proportion.
Solution: False
If b: a = c : d, then b, a, c, d are in proportion.
34. The two terms of a ratio can be in two different units_____.
Solution: False
Question 35. A ratio is a form of comparison by________.
Solution: Division
Question 36. 20 m : 70 m = ?8: ?________.
Solution:
28: We have, 20 m:70 m \(=\frac{20}{70}=\frac{2}{7}=2: 7\)
![]()
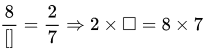
![]()
20 m : 70 m = ? 8 : ? 28
Question 37. There is a number in the box such that![]() , 24, 9, and 12 are in proportion. The number in the box is _______.
, 24, 9, and 12 are in proportion. The number in the box is _______.
Solution:
18: Since, 24, 9, and 12 are in proportion.
![]()
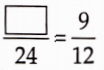
Question 38. If two ratios are equal, then they are in______.
Solution: Proportion
Question 39. The ratio of the perimeter of the boundary of the shaded portion to the perimeter of the whole figure is______.
Solution:
3:7: Since each square is of unit length. The perimeter of the shaded portion is 6 units and the perimeter of the whole figure is 14 units.
The required ratio = \(\frac{6}{14}=\frac{3}{7}=3: 7\)
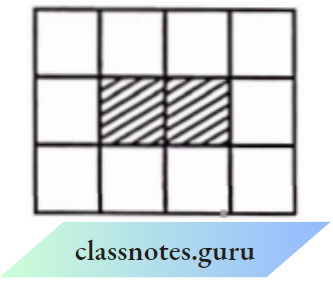
Question 40. The ratio of the area of the shaded portion to that of the whole figure is________.
Solution:
1 : 6 : Area of shaded portion = (1 unit) x (2 units) = 2 sq units
and area of whole figure = (3 units) x (4 units) = 12 sq units
The required ratio = \(\frac{2}{12}=\frac{1}{6}=1: 6\)
Question 41. The sleeping time of a python in a 24-hour clock is represented by the shaded portion in the given figure.
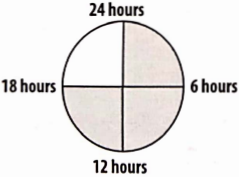
The ratio of sleeping time to awaking time is______.
Solution: 3:1: Sleeping time = 18 hours and awaking time = (24- 18) hours = 6 hours
The required ratio = \(\frac{18}{6}=\frac{3}{1}=3: 1\)
Question 42. A ratio expressed in the lowest form has no common factor other than _____ in its terms.
Solution: One
43. To find the ratio of two quantities, they must be expressed in______ units.
Solution: Same
Question 44. The ratio of 5 paise to 25 paise is the same as the ratio of 20 paise to_____.
Solution: 100 paise or 1 rupee : We have, 5 paise : 25 paise = 20 paise : ![]()
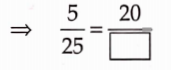
![]()
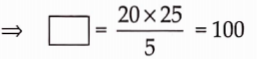
5 paise : 25 paise = 20 paise : 100 paise
Question 45. Saturn and Jupiter take 9 hours 56 minutes and 10 hours 40 minutes, respectively for one spin on their axes. The ratio of the time taken by Saturn and Jupiter in the lowest form is_______.
Solution:
Given
Saturn and Jupiter take 9 hours 56 minutes and 10 hours 40 minutes, respectively for one spin on their axes.
149 : 160: Time taken by Saturn
= 9 hours 56 minutes
= (9 x 60 + 56) minutes
= (540 + 56) minutes
= 596 minutes
Time taken by Jupiter = 10 hours 40 minutes
= (10 x 60 + 40) minutes
= 640 minutes
The required ratio = \(=\frac{\text { Time taken by Saturn }}{\text { Time taken by Jupiter }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{596 \text { minutes }}{640 \text { minutes }}=\frac{149}{160}=149: 160\)
Question 46. 10 g of caustic soda dissolved in 100 mL of water makes a solution of caustic soda. The amount of caustic soda needed for 1 litre of water to make the same type of solution is______.
Solution:
Given
10 g of caustic soda dissolved in 100 mL of water makes a solution of caustic soda.
100 g: Let the required amount of caustic soda be x g.
According to the question,
10 g: x g = 100 mL : 1 L
=> 10 g : .v g = 100 mL : 1000 mL
⇒ \(\frac{10}{x}=\frac{100}{1000} \Rightarrow \frac{10}{x}=\frac{1}{10}\)
X 1-10×10 ⇒ x — 100
The required amount of caustic soda is 100 g.
Question 47. The marked price of a table is ₹ 625 and its sale price is ₹ 500. What is the ratio of the sale price to the marked price?
Solution:
Given
The marked price of a table is ₹625 and its sale price is ₹500.
4:5: We have given the marked price = ₹625 and selling price = ₹500
The required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Selling price }}{\text { Marked price }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{₹ 500}{₹ 625}=\frac{4}{5}=4: 5\)
Question 48. Which pair of ratios are equal? And why?
- \(\frac{2}{3}, \frac{4}{6}\)
- \(\frac{8}{4}, \frac{2}{1}\)
- \(\frac{4}{5}, \frac{12}{20}\)
Solution:
1. We Have, \(\frac{2}{3} \text { and } \frac{4}{6}\)
The simplest form of \(\frac{4}{6} \text { is } \frac{2}{3}\)
⇒ \(\frac{2}{3}=\frac{4}{6}\)
2. We have, \(\frac{8}{4} \text { and } \frac{2}{1}\)
The simplest form of\(\)
⇒ \(\frac{8}{4}=\frac{2}{1}\)
3. We have, \(\frac{4}{5} \text { and } \frac{12}{20}\)
The simplest form of \(\frac{12}{20} \text { is } \frac{3}{5}\)
⇒ \(\frac{4}{5} \neq \frac{12}{20}\)
Question 49. Which ratio is larger 1 0: 21 or 21: 93?
Solution:
We have, 10: 21 \(=\frac{10}{21} \text { and } 21: 93=\frac{21}{93}\)
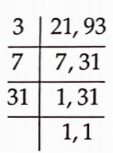
Now, the I, CM of 21; and 93 is 3 * 7 x 31 – 651 Mnking the denominator of each ratio equal to 651, we have
⇒ \(\frac{10}{21}=\frac{10 \times 31}{21 \times 31}=\frac{310}{651}\)
⇒ \(\text { and } \frac{21}{93}=\frac{21 \times 7}{93 \times 7}=\frac{147}{651}\)
⇒ \(\frac{310}{651}>\frac{147}{651}\)
⇒ \(\frac{10}{21}>\frac{21}{93}\)
Thus, the ratio 10: 21 is larger.
Question 50. Reshma prepared 18 kg of Burfi by mixing Khoya with sugar in the ratio of 7: 2. How much Khoya did she use?
Solution:
Given
Reshma prepared 18 kg of Burfi by mixing Khoya with sugar in the ratio of 7: 2.
The ratio of Khoya to sugar = 7:2
Let the quantity of Khoya be 7x kg and sugar be 2x kg.
7x + 2x =18 => 9x =18 => x = \(\frac{18}{9}=2\)
The quantity of Khoya be (7 x 2) kg = 14 kg
Question 51. A line segment 56 cm long is to be divided into two parts in the ratio of 2: 5. Find the length of each part.
Solution:
Given
A line segment 56 cm long is to be divided into two parts in the ratio of 2: 5.
The length of the line segment = 56 cm
Let the lengths of the two parts be 2 cm and 5 cm
2x + 5x = 56
7x = 56 ⇒ x \(=\frac{56}{7}=8\)
The length of one part is (2 x 8) cm =16 cm and length of other part is (5 x 8) cm = 40 cm
Question 52. The number of milk teeth in human beings is 20 and the number of permanent teeth is 32. Find the ratio of the number of milk teeth to the number of permanent teeth.
Solution:
Given
The number of milk teeth = 20
and the number of permanent teeth = 32
The required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Number of milk teeth }}{\text { Number of permanent teeth }}\)
⇒ \(\frac{20}{32}=\frac{5}{8}=5: 8\)
Question 53. The sex ratio is defined as the number of females per 1,000 males in the population. Find the sex ratio if there are 3732 females per 4000 males in a town.
Solution:
Given
The sex ratio is defined as the number of females per 1,000 males in the population.
Number of females = 3732
Number of males = 4000
The required sex ratio = \(\frac{3732}{4000}=\frac{933}{1000}\)
Thus, there are 933 females per 1000 males.
Question 54. In a year, Ravi earns? 360000 and paid? 24000 as income tax. Find the ratio of his
- Income to income tax.
- Income tax to income after paying income tax.
Solution: Ravi’s annual income =? 360000
Income tax paid by him = ? 24000
1. The required ratio \(=\frac{\text { The amount of income }}{\text { The amount of income tax }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{₹ 360000}{₹ 24000}=\frac{15}{1}=15: 1\)
After paying income tax, the remaining amount of income =? (360000- 24000) = ? 336000
The required ratio \(\begin{aligned}
& =\frac{\text { The amount of income tax }}{\text { The remaining amount of income }} \\
& \text { after paying the income tax }
\end{aligned}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{₹ 24000}{₹ 336000}=\frac{1}{14}=1: 14\)
Question 55. Ramesh earns₹ 28000 per month. His wife Rama earns₹ 36000 per month. Find the ratio of
Ramesh’s earnings to their total earnings
Rama’s earnings to their total earnings.
Ramesh’s monthly earnings =₹ 28000
Rama’s monthly earnings =₹ 36000
Their total earnings =₹ (28000 + 36000) = ₹ 64000
1. Required ratio = \(=\frac{\text { Ramesh’s monthly earnings }}{\text { Their total monthly earnings }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{₹ 28000}{₹ 64000}=\frac{7}{16}=7: 16\)
Question 56. Required ratio
⇒ \(=\frac{\text { Rama’s monthly earnings }}{\text { Their total monthly earnings }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{₹ 36000}{₹ 64000}=\frac{9}{16}=9: 16\)
Question 56. Of the 288 persons working in a company, 11 2 are men and the remaining are women. Find the ratio of the number of
- men to that of women.
- men to the total number of persons.
- women to the total number of persons
Solution:
Total number of persons working in a company = 288
Number of men = 112
Number of women = 288 -112 = 176
Required ratio=
⇒ \(=\frac{\text { Number of men }}{\text { Number of women }}=\frac{112}{176}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{7}{11}=7: 11\)
Required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Number of men }}{\text { Total number of persons }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{112}{288}=\frac{7}{18}=7: 18\)
Required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Number of women }}{\text { Total number of persons }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{176}{288}=\frac{11}{18}=11: 18\)
Question 57. A rectangular sheet of paper is of length 1.2 m and width 21 cm. Find the ratio of the width of the paper to its length.
Solution:
Given
A rectangular sheet of paper is of length 1.2 m and width 21 cm.
Length of paper = 1.2 m = 1.2 x 100 cm = 120 cm
And the width of the paper = is 21 cm
The required ratio = \(=\frac{\text { width of paper }}{\text { length of paper }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{21 \mathrm{~cm}}{120 \mathrm{~cm}}=\frac{7}{40}=7: 40\)
Question 58. A scooter travels 1 20 km in 3 hours and a train travels 1 20 km in 2 hours. Find the ratio of their speeds.
\(\left(\text { Hint: Speed }=\frac{\text { distance travelled }}{\text { time taken }}\right)\)
Solution:
Given
A scooter travels 1 20 km in 3 hours and a train travels 1 20 km in 2 hours.
We know that Speed = \(\frac{\text { Distance }}{\text { Time }}\)
The speed of the scooter = \(\frac{120 \mathrm{~km}}{3 \text { hours }}\)
= 40 km/hour
And the speed of the train = \(\frac{120 \mathrm{~km}}{2 \text { hours }}\)
Thus, the required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Speed of the scooter }}{\text { Speed of the train }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{40 \mathrm{~km} / \text { hour }}{60 \mathrm{~km} / \text { hour }}=\frac{2}{3}=2: 3\)
Question 59. An office opens at 9 a.m. and closes at 5.30 p.m. with a lunch break of 30 minutes. What is the ratio of lunch breaks to the total period in the office?
Solution:
Given
An office opens at 9 a.m. and closes at 5.30 p.m. with a lunch break of 30 minutes.
Opening time of office = 9 a.m.
Closing time of office = 5.30 p.m.
Total period in office = 8 hours 30 minutes
= (8 x 60 + 30) minutes = 510 minutes
The duration of lunch break = 30 minutes
The required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Duration of lunch break }}{\text { Total time period in office }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{30 \text { minutes }}{510 \text { minutes }}=\frac{1}{17}=1: 17\)
Question 60. The shadow of a 3 m long stick is 4 m long. At the same time of the day, if the shadow of a flagstaff is 24 m long, how tall is the flagstaff?
Solution:
Given
The shadow of a 3 m long stick is 4 m long. At the same time of the day, if the shadow of a flagstaff is 24 m long
Let the length of the flagstaff be x m.
According to the given question,
3m : xm:: 4m: 24m
⇒ \(\frac{3}{x}=\frac{4}{24} \Rightarrow 4 \times x=3 \times 24\)
⇒ \(x=\frac{3 \times 24}{4}=18\)
Thus, the length of the flagstaff is 18 m.
Question 61. A recipe calls for 1 cup of milk for every 2– cups of flour to make a cake that would feed 6 persons. How many cups of both flour and milk will be needed to make a similar cake for 8 people?
Solution:
Given
A recipe calls for 1 cup of milk for every 2– cups of flour to make a cake that would feed 6 persons.
Quantity of both milk and flour to make a cake for 6 persons
⇒ \(=\left(1+2 \frac{1}{2}\right) \mathrm{cups}\)
⇒ \(=\left(1+\frac{5}{2}\right) \text { cups }=\left(\frac{2+5}{2}\right) \mathrm{cups}=\frac{7}{2} \text { cups }\)
Let the quantity of both milk and flour to make a cake for 8 persons be x cups.
According to the given question,
⇒ \(\frac{7}{2} \text { cups : } 6 \text { persons }:: x \text { cups }: 8 \text { persons }\)
⇒ \(\frac{\frac{7}{2}}{6}=\frac{x}{8} \Rightarrow 6 \times x=8 \times \frac{7}{2}\)
⇒ \(x=\frac{28}{6} \Rightarrow x=\frac{14}{3}\)
Thus, \(\frac{14}{3}=4 \frac{2}{3} \text { cups }\) of both flour and milk will be needed to make a cake for 8 people.
Question 62. In a school, the ratio of the number of large classrooms to small classrooms is 3: 4. If the number of small rooms is 20, then find the number of large rooms.
Solution:
Given
In a school, the ratio of the number of large classrooms to small classrooms is 3: 4. If the number of small rooms is 20,
Let the number of large classrooms is 3x and the number of small classrooms be 4x.
We have given, the number of small rooms = 20
⇒ \(4 x=20 \Rightarrow x=\frac{20}{4} \Rightarrow x=5\)
The number of large classrooms is 3 x 5 = 15
Question 63. Samira sells newspapers at Janpath CCrossing daily. On a particular day, she had 312 newspapers out of which 216 were in English and the remaining in Hindi. Find the ratio of
- the number of English newspapers to the number of Hindi newspapers.
- the number of Hindi newspapers to the total number of newspapers.
Solution:
Given
Samira sells newspapers at Janpath CCrossing daily. On a particular day, she had 312 newspapers out of which 216 were in English and the remaining in Hindi.
Total number of newspapers = 312.
Number of English newspapers = 216
Number of Hindi newspapers- 31 2- 216
= 96
The required ratio
⇒ \(=\frac{\text { Number of English newspapers }}{\text { Number of Hindi newspapers }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{216}{96}=\frac{9}{4}=9: 4\)
The required ratio
⇒ \(=\frac{\text { Number of Hindi newspapers }}{\text { Total number of newspapers }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{96}{312}=\frac{4}{13}=4: 13\)
Question 64. The students of a school belong to different religious backgrounds. The number of Hindu students is 288, the number of Muslim students is 252, the number of Sikh students is 1 44 and the number of Christian students is 72. Find the ratio of
Solution: Given
The students of a school belong to different religious backgrounds. The number of Hindu students is 288, the number of Muslim students is 252, the number of Sikh students is 1 44 and the number of Christian students is 72.
The number of Hindu students to the number of Christian students.
The number of Muslim students to the total number of students.
Number of Hindu students = 288
Number of Muslim students = 252
Number of Sikh students = 144
Number of Christian students = 72
Total number of students in the school = 288 + 252 + 144 + 72 = 756
The required ratio
⇒ \(=\frac{\text { Number of Hindu students }}{\text { Number of Christian students }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{288}{72}=\frac{4}{1}=4: 1\)
The required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Number of Muslim students }}{\text { Total number of students }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{252}{756}=\frac{1}{3}=1: 3\)
Question 65. When Chinmay visited Chowpati in Mumbai on a holiday, he observed that the ratio of North Indian food stalls to South Indian food stalls is 5: 4. If the total number of food stalls is 117, find the number of each type of food stalls.
Solution:
Given
When Chinmay visited Chowpati in Mumbai on a holiday, he observed that the ratio of North Indian food stalls to South Indian food stalls is 5: 4. If the total number of food stalls is 117,
Let the number of North Indian food stalls be 5x and the number of South Indian food stalls be 4x.
The total number of food stalls = 117
5x + 4x = 117 => 9x = 117
⇒ \(x=\frac{117}{9} \Rightarrow x=13\)
Thus, the number of North Indian food stalls is 5 x 13 = 65
And the number of South Indian food stalls is 4×13 = 52
Question 66. At the parking stand of Ramleela ground, Kartik counted that there were 115 cycles, 75 scooters and 45 bikes. Find the ratio of the number of cycles to the total number of vehicles.
Solution:
Given
At the parking stand of Ramleela ground, Kartik counted that there were 115 cycles, 75 scooters and 45 bikes.
Number of cycles = 115
Number of scooters = 75
Number of bikes = 45
Total number of vehicles = 115 + 75 + 45 = 235
The required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Number of cycles }}{\text { Total number of vehicles }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{115}{235}=\frac{23}{47}=23: 47\)
Question 67. A train takes 2 hours to travel from Ajmer to Jaipur, which are 130 km apart. How much time will it take to travel from Delhi to Bhopal which are 780 km apart if the train is travelling at a uniform speed?
Solution:
Given
A train takes 2 hours to travel from Ajmer to Jaipur, which are 130 km apart.
A train covers a distance of 130 km in 2 hours and it covers a distance of 780 km in x hours.
According to the question, 130 km: 2 hours:: 780 km: x hours
⇒ \(\frac{130}{2}=\frac{780}{x} \Rightarrow 130 \times x=2 \times 780\)
⇒ \(x=\frac{2 \times 780}{130}=12\)
Thus, the required time is 12 hours.
Question 68. The length and breadth of a school ground are 150 m and 90 m respectively, while the length and breadth of a mela ground are 210 m and 126 m, respectively. Are these measurements in proportion?
Solution:
Given
The length and breadth of a school ground are 150 m and 90 m respectively, while the length and breadth of a mela ground are 210 m and 126 m, respectively.
The ratio of length to breadth of school ground = 150 m : 90 m \(=\frac{150}{90}=\frac{5}{3}=5: 3\)
The ratio of length to breadth of mela ground = 210 m: 126 m
⇒ \(=\frac{210}{126}=\frac{5}{3}=5: 3\)
Hence, both ratios are equal.
The given measurements are in proportion.
Question 69. In the given figure, the comparative areas of the continents are given :
- What is the ratio of the areas of
- Africa to Europe
- Australia to Asia
- Antarctica to a Combined area of North America and South America.
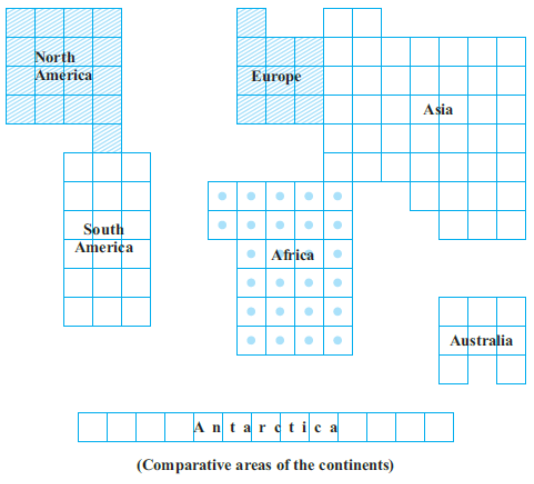
Solution:
Let each square be of unit length.
The required ratio = \(=\frac{26 \text { sq units }}{10 \text { sq units }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{13}{5}=13: 5\)
The required ratio = \(=\frac{\text { Area of Australia }}{\text { Area of Asia }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{8 \mathrm{sq} \text { units }}{44 \text { sq units }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{2}{11}:=2: 11\)
The required ratio = \(=\frac{\text { Area of Antarctica }}{\text { Area of (North America }+ \text { South America) })}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{13 \mathrm{sq} \text { units }}{(17+18) \mathrm{sq} \text { units }}=\frac{13 \mathrm{sq} \text { units }}{35 \mathrm{sq} \text { units }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{13}{35}=13: 35\)
Question 70. A tea merchant blends two varieties of tea costing her? 234 and 1 30 per kg in the ratio of their costs. If the weight of the mixture is 84 kg, then find the weight of each variety of tea.
Solution:
Given
A tea merchant blends two varieties of tea costing her? 234 and 1 30 per kg in the ratio of their costs. If the weight of the mixture is 84 kg,
The ratio of the costs of two varieties of tea is? 234 per kg? 130 per kg.
Sum of ratios = ?(234 + 130) per kg = ? 364 per kg.
Total weight of the mixture = 84 kg
The weights of each variety of tea are given by
⇒ \(\frac{234 \text { per } \mathrm{kg}}{364 \text { per } \mathrm{kg}} \times 84 \mathrm{~kg}=54 \mathrm{~kg}\)
⇒ \(\text { and } \frac{130 \text { per } \mathrm{kg}}{364 \text { per } \mathrm{kg}} \times 84 \mathrm{~kg}=30 \mathrm{~kg}\)
Question 71. An alloy contains only zinc and copper and they are in the ratio of 7: 9. If the weight of the alloy is 8 kg, then find the weight of copper in the alloy.
Solution:
Given
An alloy contains only zinc and copper and they are in the ratio of 7: 9. If the weight of the alloy is 8 kg
The ratio of the weight of zinc and copper is 7: 9.
Let the weight of zinc be lx kg and the weight of copper be 9x kg.
The weight of the alloy = 8 kg
7x + 9x = S => 16x = 8 => x \(=\frac{8}{16}=\frac{1}{2}\)
So, the weight of copper = \(9 \times \frac{1}{2} \mathrm{~kg}=\frac{9}{2} \mathrm{~kg}\)
⇒ \(=4 \frac{1}{2} \mathrm{~kg}\)
Question 72. In the following figure, each division represents 1 cm:

Express numerically the ratios of the following distances:
- AC: AF
- AG: AD
- BF: AI
- CE: DI
Solution:
1. AC:AF \(=\frac{A C}{A F}=\frac{2 \mathrm{~cm}}{5 \mathrm{~cm}}=\frac{2}{5}=2: 5\)
2. \(A G: A D=\frac{A G}{A D}=\frac{6 \mathrm{~cm}}{3 \mathrm{~cm}}=\frac{2}{1}=2: 1\)
3. \(B F: A I=\frac{B F}{A I}=\frac{4 \mathrm{~cm}}{8 \mathrm{~cm}}=\frac{1}{2}=1: 2\)
4. \(C E: D I=\frac{C E}{D I}=\frac{2 \mathrm{~cm}}{5 \mathrm{~cm}}=\frac{2}{5}=2: 5\)
Question 73. Find two numbers whose sum is 100 and whose ratio is 9: 16.
Solution:
The ratio of the two numbers is 9: 16.
Let the numbers be 9x and 16. v.
The sum of numbers = 100
⇒ 9.v + 16.v = 100 => 25.v = 100
\(x=\frac{100}{25} \Rightarrow x=4\)Thus, the required numbers are 9 x 4 = 36 and 16×4 = 64
Question 74. In Figure (1) and Figure (2), find the ratio of the area of the shaded portion to that of the whole figure:
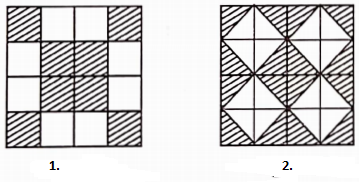
Solution:
Required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Area of the shaded portion }}{\text { Area of the whole figure }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{8 \text { sq units }}{16 \text { sq units }}=\frac{1}{2}=1: 2\)
Lei the area of each small triangle is 1 sq unit.
Required ratio
⇒ \(=\frac{\text { Area of shaded portion }}{\text { Area of the whole figure }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{16 \mathrm{sq} \text { units }}{32 \mathrm{sq} \text { units }}=\frac{1}{2}=1: 2\)
Question 75. A typist has to type a manuscript of 40 pages. She has typed 30 pages of the manuscript. What is the ratio of the number of pages typed to the number of pages left?
Solution:
Given
A typist has to type a manuscript of 40 pages. She has typed 30 pages of the manuscript.
Total number of pages = 40
Number of pages typed = 30
The number of pages left = 40- 30 = 10
The required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Number of pages typed }}{\text { Number of pages left }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{30}{10}=\frac{3}{1}=3: 1\)
Question 76. In a floral design made from tiles each of dimensions 40 cm by 60 cm (see figure), find the ratios of:
- The perimeter of the shaded portion to the perimeter of the whole design.
- The area of the shaded portion to the area of the unshaded portion.
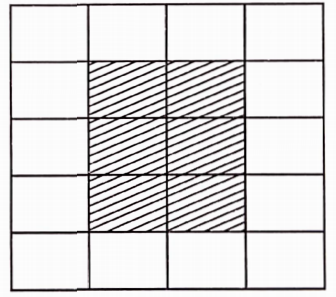
Solution:
Length of one tile = 60 cm
And the breadth of one tile = 40 cm
Required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Perimeter of shaded portion }}{\text { Perimeter of whole design }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{(4 \times 60+6 \times 40) \mathrm{cm}}{(8 \times 60+10 \times 40) \mathrm{cm}}=\frac{480 \mathrm{~m}}{880 \mathrm{~m}}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{6}{11}=6: 11\)
Area ofone tile- 60 an x 40 an = 2400 cm2 Required ratio
⇒ \(=\frac{\text { Area of the shaded portion }}{\text { Area of the unshaded portion }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{6 \times \text { area of } 1 \text { tile }}{14 \times \text { area of } 1 \text { tile }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{6 \times 2400 \mathrm{~cm}^2}{14 \times 2400 \mathrm{~cm}^2}=\frac{6}{14}=\frac{3}{7}=3: 7\)
Question 77. In the given figure, what is the ratio of the areas of
1. Shaded portion 1 to shaded portion 2?

2. shaded portion 2 to shaded portion 3?
3. shaded portions 1 and 2 taken together and shaded portion 3?
Solution:
Area of shaded portion I = 5 x 5 sq units = 25 sq units
Area of shaded portion HI = 7 x 5 sq units = 35 sq units
Area of shaded portion II = Area of the whole figure- Area of a shaded portion (I + III)
= [10 x 10- (25 + 35)] sq units
= [100- 60] sq units = 40 sq units
1. Required ratio
⇒ \(=\frac{\text { Area of shaded portion I }}{\text { Area of shaded portion II }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{25 \mathrm{sq} \text { units }}{40 \mathrm{sq} \text { units }}=\frac{5}{8}=5: 8\)
Required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Area of shaded portion II }}{\text { Area of shaded portion III }}\)
\(=\frac{40 \text { sq units }}{35 \text { sq units }}=\frac{8}{7}=8: 7\)Required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Area of shaded portion (I + II) }}{\text { Area of shaded portion III }}\)
\(=\frac{(25+40) \text { sq units }}{35 \text { sq units }}=\frac{65 \text { sq units }}{35 \text { sq units }}\) \(=\frac{13}{7}=13: 7\)Question 78. A car can travel 240 km in 15 litres of petrol. How much distance will it travel in 25 litres of petrol?
Solution:
Given
A car can travel 240 km in 15 litres of petrol.
The distance can be travelled in 15 litres of petrol = 240 km
The distance can be travelled in 1 litre of petrol \(=\frac{240}{15} \mathrm{~km}=16 \mathrm{~km}\)
Distance can be travelled in 25 litres of petrol = (25 x 16) km = 400 km
Question 79. Bachhu Manjhi earns ₹ 24000 in 8 months. At this rate,
How much does he earn in one year?
In how many months does he earn₹ 42000?
Solution:
Given
Bachhu Manjhi earns ₹ 24000 in 8 months.
In 8 months, money earned by Bachhu Manjhi = ₹ 24000
In 1 month, money earned by him
\(=₹ \frac{24000}{8}=₹ 3000\)In 1 year, he earns =? (12 x 3000)
= ₹ 36000
Number of months for earning₹ 3000 = 1
Number of months for earning₹ 42000
\(=\frac{4200}{300} = 14 \)Question 80. The yield of wheat from 8 hectares of land is 360 quintals. Find the number of hectares of land required for a yield of 540 quintals.
Solution:
Given
The yield of wheat from 8 hectares of land is 360 quintals.
Land required for a yield of 360 quintals of wheat \(=\frac{8}{360} \text { hectares }=\frac{1}{45} \text { hectares }\)
Land required for yield of 540 quintals of wheat = \(=\frac{1}{45} \times 540 \text { hectares }=12 \text { hectares }\)
Question 81. The earth rotates 360° about its axis in about 24 hours. By how many degrees will it rotate in 2 hours?
Solution:
Given
The earth rotates 360° about its axis in about 24 hours.
Rotation of earth in 24 hours = 360°
Rotation of earth in1 hour \(=\frac{360^{\circ}}{24}\) = 15°
Rotation of earth in 2 hours = 2 x 15° = 30°
Question 82. Shivangi is suffering from anaemia as the haemoglobin level in her blood is lower than the normal range. The doctor advised her to take one iron tablet two times a day. If the cost of 10 tablets₹ 17, then what amount will she be required to pay for her medical bill for 15 days?
Solution:
Given
Shivangi is suffering from anaemia as the haemoglobin level in her blood is lower than the normal range. The doctor advised her to take one iron tablet two times a day. If the cost of 10 tablets ₹ 17
Shivangi will consume 2 x 15 tablets i.e., 30 tablets in 15 days.
Cost of 10 tablets = ₹17
Thus, the cost of 30 tablets = \(₹ \frac{17}{10} \times 30\)
= ₹ 51
Question 83. The quarterly school fee in Kendriya Vidyalaya for Class VI is₹ 540. What will be the fee for seven months?
Solution:
Given
The quarterly (3 months) fee =₹ 540
The fee for 1 month = \(₹ \frac{540}{3}=₹ 180\)
Thus, the fee for 7 months =? (180 x 7)
= ₹ 1260
The fee for seven months= ₹ 1260
Question 84. In an electron, the votes cast for two of the candidates were in the ratio 5::7. If the successful candidate received 20734 votes, how many votes did his opponent receive?
Solution:
Given
In an electron, the votes cast for two of the candidates were in the ratio 5::7. If the successful candidate received 20734 votes
Let the number of votes cast for the candidates be 5x and 7x.
According to the question,
7x = 20734 => \(\)
⇒ \(x=\frac{20734}{7}=2962\)
⇒ \(x=\frac{20734}{7}=2962\)
Number of votes received by opponent candidate = 5×2962 = 14810
5. A metal pipe 3 metres long was found to weigh 7.6 kg. What would be the weight of the same kind of 7.8 m long pipe?
Solution:
Given
A metal pipe 3 metres long was found to weigh 7.6 kg.
The weight of 3 metre long pipe = 7.6 kg
The weight of1 metre long pipe = \(=\frac{7.6}{3} \mathrm{~kg}\)
Thus, the weight o7.8-metreetre long pipe \(=\frac{7.6}{3} \times 7.8 \mathrm{~kg}=19.76 \mathrm{~kg}\)
Question 86. A recipe for raspberry jelly calls for 5 cups of raspberry juice and \(2 \frac{1}{2}\) cups of sugar. Find the amount of sugar needed for 6 cups of the juice?
Solution:
Given
A recipe for raspberry jelly calls for 5 cups of raspberry juice and \(2 \frac{1}{2}\) cups of sugar.
The requirement of sugar for 5 cups of raspberry juice \(=2 \frac{1}{2} \text { cups }=\frac{5}{2} \text { cups }\)
The requirement of sugar for 1 cup of raspberry juice \(=\left(\frac{5}{2} \div 5\right) \text { cups }\)
⇒ \(\left(\frac{5}{2} \times \frac{1}{5}\right) \text { cups }=\frac{1}{2} \text { cups }\)
Thus, the requirement of sugar for 6 cups of the raspberry juice \(=6 \times \frac{1}{2} \mathrm{cups}=3 \mathrm{cups}\)
Thus, the requirement of sugar for 6 cups of raspberry juice = \(=6 \times \frac{1}{2} \text { cups }=3 \text { cups }\)
Question 87. A farmer planted 1890 tomato plants in a field in rows each having 63 plants. A certain type of worm destroyed 18 plants in each row. How many plants did the worm destroy in the whole field?
Solution:
Given
A farmer planted 1890 tomato plants in a field in rows each having 63 plants. A certain type of worm destroyed 18 plants in each row.
Total number of plants = number of rows x number of plants in each row
1890 = number of rows x 63
⇒m\(\frac{1890}{63}=\text { number of rows }\)
number of rows = 30
Now, the number of plants destroyed worms in 1 row = IS
Total number of plants destroyed by worm in 30 rows = 18 x 30 = 540
Question 88. The length and breadth of the floor of a room are 5 m and 3 m, respectively. Forty tiles, each witan h area are used to cover the floor partially. Find the ratio of the tiled and the non tiled portion of the floor.
Solution:
Given
The length and breadth of the floor of a room are 5 m and 3 m, respectively. Forty tiles, each witan h area are used to cover the floor partially.
Tire total area of the floor = 5 m x 3 m = 15 m2
Tire area covered with tiles \(=40 \times \frac{1}{16} \mathrm{~m}^2\)
⇒ \(=\frac{5}{2} \mathrm{~m}^2\)
The non tiled area = \(\left[15-\frac{5}{2}\right] \mathrm{m}^2\)
⇒ \(=\left[\frac{30-5}{2}\right] \mathrm{m}^2=\frac{25}{2} \mathrm{~m}^2\)
The required ratio \(=\frac{\text { Tiled area }}{\text { Non tiled area }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{\frac{5}{2} \mathrm{~m}^2}{\frac{25}{2} \mathrm{~m}^2}=\frac{5}{2} \times \frac{2}{25}=\frac{1}{5}=1: 5\)
Question 89. A carpenter had a board which measured 3 m x 2m. She cut out a rectangular piece of 250 cm x 90 cm. What is the ratio of the area of the cutout piece and the remaining piece?
Solution:
Given
A carpenter had a board which measured 3 m x 2m. She cut out a rectangular piece of 250 cm x 90 cm.
The area of the board = 3 m x 2 m = 6 m2 = 6 x 10000 cm2 = 60000 cm2
And the area of cut out piece = 250 cm x 90 cm = 22500 cm2
The area of remaining piece = (60000-22500) cm2
= 37500 cm2
Thus, the required ratio \(=\frac{\text { The area of cut out piece }}{\text { The area of remaining piece }}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{22500 \mathrm{~cm}^2}{37500 \mathrm{~cm}^2}=\frac{3}{5}=3: 5\)
